-
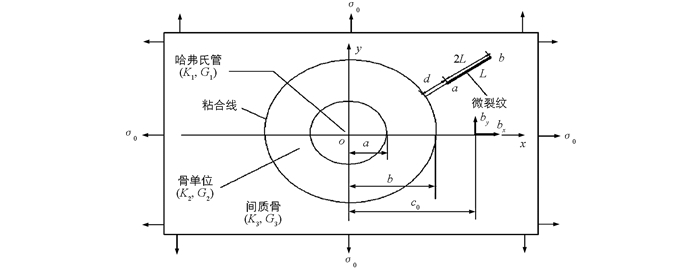
文献[1-2]研究了骨头的分层结构,骨组织可分为密质骨和松质骨.哈弗氏密质骨由骨单位和间质骨组成.骨单位是由同心圆排列的骨板围成的长筒状结构,中心有一纵向的哈弗氏管,内含血管和神经.间质骨位于骨单位之间,形状不规则,是旧的骨单位在骨的改建过程中被吸收后残留的部分[3-4].由于哈弗氏管和骨单位的微观结构对密质骨力学性能有重要影响,因而模型考虑了这些微观结构.从微观结构和力学行为出发,哈弗氏密质骨与纤维涂层复合材料相似[5]:哈弗氏管与纤维类似,骨单位与涂层类似,间质骨与基类似,粘合线相当于界面.因而,可以将密质骨的分层结构与纤维涂层复合材料类比.
文献[6-7]研究了骨的疲劳现象,这种现象在医学上被认为是应力断裂.由于日常运动的循环载荷,骨组织的微观损伤以微裂纹的形式表现出来[8-9].实验方法常用来研究骨单位的结构和断裂[10-12].骨的微结构有利于微裂纹的萌生[12],但骨单位阻碍密质骨中微裂纹的扩展,这种作用还依赖于微裂纹的长度[11-12].计算机模拟,尤其是有限元方法已应用于密质骨断裂力学问题的研究.文献[13]利用有限元方法模拟了哈弗氏密质骨骨单位附近微裂纹的扩展.理论研究,尤其是奇异积分方程方法也应用于密质骨断裂力学问题的研究[4, 14-15].文献[4]研究了密质骨骨单位与单条微裂纹的相互作用,结果表明软骨单位有利于微裂纹的扩展,而硬骨单位阻碍微裂纹沿着骨单位扩展[4].文献[14-15]研究了多个微裂纹与骨单位的相互作用,结果表明这种相互作用仅局限在骨单位附近,同时也分析了不同形态下,微裂纹相互作用的增强和屏蔽作用.但是,理论上对哈弗氏密质骨间质骨含微裂纹问题还没有研究过,因而有必要利用奇异积分方程方法研究哈弗氏密质骨间质骨含微裂纹问题.
全文HTML
-
如图 1,哈弗氏密质骨含径向微裂纹力学模型的求解可看成是以下两个基本问题A和B的叠加:
问题A 哈弗氏管和骨单位镶嵌在间质骨中,间质骨不含微裂纹,哈弗氏密质骨含径向微裂纹力学模型的边界条件为
问题B 考虑间质骨含径向直线微裂纹的应力分布问题.
问题B里,外载荷只有微裂纹表面的牵引力,这个牵引力与问题A在虚裂纹位置的应力大小相等,方向相反.哈弗氏管、骨单位和间质骨界面的牵引力和位移连续条件为:
其中τ=aeiθ,0≤θ≤2π.
其中ζ=beiθ,0≤θ≤2π.
-
问题A的应力场如下[18]:
其中:
-
令间质骨在点(x,y)=(c0,0) 的位错贝格斯分量为bx和by.利用Muskhelishvili复变函数方法[19-20],间质骨任一点P(x,y)的应力场如下:
其中hxxx,hxxy,hyyx,hyyy,hxyx,hxyy的定义见文献[21]的附录.
如果位错贝格斯分量bt和bn是L上的连续分布函数,bt沿着L,bn垂直于L,则问题B微裂纹上一点的切应力σt和正应力σn如下[22-23]:
其中ht1,ht2,hn1和hn2如下:
其中:
(xc,yc)是微裂纹中点坐标.这里,m和n定义如下:
其中,α是微裂纹与x轴的夹角.
位移单值条件如下:
分离位错密度函数的奇异性,bt(t0)和bn(t0)如下所示:
其中,Ft(t0)和Fn(t0)是-1,1上的非奇异函数.
将(27) 式和(28) 式代入(17),(18),(25) 和(26) 式,得:
方程(29)-(32) 给出了哈弗氏密质骨骨单位附近间质骨含单条径向微裂纹问题的解.
-
径向直线微裂纹尖端的应力强度因子为[16]:
2.1. 在直角坐标系下求解问题A的应力场
2.2. 利用奇异积分方程方法求解问题B
2.3. 径向直线微裂纹尖端应力强度因子
-
当α=0时,数值算例考虑了哈弗氏密质骨含径向微裂纹受双轴拉伸载荷σ0.对于软骨单位,间质骨的剪切模量为G3=15 GPa;对于硬骨单位,间质骨的剪切模量为G3=10 GPa.哈弗氏管、骨单位和间质骨的泊松比分别为v1=v2=v3=0.3.无穷远处双轴拉伸载荷σ0=10 MPa.通过利用高斯切比雪夫求积公式,对奇异积分方程组(29)-(32) 进行数值求解[16-17],讨论了微裂纹尖端应力强度因子随材料常数和几何参数的变化.
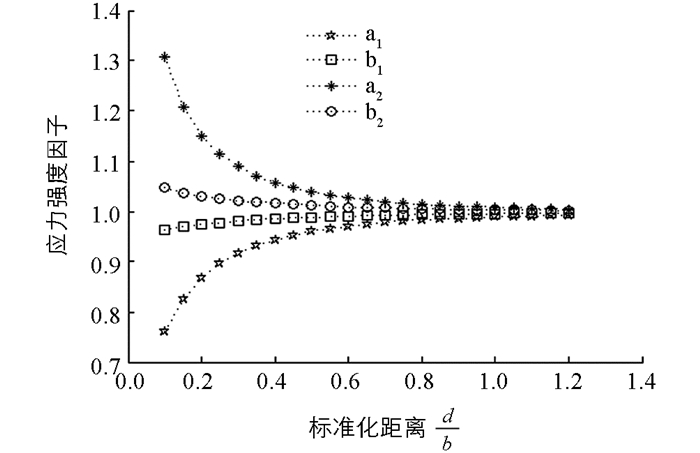
假设骨单位的半径为b=100 μm,
$ \frac{b}{a} $ =1.5,微裂纹长度L=100 μm.如图 2所示,研究了不同剪切模量比下,微裂纹尖端(ai)和(bi)的标准化应力强度因子随标准化距离$ \frac{d}{b} $ 的变化.若$ \frac{{{G_1}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =0.1,$ \frac{{{G_2}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =0.005时,当微裂纹尖端(a1)无限接近骨单位时,微裂纹尖端(a1)的应力强度因子迅速增加,而微裂纹尖端(b1)的应力强度因子则缓慢增加,说明此时骨单位有利于微裂纹的扩展.若$ \frac{{{G_1}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =10,$ \frac{{{G_2}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =200时,当微裂纹尖端(a2)无限接近骨单位时,微裂纹尖端(a2)的应力强度因子急剧下降,而微裂纹尖端(b2)的应力强度因子则缓慢减少,说明此时骨单位对微裂纹具有屏蔽效应.但是,哈弗氏管和骨单位对微裂纹尖端应力强度因子的影响只局限在骨单位附近.上述数值结果与文献[13]用有限元方法得到的结果是一致的.如图 3所示,假设骨单位的半径b=100 μm,
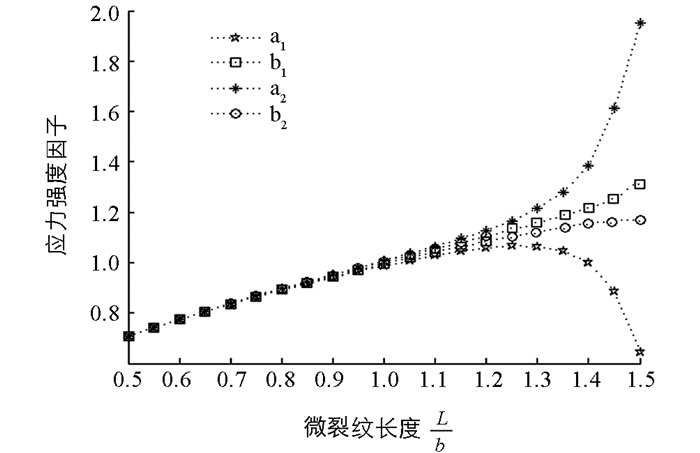
$ \frac{b}{a} $ =1.5,微裂纹尖端(b)固定.研究了不同剪切模量比下,微裂纹尖端(ai)和(bi)的应力强度因子随微裂纹长度$ \frac{L}{b} $ 的变化.当0.5≤$ \frac{L}{b} $ ≤1.2时,微裂纹尖端(ai)和(bi)的应力强度因子随微裂纹长度的增加而增加.若剪切模量比$ \frac{{{G_1}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =0.1,$ \frac{{{G_2}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =0.05时,则当微裂纹尖端(a1)接近骨单位时,微裂纹尖端(a1)和(b1)的应力强度因子迅速增加,而微裂纹尖端(a1)的应力强度因子增长更快,说明骨单位对微裂纹尖端(a1)的应力强度因子的影响更大.此时,微裂纹更容易在粘合线附近扩展.若剪切模量比$ \frac{{{G_1}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =10,$ \frac{{{G_2}}}{{{G_3}}} $ =20时,则当微裂纹尖端(a2)接近骨单位时,微裂纹尖端(a2)和(b2)的应力强度因子急剧减少,而微裂纹尖端(a2)的应力强度因子减少更快,说明骨单位对微裂纹尖端(a2)的应力强度因子的影响更大,这是因为微裂纹尖端(a2)距离骨单位更近的缘故.此时,骨单位对裂纹具有屏蔽效应.这与已有实验方法[24]得到的结果是一致的.另外也给出了一些预测结果,这些结果需要通过实验或有限元模拟来进一步验证.总的来说,不管是对于软骨单位还是硬骨单位,微裂纹与骨单位的相互作用仅局限在骨单位附近.



 下载:
下载: