-
甘蔗是我国南方的重要经济作物,在甘蔗全程机械化过程中收割机械化是最为重要的一个环节[1].但是我国的甘蔗收割机械化程度并不高,其中主要原因是由于我国甘蔗种植地区主要是丘陵和山地[2],地形起伏较大,适合机械作业的平缓坡地还不到40%[3],而现有的甘蔗收割机基本都无法根据地形变化自动调节切割刀盘的高度,造成收割质量不好,比如割茬过长、破头率高等[4],影响甘蔗第二年发苗.研究表明,甘蔗收割机在收获过程中刀盘入土一定深度进行切割可以获得更好的效果[5-6],所以设计出一套仿形系统,能不受环境因素影响(如甘蔗茎叶遮挡等),使刀盘能够随着蔗垄起伏而上下移动、始终保持在一定的入土深度进行甘蔗切割,便是我国甘蔗收割机械发展的一个重大突破口.目前虽然已经有一些关于图像处理、切割负载压力等方面的研究[7-9],但基本还没有完整可靠的仿形系统投入使用,本文提出了一种通过机械检测装置测量地面相对高度的方法,并进行了甘蔗收割机模拟试验研究.
全文HTML
-
本控制系统由三大部分构成:控制器、地面高度检测装置和液压系统.液压系统主要包括液压控制元件和执行元件,控制元件为电磁换向阀,执行元件为液压缸和液压马达.
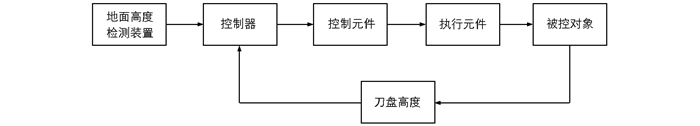
系统控制结构图如图 1所示,其中被控对象为刀盘,地面高度检测装置测量出地面相对高度后,控制器将其与刀盘高度进行比较,然后控制换向阀的开口方向,换向阀开口方向决定了液压缸上升还是下降,也就是刀盘上升还是下降.
-
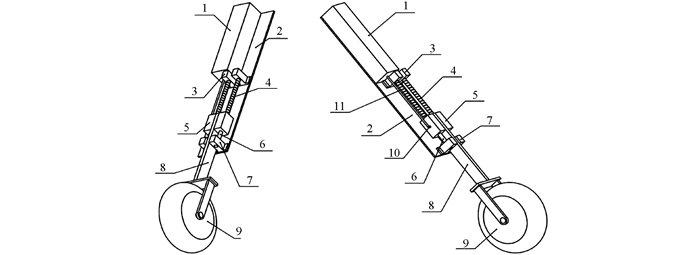
地面高度检测装置如图 2所示.仿形轮、支架和滑块构成的整体可以沿着导轨上下移动,为可伸缩部分;其余为不可伸缩部分,固定在收割机上.直线位移传感器和滑块通过连接杆连接在一起,当仿形轮随着地形起伏时,可伸缩部分也上下移动,同时带动直线位移传感器伸缩杆移动,压紧弹簧可以保证仿形轮贴地行驶.这样,传感器读数变化就可以反映出地形的起伏.
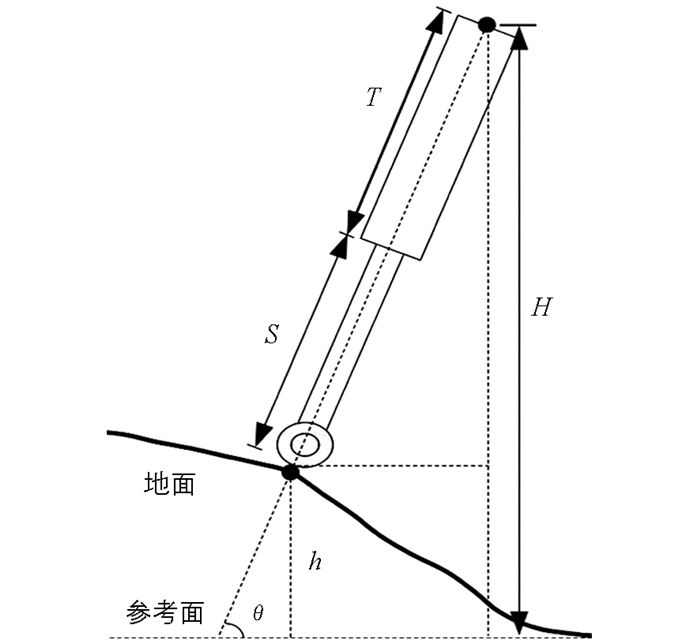
图 3为地面高度检测原理.图中地面代表的是甘蔗垄面,参考面为垄间的沟(本文中提到的地面都为甘蔗垄面,各高度都是相对于参考面而言).上方黑点假设为高度检测装置在收割机上的安装点,下方黑点为仿形轮和地面的接触点.设检测装置安装点高度为H,与水平方向夹角为θ,不可伸缩部分长度(包括轮子半径)为T,若直线位移传感器测出可伸缩部分长度为S,则地面起伏高度h的计算式为:
-
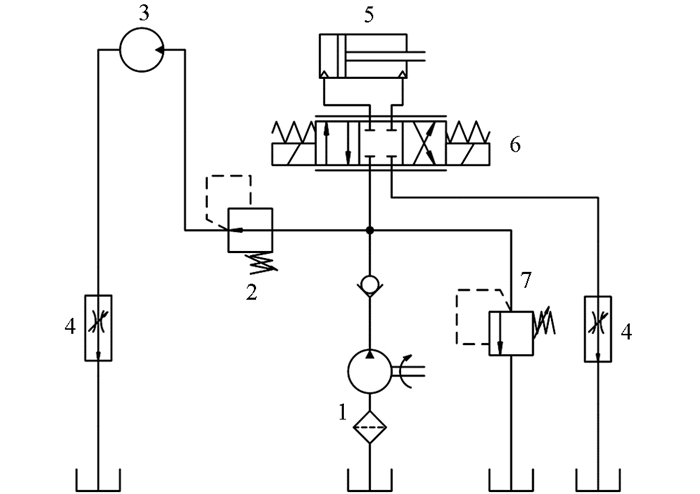
液压系统原理如图 4所示.其中调速阀用来调节液压缸和液压马达的运行速度,由于液压缸跟液压马达负载压力不同,且马达侧压力较小,所以在马达回路中加入减压阀,以保证两者都能正常运行[10-11].
液压马达、液压缸、刀盘和直线位移传感器构成本次研究所使用的甘蔗收割模拟试验机的割台部分(图 5).液压马达带动刀盘转动,液压缸带动马达跟刀盘一起上下移动,移动的距离通过直线位移传感器测出.
-
在甘蔗仿形收割过程中,为避免滞后控制,需要提前测量出地面高度,所以地面高度检测装置需安装在刀盘前方某处.当检测装置测量出某一点的地面高度后,需要把这一数据保存起来,当收割机往前运动一段时间后,刀盘到达该点,这时则根据保存好的地面高度对刀盘的高度作出调整.这中间间隔的时间取决于检测装置与刀盘之间的距离和收割机的运动速度.
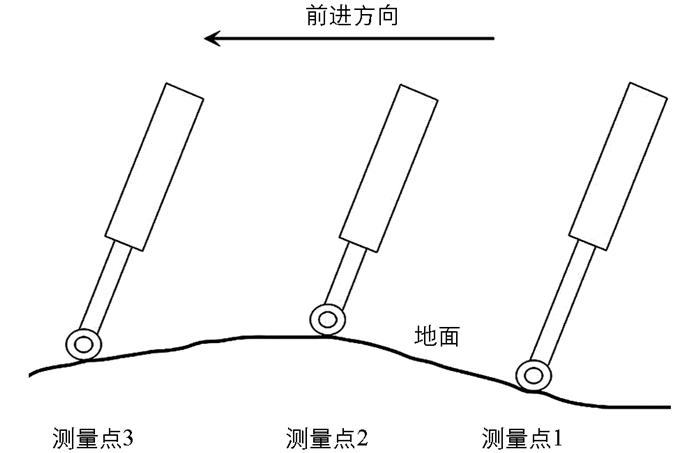
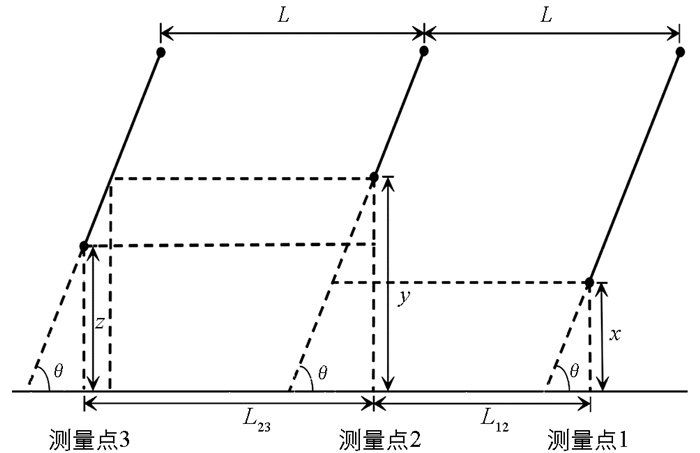
由于检测装置结构的特殊性,当其随地形上下起伏时,不仅在上下移动,其实也在左右移动,所以它与刀盘之间的距离是变化的.但是,本次研究并没有直接利用这两者之间的距离,而是利用相邻两个地面高度测量点的距离. 图 6表示的是检测装置分别位于3个测量点时的简化情形,为了便于说明,再对其进行简化,如图 7.
图 7中,3根黑实斜线代表检测装置,上端黑点表示检测装置在收割机上的安装位置,下端黑点表示检测装置与地面的接触点.由于检测装置不可伸缩部分固定在收割机上,所以将两者当作一个整体.从图中可以看出,对于该整体来说,相邻测量点之间的水平距离都为L,但是由于检测装置只有不可伸缩部分固定在收割机上,可伸缩部分会斜向伸缩,跟收割机之间有相对运动(从图中来看就是3根黑实斜线的长度不一样),所以接触点之间的水平距离并不为L,而是图中的L12和L23.
假设检测装置测量出的3个接触点的地面高度分别x、y和z,从图中可以看出y>z>x,也就是说测量点1到测量点2地面高度上升,测量点2到测量点3高度下降,分别代表检测装置在测量过程中上坡和下坡两种运动状态.通过计算可以得出:
对比两个式子可以看出,式(3)就是式(2)的变式,可以用式(2)代替,所以可将式(2)作为一般表达式.
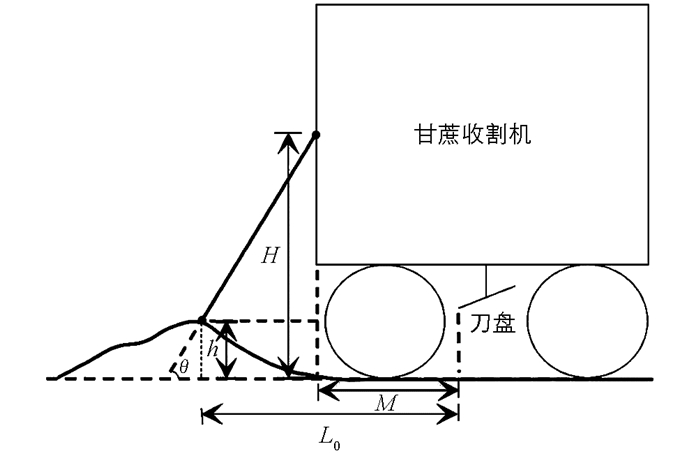
式(2)计算的是收割机每前进距离L时检测装置可伸缩部分前进的距离,也就是刀盘下一次调整高度之前收割机需要前进的距离,但该式并不适用于刀盘第一次高度调整,也就是收割机刚出发时的情况,如图 8所示.
图 8中收割机位于出发点位置,设检测装置安装高度为H,安装点与刀盘最前端的水平距离为M,测得此时的地面高度为h,则刀盘第一次调整高度之前收割机需要前进的距离L0为:
由于L0这一段距离的地面高度并没有测量,所以并不知道具体高度,为保险起见,需要让刀盘保持在一个较高的位置,或者让收割机从平坦一点的地方出发,直接将出发时测出的地面高度h当作整个L0这一段距离的地面高度,提前做出第一次刀盘高度调整,节省之后的调整时间.
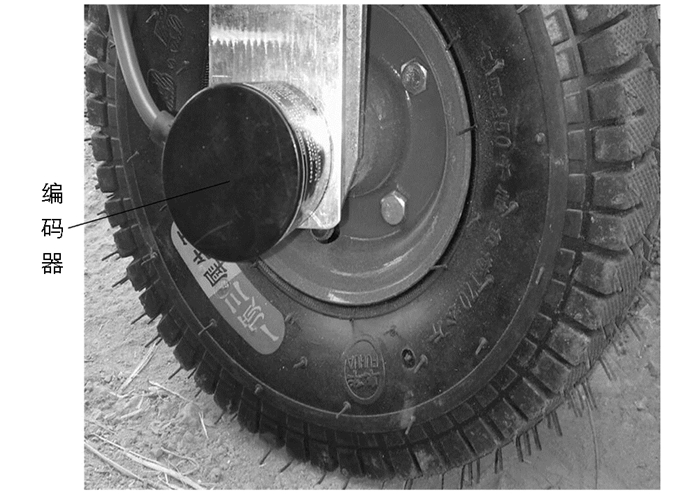
为了准确控制地面高度测量点之间的距离都为L和在收割机前进了相应距离后及时进行刀盘调整,本次试验并没有利用采集收割机前进速度进而得出前进距离的方法,因为虽然收割机在收割过程中近似于匀速前进,但实际上并不是匀速,而且本次试验中,采用人工的方式推动试验机行走,速度变化比实际收割机更大,如果使用先求速度再求距离的方法,会使计算变得复杂繁琐,而且误差很大.为了消除速度的影响,本次试验利用光电编码器直接得出试验机前进的距离.
编码器是一种把角位移或直线位移转换成电信号的传感器,本次试验使用的增量式编码器,分辨率为1 000,也就是旋转一圈可以产生1 000个脉冲,本次使用的测距轮周长约为785 mm,如图 9所示,所以测距轮每前进0.785 mm编码器产生一个脉冲,记录脉冲个数则可知道试验机前进了多少距离.
综上,把收割机前进的距离平均分为若干段,隔一段距离测量一次地面高度,并且得出这些高度测量点之间的水平距离,当收割机由一个测量点前进到下一测量点时,进行刀盘高度调整.
1.1. 系统构成
1.2. 地面高度检测装置
1.3. 液压系统
1.4. 系统控制原理
-
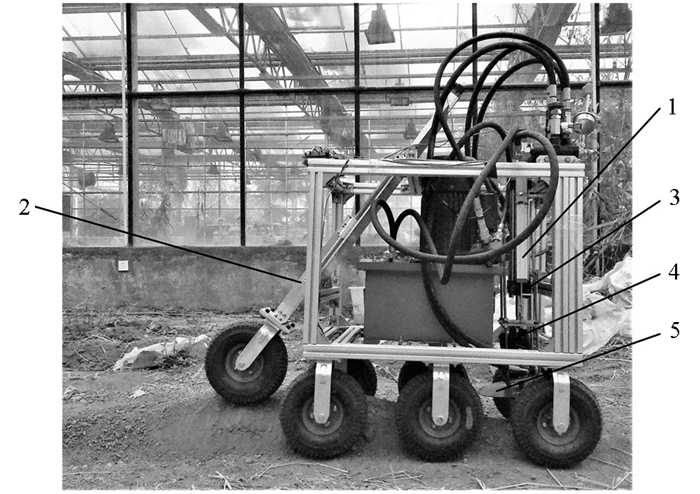
本次试验使用的是搭载刀盘自动升降系统的甘蔗收割模拟试验机,如图 10所示.车架宽度580 mm,长度800 mm,高度850 mm;高度检测装置与水平面夹角约为53度,能测量的最大地面起伏高度为300 mm,安装在整车左侧距离中心110 mm处(以仿形轮中心为基准);刀盘倾角约17度,直径300 mm,厚度2 mm,最大高度为280 mm,刀盘最前端与车架最前端的距离为450 mm.
-
本次试验场地为长度约20 m,垄宽400 mm,最大垄高220 mm,最大坡度约15°,试验机每前进1 cm测量一次垄高.
试验分为两大部分.一是单独测试地面高度检测装置:关闭液压系统,随机选取垄上某试验点,分别用尺子和检测装置测出该处的垄高并记录数据.二是测试整个刀盘高度控制系统:仍然随机选取垄上某试验点,人工测出该处的实际垄高,然后人工推动试验机前进,速度在0.5~3 m/s之间,当刀盘也运动到该处时,测出此时刀盘最低点的高度,记录数据.
为了便于观察效果,试验过程中并没有让刀盘入土切割,因为如果入土切割会损坏垄,对后续的高度测量造成影响.虽然刀盘紧贴地面移动效果最为直观,但是由于误差的存在,也会损坏垄,所以也并未采取.最终设计让刀盘在垄上方3 cm处随地形起伏,也就是说需要在测得的实际垄高基础上加上3 cm后进行结果分析.
2.1. 试验设备
2.2. 试验方法
-
1) 试验结果表明,试验机模拟甘蔗收割机切割刀盘自动升降误差在允许范围内,符合仿形要求.导致误差的主要原因有:各传感器误差和仿形轮跟地面的接触点位置不固定,可以通过使用更准确的传感器和直径更小的仿形轮等方法来减小误差;试验机行走的沟和垄一样起伏不平,是误差的一个主要来源,但这是符合实际情况的,收割机自身的避震装置可有效减少该误差;地面高度测量点之间间隔一定的距离,并不连续,而刀盘高度只能按照这些测量点的高度调整,若选取的试验点刚好在测量点之间,那么试验结果就会不准确,通过减小测量点之间的距离可以减小误差;人工测量高度也是误差来源之一.
2) 减少刀盘的振动可以提高收割质量[12],但是研究刀盘仿形系统却是主动让刀盘进行移动,有所矛盾,所以本次试验采取折中的方法,并没有连续控制刀盘移动,而是间隔一段距离移动一次,这样既可以仿形切割,也减少了刀盘的移动.
3) 本试验重点在于模拟甘蔗收割机收割过程,验证地面高度检测装置的原理,证明该装置的可行性,并未按照实际收割机量身定做,所以检测装置的尺寸大小、材料、结构、安装位置和角度,刀盘的升降速度和液压系统结构等还需进行进一步研究.
4) 影响甘蔗切割质量除了切割位置还有其它很多因素,比如收割机前进速度、刀盘倾角和转速、刀片数量和刃角等[13-14].目前,虽然甘蔗收割机割台升降速度对切割质量影响的研究还没有,但是升降速度势必会影响切割质量,比如升降速度过快时,虽然刀盘可以快速到达最佳切割位置,但是如果此时刀盘正在切割甘蔗,升降速度过快不仅可能造成甘蔗破头,还可能造成刀片损伤甚至折断,而升降速度过慢又可能导致刀盘到达不了指定位置.升降速度的确定,需要考虑所有影响因素并进行大量实验,必要时还可以加入电液控制技术,进行变速升降,最好还能检测刀盘的切割状态,当刀盘正在切割甘蔗时不进行升降,或者以较慢的速度升降,没有切割甘蔗时使刀盘贴着土壤表面移动,这样既能保护刀盘,又能迅速进入入土切割状态.由于条件的限制,本次试验并没有对刀盘的升降速度或切割状态进行研究,只是采用手动方式简单调节刀盘升降速度.



 下载:
下载: