-
分布式凸优化问题是指在缺乏全局优化问题的完整信息的情况下,系统中的多智能体协作地求解全局代价函数的最优解.这类问题的解决需要设计完全分布式的优化算法,也就是优化算法由没有中央协调器的智能体来实现.分布式优化问题最近取得了许多重要成果[1-12],基于一致的分布式策略正成为解决优化问题的主流.这已经产生了许多优化算法,包括分布式次梯度下降算法[1]、分布式对偶平均算法[2]、分布式nesterov梯度算法[3]等.随后,这一系列工作被扩展到各种现实条件下的分布式优化,如随机次梯度误差[4]、随机通信网络[5]等.实际上,上述分布式优化算法[2-5]的实现都需要构建一系列双随机矩阵,阻碍了这些算法的开发和实际应用,特别是在随时间变化的一般非平衡有向实际网络环境中,因为双随机矩阵的条件难以以分布式方式满足.为了解决上述非平衡问题,最近的文献[6-8]分别从不同的角度解决非平衡性.值得注意的是,尽管文献[6-8]中的算法避免了构造双随机矩阵,但它们都要求所有智能体准确地知道其入度邻居的出度信息进而必须构造列随机权重矩阵.然而,构造列随机矩阵在某些方案(例如基于广播的通信方案)中可能是不现实的.
当网络是非平衡有向且相应的权重矩阵是行随机时,Mai和Abed[9]提出了一种改进的分布式次梯度投影方法,用于求解具有全局约束集的分布式优化问题.在代价函数是凸且光滑的情况下,理论分析证明了文献[9]中的算法渐进收敛于优化问题的最优解.遗憾的是,文献[9]中的算法不能解决带有耦合线性约束和局部不等式约束的分布式优化问题.因此,Doan和Beck[10]开发了一种分布式拉格朗日网络资源分配方法,该方法能够很好解决带有耦合线性约束和局部不等式约束的分布式优化问题.但是,在文献[10]中,网络拓扑结构是无向的,这在实际网络环境中是不切实际的.
综上所述,在非平衡有向网络上研究带有耦合线性约束和局部不等式约束的分布式优化问题并将其应用于电力系统中分布式经济分配上将会是一项非常有意义的工作.因此,本文的主要贡献可以归纳为以下3个方面:①在非平衡有向网络上提出一种新颖的分布式原始-对偶次梯度算法解决带有耦合线性约束和局部不等式约束的分布式优化问题,与文献[10]相比,本文算法适用于非平衡有向网络;②虽然文献[9]同样考虑了行随机矩阵,但是本文算法能够处理带有耦合线性约束和局部不等式约束的分布式优化问题;③本文算法最终渐进收敛到全局优化问题的最优解.
全文HTML
-
我们用
$\mathbb{R}$ m和$\mathbb{R}$ m×m分别表示m维实向量集和m×m实矩阵集.本文出现的所有向量都是列向量.定义xi(t)为智能体i在t时刻的估计.符号()T定义为一个矩阵或向量的转置.对于一个矩阵A,aij为其第i行第j列的元素.定义1m为元素全为1的m维列向量.符号Im为m×m单位矩阵.我们用‖·‖表示一个矩阵或者向量的欧拉范数.定义向量ei=[0,…,0,1i,0,…,0]T.一个非负矩阵A是行随机的如果A1m=1m成立,A是列随机的如果AT1m=1m,A是双随机的如果A既是行随机又是列随机.给定一个任意、恰当、闭、凸函数f(x),对任意的y∈$\mathbb{R}$ m,定义f†(y)=supx∈$\mathbb{R}$ myTx-f(x)为其共轭函数.我们用G={V,E,A}表示一个非平衡有向加权网络,其中V={1,…,m}表示智能体集合,E⊆V×V表示边的集合;A=[aij]∈
$\mathbb{R}$ m×m(aij≥0)表示网络G的加权邻接矩阵.具体地,如果(j,i)∈E,∀i,j∈V成立,那么它意味着智能体i可以直接接收从智能体j传来的信息,也就是aij>0.用Niin={j|(j,i)∈E}表示智能体i的入度邻居集合.有向网络中一条从智能体i1到智能体ik的路径可以表示为一系列有向连通边(i1,i2),(i2,i3),…,(ik-1,ik),其中(ij-1,ij)∈E且j=2,…,k.在一个有向网络中如果智能体集中任意两个智能体之间总存在一条有向路径,则将这个有向网络称为强连通的. -
总的来说,本文主要考虑如下分布式约束优化问题
∀i=1,…,m,其中x=[x1,x2,…,xm]T∈
$\mathbb{R}$ m.每一个智能体i只可以获取自身的局部凸代价函数fi:$\mathbb{R}$ m→$\mathbb{R}$ .耦合线性约束集定义为M={x∈$\mathbb{R}$ m|$\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}$ xi=P},不等式约束集定义为X={x∈$\mathbb{R}$ m|limin≤xi≤limax}.假定X=X1×X2×…×Xm为Xi的笛卡儿积且S=M∩X表示优化问题(1)的可行解集.我们令x*=[x1*,…,,xm*]T,X*和f(x*)=f*分别为优化问题(1)的最优解、最优解集和最优值. -
优化问题(1)的拉格朗日函数L:X×
$\mathbb{R}$ →$\mathbb{R}$ 定义为如下形式其中λ是等式约束
$\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}$ xi-P=0的拉格朗日乘子.基于共轭函数的定义,对于一个给定的λ∈$\mathbb{R}$ ,优化问题(1)的对偶函数可以转化为如下形式其中Di(λ)=-fi†(-λ)-
$\lambda \frac{P}{m}$ 是一个凹函数.因此,优化问题(1)的对偶问题可以表示为其中D(λ)可能不可微.给定一个λ∈
$\mathbb{R}$ 且假设(3)式中相应的最小值为$\mathit{\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}$ ,那么D(λ)的次梯度为注意x*为最优解.那么,由假设1可知,问题(4)必定存在一个对偶最优解λ*满足强对偶性成立,即f(x*)=D(λ*).此外,一对最优解(x*,λ*)被称为拉格朗日函数L在集合S×
$\mathbb{R}$ 上的鞍点,即 -
注意到根据(3)式求解(4)式等价于求解下列最小化问题
其中Qi是一个凸代价函数
在假设1-3的基础上,我们提出了求解问题(7)的分布式优化算法.具体地,对于任意的t=0,1,…,我们用xi(t)和λi(t)两个状态分别去估计原始最优解xi*和对偶最优解λ*,用zi(t)去消除网络的非平衡性.假设每个智能体i的初始值为xi(0)∈Xi,λi(0)∈
$\mathbb{R}$ 和zi(0)=ei∈$\mathbb{R}$ m.由此,变量xi(t),λi(t)和zi(t)的更新规则如下其中:α(t)是步长,zi(t)=[zi1(t),…,zim(t)]T,▽Qi(t)是函数Qi(λ)在λ=
$\sum_{j=1}^{m}$ aijλj(t)上的次梯度.此外,我们有如下的假设.假设1 非平衡有向网络G是强连通的.
假设2 对于任意的i=1,…,m,函数fi是可微的且其次梯度▽fi是利普希茨连续的,利普希茨系数为σi.也就是说,对于任意的y,x∈
$\mathbb{R}$ ,▽fi满足如下的不等式假设3 权重矩阵A=[aij]∈
$\mathbb{R}$ m×m是行随机的且其对角元素是正的.假设4 步长α(t)是正的且满足supt≥0α(t)≤1,
$\sum\limits_{t=0}^{\infty} \alpha(t)=\infty$ 和$\sum\limits_{t=0}^{\infty} \alpha^{2}(t) < \infty$ .
1.1. 问题模型
1.2. 问题转化
1.3. 分布式原始对偶算法
-
注意到算法(11)是一个一致迭代过程,其最终迭代到矩阵A的一个左perron向量估计π=[π1,…,πm]T满足1mTπ=1.针对这个perron向量,我们有如下的两个引理.
引理1 让假设1和3成立,那么π是一个严格正向量且满足
引理1是Perron-Frobenius定理的一个主要结论.此外,引理1收敛速度是几何的.
引理2[9] 设假设1和3成立,考虑到算法(10)和(11),那么对任意的i,j∈V和t≥0,存在C>0和γ∈(0,1)满足下面的不等式成立
其次,算法(10)可以转化为如下形式
其中
因此,我们有
其中用到条件‖▽Qi(t)‖≤L,∀i∈V(根据假设2可知L存在).注意到zii(t)>0,∀t≥0且
可以得到{zii-1(t)}t=0∞是一个正有界序列.根据假设4,可以得到
由(15)式可知
$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty}$ ‖ε(t)‖=0.定义λ(t)=$\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m} \pi_{i} \lambda_{i}(t)$ .由文献[9]易得如下引理3,4.
引理3 若假设1-4成立,根据算法(10)和(11),可以得到下面条件成立
证 由上面分析可知,
$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty}\|\varepsilon(t)\|=0$ 成立.因此,引理3的证明可以直接从文献[9]获得.下面给出一个重要引理,这个引理对算法的收敛性分析起到了至关重要的作用.
引理4 若假设1-4成立,考虑算法(10)和(11),那么存在γ∈(0,1)和t0>0满足对任意u∈
$\mathbb{R}$ 和t≥t0下面的不等式成立其中
和
证 定义vi(t)=∑j=1maijλj(t).对任意的u∈
$\mathbb{R}$ ,从算法(11)可以很容易得到其中使用条件
和
得到(18)式. (18)式右边的第一项上界为
(18) 式右边的第二项的上界为
其中使用Qi的凸性和次梯度有界性得到式(20).从(18)-(20)式可以得到
(21) 式两边同时乘以πi然后在i求和得
其中πTA=πT.又因为
此外,
根据(22)-(24)式,可以很容易得到引理4的结果.
本文的第一个主要结果在下面的定理中指出.
定理1 若假设1-4成立,序列{xi(t)}和{λi(t)}由算法(9)-(11)更新,可以推出
$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty} \lambda_{i}(t)=\lambda^{*}$ 对任意i∈V都成立.证 定理1的证明可以分为两部分.第一部分需要证明对偶状态的平均λ(t)随着t→∞渐进收敛到对偶最优解λ*.根据引理3可知每个对偶状态λi(t)随着t→∞都渐进收敛到对偶状态的平均λ(t).因此,第二部分通过结合第一部分和引理3进而得定理1的结论.因为引理4得到的结论与文献[9]的定理1结论类似,所以可以参照文献[9]直观得到第一部分结论.因此,本文定理1的余下证明在这里省略.
接下来,给出本文的第二个主要结果.
定理2 若假设1-4成立,序列{xi(t)}和{λi(t)}由算法(9)-(11)更新,可以推出
$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty} x_{i}(t)=x_{i}^{*}$ 对任意i∈V都成立.证 对于拉格朗日对偶问题(4),可以推出至少存在一个对偶最优解λ*和原问题(1)的唯一最优解xi*满足xi*=xi(λ*)对任意i∈V都成立.由定理1可知
$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty} \lambda_{i}(t)=\lambda^{*}$ 对任意i∈V都成立.因此,由$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty} \lambda_{i}(t)=\lambda^{*}$ 可以得到每个原始状态xi(t)都随着t→∞渐进收敛到一个唯一最优解xi*,也就是$\lim\limits_{t \rightarrow \infty}$ xi(t)=xi*对任意i∈V都成立.证明结束.
-
通过电力系统中分布式经济调度问题的仿真实例来验证所提出算法的有效性和分析过程的正确性.研究IEEE-14总线系统的经济调度问题,该总线系统结构可以参照文献[12].系统的通信结构由一个非平衡有向网络表示.在仿真中,假设每个发电机i存在其自身的代价函数Yi(Pi)=aiPi+biPi2,其中ai和bi是每个发电机i可调控的代价增益.考虑实际环境,不同发电机产生的功率可能不相同,因此所产生的功率都具有有限界限[0,Pimax].假设每个发电机都知道系统总需求P=300 MW.最后,每个发电机参数ai,bi和Pimax的取值参照文献[10].
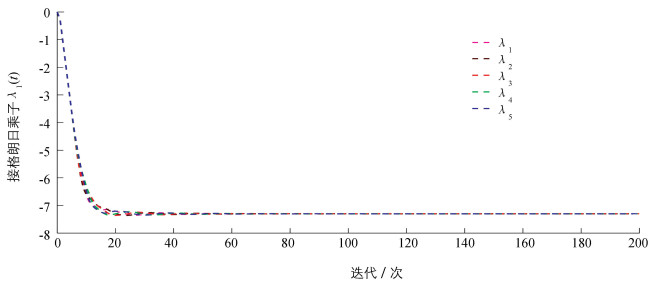
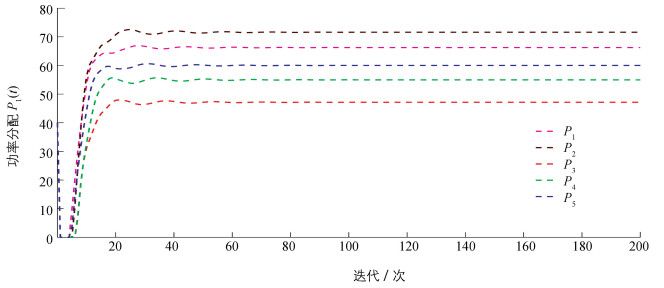
基于以上的参数设计,算法(9)-(11)的仿真结果如图 1和图 2所示.从图中可以看出本文算法成功地为每个发电机分配最优功率,并且每个拉格朗日乘子收敛到对偶最优解.具体的最优功率分配为:P1*=66.24 MW,P2*=71.62 MW,P3*=47.15 MW,P4*=54.99 MW和P5*=60.00 MW;对偶最优解λ*=-7.301.
-
本文开发并分析了一种完全分布式的原始-对偶算法,用于处理带有耦合线性约束和不等式约束的分布式经济分配问题.本文算法采用了行随机权重矩阵并且被证明是适用于非平衡有向网络.在代价函数是凸且利普希茨连续的假设下,所提出的算法渐进收敛到全局优化问题的精确最优解.此外,通过电力系统中分布式经济分配问题的仿真实例验证了算法的性能.在未来的研究中,将本文的工作扩展到智能体在时变非平衡有向网络上的事件触发,异步和量化通信的情况是非常有意义的.



 下载:
下载: