-
枇杷[Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl.]是蔷薇科、枇杷属的亚热带常绿果树,同时也是我国重要的传统中药,其临床应用已有几千年的历史.枇杷叶和花均可入药,据《本草纲目》记载,枇杷主要用于治疗肺热、咳喘、吐逆、烦渴.现代研究表明,枇杷还具有止痛、抗病毒、保肝、抗肿瘤、降血糖和促进免疫的作用,其应用范围日益扩大.
近年来的药理研究表明,植物的药用价值与其抗氧化能力密切相关[1-2].黄酮类化合物和酚类物质均为天然的抗氧化成分,黄酮是一种强氧化剂,可有效清除体内过剩的活性自由基,防止细胞衰老和氧化[3].酚类化合物是植物产生的一种重要次生代谢物质,存在于植物体不同的组织中,能够抑制自由基的产生,具有较强的抗氧化活性[4].
我国具有丰富的枇杷资源[5-6],已有研究报道显示,枇杷中含有丰富的黄酮类和酚类物质[7-8],不同品种的酚类和黄酮类化合物的质量分数及其抗氧化活性存在较大差异.陈俊伟等[9]、徐红霞等[10]和林素英等[11]对不同品种枇杷果实抗氧化活性进行了研究分析,筛选出“软条白沙” “塔下红” “宁海白”和“解放钟”抗氧化活性高的枇杷品种. Hong等[12]对枇杷野生资源研究表明:“台湾枇杷” “恒春枇杷” “西藏枇杷”和“孟加拉枇杷”等6种野生枇杷总黄酮、总酚及其抗氧化活性比栽培品种早钟6号高.洪燕萍等[13]在香花枇杷与普通枇杷抗氧化活性成分比较中,发现野生香花枇杷叶片的抗氧化活性高于普通枇杷.由此可见,枇杷野生资源蕴含很大的发展趋势和利用前景.
本试验以8份枇杷的叶片和花蕾为试验材料,采用分光光度法测定枇杷的总黄酮和总酚质量分数,利用DPPH和FRAP法来评价其抗氧化活性,以期能够筛选出抗氧化活性强、药用价值高的枇杷材料,同时也为枇杷种质资源的开发利用提供一定的理论依据.
全文HTML
-
本试验材料来源于西南大学园艺园林学院歇马基地,供试材料如表 1,分别采取秋梢第5片枇杷叶和含苞待放的枇杷花蕾.将叶片清洗干净,装进信封中,放入65 ℃烘箱中烘至恒质量,用粉碎机粉碎,0.2 mm的筛子过滤,放入干燥器中备用.
-
参照张敏等[14]方法,略作改动.
1) 标准曲线的建立
称取芦丁(Rutin) 5 mg,置于25 mL容量瓶中,加适量70%乙醇,超声10 min,全部溶解后,放至室温,以70%乙醇定容,即得对照品溶液;精密量取0,0.5,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0 mL对照品溶液,分别置10 mL的容量瓶中;加5%亚硝酸钠溶液0.3 mL,摇匀,放置6 min;再加10%硝酸铝溶液0.3 mL,摇匀,放置6 min;再加4%氢氧化钠溶液4 mL,用70%乙醇将反应溶液体积补充到10 mL,放置15 min;用可见光分光光度计在510 nm波长处测定吸光度,以吸光度为纵坐标,芦丁质量分数为横坐标绘制标准曲线,标准曲线回归方程为y=0.077 5x-0.000 5(R2=0.999 6).
2) 样品总黄酮质量分数的测定
取枇杷叶、花细粉各0.5 g,置于50 mL容量瓶中,加入20 mL石油醚,浸泡1.5 h,超声20 min,滤去液体、残渣挥干至无石油醚;在残渣中加入70%乙醇20 mL,浸泡30 min,超声提取2次,每次20 min,提取液合并,70%乙醇定容至50 mL,即得总黄酮提取液;吸取样品总黄酮提取液0.5 mL,按标准曲线测定的方法,依次加入各试剂,测定510 nm处的吸光值,根据标准曲线计算样品中的总黄酮质量分数.
-
参照尚红梅等[15]方法,略作修改.
1) 标准曲线的建立
称取0.01 g的没食子酸,用50 mL容量瓶定容,得到0.2 mg/mL的溶液溶度,准确量取0,1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0 mL溶液用10 mL容量瓶定容,取0.5 mL稀释液反应.以没食子酸为标准曲线品绘制标准曲线,标准曲线回归方程为y=0.007 8x-0.000 1(R2=0.998 1).
2) 样品总酚的测定
样品稀释10倍,0.5 mL的提取液加4.5 mL去离子水,取0.5 mL的稀释液和0.5 mL的Folin-Ciocalteu试剂反应.摇匀后,加入4 mL的75%碳酸钠溶液,在25 ℃反应30 min.用可见光分光光度计在760 nm处测吸光度,以蒸馏水为空白对照.
-
每个试验重复3次,结果以x(平均值)±s(标准差)表示,实验数据用SPSS软件进行统计处理和差异显著性(p<5%)分析.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 总黄酮的测定
1.2.2. 总酚的测定
1.2.3. 抗氧化性的测定
1.2.4. 数据处理
-
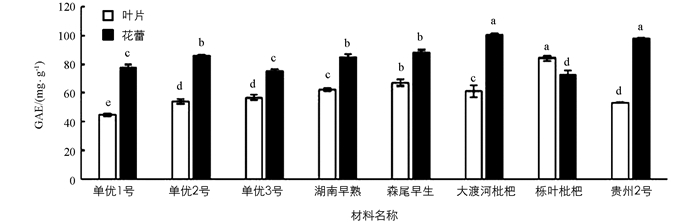
由图 1可知,8份枇杷叶片总黄酮的质量分数(以每克干物质含芦丁的毫克数计)在94.48~244.76 mg/g之间,各品种枇杷叶片黄酮质量分数排序由高到低依次为湖南早熟、栎叶枇杷、大渡河枇杷、单优3号、贵州2号、森尾早生、单优2号、单优1号.其中湖南早熟叶片的总黄酮质量分数最高,为244.76 mg/g,与其他7份枇杷叶片差异有统计学意义(p<0.05).单优1号叶片的总黄酮质量分数最低,为94.48 mg/g,湖南早熟叶片的黄酮比单优1号高2.59倍.
8份枇杷花蕾总黄酮的质量分数在162.40~229.57 mg/g之间,单优2号枇杷花蕾总黄酮质量分数最高,为229.57 mg/g,湖南早熟、森尾早生、大渡河枇杷、栎叶枇杷次之,但与单优2号差异无统计学意义(p<0.05).单优1号和单优3号的总黄酮质量分数最低,都为162.40 mg/g.
8份枇杷材料中只有湖南早熟的叶片总黄酮质量分数比花蕾的总黄酮质量分数高,其余的7份枇杷材料叶片的总黄酮质量分数比花蕾的总黄酮质量分数低.
-
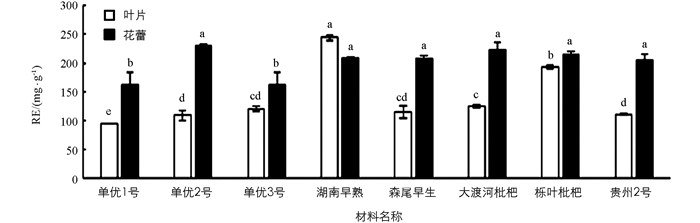
8份枇杷材料叶片和花蕾总酚的质量分数(以每克干物质含没食子酸的毫克数计)如图 2. 8份枇杷叶片材料总酚质量分数排序由高到低依次为栎叶枇杷、森尾早生、大渡河枇杷、湖南早熟、单优3号、单优2号、贵州2号、单优1号.栎叶枇杷叶片的总酚质量分数最高,为84.22 mg/g,与其他品种差异有统计学意义(p<0.05);森尾早生次之,与其他品种差异有统计学意义(p<0.05).单优1号叶片的总酚质量分数最低,为44.85 mg/g,栎叶枇杷叶片总酚质量分数比单优1号叶片总酚质量分数高1.88倍.
对枇杷花蕾总酚质量分数分析可得:8份枇杷花蕾材料中,总酚质量分数排序由高到低依次为大渡河枇杷、贵州2号、森尾早生、单优2号、湖南早熟、单优1号、单优3号、栎叶枇杷,大渡河枇杷花蕾总酚的质量分数最高,贵州2号次之,总酚质量分数分别为100.28 mg/g,97.63 mg/g,与其他材料差异有统计学意义(p<0.05).栎叶枇杷花蕾的总酚质量分数最低,为72.41 mg/g.
除栎叶枇杷叶片的总酚质量分数比花蕾高外,其余7份枇杷材料叶片的总酚质量分数均低于花蕾的总酚质量分数.
-
本试验采用DPPH和FRAP 2个方法来评价不同品种枇杷叶片和花蕾的抗氧化性(表 2).其中DPPH表示物质清除自由基的能力,而FRAP表示物质的还原能力.叶片中,DPPH自由基清除能力最强的是森尾早生(602.50 μmol/g),栎叶枇杷(473.88 μmol/g)次之.单优3号的质量分数最低,为221.44 μmol/g. FRAP还原能力最强的为栎叶枇杷(566.96 μmol/g),森尾早生(545.59 μmol/g)次之,FRAP还原能力最低的为单优1号.枇杷花蕾中,贵州2号的DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力均最强, 分别为799.14 μmol/g,943.44 μmol/g,与其他品种差异有统计学意义(p<0.05),栎叶枇杷的DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力低,为515.30 μmol/g,590.80 μmol/g,贵州2号枇杷的DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力与其他枇杷差异有统计学意义.
-
由表 3分析可知,枇杷叶片和花蕾总黄酮、总酚质量分数与DPPH和FRAP呈正相关.枇杷叶片总黄酮质量分数与FRAP显著性相关;DPPH与总酚质量分数,FRAP与总酚质量分数呈极显著相关关系,而总黄酮质量分数与DPPH相关性不显著,且相关性系数较低,为0.270.枇杷花蕾总黄酮质量分数与DPPH呈显著性相关;DPPH与总酚质量分数,FRAP与总酚质量分数呈极显著相关关系,而总黄酮质量分数与FRAP相关性不显著.可见不同组织中,枇杷总黄酮质量分数与DPPH和FRAP的相关性存在一定的差异,而总酚质量分数与抗氧化活性相关.
2.1. 不同枇杷材料叶片和花蕾总黄酮质量分数分析
2.2. 不同枇杷材料叶片和花蕾总酚质量分数分析
2.3. 8份枇杷材料叶片和花蕾抗氧化活性分析
2.4. 8份枇杷材料叶片和花蕾总黄酮、总酚及其抗氧化活性相关性分析
-
本试验对8份枇杷材料不同部位(叶片和花蕾)总黄酮质量分数进行了研究,我们发现,湖南早熟和栎叶枇杷叶片中总黄酮质量分数显著性高于其他材料,分别为244.76 mg/g和193.3 mg/g.这一结果比吴媛琳等[1]、王长春等[18]研究枇杷叶片总黄酮质量分数110.0 mg/g高,这可能是由于本研究与其所用供试材料不同造成;花蕾总黄酮质量分数在162.40~229.57 mg/g,与吴媛琳等[1]、郑美瑜等[19]、Pande G等[20]研究结果相一致.此外,除单优1号和单优3号外,其余品种之间差异无统计学意义.
总酚质量分数研究表明,叶片和花蕾总酚质量分数变化范围分别为44.85~84.22 mg/g,72.41~100.28 mg/g,其中野生材料栎叶枇杷(叶片)、大渡河枇杷(花蕾)和贵州2号(花蕾)显著高于其他材料,此外,除栎叶枇杷外,同一品种不同部位枇杷总酚质量分数花蕾高于叶片.吴媛琳等[1]对枇杷不同部位主要有效成分分析也表明枇杷不同部位总酚质量分数花蕾高于叶片,本研究结果与其一致,这可能是由于次生代谢物质在植物的生长代谢过程中不断地往生长旺盛部位运输有关.
本试验利用DPPH和FRAP法对枇杷抗氧化能力进行评估[21],研究结果表明,不同枇杷材料叶片和花蕾都具有抗氧化活性且存在差异.其中,森尾早生和栎叶枇杷叶片中,DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力强;贵州2号的花蕾中DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力强.目前,根据相关性分析研究表明,总黄酮、总酚质量分数与抗氧化能力呈正相关,而总酚与抗氧化活性强度比总黄酮相关性高.而且大多数学者研究表明,枇杷叶片、花蕾中黄酮及酚的质量分数与抗氧化能力呈正相关[22-24].但在本研究中,DPPH和FRAP测定枇杷叶片和花蕾的抗氧化活性相关性显示,DPPH与叶片中总黄酮质量分数相关性不显著,FRAP与花蕾中总黄酮质量分数相关性不显著,这可能是由不同组织中黄酮类活性物质的组成成分不同造成的,本研究供试材料总黄酮、总酚质量分数的定性、定量分析有待进一步研究.
在生产中为提高枇杷的坐果率,花期要进行大量的疏花[25],本研究表明枇杷花蕾中含有比叶片丰富的总黄酮、总酚及其抗氧化活性,可以合理地开发利用枇杷花,进一步提高枇杷种植的经济效益.总之,枇杷花蕾的总黄酮、总酚质量分数及其抗氧化活性总体高于叶片,其中森尾早生叶片的抗氧化活性显著高于其他材料,可作为枇杷叶片开发的资源,而野生材料贵州2号可作为枇杷花蕾开发利用的资源.此外,以后将进一步扩大样本数量,并结合果肉、果皮、种子等其他部位的总黄酮、总酚质量分数测定及抗氧化活性分析,对不同枇杷种质资源的抗氧化能力进行全面的解析比较,为枇杷资源的有效开发利用奠定基础.



 下载:
下载: