-
嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)属于弧菌科气单胞菌属, 是水产动物尤其鱼类常见的致病菌[1-2], 导致水产动物体表、内脏器官以及组织器官出血和炎症, 并引起大量死亡[3-5], 给水产养殖业造成严重的经济损失, 已引起人们的广泛关注[6].
目前, 对嗜水气单胞菌引起病害的防治方法主要有抗生素法、中草药防治法、疫苗法以及益生菌防控法[7], 其中以抗生素法为主.然而大量、频繁的用药导致细菌耐药性和环境污染等问题[8-9], 致使防治效果逐年下降, 使得抗生素的使用量越来越大.因此, 从生态友好的角度出发, 拮抗菌凭借防治病害、增进健康、无抗药性、无残留等优点[10], 正受到国内外研究学者越来越多的关注.微生物制剂在水产养殖上的应用始于1986年, 由于其广阔的应用前景, 已取得了广泛应用, 许多革兰氏阳性菌(如:芽孢杆菌属、节杆菌属、肠球菌、乳酸菌、乳球菌、小球菌)和革兰氏阴性菌(如:气单胞菌属、肠杆菌属、弧球菌属、假单胞菌属、伯克氏菌属)都作为益生菌应用于水产养殖过程中, 来促进水产动物的生长及健康水平, 其中芽孢杆菌属应用最广[11], 如短小芽孢杆菌B1能抑制副溶血弧菌[12]; 来自黄颡鱼肠道的枯草芽孢杆菌对温和气单胞菌、嗜水气单胞菌、大肠杆菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌及柱状嗜纤维菌都有很强的拮抗作用[13]; 地衣芽孢杆菌能有效抑制中华绒螯蟹致病性嗜水气单胞菌等[14].
目前已研究报道的对嗜水气单胞菌具有拮抗作用的菌株主要有乳酸杆菌、蛭弧菌、假单胞菌属以及芽孢杆菌属等[15], 但大多数拮抗菌株防治范围较小, 并且存在定殖能力弱、拮抗能力退化快、效果不稳定等问题.鉴此, 本试验从草鱼养殖池塘中分离、筛选出对病原性嗜水气单胞菌有较强拮抗作用的潜在益生菌, 并对其进行菌株鉴定, 以期为水产养殖过程中嗜水气单胞菌的生物防治提供微生物资源.
全文HTML
-
嗜水气单胞菌(Aeromonas hydrophila)由西南大学动物科技学院吴荣华老师提供.
-
水样和池塘底泥取自重庆市吉冠水产养殖有限公司草鱼养殖池塘.
-
LB培养基(g/L):胰蛋白胨10 g, 酵母提取物5 g, 氯化钠5 g, pH值为7.0~7.2.
-
水样:无菌条件下, 用灭菌生理盐水将水样进行梯度稀释, 取10-6, 10-7, 10-8稀释倍数的水样, 分别装入20 mL已灭菌喷壶内, 存于4 ℃冰箱待用.
底泥:无菌条件下, 称取约1 g底泥, 用灭菌生理盐水稀释, 取稀释梯度为10-5, 10-6, 10-7上清液, 分别装入20 mL已灭菌喷壶内, 存于4 ℃冰箱待用.
-
初筛采用点喷法:取1×108 cfu/mL的指示菌菌液100 μL, 涂布于LB培养平板上, 置于37 ℃培养2 h; 然后用1.2.1中的喷壶将稀释样品点喷于涂有指示菌的LB平板上, 倒置于37 ℃恒温培养24 h, 观察点喷菌落周围是否产生抑菌圈.对周围产生抑菌圈的菌落进一步分离纯化, 反复筛选, 直至获得纯种培养物, 存于4 ℃冰箱备用.
复筛采用牛津杯法:用无菌镊子取灭菌后的牛津杯置于涂有指示菌的LB平板上, 轻压, 使杯底紧贴于培养基上; 每个牛津杯加入100 μL初筛纯培养物无菌发酵液, 置于37 ℃恒温培养24 h, 去掉牛津杯, 测量抑菌圈直径(包括牛津杯直径).试验重复3次, 结果用“平均值±SD”表示.
-
用梯度稀释法对复筛得到的菌株进行涂板分离, 于37 ℃培养24 h观察菌落形态、大小、颜色、质地、边缘等.同时进行革兰氏染色和芽孢染色, 油镜观察(×100) 菌体形态.
-
将种子液接种到100 mL LB培养基中, 终浓度为1×107 cfu/mL.定期取样测定OD600, 并稀释涂板计数, 得到拮抗菌的生长曲线.
-
采用CTAB-SDS法提取分离菌株基因组, 利用原核生物16S rDNA通用引物进行目的基因扩增. 16S rDNA基因的通用引物:27F正向引物:5′-GAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′, 1392R反向引物:5′-ACGGGCGGTGTGTRC-3′.在25 μL反应体系中含有:无菌蒸馏水17.25 μL, 10×PCR缓冲液2.5 μL, 4×dNTP混合物2.0 μL, 引物各1.0 μL, 0.5 U/μL的Taq DNA聚合酶0.25 μL, 模板DNA 1.0 μL. PCR反应条件:95 ℃预变性5 min; 94 ℃变性30 s; 55 ℃复性30 s; 72 ℃延伸1 min; 30个循环; 72 ℃温育4 min.扩增产物用1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行检测, 由上海生工生物工程股份有限公司完成16S rDNA基因序列测定.
-
对分离菌株的16S rDNA基因序列通过NCBI的Blast检索系统进行序列同源性分析, 选取同源性较高的序列在ClusterX软件完成序列比对, 使用MEGA4.0软件, 采用最大简约法构建系统进化树, 并通过Bootstrap法检验, 1 000次重复.
-
用Excel中统计软件对试验数据进行处理, 描述性统计值使用“平均值±SD”表示, n=3.
1.1. 材料
1.1.1. 指示菌
1.1.2. 样品
1.1.3. 培养基
1.2. 嗜水气单胞菌拮抗菌的分离与筛选
1.2.1. 样品稀释
1.2.2. 拮抗菌株的筛选
1.3. 拮抗菌的鉴定
1.3.1. 菌落形态观察
1.3.2. 生理生化鉴定
1.3.3. 生长曲线测定
1.3.4. 16S rDNA扩增及序列测定
1.3.5. 构建16S rDNA基因序列系统发育树
1.4. 数据处理
-
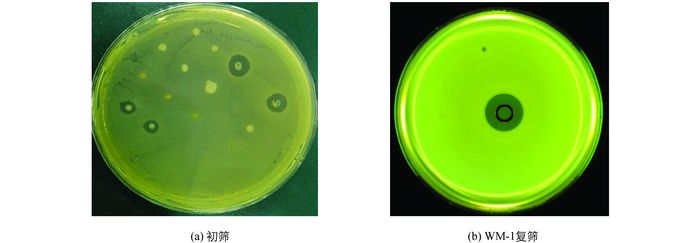
从池塘底泥及水样分离筛选得到8株嗜水气单胞菌拮抗菌(表 1).通过进一步测定, 比较其对嗜水气单胞菌的拮抗活性, 最终筛选出1株对嗜水气单胞菌具有良好拮抗活性的菌株, 命名为WM-1, LB平板培养24 h后, 其抑菌圈直径达21.8±0.763 mm(图 1).
-
37 ℃培养24 h后观察, 其菌落呈圆形, 乳白色, 表面有裙皱状突起, 边缘锯齿状, 不透明, 粘质, 不易乳化; 培养48 h后, 菌落表面变得干燥, 呈煎蛋状; 在液体培养基中, 静置时表面容易形成白色粘质膜.革兰氏染色呈阳性, 短杆状, 芽孢中生.具体菌落形态见图 2.
-
菌株生理生化试验结果(表 2)表明, WM-1菌株接触酶、葡萄糖产酸、硝酸盐还原反应呈阳性; 柠檬酸盐分解、丙二酸盐试验、H2S产生呈阴性, 不能在7% NaCl培养基上生长.
-
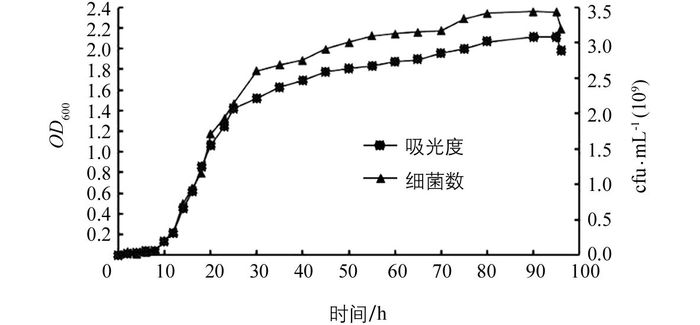
菌株生长曲线如图 3.0~8 h为迟缓期, 8~25 h为生长对数期, 25~90 h为生长稳定期, 之后为衰亡期.细菌发酵培养后最高浓度可达到3.5×109 cfu/mL, 且能长时间保持稳定, 表明该拮抗菌具有良好的生长能力和活性保持能力, 具有良好的应用前景.
-
分离菌株WM-1所扩增的16S rDNA基因序列长度为1 350 bp, 将序列相关信息提交到GenBank, 获得登录号KY235674, 利用NCBI上Blast程序进行同源性检索, 发现分离菌株的16S rDNA序列与甲基营养型芽孢杆菌亲缘关系最近, 同源性高达99%, 其系统发育树见图 4.最后, 综合形态与生理生化特征, 以及16S rDNA序列分析结果, 鉴定菌株WM-1为甲基营养型芽孢杆菌(Bacillus methylotrophicus).
2.1. 嗜水气单胞菌拮抗菌的分离与鉴定
2.2. 细菌的鉴定
2.2.1. 形态学特征
2.2.2. 生理生化特征
2.2.3. 生长曲线
2.2.4. 16S rDNA基因序列与系统发育树
-
在抗生素滥用的今天, 积极寻找微生态制剂已成为国内外水产疾病防治的热点[11], 从健康养殖环境或动物体内获取拮抗菌是公认的方法[18].本研究从健康养殖池塘中筛选到1株对致病性嗜水气单胞菌有良好拮抗活性的甲基营养型芽孢杆菌, 从现有文献报道来看, 其主要应用于植物病害防治方面[19-21], 目前国内尚无关于甲基营养型芽孢杆菌作为水产益生菌的报道, 本试验拓展了其功能.
点种法是筛选和研究拮抗微生物的常用方法之一, 但其操作复杂, 需先将待测样品中的微生物进行分离纯化, 而本试验对Smith等[22]的点种法稍作修改, 采用点喷法, 即将待测样品直接点喷在涂有病原菌的平板上, 此方法不仅可以直接观察到拮抗菌产生的抑菌圈, 通过抑菌圈的大小, 清楚地比较菌株抑菌活性的强弱, 还能简化操作, 节约筛选时间.但使用此方法需将待测样品稀释到适宜浓度, 使细菌在平板上呈单菌落, 以便观察具有生长优势细菌的拮抗作用.
本试验对分离得到的拮抗菌株进行了生理生化鉴定及16S rDNA序列分析, 最终鉴定为甲基营养型芽孢杆菌, 其抑菌圈直径达21.8 mm, 优于刘亚楠等[23]从养殖团头鲂肠道筛选的1株解淀粉芽孢杆菌(抑菌圈13 mm), 也好于蒋启欢等[24]从银鲫肠道筛选的潜在益生菌(抑菌圈15 mm), 以及周金敏等[13]从黄颡鱼肠道分离出的3株对嗜水气单胞菌有很强抑菌活性的枯草芽孢杆菌(抑菌圈14 mm), 因此与以往报道的嗜水气单胞菌拮抗菌相比, 其拮抗效果更强.
由于同一菌株在不同的生长条件如:pH值、盐度、温度、培养基的成分等产生的抗性物质或抗性物质的多少都有所差异[25].本试验完全是在实验室条件下进行, 因此筛选到的1株拮抗菌只能说明在实验室条件下, 具有较好的拮抗活性, 但在自然养殖条件下, 它们对嗜水气单胞菌会不会有同样的拮抗作用, 有待进一步的探讨研究.另外, 拮抗菌在实际应用中受到很多因素影响, 例如在宿主体内的定殖模式、对肠道菌群的调节机制以及抑菌机理等[26].因此, 对本试验筛选到的拮抗芽孢杆菌, 需要进一步研究其拮抗特性及安全性, 并对其实际抑菌与应用效果进行评估, 使其成为真正实用的益生菌, 应用于养殖生产实践中.



 下载:
下载: