-
土地利用是人类结合区域自然环境特征对土地开发利用的结果[1-3].土地利用的空间分布可以用土地利用特征与空间数据关系来表达[4],土地利用包含区域自然因子信息.而地形因子是决定区域土地利用类别空间分布的关键因素之一[5-6],不仅为土地利用格局的形成提供基础,其空间分布特征也影响着土地利用的演变过程[7].不同的地形因子从不同的侧面反映地形特征,高程和坡向决定区域局部的温度和光照状况,坡度和沟壑密度影响局部的土壤保持和涵养水源能力,影响人类利用土地的难易程度[8-9].
近年,相关研究大多是基于小流域土地利用空间分布与其坡度、坡向、海拔间关系特征的研究[10],对大流域且地形复杂多样的青藏高原区土地利用空间分布与地形因子关系研究甚少.同时土地利用空间分布不仅与当前地形因子间关系密切,随着时间的推移,同一地区地形因子对土地利用也发生着影响.鉴于此,本文以西藏“一江两河”流域为例,探讨地形因子与土地利用类型时空分布的相互关系,以期为流域土地利用在不同等级地形上合理布局提供科学依据.
全文HTML
-
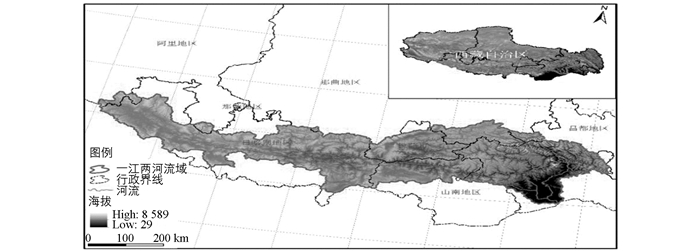
“一江两河”流域主要包括雅鲁藏布江及其支流拉萨河与年楚河,位于青藏高原的中南部(图 1),经纬度为27°49′-31°19′N,82°01′-93°06′E,流域总面积约26万km2,占西藏土地总面积的20.31%.地形以高原、山地、河谷为主,南北宽度245.5 km,东西长为512.8 km.地势呈南北高中间低,平均海拔从西至东约为4 050~3 500 m,最低海拔29 m,最高海拔达8 589 m.该流域河谷地形特点为宽谷、峡谷相间,沿谷宽度一般约为5 km,大支流交汇处宽度可达10 km以上.沟壑密度反映地表复杂程度,研究区平均沟壑密度为2.78 km/km2,表明流域地形较为破碎,地表复杂.研究区气候类型为高原季风温带半干旱性气候,年均温较低,约6~8 ℃,无霜期长达130~140天,年均降水量约为251.7~580.0 mm,拉萨市、日喀则、山南等地区的降雨量占该流域全年降雨量的比重超过80%[11].年楚河谷、拉萨河谷与雅鲁藏布江山南地区的干流谷地并称为西藏的“三大粮仓”,其中种植业是流域农业生产中最重要的传统方式之一,主要农作物为青稞、春小麦、冬小麦、油菜等[12].
-
利用ArcGIS软件的水文分析模块确定西藏“一江两河”流域研究区;所采用的地形数据空间分辨率为30 m的Aster.gdem.v2数字高程模型(DEM),来源于中国科学院计算机网络信息中心地理空间数据云平台(http://www.gscloud.cn);土地利用现状数据来自中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心共享网络提供的1:10万1990年、2000年、2010年、2015年4期土地利用数据;行政区划数据来源于2015年全国县级矢量数据图.
土地利用类型分类依据LUCC分类体系,提取耕地、林地、草地、水域、居民地、未利用土地6个地类. DEM数据与土地利用栅格数据大小均定义为1 000 m×1 000 m.
-
沟壑密度是描述地面被水道切割破碎程度的一个指标[13],是气候、地形、岩性、植被等因素综合影响的反映.计算沟壑密度是为了揭示研究区地表复杂程度,公式为:
式中:Ds为沟壑密度;∑L为研究区域内的沟壑总长度;A为研究区域面积.
-
土地利用变化强度指数可以反映土地类型面积的变化幅度[14-15],其公式为:
式中:k为时间段内第j类土地利用类型变化强度指数;Ubj,Uaj分布为研究末期(b)和初期(a)第j类土地利用类型的面积;T为时间间隔期,以年为单位.
-
土地利用的分布概率受不同地形等级区段的面积差异和各土地利用面积比重差异的影响[16],为避免不同土地利用类型面积对其不同地形梯度区间出现频率的影响,引入地形分布指数(land distribution index,LDI)消除面积差异量纲的影响[17-18].该指数是一个标准化、无量纲的指标[19],其计算公式为:
式中:LDIie为第i种土地类型在第e级地形上的分布优势指数;分子表示i种地类在第e级地形面积所占比重,分母表示i地类面积所占总流域面积的比重;Xie为i地类在第e级地形面积;i为不同地类,i=1,2,…,m;e为地形因子,e=1,2,…,n.其值范围在[0,+∞]. LDIie>1,则表明在某一等级下i地类在e地形处于优势分布,其值越大,分布优势越显著;反之,LDIie<1,则表明在这一等级地形上该地类在处于劣势分布.
-
土地利用转移分布指数表征了土地利用转移的相对水平,对各地类在各级别地形区域的转移相对程度具有指示意义[20]. 1990-2015年“一江两河”流域各类用地存在相互转化,本文构建土地利用转移分布指数来探讨地理因子对土地利用转移变化的影响.
式中:pij为第i种地类在第j级地形的转移分布指数;Qij为第i种地类在第j级地形区域发生转移面积;Qi为研究期第i种地类发生转移的土地面积总和;Qj为研究期第j级地形区域发生转移的土地面积总和;Q为研究期整个区域发生转移的土地面积总和.若pij值大于1,表明第i类土地在第j级区域转移水平大于区域平均水平,在第j级地形区域的转移具有优势地位,pij值越大,表明转移程度越高.在同一级地形级别区域内,地类转移分布指数的差异反映该地形区域内地形因子对地类转移过程影响作用的大小,转移分布指数越大,表明在同一地形区域内该地类转移相对容易[20].
-
本文以ArcGIS空间分析为技术支持,在流域DEM的基础上提取坡度、坡向和高程.采用1990-2015年4期土地利用数据与地形因子进行空间叠加,结合地形分布指数、变化强度指数和转移分布指数揭示高原山地区土地利用与地形因子时空分布关系.
DEM派生数据坡度、坡向和高程的分级,既要建立在流域土地利用现状的基础上,又要结合其地形特征,符合经济规律和自然规律[21].本文根据“一江两河”流域高程地形特征将其划分为6级;坡向是方位角,我国通常把南坡作为标准的阳坡,北坡作为标准的阴坡,将其分为9个方向[22],本文为了便于统计,将9个方向的坡向合并为5个,并划分为5级;坡度依据《土地利用现状调查技术规程》分为6级.具体划分标准和各地类面积统计结果见表 1、表 2.
2.1. 数据来源及处理
2.2. 研究指标
2.2.1. 沟壑密度计算
2.2.2. 土地利用变化强度指数
2.2.3. 地形分布指数
2.2.4. 土地利用转移分布指数
2.3. 土地利用与地形因子时空分布关系分析
-
从表 2和表 3中可以看出,1990-2015年,居民地呈增长的趋势,从1990年的98 km2(0.04%)增长到2015年的194 km2(0.08%);水域从1990年的11 826 km2(4.55%)增长到2015年的11 844 km2(4.56%),整体增加了18 km2;与之相反的是耕地、草地与林地呈逐年减少的趋势.耕地从1990年的3 395 km2(1.31%)减少到2015年的3 336 km2(1.29%),减少了59 km2,这与该流域人口的流动以及居民地占用耕地有很大关联;林地从1990年的35 627 km2(13.72%)减少到2015年的35 548 km2(13.69%),森林面积减少79 km2,其中2000年以来林地面积呈上升的趋势,这与政府大力倡导植树造林有关;草地在该流域所占比重均超过60%,但从1990年的163 016 km2(62.79%)降到2015年的162 897 km2(62.76%),减少119 km2(0.02%),这与当地过度放牧有很大关联.未利用地比较稳定,变化趋势不明显.从强度指数看,25年间居民地和水域强度指数呈上升的趋势,且均为正值,特别是2010-2015年期间强度指数值达到7.32%,显著大于其余地类,说明居民地不断开发,水域面积扩大;耕地强度指数在各时期均为负值,说明其面积在不断减少;其余地类在3个时段内强度指数均有正有负,但波动均相对较小(<1%),所以其地类面积变化整体较为稳定.
-
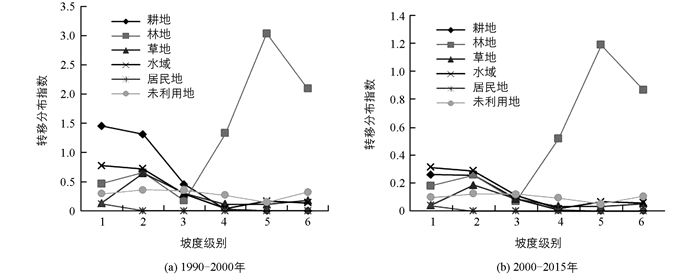
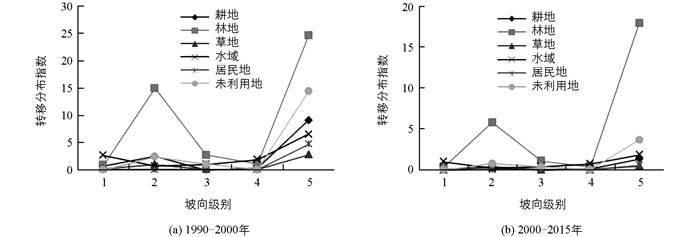
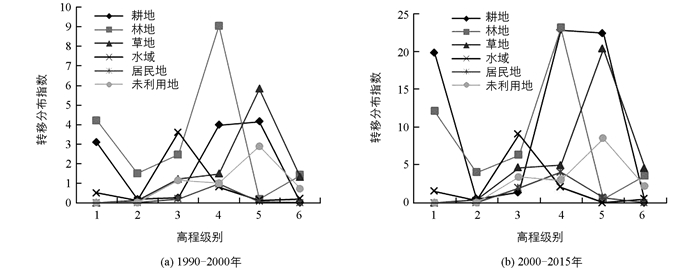
1990-2015年“一江两河”流域各类用地相互之间的转换频繁,地形因子对其转换有很大影响.根据公式(4),计算得到1990-2015年各地类在地形因子中转移分布指数.由图可知(图 2,3,4),地形因子对土地转移变化均有约束作用,不同地形区域中各土地利用类型的转移存在较大差异.
-
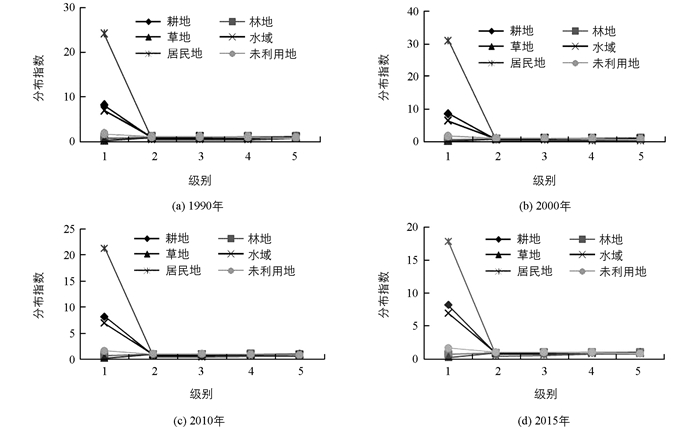
图 2显示的是“一江两河”流域各地类在不同坡度带上的转移分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从各级别转移分布看,1990-2000年坡度转移分布中耕地资源在第1,2级中的转移指数最大(pij>1),说明在此坡度级上,耕地转移相对容易;林地在第4,5,6级别内转移分布指数最大(pij>1),表明在此坡度级上,以林地转移为主,其他地类转移不明显.在2000-2015年间林地转移也主要集中在第5,6级上,表明在此时间段内,其余地类转移相对停滞,林地转移还在持续. ②从土地利用类型转移分布指数变化程度来看,林地随着坡度级别的上升其转移指数上升,其余用地呈现不断走低的趋势.说明在25年时间段内,林地转移是最容易发生的,这与人类退耕还林、森林砍伐有很大关联.
-
图 3显示的是“一江两河”流域各地类在不同坡向带上的转移分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从各级别转移分布看,1990-2000年坡向转移分布中,林地在第2级中的转移明显(pij>1),说明第2级坡向内,林地转移相对容易;在第5级别内各地类转移指数均较大(pij>2),说明在阳坡上,各地类转移频发,表明土地易向光照充足气候温暖的坡向上转移;2000-2015年间林地转移也集中在第2级上(pij>5),其余地类转移指数偏低(pij<1),表明在时间段内,其余地类转移相对停滞,林地转移还在持续. ②从土地利用类型转移分布指数变化程度来看,随着坡向级别的上升,林地转移指数呈先上升后下降再上升的趋势,其余用地波动不明显.说明25年的时间段内,坡向上林地转移是最容易发生的,这与坡向影响降水和气温的分布有很大关联.
-
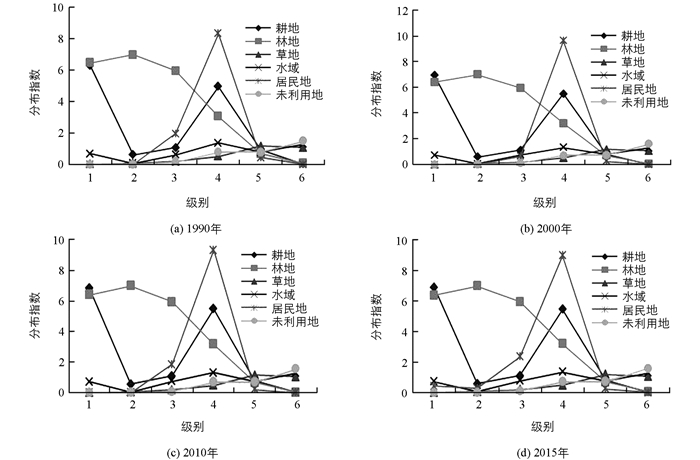
图 4显示的是“一江两河”流域各地类在不同高程带上的转移分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从各级别转移分布看,高程对各地类转移分布指数影响差异很大. 1990-2000年高程影响下转移分布指数在第1级别中,耕地(pij>10)和林地(pij>15)转移指数最高,说明在低海拔内,林地与耕地的转移最为显著.在第4、第5级别内,耕地、林地、草地转移最为显著,与这几个高程带内受人类活动影响较大、砍伐与放牧较为集中有关. 2000-2015年间,各地类转移指数相对降低(pij<10),说明各类地转移有所放缓. ②从土地利用类型转移分布指数变化程度来看,随着高程级别的上升,各地类波动幅度明显.说明在25年的时间段内,高程上各地类都容易发生转移,这与高山具有的垂直地带性差异有很大关联.
-
土地利用的空间分布可以用土地利用类型与地形指数的关系来表达,这种关系的时间变化,构成了土地利用时空分布格局[8, 23].根据公式(3),计算1990-2015年6种地类的地形优势分布指数.从图中可以看出,该流域的地形因子对其土地利用时空分布的约束作用十分突出,各土地利用类型在地形梯度带上的分布格局变化显著.
-
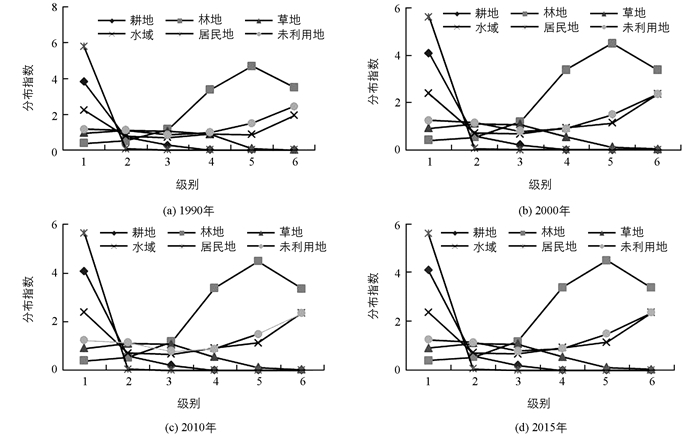
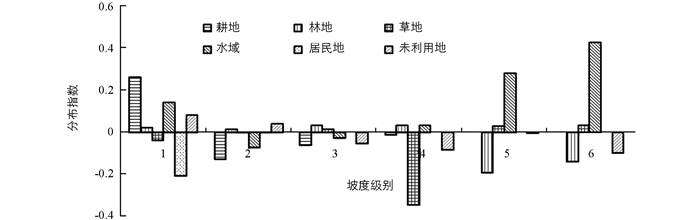
图 5显示的是“一江两河”流域各地类在不同坡度带上的优势分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从级别优势分布看,水域用地、耕地、居民地在第1级别的分布优势明显,特别是居民地、耕地在第1级分布指数呈现最大值,这与坡度低、利于人类活动、适宜耕种有关.随着坡度级别的上升,林地、未利用地、水域呈现上升趋势,林地优势显著突出. ②从土地利用类型分布指数变化程度来看,居民地在第1级变化明显,其后趋于平缓,基本没有起伏,主要是居民地主要集中在坡度大于6°的地区,该区域适合村镇、城市建设.耕地随着坡度级别的上升,面积逐渐减少,坡度大于25°的区域基本没有耕地,这与退耕还林、还草有很大关联.相反,林地随着坡度的上升,分布指数呈不断上升的趋势.未利用、草地、水域的分布指数较为均一,起伏和缓.
-
图 6为“一江两河”流域1990-2015年土地利用类型在不同坡度带上优势分布指数变化情况,2期相比较,在第2,3级坡别上,分布指数变化幅度小(-0.1,+0.1),说明在这2级坡度带上各地类优势分布指数变化不明显.耕地、居民地在第1级别坡度范围内分布指数增加,在其它区间分布指数减小,说明25年期间耕地在缓坡区分布优势继续扩大,这与我国实施退耕还林、还草密不可分;在第5,6级别上水域分布优势继续扩大,而林地优势缩小,在第4级别上草地分布指数最低,说明在此区间陡山冰雪融水增加,林地草地锐减.
-
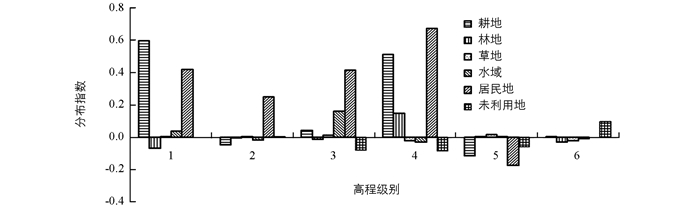
图 7显示了“一江两河”流域各地类在不同高程带上的分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从高程级别优势分布看,林地、耕地和居民地在第1级的分布优势明显(LDI>5),特别是林地在第1,2,3级中分布指数呈现最大优势;在第4级上,水域与居民地优势突出(LDI>4),这与流域内人类活动主要集中在这一海拔高度有关(平均海拔约40 00 m). ②林地随着高程的上升,分布指数呈不断递减的趋势;水域和耕地分布指数呈两头低、中部凸起的形态;草地和未利用地在分布指数随高程级别变化中呈稳定趋势,变化不明显,受海拔影响较小.
-
由图 8可以看出“一江两河”流域1990-2015年土地利用类型在不同高程带上优势分布指数变化情况,与1990年相比较,2015年耕地和居民地分布指数在第1,2,3,4级上明显增加,说明居民地和耕地在25年期间内在高程L<4 000 m区间分布优势继续扩大;除水域和林地在第3,4级继续有一定优势分布外,其余地类分布指数变化都很小(-0.1-0.1),说明该时段内优势分布差异变化不显著.
-
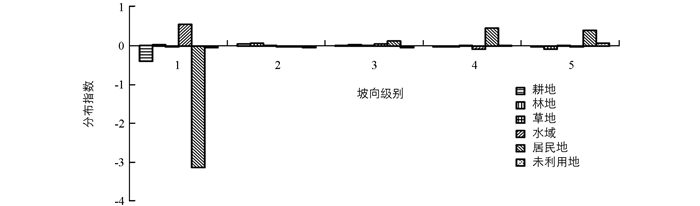
图 9显示的是“一江两河”流域各地类在不同坡向上的分布指数变化特征,从中可以看出:①从级别优势分布看,居民地、耕地和水域在第1级别的分布优势明显,特别是居民地在第1级分布指数呈现最大值,说明居民地主要集中在无坡向地区,以及水域和耕地集中的区域. ②从土地利用类型分布指数变化程度来看,居民地、耕地、水域在第1级向第2级变化中急剧下降,第2级之后趋于和缓.其余地类的坡向分布呈稳定趋势,起伏缓和,基本无变化.说明除居住地、耕地和水域外,其他土地利用类型几乎不受坡向的影响.
-
由图 10可以看出“一江两河”流域在1990-2015年期间土地利用类型在不同坡向带上分布指数变化情况,与1990年相比较,2015年第1级坡向级别内的居民地分布优势指数明显减少,说明居民地在25年期间在无坡区分布优势不断缩小.其余地类在坡向条件下变化不大,优势分布指数在-0.5~0.5之间,这说明1990-2015年各地类在坡向上的变化都不大,即坡向对土地利用类型约束性比较小.
3.1. 土地利用及其强度变化分析
3.2. 土地利用转移变化与地形因子的关系
3.2.1. 坡度上转移分布指数特征
3.2.2. 坡向上转移分布指数特征
3.2.3. 高程内转移分布指数特征
3.3. 土地利用时空优势分布与地形因子的关系
3.3.1. 土地利用类型在坡度上分布特征
3.3.2. 1990-2015年土地利用类型在坡度上分布变化
3.3.3. 不同高程上土地利用时空分布特征
3.3.4. 1990-2015年土地利用类型在高程上分布变化
3.3.5. 不同坡向上土地利用时空分布特征
3.3.6. 1990-2015年土地利用类型的坡向分布变化
-
本文以西藏“一江两河”流域为研究区域,打破了行政区界限,这与传统意义的西藏“一江两河”地区范围有差异.近20年来,在政府主导下,该流域一直大力推行植树造林,拉萨市的沙尘天气已经大量减少,但4期数据分析表明,林地面积有减有增,整体呈减少态势,这与实际感观不符,造成这种现象的原因可能是数据获取时存在精度误差或是地域差异造成的.一般情况下,引起耕地变化主要由建设用地占用、农业人口流动、气候变化、产业结构调和政策引导等因素引起.从现有数据的时间尺度来看,研究区内居住地和耕地多分布在较为平坦开阔的共生地带,由于居住地处于扩张态势,使得居住地在一定程度占用耕地,使耕地减少,但建设用地占用了多少耕地,对耕地的影响大小以及各影响因素对耕地变化的贡献程度还需作进一步研究分析,不能一言以概之.
-
本文基于GIS空间分析技术,以1990-2015年期间4期土地利用遥感数据和数字高程模型(DEM)为基础数据源,分别从土地变化强度指数(K)、土地分布指数(LDI)和土地转移分布指数(p)揭示地形因子与土地利用时空分布之间的关系.
1) 1990-2015年期间,研究区土地总面积变化不大,但区域内一种土地利用类型面积的增加必然伴随着其他类型面积减少;期间居住地变化最为显著,居住地和水域呈不断扩张的趋势,其余地类有一定的减少.
2) 土地利用的迁移转化程度与地形因子间也存在较高相关性,高程和坡度对土地利用转移的影响较为一致.耕地转移分布主要集中在第1,2级坡度,即坡度小、高程低,阳坡半阳坡的区域;林地转移分布集中在坡度较大的区域,并呈现出向高海拔转移的趋势;草地主要向高海拔区域转移;其余各类地转移不明显.
3) 优势分布指数可以很大程度避免地形分级所带来的面积不等和各类地面积差,其对“一江两河”流域土地利用空间分布约束作用显著,地形梯度上空间分布格局呈显著变化.坡度上,水域用地、耕地、居民地在第1级别的分布优势明显,随着坡度级别的上升,林地、未利用地、水域呈上升趋势,林地优势显著突出.高程上,林地、耕地、居民地在第1级别的分布优势明显,特别是林地在第1,2,3级中分布指数呈现最大优势,在高程第4级别中,水域与居民地优势突出.坡向上,居民地、耕地、水域在第1级别的分布优势较为明显,其余地类变化不显著,表明坡向对土地利用类型约束性比较小.
4) 综合来看,在高程、坡度和坡向3个地形因子中,高程和坡度对土地利用分布影响大,坡向影响相对较小.



 下载:
下载: