-
颗粒物是我国大气环境污染的首要污染物之一,而扬尘是大气颗粒物的主要来源,已经严重影响到大气质量及人们的生存环境[1-3].堆场扬尘具有间歇性排放的特征,其源自工业生产中的各种各样的原料堆、工业固体废弃物、工程建筑渣土、工程垃圾和建筑工人的生活垃圾,这些料堆和垃圾在装卸、传送和堆积的过程中经风蚀作用形成扬尘[4].城市中的各种料堆不计其数,随处可见,而且大部分都没有采取有效的防控措施,在不利的气象条件下,对城市大气环境造成严重污染.从环境与经济的效益出发,堆场扬尘控制比施工扬尘受到的关注更多,相关研究也较多,我国很多城市对解决堆场扬尘污染问题已经明确了相关要求[5].
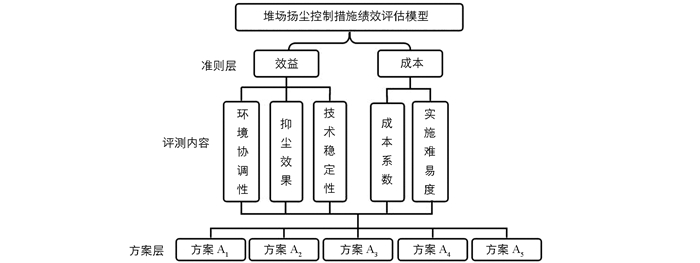
目前,国内外堆场扬尘污染的控制措施有雾化喷淋、固化抑尘剂、防风网、射雾抑尘等,单一从技术角度考虑,大部分扬尘控制措施的技术趋于成熟,而依据实际情况从多角度进行综合选择成为关键[6-9].堆场扬尘污染控制是一类典型的多目标决策问题,需要对众多方案的性能进行系统绩效评估,近年来,相关学者专家针对多目标综合决策问题提出了一系列不同的方法[10-12].本研究针对堆场扬尘污染的控制,建立了堆场扬尘污染控制措施的绩效评价指标,通过试验研究了不同措施的控制效果,并引入熵权理论确定堆场扬尘控制技术措施各个评价指标的权重,从而为堆场扬尘控制技术措施的优选提供科学决策.
HTML
-
影响堆场起尘的的因素有很多,包括温度、湿度和风度等气象条件;而同一季节中排除了气象条件对堆料的影响,则影响颗粒物起尘的的因素与不同物料颗粒表面含水率、起动风速、粒径、安息角和现场作业状况有关[13],开展绩效评估,其方案设计尤为重要.
-
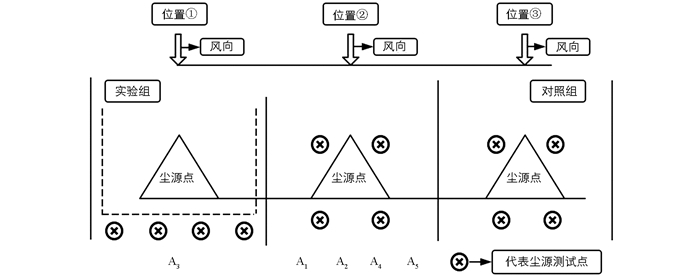
本研究拟针对煤料堆场开展试验,通过不同控制措施下的模拟试验进行评估指标的获取.结合国内外现有堆场污染控制技术措施,对模拟煤料堆场采取了5种控制方案,依次是A1洒水、A2固化剂、A3抑尘网、A4高空射雾、A5高空射雾+固化剂.其中高空射雾采用的是秦皇岛首创思泰意达环保科技有限公司最新研发的高空射雾车,固化剂选用兰州天际环保有限公司生产的固化剂.不同控制方案的特征和局限性如表 2所示.
2018年10月在河北秦皇岛市开展试验,单个堆场面积为50 m2,堆料高度最高为2 m,每种方案3个重复,另外设有对照组.各堆场与该季节常见风向垂直排列,间隔5 m,为了避免相互间的干扰,各堆场间用高4 m的隔板分隔.测试点布局及场地如图 2所示.因抑尘机理与过程不同,A1,A2,A4,A5方案是在试验覆盖范围内设置了4个监测点,防风抑尘网主要是防止扬尘的扩散,因此A3方案是在试验覆盖范围外部(堆场外侧下风向距离抑尘网5m处)设置4个监测点,采用Dusttrak设备监测堆场扬尘排放的PM10质量浓度(数据取平均值).因堆场的特殊性(一般堆积不超过1个月),本研究的评估时间为1个月,试验期间平均风速为2~4 m/s.
-
信息熵可以将信息从一个相对模糊概念转变为精确概念,其反映了信息源的混沌程度,并可利用熵值计算客观权重,在诸多领域得到了广泛应用[14-17].同时,信息熵指标属性的混沌程度也反映了信息量的多少,并决定了综合决策的可靠性[18-19].
-
根据方案绩效评估指标的评价值构造原始数据矩阵:
式中:Xij为mi方案的第j个指标值.
-
鉴于扬尘控制方案优选的绩效评估指标体系中各测评指标的不同属性,很难实现指标间的直接对比,进行多目标综合绩效评估的指标属性值必须经过归一处理,其处理方法如下[21-22]:
效益型指标归一化:
成本型指标归一化:
Xij为第mi个方案的第j个指标的数值(i=1,2…,m;j=1,2,…,n).
针对评价指标的不同属性,经式(2)或式(3)对R′进行处理得归一化矩阵:
式中:i=1,2,…,m;j=1,2,…,n.
-
对于(m,n)堆场扬尘控制方案优选绩效评估问题,定义第j个评估指标的信息熵:
式中:Hj为概率集P11,P21,…,Pij的熵;i=1,2,…,m;j=1,2,…,n.
第j个指标下第mi个方案指标值的比重为:
显然,当Pij=0时,lnPij无意义,故需对Pij加以修正,修正表达式如下:
第j个指标的权重dj可以定义为:
-
将堆场扬尘控制的可行方案影射到“空间距离”Lp(d,j)作为综合绩效评估值:
一般情况下,取p=1,则空间距离L1(d,j)如下:
评价准则:空间距离L1(d,j)越小者越接近理想方案,即L1(d,j)越小的方案越优.
2.1. 堆场扬尘污染控制措施的绩效评估试验
2.2. 基于信息熵的堆场扬尘污染控制措施的绩效评估方法
2.2.1. 引入信息熵
2.2.2. 构造原始数据矩阵
2.2.3. 指标的归一化
2.2.4. 确定各绩效评估指标的权重
2.2.5. 优序绩效评估准则
-
通过一个月的监测试验,得到了各方案量化指标的实际值,构成原始数据矩阵R′(表 3).
-
采用式(2)或式(3)对表 3中不同方案各量化指标的实际数据进行归一化处理,并通过式(5)-(8)计算得到堆场扬尘控制方案的各评价指标的信息熵及熵权(表 4),并且环境协调性和技术稳定性对堆场扬尘控制方案优选绩效评估的影响较大.
-
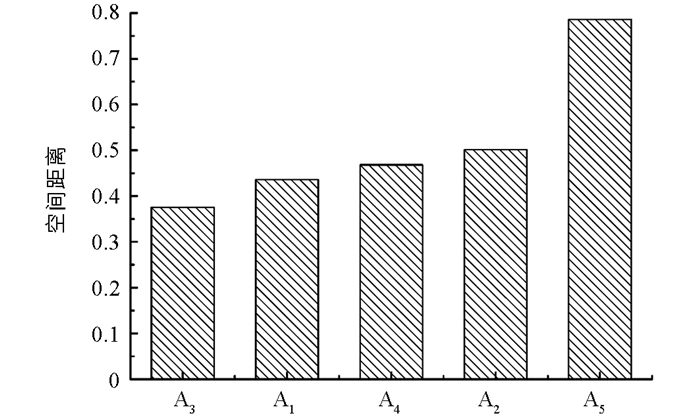
根据优序绩效评估准则,由式(10)计算出各个方案的空间距离即综合评价值L1(d,j)如下:L1(d,3)0.375 5 < L1(d,1)0.435 7 < L1(d,4)0.468 0 < L1(d,2)0.501 2 < L1(d,5)0.786 0. 5种方案的优选排序从高到低依次为(图 3):A3抑尘网、A1洒水、A4高空射雾、A2固化剂、A5高空射雾+固化剂,其中方案3的空间距离最小,方案5的空间距离最大,方案2和方案4的空间距离相近.因此,应优选A3抑尘网作为城市堆场扬尘控制方案,A1洒水的空间距离仅次于A3,可作为备选方案.
3.1. 构建堆场扬尘控制方案测评指标原始数据矩阵
3.2. 测评指标归一化与权重的确定
3.3. 城市堆场扬尘控制方案绩效评估
-
本研究以堆场扬尘为研究对象,通过现场试验、实地监测和模型评价等方法对扬尘控制进行了研究,主要研究结论如下:
1) 结合国内外研究进展和咨询专家,从控制方案的效益和成本两个层面构建出包括抑尘效果、环境协调性、技术稳定性、成本系数和实施难易度在内的堆场扬尘控制方案优选的绩效评估模型;
2) 方案优化选择是科学控制堆场扬尘的重要环节,鉴于决策目标的不确定性,在信息熵理论的基础上对城市堆场扬尘5种控制方案进行绩效评估优选分析,研究认为,环境协调性和技术稳定性对方案绩效评估的影响较大,试验条件下A3抑尘网作为堆场扬尘控制方案的绩效评估结果最优,A1洒水可作为备选方案.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: