-
化脓隐秘杆菌Trueperella pyogenes以前被称为化脓放线菌Actinomyces pyogenes和化脓棒状杆菌Corynebacterium pyogenes,属于放线菌科Actinomycetaceae隐秘杆菌属Arcanobacterium[1]. 化脓隐秘杆菌是一种重要的条件性致病菌,主要感染猪、牛、羊等多种动物和人,引发皮下、内脏器官及肌肉组织脓肿,亦可造成肺炎、胸膜炎、关节炎、心内膜炎和乳腺炎等多种病症,给养殖业带来重大的经济损失[1]. 化脓隐秘杆菌感染致病与其表达的毒力因子有关,目前报道的毒力因子包括溶血素(Plo)[2-3]、胶原结合蛋白(CbpA)、神经氨酸酶(Nan)及菌毛合成蛋白(Fim)等[4-7],这些毒力因子在该病原感染致病中发挥重要作用.
本实验室从重庆市璧山区一起屠宰猪肉中出现的草绿色化脓病料样本中分离出一株溶血性极强的细菌,经常规形态学鉴定、16S rRNA测序分析、毒力基因和耐药谱检测,将其鉴定为化脓隐秘杆菌. 结合化脓隐秘杆菌感染宿主后主要引起炎性脓肿的致病特征,研究其作用巨噬细胞对促炎细胞因子IL-6和TNF-α分泌的影响,以期为猪化脓隐秘杆菌病的防控及致病机理研究提供参考.
HTML
-
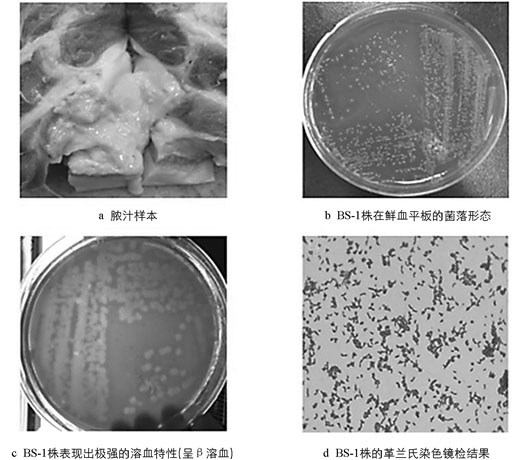
重庆市璧山区一起屠宰猪肉中出现的草绿色粘稠的脓汁(图 1a),以灭菌离心管采集后,低温冷藏送检.
-
药敏纸片购于杭州滨和微生物试剂有限公司;Lysis Buffer for Microorganism to Direct PCR、preMix 2× Taq和DNA Marker购于大连宝生物有限公司;胎牛血清购自于Biological Industries公司;IL-6和TNF-α ELISA检测试剂盒购自Thermo Fisher Scientific(USA). J774A.1巨噬细胞由西南大学动物科学学院周洋博士惠赠.
-
以Li等[8]报道的细菌16S rRNA基因及Rzewuska等[9]报道的化脓隐秘杆菌Plo,CbpA,NanP,NanH,FimA和FimC毒力基因引物为检测引物(表 1),由上海百力格生物技术服务有限公司合成.
-
C57BL/6小鼠,体质量18~22 g,购自重庆市中药研究院.
-
将病料接种于鲜血琼脂培养基上,37 ℃培养48 h,观察菌落形态. 挑取单个菌落纯化培养和革兰氏染色镜检. 将分离菌(BS-1)菌液按0.3 mL/只(1.2×109 CFU/mL)腹腔注射C57BL/6小鼠,观察其致病性.
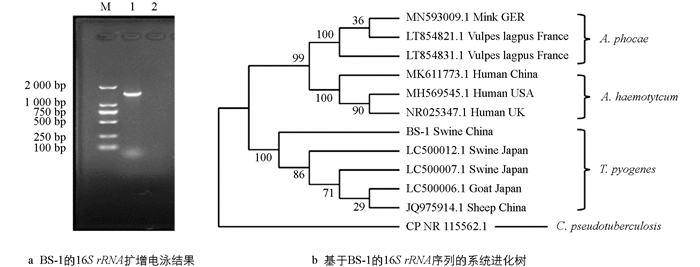
用Lysis Buffer for Microorganism to Direct PCR裂解细菌获得基因组DNA,以16S rRNA引物进行PCR扩增. PCR扩增体系为基因组DNA 2 μL,premix 2×Taq 12.5 μL,上、下游引物各1 μL,用dd H2O补至25 μL. PCR扩增条件为94 ℃预变性5 min;94 ℃变性30 s,54 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1.5 min,30个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min. 经电泳检测后,将PCR产物送往重庆擎科兴业生物技术有限公司测序. 测序结果进行BLAST在线相似度比对. 以放线菌科的伪结核棒状杆菌Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis 16S rRNA为外群,选取猪、山羊、绵羊和牛源化脓隐秘杆菌T. pyogenes、感染人的溶血隐秘杆菌Arcanobacterium haemolyticum、感染狐和貂的phocae隐秘杆菌A. phocae 16S rRNA序列(表 2),以CLUSTAL X进行多重序列比对,采用MEGA 8.0构建系统进化树,分析BS-1株的16S rRNA聚类情况.
-
将分离菌(BS-1株)接种于含10%血清的LB(lysogeny broth)肉汤中,37 ℃培养48 h,制成0.5个麦氏单位的菌悬液,吸取100 μL均匀涂布在鲜血琼脂平板表面,待菌液吸收后,贴上药敏纸片,37 ℃培养48 h,记录抑菌圈大小.
-
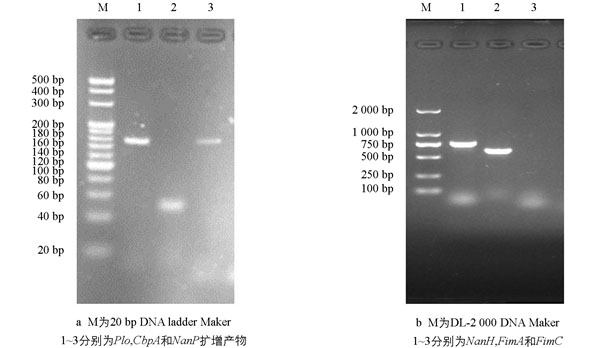
制备BS-1株的基因组DNA,检测毒力基因携带情况. PCR扩增条件为94 ℃预变性10 min;94 ℃变性30 s,57 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1.5 min,35个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min. PCR扩增产物分别用4%(Plo,CbpA,NanP)和1%(NanH,FimA,FimC)的琼脂糖凝胶进行电泳检测.
-
培养BS-1株菌液,以感染复数为10(MOI=10)作用J774A.1巨噬细胞1 h,更换含庆大霉素培养液继续培养,24 h后收集培养上清,按照ELISA试剂盒说明书检测IL-6和TNF-α含量. 用SPSS软件分析数据差异性.
1.1. 试验材料
1.1.1. 病料来源
1.1.2. 主要试剂及细胞
1.1.3. 检测引物
1.1.4. 试验动物
1.2. 试验方法
1.2.1. 细菌的分离鉴定及致病性试验
1.2.2. 分离菌药敏试验
1.2.3. 分离菌毒力基因检测
1.2.4. 分离菌株对巨噬细胞IL-6和TNF-α分泌的影响
-
以待检脓汁划线接种后分离获得形态单一、溶血性极强(呈β溶血)约1 mm大小的菌落,其表面光滑,呈半湿润状、灰白色(图 1b、图 1c). 染色镜检显示该分离菌(BS-1)为革兰氏阳性杆菌,呈散在分布的形态多样的短小杆菌(图 1d). BS-1株接种3 h后,小鼠表现为精神萎靡、反应迟钝、动作缓慢等症状,并于7 h内全部死亡,解剖发现肝肿大、脾肿大且有出血点. 对照组小鼠无明显眼观症状和死亡.
对BS-1株16S rRNA基因扩增获得1 500 bp左右的条带(图 2a),测序及系统进化分析发现该菌16S rRNA序列与化脓隐秘杆菌序列相似度较高,其中与NIAH13535株(LC500012.1)相似度最高,为97.26%. 系统进化分析显示,该菌与化脓隐秘杆菌聚类到一个分支(图 2b). 结合病原形态特征,将该BS-1株鉴定为化脓隐秘杆菌.
-
根据美国实验标准委员会(NCCLS)药敏纸片扩散法规标准,以常见的18种抗菌药物进行药敏试验,发现BS-1株仅对克拉霉素和罗红霉素中度敏感,而对青霉素G、庆大霉素、万古霉素、诺氟沙星、氯霉素、米诺环素(甲)、阿莫西林等耐药(表 3).
-
毒力基因检测显示BS-1株携带有Plo,NanP,NanH和FimA共4个毒力基因,未检测到CbpA和FimC基因(图 3).
-
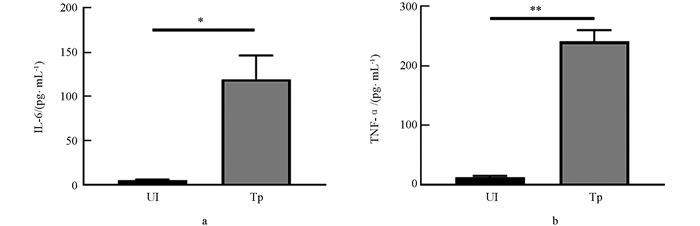
化脓隐秘杆菌感染宿主后所引起的化脓性病变本质为炎症反应,因此本研究检测了该病原感染巨噬细胞后促炎细胞因子分泌情况. 结果发现,与未受感染的J774 A.1巨噬细胞相比,BS-1株感染巨噬细胞IL-6和TNF-α分泌水平显著增加(图 4).
2.1. 细菌的分离鉴定结果
2.2. BS-1株的药敏试验结果
2.3. BS-1株的毒力基因检测结果
2.4. BS-1株感染对J774A.1巨噬细胞IL-6和TNF-α分泌的影响
-
化脓隐秘杆菌与马红球菌及伪结核棒状杆菌相似,均为放线菌属病原中引起化脓性感染的重要病原[1]. 近年来关于该病原感染猪的病例报道渐多,其分离地点包括广东、上海、吉林、河南、天津和四川等地[4, 10-16],表明化脓隐秘杆菌感染猪致病的现象日益严重. 化脓隐秘杆菌可与副猪嗜血杆菌、多杀性巴氏杆菌、致病性大肠杆菌混合感染,对猪的致病性增强,为疾病诊断和防治带来很大的困难[10, 16]. 本文从重庆地区屠宰猪的肌肉脓汁中分离出具有较强致病力的化脓隐秘杆菌,提示当地养猪场需注意对该病原做好防控工作. 掌握病原菌对药物的敏感性情况是有效防控其感染致病的关键,本研究发现化脓隐秘杆菌BS-1株仅对克拉霉素和罗红霉素中度敏感,而对青霉素G、万古霉素、诺氟沙星、氯霉素、阿莫西林等耐药,与Santos等[17]的研究结果类似. 这可能与近年来该地区部分猪场不合理使用抗菌药物有关.
病原菌毒力基因的携带水平大都与其致病能力密切相关,蔡瑶等[10]报道分离自四川浦江的猪源化脓隐秘杆菌携带有plo基,NanH,FimA,FimC和FimG因,无NanP,CbpA和FimE基因. 董文龙等[14]报道分离自吉林省的8株猪源化脓隐秘杆菌均携带有Plo基因,但均缺失CbpA基因,NanH及NanP基因携带水平分别为25%和50%. 本研究发现BS-1株携带了Plo,NanP,NanH和FimA基因,但没有CbpA和FimC基因,与蔡瑶等[10]和董文龙等[14]报道的化脓隐秘杆菌均携带有Plo基因相同,而其他基因携带水平有一定的差异,其原因可能与化脓隐秘杆菌不同来源地有关.
化脓隐秘杆菌感染宿主后主要引起炎性脓肿的致病特征,促炎性细胞因子在该病原感染致炎中起了重要作用. TNF-α和IL-6均是由单核巨噬细胞等产生的重要促炎细胞因子,与多杀性巴氏杆菌、伪结核棒状杆菌等病原感染巨噬细胞诱发大量的TNF-α和IL-6分泌相似[18-19]. 本研究表明化脓隐秘杆菌感染可诱发巨噬细胞大量分泌TNF-α和IL-6,其诱发机理及在该病原感染致病中的作用机制有待进一步研究.
重庆璧山区该起屠宰猪肉中的脓肿病变由化脓隐秘杆菌感染引起,该病原耐药性较强,携带有多种毒力基因,可激活巨噬细胞分泌TNF-α和IL-6. 本研究为化脓隐秘杆菌的防控及致病机理研究提供了资料.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: