-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
手机依赖已成为年轻人的重要标志,大学生作为使用手机的主力军,更容易受到手机依赖的影响[1]. 过度的手机依赖会对人生理与心理的诸多方面产生负面影响[2],同时还会让学生产生学习倦怠[3],而学习倦怠会显著负向预测学习投入[4],这就意味着较高的手机依赖会导致学生学习投入显著降低. 因此探究大学生手机依赖对学习投入的影响及其作用机制,对矫正大学生手机依赖、促进大学生学习发展具有重要的现实意义.
已有研究表明,手机依赖对学生课堂与学习行为具有消极影响[5],在手机的使用上大学生更多的是打电话、拍照、上网而不是学习[6]. 盛忠光[7]系统探讨了手机依赖对大学生学习投入产生影响的机制,指出手机依赖通过戒断症状、突显行为、社交抚慰、心境改变4个维度对大学生的学习动机、学习过程、学习结果产生显著的负面影响. 但该研究仅止步于探讨二者间负面影响的直接关系,并未对其间的过程性因素做进一步挖掘. 目前针对手机依赖与学习投入相关的研究虽然不少,但多为研究两者的直接关系,缺乏过程性因素探索. 本研究在探究手机依赖与学习投入之间关系的基础之上,引入社会支持和延迟满足2个中介变量,对此进行深入研究.
就社会支持与学习投入的关系而言,有研究表明,高社会支持可以缓解学生的孤独感,提升主观幸福感[8],并通过大学生主观支持感知、客观支持转化和支持利用度影响学习投入[9],大学生的教师、家庭、同伴支持与大学生学习适应水平呈显著正相关[10]. 就社会支持与手机依赖的关系而言,当个体的社会支持缺乏时,会选择网络这种媒介满足自身需要[11],从而导致对手机的依赖,但手机依赖越强的大学生会获得越低的社会支持[12],手机依赖减少了个体间的面对面交流,导致个体产生人际关系问题[13]. 由于社会支持与手机依赖、学习投入都存在关系,故本研究假设:社会支持在手机依赖与大学生学习投入关系中起中介作用.
作为个体成功适应社会的核心能力之一,延迟满足能力可以有效预测儿童日后的学业表现和社会适应[14],促进学习者的学习及信息加工[15]. 有研究发现[16],自控能力低的个体趋于选择及时行乐而拖延学业,且有研究[17]表明手机依赖能负向预测学生自我效能感、社会适应以及自我控制,因此手机依赖对延迟满足可能具有负向预测作用. 此外亦有研究[18]表明学业延迟满足在手机依赖对学业拖延的影响中起部分中介作用,故本研究假设:延迟满足在手机依赖与大学生学习投入中起中介作用.
有研究表明,社会支持会通过影响延迟满足作用于学生的学习品质,教师支持作为学生社会支持系统的重要组成部分[19],对学生坚毅品质具有重要影响[20],而教师支持正是通过延迟满足作用于学生的坚毅品质[19]. 延迟满足的冷热框架系统会受社会支持的刺激,表现为高低不同的自我控制能力,进而影响学习生活. 延迟满足的冷热框架系统[20]认为,热系统的激活会削弱控制冲动的能力,而冷系统的激活则会提高抵御诱惑的能力,且热系统可以通过一定的策略被转化为“冷系统”,从而达到为实现长远目标提高自我控制力的目的. 社会支持可以提高个体的自我控制能力[21],当个体的自我控制行为或观念得到周围群体的支持后会激活“冷系统”,个体自信心得到强化并促使其完成自我控制行为,从而更好地投入到学习生活中. 相关实验也表明[22],延迟满足感较低的个体得到了较高的社会支持后,会在实践中与延迟满足感高的人一样选择延迟满足. 故本研究假设:手机依赖通过依次影响社会支持与延迟满足,间接影响大学生学习投入,即社会支持与延迟满足在手机依赖对大学生学习投入的影响中起链式中介作用.
HTML
-
采用随机抽样的方法从重点大学、一般大学共抽取600名大学生作为研究对象,线上线下共发放600份问卷,回收问卷520份,剔除流失被试并进行问卷整理后获得有效问卷472份,有效回收率为78.67%. 其中,男生180人(38.14%),女生292人(61.86%);重点大学277人(58.69%),一般大学195人(41.31%);大一学生52人(11.02%),大二学生196人(41.53%),大三学生156人(33.05%),大四学生68人(14.41%).
-
采用熊婕等[23]编制的手机成瘾量表(MPATS),该量表共16道题,包括戒断症状、凸显行为、社交抚慰、心境改变4个维度. 采用5点评分法,1代表“完全不符合”,5代表“完全符合”,得分越高表明个体手机依赖程度越高. 该量表的Cronbach's α系数在本研究中为0.91.
-
采用Blumenthal等[24]编制、姜乾金[25]翻译并修编的领悟社会支持量表(PSSS),该量表共12道题,包括家庭、朋友及社会支持3个部分. 采用5点评分法,1代表“完全不符合”,5代表“完全符合”,得分越高表明个体感受到的社会支持越多. 该量表的Cronbach's α系数在本研究中为0.92.
-
采用Ray等[26]编制的延迟满足量表,该量表由冯华萍[27]翻译并修编,该量表共11道题,包括克制、冲动满足2个维度. 采用5点评分法,1代表“完全不符合”,5代表“完全符合”,得分越高表明个体延迟满足能力越强. 该量表的Cronbach's α系数在本研究中为0.83.
-
采用廖友国[28]编制的大学生学习投入量表. 该量表共20道题,包括认知投入、行为投入、情感投入3个维度. 采用5点评分法,1代表“完全不符合”,5代表“完全符合”,得分越高表明个体学习投入越高. 该量表的Cronbach's α系数在本研究中为0.94.
-
采用SPSS 22.0以及Hayes开发的SPSS宏程序PROCESS进行数据的整理与分析.
1.1. 研究对象
1.2. 研究工具
1.2.1. 手机依赖量表
1.2.2. 社会支持量表
1.2.3. 延迟满足量表
1.2.4. 学习投入量表
1.3. 数据分析
-
本研究在测试过程中采用不记名方法、一些条目反向计分方式等进行控制,收集数据之后,采用Harman单因子检验法对共同方法偏差进行检验[29]. 结果显示,共有10个因子的特征值大于1,并且第一个因子只解释了26.49%,远小于临界值40%,表明共同方法偏差不会对研究结果造成显著影响.
-
描述及相关分析结果表明(表 1),手机依赖与延迟满足、学习投入、社会支持均呈显著负相关;延迟满足与学习投入、社会支持呈显著正相关;社会支持与学习投入呈显著正相关. 该分析结果符合中介调节效应检验的条件,适合进一步做中介效应分析.
-
本研究相关分析结果符合进一步对社会支持和延迟满足进行中介效应检验的统计学要求[30]. 使用Hayes[31]编制的SPSS宏程序,利用Bootstrapping的方法重复抽样5 000次,构建95%的无偏校正置信区间. 使用PROCESS插件中模型6即链式中介模型检验,同时放入2个中介变量的链式作用,控制性别、学校、年级、专业等人口学信息.
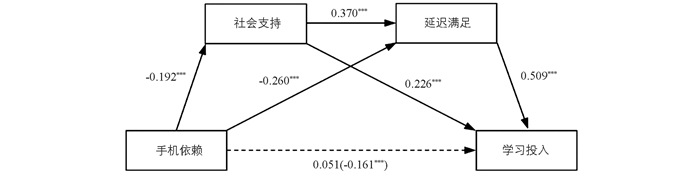
回归分析的结果显示(表 1),手机依赖显著负向预测学习投入(β=-0.16,p<0. 001);将社会支持和延迟满足纳入回归方程后,回归分析结果显示(表 2),手机依赖显著负向预测社会支持(β=-0.19,p<0. 001)和延迟满足(β=-0.26,p<0. 001);社会支持显著正向预测延迟满足(β=0.37,p<0. 001),显著正向预测学习投入(β=0.23,p<0. 001);延迟满足显著正向预测学习投入(β=0.51,p<0. 001);此时手机依赖未能显著预测学习投入(β=0.05,p>0. 05).
中介效应量分析结果显示(表 3,图 1),社会支持和延迟满足在手机依赖与学习投入间起显著的中介作用,总的标准化中介效应值为-0.21. 中介效应具体由3条路径产生的间接效应组成:手机依赖→社会支持→学习投入的路径形成的间接效应1(效应值-0. 04);手机依赖→延迟满足→学习投入的路径形成的间接效应2(效应值-0.13);手机依赖→社会支持→延迟满足→学习投入的路径形成的间接效应3(效应值-0.04),3个间接效应占总效应的比值分别为16.58%、50.38%和13.80%,且以上间接效应的95%置信区间均不包含0值,表明3个间接效应均达到显著水平. 选择PROCESS插件中模型6的间接效应比较选项,对不同路径的间接效应进行两两比较,考察是否存在显著的路径差异:比较1表明,间接效应1与间接效应2差异的Bootstrap95%置信区间不包含0值,表明间接效应1与间接效应2存在显著差异;采用同样的思路,间接效应1和间接效应3不存在显著差异;间接效应2和间接效应3存在显著差异.
2.1. 共同方法偏差控制与检验
2.2. 主要变量的描述统计及其相关分析
2.3. 社会支持和延迟满足的中介作用
-
本研究结果显示手机依赖能显著负向预测大学生学习投入,这与以往的研究结果相一致[7]. Kahneman提出的注意资源理论(注意的能量分配模型)认为,个体的心理资源分配到2个以上任务,会形成对注意资源的争夺[32]. 已有研究显示,大学生多将手机用于游戏、网购等与学习无关的活动,因此手机依赖会阻碍注意资源分配到学习上,但本研究引入社会支持和延迟满足2个中介变量后发现,手机依赖对大学生学习投入的直接预测作用并不显著,说明手机依赖对学习投入的负向影响并不是根据注意资源竞争的机制直接起作用,而是通过减少社会支持及减弱延迟满足来间接起作用. 这打破了手机依赖会直接影响学生学习的一般印象,既说明手机依赖对学生学习的影响并没有那么直接和明显,也说明手机依赖对学生学习的影响机理很复杂.
-
从社会支持的单独中介作用来看,高手机依赖会影响个体心理健康,使个体更容易产生孤独感及更高的焦虑抑郁状态[33],更重要的是沉迷网络疏远现实会影响人际交往,导致领悟社会支持感降低[10]. 而领悟社会支持对个体心理健康的增益性功能显著[34],有利于缓解孤独感,提升主观幸福感[8],从而提升大学生学习投入. 可见高手机依赖的学生由于社会互动匮乏,人际关系闭塞,很难感受到社会的支持,导致其学习动力不足,影响学习投入.
从延迟满足的单独中介作用来看,过度使用手机会产生焦虑等负面情绪,出现失眠等不良生理状况[35],减弱学生的自我控制力,从而降低学生的延迟满足水平. 高延迟满足的大学生,会放弃即时满足的短期利益[15],具备实现既定目标的坚毅品质[19],更擅长制订适宜的学习计划并付诸实践,表现出高度的学习投入;相反低延迟满足的大学生易被外界诱惑因素干扰,容易为及时享乐而放弃长远目标,具体表现为学业拖延与学业倦怠等.
社会支持和延迟满足的单独中介效应存在显著差异,即手机依赖对延迟满足的负向预测作用要大于对社会支持的预测作用,且延迟满足对学习投入的正向预测作用要大于社会支持的预测作用. 手机依赖程度直接影响延迟满足表现为学生自控能力强弱. 手机依赖对社会支持的影响则处于个体与环境交互的水平,需通过外界环境产生作用,因此手机依赖与延迟满足的关系更密切. 内因是事物变化发展的根据,外因是事物变化发展的条件,外因通过内因起作用,当学生自控能力更强时,学习投入程度更高. 因此延迟满足(内因)与学习投入的关系比社会支持(外因)更密切.
-
本研究结果表明,社会支持可显著正向预测延迟满足,这与研究假设相一致,同时也验证了社会支持的主效应模型与社会支持缓冲器模型,即社会支持能够通过各种因素促进个体心理健康水平的提高. 个体在无法感知较强烈的社会支持后会逐渐对自己正确的行为与判断产生动摇,即低社会支持非常容易使个体的自我控制能力发展受到限制,而自我控制能力是延迟满足的关键因素. 依据延迟满足的冷热框架系统[20],较低的自我控制能力难以使个体的冷系统被激活,在这样的情况下,个体选择即时满足(手机依赖)的倾向性会增加,而选择延迟满足(学习投入)的倾向性会降低. 从现实情况看,相较于高中生涯,大学生活往往远离家乡、父母和朋友,且大学老师、学校与大学生的关系相较于高中阶段也更为疏远,因此大学生的社会支持来源相较更少. 此外,大学生由于地区、习惯差异以及群体住宿的影响,矛盾极容易在日常的宿舍相处中被激发,这使得社会支持的来源减少更严重. 因此在社会支持相较于高中阶段大幅降低之后,大学生的自我控制能力急剧下降,延迟满足能力受挫,最终严重影响大学生的学习投入水平.
3.1. 手机依赖与大学生学习投入的关系
3.2. 社会支持和延迟满足的单独中介作用
3.3. 社会支持与延迟满足的链式中介作用
-
1) 手机依赖、社会支持、延迟满足和大学生学习投入之间两两显著相关,且手机依赖能显著负向预测大学生学习投入.
2) 手机依赖并不直接影响学习投入,社会支持和延迟满足在手机依赖与大学生学习投入之间起完全中介作用,社会支持和延迟满足都单独具有中介作用,同时社会支持通过作用于延迟满足而产生链式中介作用.
本研究的启示是:社会支持与延迟满足对学习投入具有直接作用,要降低手机依赖对学习投入的负面影响,应抑制其对社会支持和延迟满足的破坏性影响.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: