-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
人参Panax ginseng被称为“百草之王”,是我国应用最广泛的名贵中药材,其地理分布有局限性,对生态环境要求甚严,其野生资源由于长期无控制地采挖几近枯竭,被列入《国家重点保护野生药材物种名录》. 同时,人参作为馈赠佳品经常被游客携带或邮寄跨境,是海关植物检疫工作中非贸渠道执法时高频截获物之一. 由于人参中的俄罗斯联邦种群属于濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约(CITES)附录II中所列物种,因此探索人参种类鉴定方法,积极履行CITES公约,有助于保护其濒危野生资源. 同时,市面上使用华山参根、商陆根、紫茉莉根、栌兰根等冒充人参的现象屡见不鲜,为人参的鉴定工作增加了很大的难度,因此亟待建立准确快速的人参鉴定技术.
人参类中药的传统鉴定方法主要有基原鉴定、性状鉴定、显微鉴定、理化鉴定和病原鉴定[1-3]. 传统鉴定方法的理论基础建立于分类群的性状特征分析,这些性状特征是与环境紧密相关的表型,受环境影响较大. 从分子遗传学角度来看,物种表型的差异归根结底应追溯到其基因型的差异,即DNA序列差异[4]. 因此,对基因组序列差异的比较研究无疑为植物分类和鉴定提供了重要依据.
随着分子生物学的迅猛发展,基于DNA分子标记技术鉴定中药材的研究应运而生,并取得了快速发展. 从1994年随机引物PCR(arbitrarily primed PCR,AP-PCR)首次用于人参、西洋参的鉴别以来[5],DNA分子标记鉴定技术应用于参类药材鉴别已有不少报道,restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP)、random amplified polymorphic DNA(RAPD)、amplified fragment length polymorphism(AFLP)、sequence characterized amplified region(SCAR)、single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP)[6-10]等技术相继应用于参类药材的鉴别鉴定. 然而,这些技术存在操作步骤繁琐、工作量大、实验结果重复性差等缺点.
实时荧光定量PCR作为基因检测的重要手段,具有操作方便、灵敏、快捷、结果准确的特点[11-13]. 本文开发了一种适用于人参的实时荧光定量PCR鉴定方法,以期为我国CITES履约、海关执法、市场监管等提供更加科学准确的技术依据.
HTML
-
供试样品包括30个人参样品以及其他人参属或形态近似的16个物种的28个样品,共计17种58个样品(表 1). 样品经本实验室鉴定后,结合Internal Transcribed Spacer(ITS)序列测序鉴定确定种名. 样品保存于国家中药材物种鉴定及质量安全检测重点实验室.
-
磁珠法植物基因组DNA提取试剂盒购自珠海宝瑞生物公司;Premix Taq © Version 2.0、Premix Ex Taq(Probe qPCR)购自宝生物(大连)有限公司. 球磨仪(德国莱驰的MM400),全自动核酸提取仪(赛默飞世尔Kingfisher Duoprime),实时荧光PCR仪(美国ABI stepone plus).
-
用70%酒精对样品进行擦洗,再在无水乙醇中浸泡5 min,晾干后用球磨仪将样品研磨成粉[14]. 按照磁珠法植物基因组DNA提取试剂盒说明书方法进行样品DNA提取,提取的DNA用Nanodrop One超微量核酸蛋白检测仪测定核酸质量和浓度,随后保存于-20 ℃冰箱备用.
-
分别比对分析人参属物种及人参常见伪混品的常用备选条码基因及18S rRNA基因序列,筛选人参种内保守、种间特异区域. 在18S rRNA基因序列中,发现人参在497 bp和501 bp处为G和C,其他物种为C和G,且种内高度保守(图 1). 据此用Primer Express 3.0软件设计特异引物探针,引物为Pgf(5′-CACGGGGAGGTAGTGACAATA-3′)/ Pgr(5′-AGACTTGCCCTCCAATGGAT 3′),探针为Pgp(FAM- CGGGCTGATTCAGTCT-MGB),由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成.
-
PCR反应体系为20 μL,包括10 μL 2×荧光PCR反应预混液,上下游引物各0.4 μL(10 μmol/L),探针0.8 μL(10 μmol/L),DNA模板4 μL,灭菌去离子水补至20 μL.
实时荧光PCR反应程序为:95 ℃预变性30 s;然后以95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 30 s进行40个循环. 每个循环中60 ℃ 30 s结束时设置荧光通道采集荧光.
-
将阳性样品RS-06的DNA测定核酸浓度后进行10倍梯度稀释,共稀释成8个浓度梯度,然后按照1.5中的方法进行实时荧光PCR扩增,测试引物探针的检测灵敏度.
1.1. 试验材料
1.2. 试剂与仪器
1.3. DNA提取
1.4. 引物与探针设计
1.5. 实时荧光PCR
1.6. 灵敏度测试
-
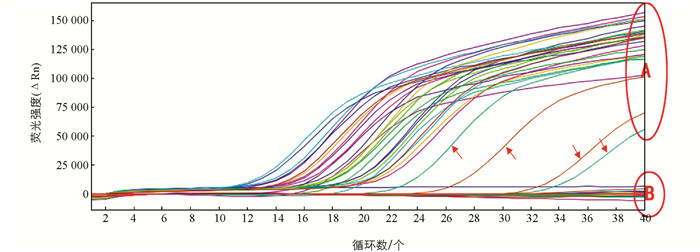
利用设计的引物探针对58份DNA样品进行实时荧光PCR检测,结果表明30份人参样品DNA均有特异扩增曲线,而供试的其他28份样品DNA及空白对照均无扩增曲线(图 2). 其中,4个人参片/粉剂的CT值相对偏高,可能是因为炮制工艺导致(箭头所示). 结合在美国国家生物技术信息中心(NCBI)中的同源性与特异性比较结果,说明该引物与探针用于人参检测具有良好的特异性.
-
用灭菌去离子水将提取的人参(样品编号RS-06)DNA(初始浓度为3.04×104 pg/μL)10倍梯度稀释成8个系列梯度,稀释后浓度分别为3.04×104 pg/μL~3.04×10-3 pg/μL,取4 μL作为模板用于灵敏度检测,结果表明DNA原液及101~106倍稀释液样品均得到典型的扩增曲线(图 3).
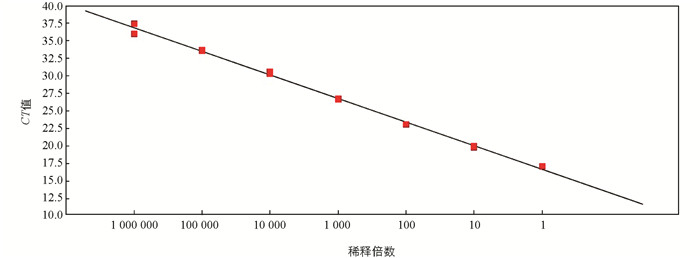
DNA浓度从3.04×104 pg/μL~3.04×10-2 pg/μL对应的CT值分别为17.11,19.95,23.08,26.67,30.3,33.63,36.74. 以扩增曲线的CT值为纵坐标,相应浓度为横坐标,绘制标准曲线(图 4). 所得线性方程为y=-3.375x+ 40.275,标准曲线相关系数为0.997,扩增效率为97.83%,最低检测限是0.03 pg/μL反应.
2.1. 探针特异性
2.2. 灵敏度检测
-
传统的中药材鉴定手段由于易受环境条件的影响或植物本身的限制,人为干扰因素较多,无法直接体现种质的遗传特征,难以快速得到准确的结果. DNA分子鉴定技术因其准确性和客观性,在中药材鉴定中的应用越来越受到人们的重视. DNA条形码分子鉴定法是利用基因组中一段公认的、相对较短的DNA序列来进行物种鉴定的一种DNA分子鉴定技术,具有适应性广、样品用量少、结果准确性高及可重复性好等优点[15-17]. 然而,一些中药材在生产过程中的加工工艺会引起DNA的严重降解,提取到的DNA往往浓度较低、质量较差,且易含较多的PCR抑制剂[18-19],这时使用DNA条形码鉴定法较难取得理想的效果. 本研究中的样品RS-29和RS-30人参粉产品,利用普通PCR进行ITS序列扩增时发现条带较弱,送样后因浓度较低无法测序,但利用实时荧光PCR检测时却有典型的扩增曲线,CT值分别为32.95和33.42,说明实时荧光定量PCR较普通PCR能更好地克服中药材DNA部分降解造成的缺陷.
本研究通过BLAST序列比对,选取人参18S rRNA序列,设计开发了人参特异性引物探针. 该引物探针可将其他人参属中药材和市场上常见伪品与人参进行区分,表现出良好的特异性. 李忠华等[20]根据人参的5.8S rRNA及ITS2序列与常见近源物种的差异设计引物探针,研究了人参的实时荧光定量PCR鉴定,其灵敏度达到1 pg/μL反应. 本研究的实时荧光定量PCR法灵敏度达到0.03 pg/μL反应,灵敏度有所提高.
本方法的建立有助于人参及其加工品被快速、准确、灵敏地鉴定,也可有效地区分形态近似的伪混品,可在实际应用中进行推广,以期为人参药材鉴定、市场监管等提供更加科学准确的依据. 同时,本方法的建立有助于进一步规范出入境人参的监管,为口岸快速、准确地鉴定提供依据,对防止人参种质资源流失,维护我国物种资源安全有着重要的意义.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: