-
随着混沌科学的发展,混沌在保密通信中的应用越来越广泛[1-3].近年来,多种计算混沌序列复杂度的算法被提出[4-14],其中强度统计算法[10-11]是在排列熵(PE)算法[12]的基础上,通过增加Jensen-Shannon分歧定义不均衡得到.由于强度统计算法能体现序列的相关结构,因此能更好地测度系统的复杂性.但强度统计算法不适用于周期序列的复杂度分析,而且也无法区分周期序列和混沌序列的复杂度.
本文研究发现虽然强度统计算法无法区分周期序列和混沌序列的复杂度,但在计算序列复杂度的过程中,其对周期序列计算得到的“系统在相空间中总的状态数目”要远远小于混沌序列.因此,本文在原强度统计算法的基础上,引入了“系统在相空间中总的状态数目”作为条件判断和加权值,提出了一种改进的强度统计算法,并对多个超混沌、混沌系统产生的超混沌、混沌和周期序列的复杂度进行了分析.
HTML
-
强度统计算法是一种计算序列复杂度的算法,其序列复杂度与强度统计复杂度测度CJ[P]相关,CJ[P]计算公式为
其中:S为Shannon熵;QJ是根据Jensen-Shannon分歧定义的不均衡;P表示一种动态系统产生的时间序列的概率分布;Pe表示均匀分布,即
$P_{e}=\left\{\frac{1}{N}, \cdots, \frac{1}{N}\right\}$ ,N代表系统在相空间中总的状态数目;S[P]=$-\sum\limits_{j=1}^{N} p_{j} \ln \left(p_{j}\right)$ ,Smax=S[Pe]=lnN;Q0是归一化常数且根据上述描述可知,0≤HS[P]≤1,0≤QJ[P,Pe]≤1,CJ[P]能呈现动态系统产生的时间序列的相关结构,且复杂度测度值CJ[P]越小,序列复杂度越大,反之亦然,而对没有任何结构的完全随机序列,CJ[P]=0.
概率分布P采用Bandt-Pompe提出的方法进行计算[12].给定时间序列{xt|t=1,…,T}和一个嵌入维D>1,对每一时刻i(i=1,2,…,T-D+1),其D阶顺次模式是由时刻{i,i+1,…,i+D-1}的值组成的D维向量
显然,D越大,向量提供的信息越多.通过和时刻i联系的“顺次模式”,定义(0,1,…,D-1)的一个排列G=(r0,r1,…,rD-1)为
若
$x_{i+r_{i}}=x_{i+r_{i-1}}$ ,则ri < ri-1.因此,对所有可能的D!个D阶排列π,概率分布P={p(π)}定义为其中card表示求集合元素个数.需要指出的是,按此种排序求得的对于周期序列的概率会出错[11],因此该强度统计算法不适用于周期序列,也不能区分周期序列和混沌序列的复杂度.
-
针对强度统计算法存在的问题,本文研究发现虽然强度统计算法无法区分周期序列和混沌序列的复杂度,但在计算序列复杂度的过程中,其对周期序列计算得到的“系统在相空间中总的状态数目”要远远小于混沌序列.因此,本文在原强度统计算法的基础上,引入了系统在相空间中总的状态数目N作为条件判断和加权值,提出了一个改进强度统计复杂度测度IMCJ[P],即
其中:min(D!,T-D+1)为系统在相空间中总的状态数目N的最大值,
$\frac{N}{\min (D!, T-D+1)}$ 为在原强度统计算法上引入的加权值.对于改进强度统计算法,复杂度测度值IMCJ[P]越大,则序列复杂度越大,反之亦然.
1.1. 强度统计算法描述
1.2. 改进强度统计算法
-
文献[15]在典型的三维Lorenz系统上构造的四维超混沌Lorenz系统如下:
其中:系统参数a=10,
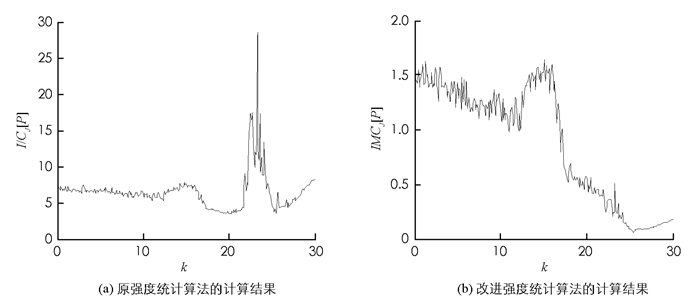
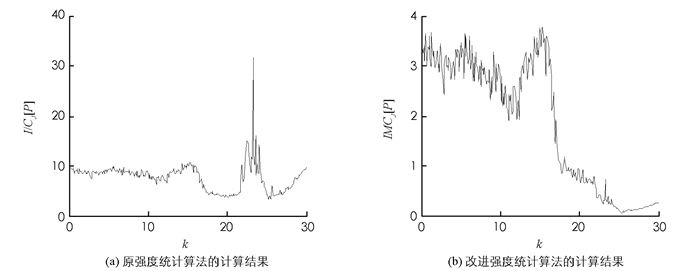
$b=\frac{8}{3}$ ,c=28,k为待定常数,且当k∈(0,16.6]时,系统(10)产生超混沌序列;当k∈(16.6,21.75]时,系统(10)产生混沌序列;当k∈(21.75,30]时,系统(10)产生周期序列.取嵌入维数D=7和D=8,利用原强度统计算法和改进强度统计算法对系统(10)随参数k变化的复杂度进行计算,得到的复杂度分布如图 1,2所示.
从图 1(a)和图 2(a)可以看出,通过原强度统计算法计算得到的超混沌序列复杂度大于混沌序列,但周期序列的复杂度有部分比超混沌序列的复杂度还大,显然这是一个错误结果,表明原强度统计算法不能区分周期序列与超混沌和混沌序列的复杂度;从图 1(b)和图 2(b)可以看出,通过改进强度统计算法计算得到的超混沌序列复杂度大于混沌序列,混沌序列的复杂度大于周期序列,表明改进强度统计算法能正确地区分超混沌、混沌和周期序列的复杂度,验证了本文提出的改进强度统计算法的有效性.
-
本文提出了一种改进的强度统计算法,解决了原强度统计算法不能区分混沌序列和周期序列复杂度的问题.利用改进强度统计算法对多个超混沌、混沌系统产生的超混沌、混沌和周期序列的复杂度进行数值计算,结果表明超混沌序列的复杂度大于混沌序列,混沌序列的复杂度大于周期序列,从而验证了该改进强度统计算法能有效地区分混沌序列和周期序列的复杂度,弥补了原强度统计算法的不足.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: