-
过去,对艾滋病(AIDS)发病率数据来源有回顾性计算模式[1-2]和Cohort法[3-4]两种,其中:回顾性计算模式不能提供现时的传播情况且很难估计从HIV感染到出现AIDS症状的时间;Cohort法适用于小的特定人群,不能提供总体人群基础上的数据,也不能预测发病率发展趋势.
建立实验室检测技术以区分新近感染和长期感染使得我们可以直接测量HIV的感染情况并计算发病率.用该技术可对以人群为基础的HIV发病率进行直接监测.
美国CDC发明了3种对HIV新近感染进行检测的ELISA方法:抗体捕获酶联免疫检测(IgG-Fc capture enzyme immunoassay,IgG-CEIA)、有限抗原亲和力酶联免疫检测(limiting antigen avidity enzyme immunoassay,LAg-EIA)、亲和力指数酶联免疫检测(avidity index enzyme immunoassay,AI-EIA)[5-14].目前多数实验室使用的是IgG-CEIA法[9-13].
美国CDC近年又使用重组蛋白rIDR-M代替合成肽BED[14-16]. rIDR-M包含了HIV-1 M群gp41三种主要变异体(variants)的免疫优势区(immunodominant region,IDR). LAg-EIA和AI-EIA法使用的抗原是rIDR-M.
本文对LAg-EIA法和AI-EIA法的一致性进行了评价分析.结果表明,这两种方法以血清作为检测材料,在时隔两年的不同检测者和同一检测者不同检测批次间结果稳定,LAg-EIA的R2达到93%~99%,AI-EIA的R2达到90%~96%.另外,用LAg-EIA对南京市3年的男男性行为人群确证阳性血清进行检测,试图通过该检测了解近期感染和长期感染者的比例和变化,结果发现该人群总体确证时间偏迟,3年数据表明至少超过
$\frac{1}{3}$ 的确证者是感染后156 d以后才进行确证检测的,这极不利于该病的预防.本检测为该人群HIV-1感染的预防、控制提供了支持性数据.
HTML
-
1) 重组蛋白及抗原包被:rIDR-M蛋白贮存液(每管200 μL,质量浓度1 mg/mL,含DMSO,冻存于-20 ℃),用包被液(0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (PBS),pH 7.2 with 0.1% Na Azide)稀释至终浓度,96孔酶联板(Nunc Maxisorp Plates,8 wells/strip,#62409-261)每孔加100 μL.用膜封板后4 ℃过夜.次日,用洗涤液(0.1% Triton X-100 in 0.01M PBS/pH 7.2)洗板2次,再用封闭液(含5%脱脂奶粉的洗涤液,现配现用)250 μL/孔于37 ℃封闭60 min.洗板2次后于37 ℃温箱中30~60 min干燥.膜封板后置于密封袋,贴标签后存于-20 ℃. 48 h后使用.
2) LAg-EIA检测:包被抗原终浓度为0.063 μg/mL.每孔加1:100稀释(稀释液同包被液,现配现用)的血清或4个标准对照100 μL,每个样本1孔,对照重复3孔,封板,37 ℃孵育60 min,洗板4次,于纸上拍去余液,每孔加200 μL解离液(0.1 M柠檬酸缓冲液,pH 3,Fisher,Cat#50842999),封板,37 ℃孵育15 min,洗板4次,拍板,加山羊抗人IgG-HRP conjugate (KPL,Cat#474-1002,1 mg/mL.用封闭液1:3500—1:5000稀释,不同批次板需要证实其合适的稀释度,现配现用)100 μL/孔,封板,37 ℃孵育30 min,洗板4次,拍板,每孔加100 μL TMB(KPL,Cat#52-00-02)显色,不封板,25 ℃孵育15 min,每孔加100 μL 1 N H2SO4(Fisher,Cat#SA212-1)终止反应,于450 nm(参考波长630 nm)读取OD值.用公式计算ODn. ODn=OD of sample/OD of Calibritor.若阴性对照、Calibritor、弱阳性对照、强阳性对照都在相应范围内,则数据有效,否则重做.
3) AI-EIA检测:包被抗原终浓度为0.125 μg/mL.每孔加1:100稀释(稀释液同包被液,现配现用)的血清或4个标准对照100 μL,每个样本2孔,对照重复4孔,封板,37 ℃孵育60 min,洗板4次,于纸上拍去余液,每孔加200 μL洗涤液或解离液,封板,37 ℃孵育15 min,洗板4次,拍板,加山羊抗人IgG-HRP conjugate.用封闭液1:3500~1:5000稀释,(不同批次板需要证实其合适的稀释度,现配现用)100 μL/孔,封板,37 ℃孵育30 min,洗板4次,拍板,每孔加100 μL TMB,不封板,25 ℃孵育15 min,每孔加1001 N H2SO4,于450nm(参考波长630 nm)读取OD值.用公式计算ODn. ODn=(OD of洗涤液处理/OD of解离液处理)*100.阴性对照、Calibritor、弱阳性对照、强阳性对照都在相应范围内,则数据有效,否则重做.
4) 检测一致性的实验设计:用4个对照血清进行板内、板间、批次间一致性检测,然后用101份博卡血清样进行不同操作者2年间的一致性及同一操作者两次结果的一致性比较.
5) 对MSM人群确证阳性血清的检测:收集2013年、2015年及2016年的MSM确证阳性血浆,排除艾滋病病人、接受抗病毒治疗者、CD4细胞小于200者、诊断时间大于6个月的感染者以及严重溶血的血浆.按照LAg-EIA方法进行操作,血清稀释1:100,ODn < 1.5为近期感染(我国为156 d内),ODn≥1.5为长期感染(我国为156 d以上).
6) 统计方法:用SPASS软件进行方差分析、回归分析,一致性用回归R2表示,R2最大是1.
-
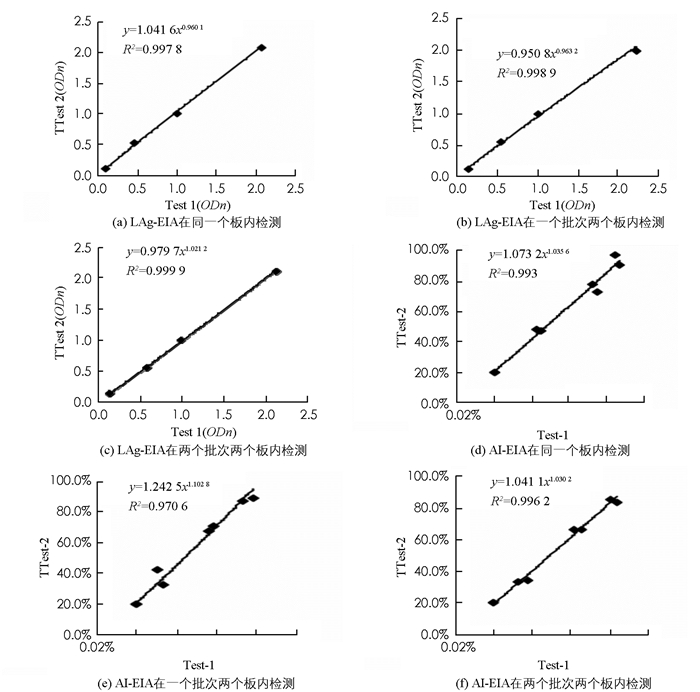
如图 1所示,指数回归方程结果表明:LAg-EIA检测在一个板中,两个板间以及包被批次之间标准血清的一致性分别为99.78%(图 1(a)),99.89%(图 1(b))及99.99%(图 1(c));AI-EIA检测在一个板中,两个板间以及包被批次之间标准血清的一致性分别为99.30%(图 1(d)),97.06%(图 1(e))及99.62%(图 1(f)).
-
如图 2所示,将101份博卡血清在2009年的检测结果作为CDC的期望值. 2011年4月和5月对相同样本分别进行检测.指数回归方程结果表明LAg-EIA检测2个月与CDC的期望值的重复性分别为97.22%(图 2(a))和98.94%(图 2(b)). 2011年4月和5月间的一致性为97.83%(图 2(c)). AI-EIA检测2个月与CDC的期望值的重复性分别为90.00%(图 2(d))和93.37%(图 2(e)). 2011年4月和5月间的一致性为93.56%(图 2(f)).
-
通过线性回归分析可知一致性相对指数回归有所下降.如表 1所示,指数回归分析LAg-EIA与AI-EIA的一致性都在90.00%以上,2011年4月份与5月份的结果R2值为93.56%以上,表明操作者的一致性较好.线性回归分析表明LAg-EIA的一致性仍然在93.00%以上,而AI-EIA的一致性在2011年4月的结果降到85.20%.与美国CDC 2009年的数据相比较,2011年4月的一致性比5月份的一致性低,原因是操作者的熟练程度不同,5月份的操作更熟练.另外,实验条件(例如时间控制)更严谨.总体来说,LAg-EIA比AI-EIA的一致性高.方差分析结果表明,两种方法的一致性都很高.
-
2013年共检测21份HIV确证阳性血浆,9份为近期感染,占42.8%,12份为长期感染,占57.1%. 2015年和2016年的近期感染分别为65.7%(23/35)和40.0%(8/20),长期感染分别为34.2%(12/35)和60.0%(12/20).总的来看,3年分别有57.1%,34.2%和60.0%的首次确证阳性的HIV感染者第一次检测的时间在165 d以后.从近期感染和长期感染的比例来看,3年分别为0.75(9:12),11.5(23:12)和0.67(8:12),2013年和2016年的比例接近,而2015年比值很高,提示2015年近期感染人数突然增加了.
2.1. LAg-EIA检测法和AI-EIA检测法的一致性实验
2.2. LAg-EIA检测法和AI-EIA检测法对101博卡血清的一致性实验
2.3. 两种方法一致性结果小结
2.4. 南京市MSM确证阳性血浆的检测结果
-
新兴的HIV/AIDS感染和发病率检测方法包括:
1) 抗体出现前的检测.主要检测病毒RNA和P24抗原.但它们只存在1~2周,所以实际上操作起来很困难,大量人群往往不能在这个时间内检测所以捕捉不到目标,而且技术要求高,不象血清学检测那样使用方便和广泛.
2) 敏感/不太敏感检测策略.用1:400和1:20 000的两种稀释度来区分两种感染.存在有些亚型不能很好区分的问题,并且1:20 000的稀释度在实际操作中对人员和技术以及机器的要求非常高,实施有难度.
3) IgG-捕获BED-EIA检测法(IgG-CEIA).该方法由美国CDC建立,已在中国推广.存在的问题是对于总抗体水平高的人群(像非洲人群)可能会得到较高的发病率.江苏省用该法研究新发感染的影响因素,结果发现同性传播的HIV/AIDS中新发感染比例最高[17].
4) 基于抗体亲和力的检测,包括有限抗原亲和力(LAG)和亲和力指数(AI)两个检测方法.该技术由美国CDC建立,经过优化已在中国应用[18],其他国家和地区未见研究报道.该技术的优点是对不同亚型的病毒都能同时检测,结果不受抗体稀释度的影响,能够区分HIV感染2~6个月以及长期感染者,更具有操作性.该技术还包括对不同样本的检测,包括血清、血浆、干血片,且能快速检测.如果能实现标准的一体化,尤其是干血片及快速检测方法,对于物资相对匮乏以及运输相对困难的发展中国家和地区是非常有意义的.干血片可以在常温下长期保存,快速法在现场短时间内就可以得到结果[14-16].
另外,无论用哪种方法进行检测,进行严格的质量控制都很重要.例如,使用稳定的对照和CALIBRATOR,如果对照超出允许范围,这个检测将需要重做.即使对照没有超出范围,而是在边缘,也可能会影响结果一致性.所以,尽量将对照结果控制在允许范围中间,就能获得较好的一致性和重复性.而且每个操作者的手法、习惯和熟练程度不同,对结果的一致性也有影响.以本实验的4月份和5月份的结果为例,两次操作的熟练程度不同,导致其与以前其他操作者检测结果一致性的差异.熟练程度决定加样的一致性、加样的速度、时间控制等等.例如排枪的使用,若排枪使用不熟练,从加对照到加完整板需要30 s,然后放到温箱避光孵育15 min,加终止液又需要30 s,而熟练者可以将排枪使用时间从60 s减少到10 s,这些操作都是在有光环境下操作,而底物对光线又很敏感,这就有可能造成检测结果差别,对数据的一致性造成影响.使用自动酶联检测仪则有可能取得更高的一致性.除此以外,使用不同的统计学工具和模型,对于结果也有不同的解释,这也是需要注意的.总之,本文通过对101个BOCA血清样本进行检测,在严格的操作要求下,基于抗体亲和力的检测技术方法很稳定,两种方法数据一致性高于90%.其中LAg-EIA的一致性高于AI-EIA.
本文采用了LAg-EIA对南京市男男性行为人群确证阳性血清进行了检测,发现与2013年和2016年相比,2015年新近感染的比例最高,长期感染的比例最低,也就是该人群进行确证检测的时间距离感染相对时间较短,可能与样本采集方式有关,如同伴推动采样.从新近感染和长期感染的比例来看,2015年也远高于其他2年,提示该年份可能有促进新近感染增加的事件发生,应该加强预防控制和宣传教育.但是,总的来看,长期感染,即感染超过156 d才确证的比例高达34.2%~60.0%,也就是至少
$\frac{1}{3}$ 的确证阳性是在感染156 d以后才确定的.而HIV感染初期的传染性最强,其在血液中有短暂的高浓度时期,而在这期间没有做确证检测,对该病毒的预防和控制是极大的挑战,这也很可能是该群体HIV传播相对比例较高的重要原因之一.本检测结果提醒有高危行为的人群要早做检测,才能尽早采取措施预防和控制HIV的传播.但是,由于数量局限性,本文的数据仅供该病防控参考.要获得更详实的数据,需要加大采样力度,扩大调查面,这也为我们将来的工作提出了更高的要求,需要对该人群做更多更细的工作,为我国艾滋病预防工作提供更多的数据支持.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: