-
城市是人类活动最为强烈的地区,其环境受到人类活动的深刻影响.城市不透水地面的迅速增加改变了地表污染物的累积和冲刷规律,使非点源污染的“源”“过程”“汇”都发生了变化[1].城市地表灰尘在一定外动力条件下较易扬起,污染物通过呼吸吸入和皮肤接触等途径进入人体,从而影响公众健康; 另外,由于不透水地面具有强烈的水文活动,灰尘中携带的大量污染物质在径流的搬运下进入地表水,恶化城市水环境.
在城市地表灰尘中,重金属是富集较为明显且研究较多的一类有毒有害物质,重金属元素具有难降解性和持久性.很多学者对国内部分大城市地表灰尘重金属污染及健康风险进行了研究[2-4],但对于济南市的相关研究鲜有报道.仅有陈青林等[5]对济南市地表灰尘重金属污染进行评价,但未开展健康风险评估的工作.
本研究选取济南市东泺河城市汇水区为研究区域,一方面济南市东泺河有泉水补充,为常年性河流,入小清河,地表灰尘重金属可能随降雨径流进入河道,成为河道底泥重金属的来源之一.另一方面,研究区域穿过城市主城区,其汇水区为城市中心区,人口密度高.因此,旨为在小清河水环境质量改善和城市路面灰尘污染治理提供依据,本研究分析该区地表灰尘中Cd,Cr,Cu,Pb,Zn,Hg,As 7种重金属的污染状况,并对研究区居民暴露在道路灰尘环境中的潜在健康风险进行评估.以期为济南市街道扬尘管理和河道水环境质量改善提供技术支撑.
HTML
-
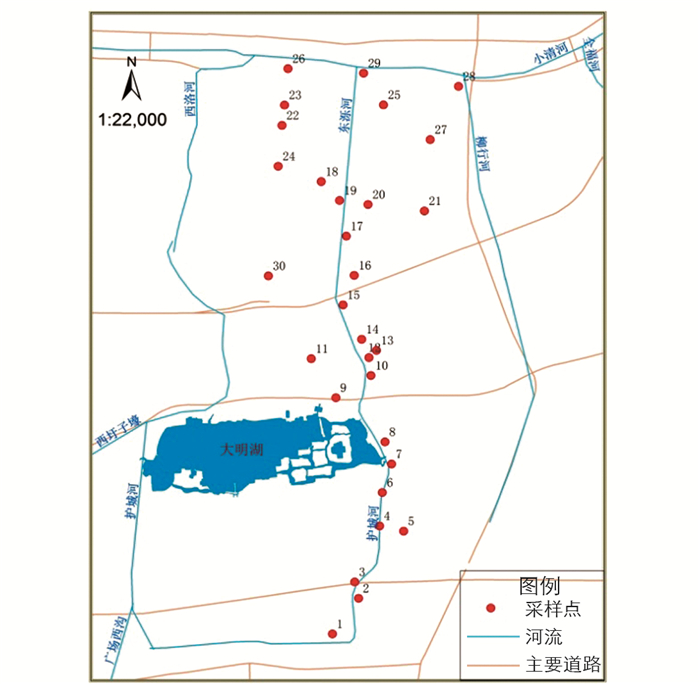
据东泺河周边地形地貌、雨水口调查排查及老城区雨污分流改造规划等资料,确定东泺河雨水汇水区为以东泺河为中心,北至滨海南路,南至泺源大街,西至水屯路,东至历山路,面积约10.8 km2.覆盖所有的用地类型,包括工业区(虽无工业用地,但有不锈钢和建材加工企业)、商业区、文教区、医院集中区、公园、绿地、交通区、道路等.在该区域内均匀布置约30个采样点(图 1),分采暖季和非采暖季两次进行样品采集,采集工作至少在雨后3天后进行.采样时间为2016年12月2日和2017年5月18日.每个样点根据情况,在距路缘石0.5 m范围内取0.5 m宽,适当长度的样区,用干净的毛刷来回清扫3次,收集大概30 g以上灰尘至塑料密封袋,研究区各监测点位介绍如表 1所示.
检测样品中Cd,Cr,Cu,Pb,Zn,Hg,As等7种重金属质量分数监测方法为:Cd和Pb依据GB/T17141-1997、Cr依据HJ 491-2009、Cu和Zn依据GB/T 17138-1997、Hg依据HJ 680-2013、As依据土壤元素的近代分析方法5.1.4.数据质量控制严格按照相关标准开展了样品空白、平行样、标样、加标回收等质控措施.
-
本研究采用美国环境保护署(USEPA)提出的健康风险评估模型对研究区地表灰尘重金属暴露剂量进行估算.该模型仅考虑重金属通过手口、吸入和皮肤3种途径,没有考虑重金属通过食物富集、饮用水等其他途径摄入量.本研究仅考虑7种重金属对人体的影响,未涉及重金属的化学形态.
-
地表灰尘重金属进入人体的途径主要有3种,即经手口途径直接摄入、呼吸系统吸入和皮肤接触.本研究的7种重金属对人体均有非致癌风险,Cd,Cr,As 3种重金属还有致癌风险.
非致癌风险暴露量计算模型见公式(1)-(3),致癌重金属吸入途径终身日平均暴露量计算模型见公式(4)[6].
式中:ADDing为手—口摄食途径的灰尘颗粒日平均暴露量[mg/(kg·d)]; ADDinh为吸入途径的灰尘颗粒日平均暴露量[mg/(kg·d)]; ADDdermal为皮肤接触途径的灰尘颗粒日平均暴露量[mg/(kg·d)]; LADDinh为致癌重金属吸入途径的终身日平均暴露量[mg/(kg·d)],其他参数如表 2所示.
-
对于非致癌风险,通常利用危害商来度量,模型见公式5和6.
式中:HI为多种污染物多种暴露途径下总的非致癌风险,为所有途径所有污染物总非致癌风险的加和; HQij为第i种污染物第j种暴露途径的非致癌风险商,表征单种污染物通过某一途径的非致癌风险; ADDij为第i种污染物第j种暴露途径非致癌暴露量; RfDij为第i种污染物第j种暴露途径的参考剂量,表示在单位时间、单位体质量摄取的不会引起人体不良反应的污染物最大量[mg/(kg·d)],如表 3所示.
对于致癌风险,一般采用终生日暴露量与致癌斜率因子的乘积来度量,模型见公式7和8.
式中:RTotal为多种污染物多暴露途径的致癌风险,表示癌症发生的概率; LADDij为第i种污染物在第j种暴露途径下的终生日均暴露量[mg/(kg·d)]; SFij为第i种污染物在第j种暴露途径下致癌斜率因子[11-14].
-
HI<1,认为风险较小或可以忽略; 当HI>1时,认为存在非致癌风险,需引起重视.尽管目前国内外对于致癌风险还没有统一、公认的评价标准,但从已有研究来看,一般都是采用美国国家环保局(USEPA)推荐值10-6~10-4或国际辐射防护委员会(ICRP)的最大可接受风险值5×10-5作为健康风险的判别依据[15].
1.1. 采样和分析
1.2. 健康风险评估方法
1.2.1. 暴露量模型
1.2.2. 风险值模型
1.2.3. 风险标准
-
采用SPSS软件,对地表灰尘重金属质量分数进行统计分析(表 4).从各点位平均值来看各种金属的富集情况,Hg和As低于背景值,Cd,Cr,Cu,Pb,Zn高于背景值,两季均值是背景值的11.17,3.91,5.60,2.82,4.31倍.从各点位平均值来看各种金属超标情况,Cr和Zn无标准值,Cd,Cu,Pb,Hg,As低于土壤标准值. Cd,Zn和As的重金属质量分数采暖季大于非采暖季,采暖季分别是非采暖季的2.38,1.02,4.37倍.这可能与采暖季大气降尘有关[16]. Cr,Cu,Pb,Hg的重金属质量分数采暖季小于非采暖季,采暖季分别是非采暖季的0.37,0.53,0.32,0.31倍.这可能是非采暖期人类生产及交通活动频繁所致[16].
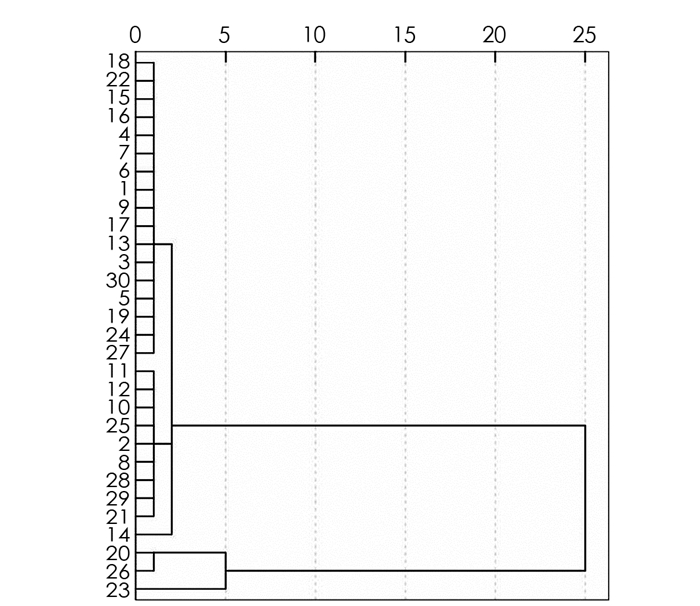
不同土地利用方式下重金属的积累也不同[19],因研究区域各类用地交错,难以按照工业区、商业区、文教区等进行分类,现利用SPSS软件,依据各点位的两季地表灰尘重金属质量分数数据,对30个点位进行聚类分析,结果如图 2所示.结果表明,点位20,26,23重金属污染状况异于其他点位.为便于分析,将点20,26,23定义为B类点位,其他点位定义为A类点位.
从表 4可以看出,除Hg和As外,A类和B类点位的均值和95%UCL差别较大的重金属为Cr和Cu,其他重金属差别较小. Cr主要在电镀、染料、制药、皮革、颜料等化合物制造企业和建材活动中质量分数较丰富[20],Cr,Cu主要来源于汽车金属部件的磨损[21-22]. B类点位中,点20附近为某小区停车位,点26附近曾有小型不锈钢和建材加工企业,点23附件有一处加油站.这导致B类点位Cr,Cu质量分数远大于A类点位.这说明车辆、建材企业和加油站等对地表灰尘重金属质量分数影响较大.
-
暴露量计算采用的重金属质量分数选取95%UCL置信上限进行计算(表 5).各重金属两季平均的非致癌风险暴露量由大到小依次为:Cr,Zn,Cu,Pb,Cd,As,Hg,重金属质量分数越大,暴露量越大. 3种非致癌暴露途径的暴露量由大到小依次为:非致癌手口、非致癌皮肤、非致癌呼吸,其中各重金属儿童和成人非致癌手口途径分别占各自总非致癌暴露量的99.82%和99.64%.儿童的暴露量高于成人,儿童非致癌手口、非致癌皮肤、非致癌呼吸、总非致癌的暴露量分别是成人的7.14,1.85,3.67,7.13倍.
-
如表 6所示,非致癌健康风险结果为:成人两季可忽略,儿童采暖季可忽略,非采暖季存在非致癌风险.成人两季和儿童采暖季HI均小于1,儿童非采暖季HI为2.36.儿童风险高于成人,儿童两季平均HI是成人的6.68倍.致癌风险结果为:两季风险均小于最大可接受风险值.
健康风险非采暖季高于采暖季,非采暖季HI和RTotal约为采暖季的3倍.但是分别在采暖季和非采暖季仅采样一次,存在偶然性.非致癌风险各金属的贡献前三位的均为:Cr>Pb>Cu.以成人两季平均占比为例,3种重金属占总非致癌风险的79.42%,14.86%,2.58%,三者共占总非致癌风险的95%以上.致癌风险中,Cr占总致癌风险的99.5%以上,为主要贡献的金属.
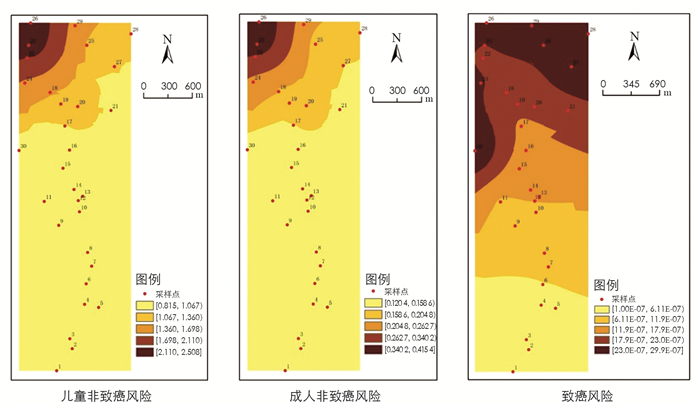
研究区健康风险空间分布如图 3所示.风险较高的区域均集中在研究区的西北方向.这主要是因为B类点位全部位于西北方向,重金属质量分数较高,导致暴露量和风险均较高.从表 7可以看出,A类点位风险低于总体情况,A类点位两季平均的儿童非致癌风险、成人非致癌风险、致癌风险分别是总体两季平均值得0.65,0.65,0.57倍. B类点位风险明显高于总体情况,B类点位两季平均的儿童非致癌风险、成人非致癌风险、致癌风险分别是总体两季平均值的4.79,4.84,5.63倍. A,B类点位致癌风险均小于最大可接受风险值. A类点位在非采暖季存在儿童非致癌风险,其他风险可忽略. B类点位在采暖季和非采暖季均存在儿童非致癌风险,其他风险可忽略. 3个B类点位拉高了研究区域的风险水平.
由表 8可以看出,研究区健康风险较其他城市属于中等偏高水平.非致癌风险低于西安市,高于保定市、北京市、合肥市等.致癌风险低于开封市、保定市,高于北京市、合肥市、兰州市等.研究区A类点位健康风险较其他城市属于中等水平.非致癌风险与合肥市、开封市和兰州市水平基本一致,低于西安市.致癌风险与北京市、合肥市、兰州市、芜湖市、西安市水平基本一致.
-
采用Pearson相关系数法,分析研究区地表灰尘中重金属之间的相关性.判断标准:置信度小于0.05,表明相关系数有统计学意义,否则就是无统计学意义; 相关系数[0.8,1.0)为极强相关,[0.6,0.8)为强相关,[0.4,0.6)为中等程度相关,[0.2,0.4)为弱相关,[0.0,0.2)为极弱相关或无相关.本研究认为弱相关、极弱相关和无相关均为无统计学意义.从表 9可以看出,相关有统计学意义的组合为Cd-Pb,Cd-As,Cr-Cu,Cr-Pb,Cu-Pb,Cu-Hg,Pb-As.
对地表灰尘中重金属进行主成分分析.提取前两个主成分,解释总方差为64.11%. KMO统计量为0.625,小于0.7,Bartlett球形检验统计量的sig < 0.01,由此否定相关矩阵为单位矩阵的零假设,即认为各变量之间的相关性有统计学意义.第一主成分贡献率为40.58%,Cr,Cu,Pb,Hg在第一主成分上有较高载荷.第二主成分贡献率为23.53%,Cd,As,Zn在第二主成分上有较高载荷.
因Hg和As质量分数不高于背景值,暂不讨论这两类重金属.从相关性分析可以看出,Cd,Cr,Cu和Pb污染源可能相似.从主成分分析可以看出,Cr,Cu,Pb污染源可能相似,为第一主成分. Cd,Zn污染源可能相似,为第二主成分.
Cr和Cu的来源在前文2.1中已讨论. Cu,Pb为亲铜成矿元素组合,污染可能主要源于交通[21],Pb主要来自汽车尾气和煤炭燃烧等.第一主成分可能为交通源. Cd可能来自电镀冶金等行业三废排放[27],Zn主要来源于轮胎的磨损、润滑剂等[21].第二主成分可能为小型建材企业,如不锈钢城等.
2.1. 质量分数特征
2.2. 暴露量计算
2.3. 健康风险计算
2.4. 来源分析
-
研究区地表灰尘中Hg和As低于背景值,Cd,Cr,Cu,Pb,Zn质量分数高于背景值. Cr和Zn无标准值,Cd,Cu,Pb,Hg,As低于土壤标准值.除儿童非致癌风险外,健康风险均可忽略.非致癌健康风险结果为:成人两季可忽略,儿童采暖季可忽略,非采暖季存在非致癌风险; 各金属的贡献前三位为:Cr>Pb>Cu,三者共占总非致癌风险的95%以上.致癌风险结果为:两季风险均小于最大可接受风险值,Cr占总致癌风险的99.5%以上,为主要贡献的金属.风险较高的区域均集中在研究区的西北方向. Cr,Cu,Pb污染源可能为交通源,Cd,Zn污染源可能为历史上或是现存小型建材企业.研究区域地表灰尘通过降雨等途径进入东泺河,将增加东泺河的重金属污染负荷,从而影响水质和底泥质量.已有研究表明该区域表层沉积物中存在重金属超标现象[28].但本研究未对地表灰尘重金属对东泺河和小清河的环境影响进行定量分析.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: