-
粒子群优化算法常常被定义成一种通过个体已发现的最有利位置和种群最有优势位置来反复迭代从而引领该群体搜寻最有利位置的优化算法[1]. 与其余各种算法相比而言,粒子群体所需要调节的参数较少、收敛速度快[2],已经广泛应用于全局优化、人工智能等诸多领域[3-11]. 粒子群优化算法因为收敛速度快以至于很容易陷入局部最优值.
文献[12]提出的多种优化策略混合粒子群优化算法属于准PSO系列的概率优化算法,虽然优势明显,但对其实现方式的分析尚不完善.
鉴于粒子间信息共享机制粗略,针对粒子群优化算法进行多极值函数优化时极易出现的早熟和搜索效率不明显的问题[13],提出了一种采用交叉策略的方法来使得粒子能够快速有效地脱离陷阱,不但提高了收敛精度以及收敛速度,还能在全面和部分搜索区域之间维持良好的平衡状态,具有良好的普适性.
HTML
-
设:xi(i=1,2,…,n)表示第i个粒子的当前位置,pi(i=1,2,…,n)表示第i个粒子历史认知中的最优位置,具体公式如下:
其中:c1与c2为学习因子,r1与r2表示随机数,ω表示惯性权重. 惯性权重ω计算公式如下
其中:ωs与ωe分别表示初始与末尾值,Tm与Tc分别表示最大迭代次数与当前的迭代次数.
-
使用概率的方法来选择一定数量的粒子成对进行杂交,并产生相同数目的粒子进行更新替换,公式如下:
式(4)中p表示随机数,xold1,xold2表示种群上一次寻优的位置. 更新替换后公式:
-
在表 1中,CSPSO算法的各个参数含义如下:D表示函数的维数,N表示粒子数目,c1与c2表示学习因子,pc表示杂交概率,sp表示杂交区域的大小比例,f表示计算值,a与b表示实验范围,DTmax表示最大迭代次数.
2.1. 原理
2.2. CSPSO算法
-
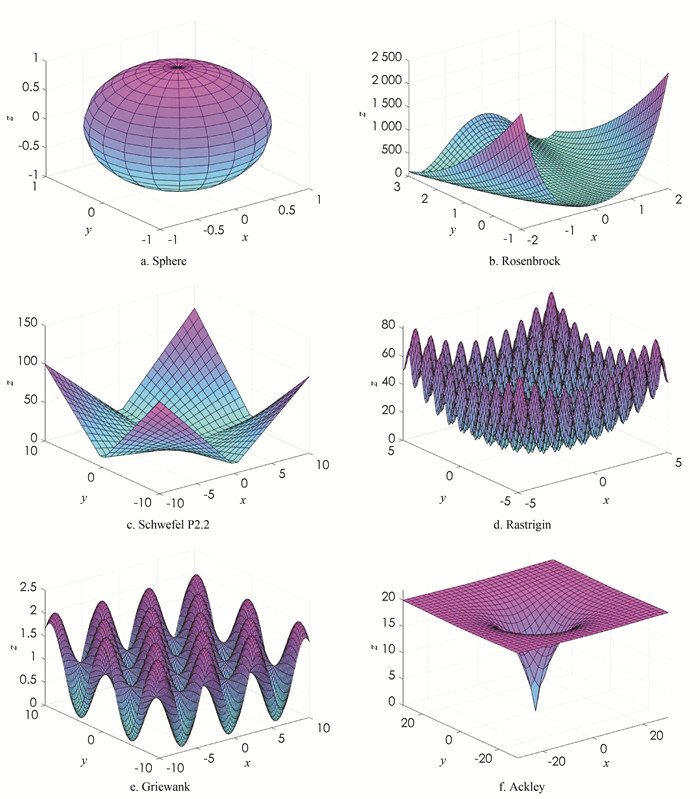
将本文提出的CSPSO算法与参考文献[14]中算法进行对比实验. 所有算法参数采用参考文献[14]的设置:N=30,c1=c2=2,ω=[0.9,0.4],pc=0.9,每组测试函数运行20次,每次迭代1000轮,测试范围均为[-50, 50]. 首先给出6个测试函数及其函数图形(图 1).
单峰函数:
1) Sphere函数:
$f_1=\sum\limits_{i=1}^D x_i^2$ 2) Rosenbrock函数:
$f_2=\sum\limits_{i=1}^D\left[100\left(x_{i+1}-x_i^2\right)^2+\left(x_i-1\right)^2\right]$ 3) Schwefel P2.2函数:
${{f}_{3}}=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{D}{\left| {{x}_{i}} \right|}+\prod\limits_{i=1}^{D}{\left| {{x}_{i}} \right|}$ 多峰函数:
4) Rastrigin函数:
$: f_4=\sum\limits_{i=1}^D\left[x_i^2-10 \cos \left(2 \pi x_i\right)+10\right]$ 5) Griewank函数:
$f_5=\frac{1}{4000} \sum\limits_{i=1}^D x_i^2-\prod_{i=1}^D \cos \left(\frac{x_i}{\sqrt{i}}\right)+1$ 6) Ackley函数:
$f_6=20+\exp (1)-20 \exp \left[-0.2 \sqrt{\frac{1}{D} \sum\limits_{i=1}^D x_i^2}\right]-\exp \left[\frac{1}{D} \sum\limits_{i=1}^D \cos \left(2 \pi x_i\right)\right]$ 以上6个测试函数在[-50, 50]上均有最优值0.
-
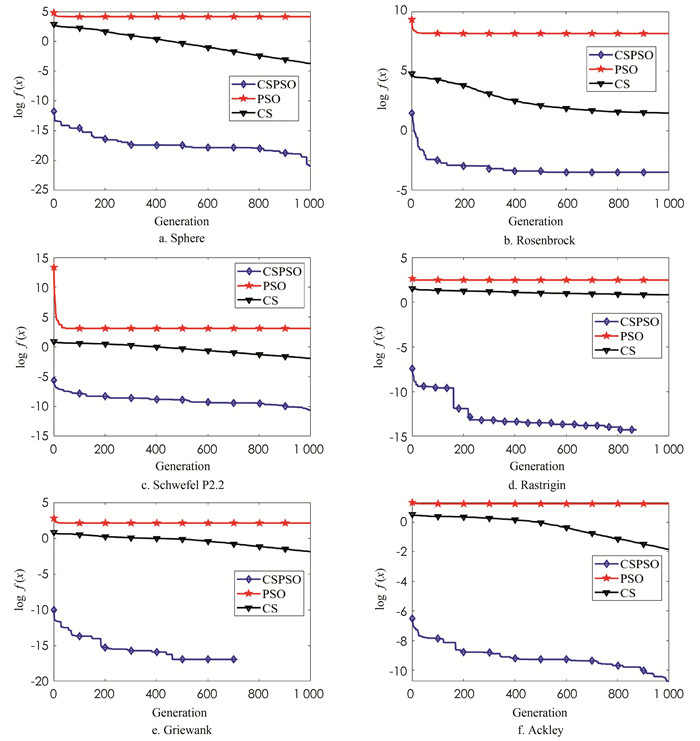
本文以平均值、标准偏差为主要对比数据,迭代1 000轮,种群维度D=30的仿真实验值:
图 2中横坐标Generation表示迭代次数,纵坐标log f(x)表示适应函数值的对数值以10为底,从图 2可以看出:CSPSO在6组测试函数上的结果都好于PSO和CS,全局搜索能力较强.
由本文与参考文献[14]中的仿真结果(表 2)可知,本文的CSPSO算法优于其他几种算法.
3.1. 对比样例与测试函数
3.2. 测试结果与分析
-
本文提出了一种基于交叉策略的混合优化算法,将粒子两两进行交叉变异进而得到相同数目的子代粒子来更新替代亲代粒子,在避免陷入局部最优值的同时提升了算法的精度.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: