-
特征值问题有着重要的物理背景,它在量子力学、流体力学和随机过程等方面有着广泛的应用[1-5].关于特征值问题的数值计算,主要的方法有有限元方法[6-9]、有限差分法[10]、三角域谱方法[11-15]等.然而,对于圆域上的特征值问题,由于涉及曲边边界,要获得高精度的数值解,通常的有限元方法需要花费大量的计算时间和内存容量.因此,提出圆形区域上二阶椭圆特征值问题的一些高精度的数值算法是有意义的,作为一个模型问题,我们考虑下面的二阶椭圆特征值问题:
其中β是非负常数,Ω是圆盘区域或圆环区域,∂Ω为区域Ω的边界.如何用有限元方法有效地求解这些特殊区域上的二阶椭圆特征值问题?据我们所知,很少有相关的研究和报道.因此,本文针对圆域上二阶椭圆特征值问题,提出了一种基于降维格式的有限元方法.首先,利用极坐标变换,将原问题转化为一系列的一维特征值问题.对每个一维特征值问题,引入了适当的Sobolev空间,推导了弱形式和相应的离散格式.其次,利用紧算子的谱理论和插值算子的逼近性质证明了逼近特征值和特征值向量的误差估计.最后,我们给出了一些数值例子,数值结果表明我们的算法是非常有效的.
本文的组织如下:在第1部分,推导了二阶椭圆特征值问题的降维格式;在第2部分,推导了弱形式和相应的离散格式;在第3部分,证明了逼近特征值和特征向量的误差估计;在第4部分,详细描述了算法的有效实现;在第5部分,给出了一些数值算例.
HTML
-
设
$ \mathit{\Omega} =\left\{ x\in {{\mathbb{R}}^{2}};{{R}_{1}}<|x|<{{R}_{2}} \right\} $ ,其中$ |x|=\sqrt{x_{1}^{2}+x_{2}^{2}} $ .定义微分算子:则当R1=0时,由极坐标变换:x1=rcos θ,x2=rsin θ,方程(1)可化为
其中
$ Q=\left( 0, {{R}_{2}} \right)\times \left[ 0, \left. 2\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ } \right) \right., \psi \left( r, \theta \right)=u\left( r\cos \theta , r\sin \theta \right) $ .由于ψ在θ方向上是以2π为周期的,则由傅里叶基函数展开得由(3)式我们有
使得(4)式有意义的本质极条件为
即
令
将(3)式代入(2)式,对于每一个傅里叶模m,我们可得到一系列等价的一维特征值问题:
令
$ r = x, {u_m}\left( x \right) = {\widetilde \psi _m} $ .那么(5)-(7)式等价于和
其中,|m|≥1.
对于R1>0,类似于R1=0的推导,方程(1)等价于
-
这一部分我们将推导弱形式和相应的离散格式,我们只考虑m≥0的情形,m<0的情况可以类似地推导.定义通常的带权Sobolev空间
相应的内积和范数分别为
其中ω=x是权函数,I=(R1,R2).当R1=0时,再引入非一致带权Sobolev空间
$ H_{0, \omega , m}^1\left( I \right) $ :相应的内积和范数分别为
则(8)-(9)式的弱形式为:找
$ \left( {{\lambda }_{m}}, {{u}_{m}} \right)\in \mathbb{R}\times H_{0, \omega , m}^{1}\left( I \right) $ ,使得其中
对于R1>0的情况,引入下面的Sobolev空间:
相应的内积和范数分别为
则(10)式的弱形式为:找
$ \left( {{\lambda }_{m}}, {{u}_{m}} \right)\in \mathbb{R}\times H_{0}^{1}\left( I \right) $ ,使得现在定义有限元逼近空间
$ {{S}_{h}}\left( m \right)={{U}_{h}}\bigcap H_{0, \omega , m}^{1}\left( I \right)和 {{\overline{S}}_{h}}={{U}_{h}}\bigcap H_{0}^{1}\left( I \right) $ ,其中Uh表示分片线性插值函数空间,则(11)式的离散格式为:找$ \left( {{\lambda }_{mh}}, {{u}_{mh}} \right)\in \mathbb{R}\times {{S}_{h}}\left( m \right) $ ,使得(12) 式的离散格式为:找
$ \left( {{\lambda }_{mh}}, {{u}_{mh}} \right)\in \mathbb{R}\times {{\overline{S}}_{h}} $ ,使得
-
为了简便起见,我们仅对R1>0的情况给出误差分析.对于R1=0的情况能够类似地推导.我们用
$ a \lesssim b $ 表示a≤Cb,其中C为正常数.定理1 am(u,v)是定义在H01(I)×H01(I)上的正定连续的双线性形式,即
证 由于x∈(R1,R2),则由Cauchy-Schwartz不等式可得
类似于定理1的证明,我们可得:
定理2 b(u,v)是定义在L2(I)×L2(I)上的正定连续的双线性形式,即
假设V(λm)和V(λmh)分别为λm和λmh相应的特征函数空间.令
其中
由于H01(I)紧嵌入L2(I),那么由定理1和定理2以及自共轭正定特征值问题的谱理论有下面的定理:
定理3 令(λm,um)和(λmh,umh)分别为(12)式和(14)式的特征对,则有
定义插值投影Ihu:H01(I)Uh,根据文献[16]中的分段线性插值理论,有下面的定理:
定理4 对于u∈H01(I),如果u(x)在区间I上有连续导数,则
定理5 令(λm,um)和(λmh,umh)分别是(12)式和(14)式的特征对,则有
证 由于
结合定理3和定理4可得(18)式.
-
在这一部分,我们将给出如何求解(13)式和(14)式的方法.构造一组山形基函数:
其中i=1,…,n-1.则有
当R1=0,m=0时,令
将表达式(19)代入(13)式,然后让vh取遍Sh(0)中的基函数,得到以下的线性特征值系统:
其中
类似地,当R1=0,m≥1和R1>0时,可分别得到下面相应的线性特征值系统:
由山形基函数的性质可知(20)式和(21)式中的刚度矩阵和质量矩阵都是三对角的稀疏矩阵.
-
为了表明算法的有效性,我们进行了一系列的数值实验,在MATLAB R2016b平台上进行编程计算.
例1 取R1=0,R2=1,β=1和m=0,1.对于不同的m和h,前4个特征值的数值结果分别在表 1、表 2中被列出.
从表 1、表 2可知,当
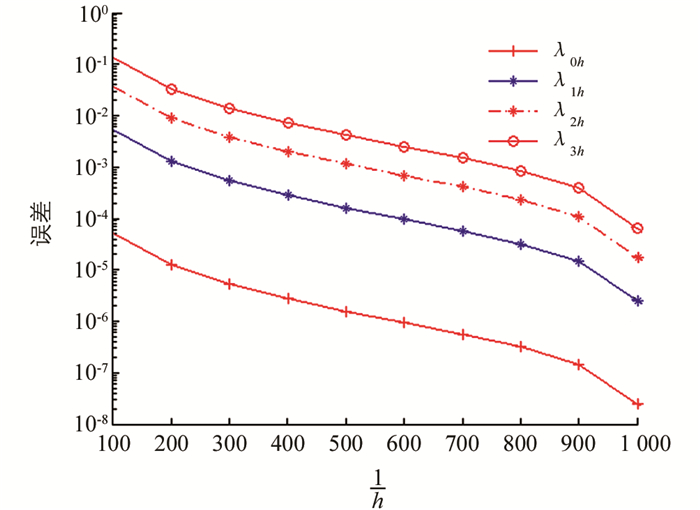
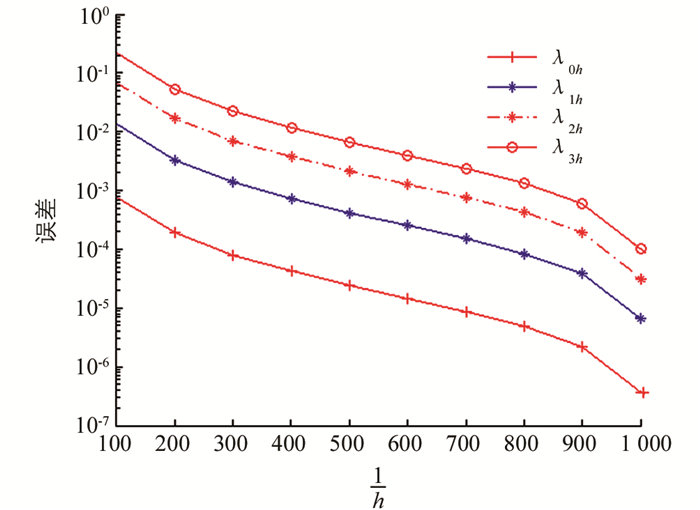
$ h\le \frac{1}{512} $ 时,前4个特征值至少达到4位有效数字的精度.为了进一步表明算法的精度和有效性,我们取$ h=\frac{1}{1\ 024} $ 时的数值解作为参考解,对于不同的m,在图 1和图 2中画出了逼近特征值与参考解之间的误差.例2 我们取R1=1,R2=2,β=1和m=0,1.对于不同的m和h,前4个特征值的数值结果在表 3、表 4中被列出.
-
本文针对二阶椭圆特征值问题,提出了一种基于降维格式的有限元方法.该方法主要通过极坐标变换将二维问题转化为一系列相互独立的一维特征值问题,从而可以并行求解,大大地节约了计算时间和内存容量.另外,利用紧算子的谱理论以及插值算子的逼近性质证明了逼近特征值和特征函数的误差估计,而且数值实验表明我们提出的算法是非常有效的.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: