-
栝楼Trichosanthes kirilowii隶属于葫芦科Cucurbitaceae栝楼属Trichosanthes L.植物,是市场上常见中药材,具有广泛的药理作用. 2010年《中国药典》中记载,栝楼属植物栝楼Trichosanthes kirillowii或中华栝楼Trichosanthes rosthorrii干燥成熟果实的种子、果皮和根均可入药,具有润肺化痰、滑肠通便、清热化痰、利气宽胸、消肿排脓等功效[1].此外,天花粉蛋白(Trichosanthin,即TCS)是从其块根中提取的一种核糖体失活蛋白,被用于引产,治疗葡萄胎、恶性葡萄胎、宫外孕及抗肿瘤等方面.栝楼除传统药用价值外,近年来又发现了新的药用、保健和食用价值[2].但是,目前市场上栝楼的混淆品种类众多,常见的混淆品有旋花科植物番薯Ipomoea batatas;萝藦科植物隔山消Cynanchum wilfordii、飞来鹤Cynanchum auriculatum;毛茛科植物猫爪草Ranunculus ternatus;葫芦科植物湖北栝楼Trichosanthes hupehensis、川贵栝楼Trichosanthes crenulata、罗汉果Siraitia grosvenorii、木鳖子Momordica cochinchinensis等.因此,对药用植物栝楼的基源鉴定是用药安全的重要保证.
传统栝楼真伪鉴别常依赖于形态学鉴定,对鉴定材料、鉴定人员都有严格要求.黄璐琦等[3]采用形态学方法,借助花粉粒类型、种皮类型的划分对栝楼植物进行鉴定,但因鉴定的性状较少,即使同一器官因受环境、部位等影响也不尽相同,仅依据植物形态的差异进行划分容易引起争议[2];季龙宝等[4]根据断面质地、味、根横切面、粉末等特征对天花粉与伪品湖北栝楼进行鉴定;巢志茂等[5-6]对栝楼干燥成熟果实的甲醇渗漉物进行化学成分研究,得出半乳糖酸γ-内脂和半乳糖为该属植物特征化学成分,可用于该属植物鉴定;黄婷霞等[7]采用蛋白电泳的方法对栝楼属种子类药材进行鉴别,取得了良好的鉴定效果;黄璐琦等[8]、宁志怨等[9]利用分子标记RAPD方法对栝楼植物进行鉴定,并对栝楼属植物种质资源亲缘关系进行分析,将分子生物学方法运用于栝楼属植物鉴定中,但最新分子生物学技术DNA条形码未见在药用植物栝楼及其伪品鉴定中应用.本研究以现有栝楼植物形态鉴定为基础,利用DNA条形码技术及分子系统学的方法对栝楼及其混淆品植物根部药材进行分子鉴定,建立栝楼中药材基原植物栝楼的“分子身份证”,提供药用植物栝楼正品与混淆品的分子鉴定依据,进而为其他药用植物分子鉴定提供方法借鉴.此研究对丰富药用植物栝楼的鉴定方法、特有资源的保护和利用具有重要的理论和实践价值.
HTML
-
8份中药材植物成熟根部材料中栝楼、罗汉果、隔山消、飞来鹤、猫爪草和番薯于2015年购于重庆市中药材批发市场,湖北栝楼和川贵栝楼分别购于湖北和贵州中药材市场;其余7种选用Genbank数据库已公布的ITS2序列.各中药材植物材料ITS2序列信息见表 1.
-
中药材根部经变色硅胶干燥后,称取200 mg左右,加入少量非溶性聚乙烯吡咯烷酮PVP,在液氮条件下迅速研磨.研磨后的样品使用CTAB法提取基因组总DNA,采用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳法检测其提取质量.
采用PTC-100 PCR仪对基因组DNA进行聚合酶链式反应(PCR),反应体系及扩增条件参照文献[10],即反应体系为dNTP Mixture(2.5mM)2 μL、PCR buffer(10 ×)2.5 μL、正反向引物(2.5 μM)各1.0 μL、Taq DNA聚合酶1 μL、总DNA约1 μL(30~50 ng),其余用ddH2O补至25 μL. PCR扩增引物ITS2,正向序列ATGCGATACTTGGTGTGAAT,反向序列GACGCTTCTCCAGACTACAAT.扩增程序如下:95 ℃预变性5 min;94 ℃变性30 s,退火温度55 ℃持续30 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,34个循环;最后72 ℃延伸7 min;12 ℃保温10 min.用1%琼脂糖电泳检测PCR扩增情况,得到的PCR产物送北京华大科技有限责任公司进行序列纯化及测定.为保证测序的准确性,采用正、反双向测序.
实验所得序列与GenBank数据库下载序列利用软件Clustal X对齐,BioEdit辅以人工校正,去除引物区及测序质量较差的区域,得到供分析的ITS2序列;利用MEGA5.05软件分析各中药材植物序列间的变异频率,计算各物种种内、种间距离;采用K2P距离法构建NJ(Neighbor-Joining)树和ML(Maximum Likelihood)距离树,利用Bootstrap(1 000次重复)检验各分支的支持率.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
-
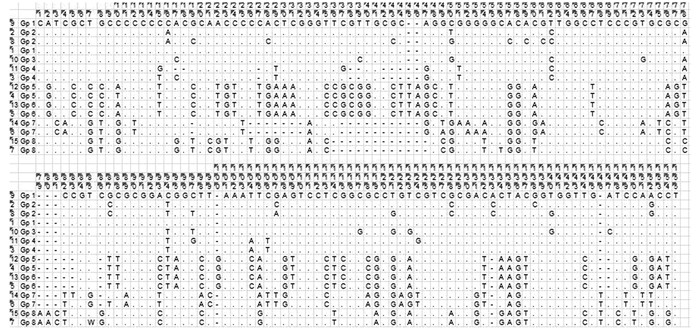
药用植物栝楼及混淆品的ITS2序列经ClustalX软件比对后总长度为155 bp,其中保守位点为53 bp,变异位点为102 bp,信息位点为95 bp,蛋白位点为7 bp;碱基转换率为21%,颠换率为21%(图 1).
-
通过软件MEGA5.0对药用植物栝楼及混淆品植物各物种内遗传距离和种间遗传距离进行计算,种内遗传距离变异范围为0~0.077 9,平均变异值为0.019;种间遗传距离变异范围为0.004~0.594,平均变异值为0.436.种间变异显著大于种内变异,符合条形码鉴定物种种间变异大于种内变异的要求.
-
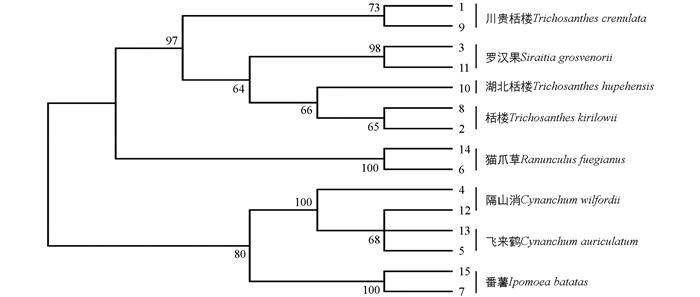
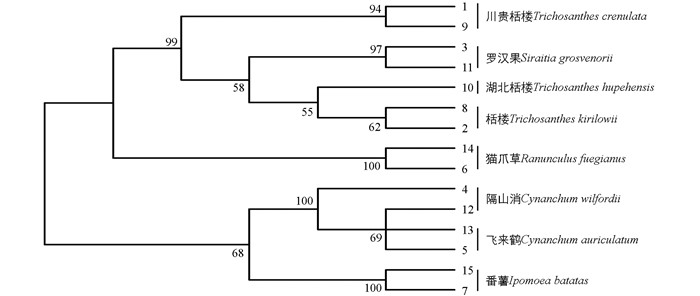
利用软件MEGA5.0的K-2P距离法对所有序列构建NJ树(图 2)和ML树(图 3),用1 000次重复的自展检测评估拓扑结构的可靠性.
由NJ树(图 2)可知,药用植物各物种自上而下依次为川贵栝楼Trichosanthes crenulata、罗汉果Siraitia grosvenorii、湖北栝楼Trichosanthes hupehensis、栝楼Trichosanthes kirilowii、猫爪草Ranunculus fuegianus、隔山消Cynanchum wilfordii、飞来鹤Cynanchum auriculatum和番薯Ipomoea batatas.川贵栝楼2条序列1与9聚为一支,支持率为73%;罗汉果2条序列3,11聚为一支,支持率为98%;栝楼2条序列2,8聚为一支,支持率为65%;湖北栝楼序列10与栝楼序列2,8聚为一支,支持率为66%;猫爪草2条序列6,14聚为一支,支持率为100%;隔山消2条序列4,12与飞来鹤2条序列5,13聚为一支,支持率为100%,其中序列5,12,13聚为一支的支持率为68%;番薯2条序列7,15聚为一支,支持率为100%;番薯、隔山消、飞来鹤所有序列聚为一支,支持率为80%.
ML树(图 3)的聚类形态与NJ树一致,但是各分支的Bootstrap支持率稍有差异.川贵栝楼2条序列聚为一支的支持率在NJ中为73%,在ML树中为94%;罗汉果序列在NJ中支持率为98%,而在ML中为97%,略有差异;栝楼2条序列在NJ中支持率为65%,湖北栝楼与栝楼序列聚为一支的支持率为66%,而在ML中,栝楼序列的支持率为62%,湖北栝楼与栝楼聚为一支的支持率为55%;番薯、隔山消和飞来鹤所有物种聚为一支的支持率在NJ中为80%,高于ML树的支持率68%.
从NJ和ML 2个系统进化树对比可以看出,药用植物栝楼及混淆品各物种形成单系类群,而且2个系统发育树的Bootstrap支持率差异较小,满足DNA条形码鉴别要求,具有较好的鉴定效果.
2.1. 药用植物栝楼及混淆品的序列比对信息分析
2.2. 种内和种间差异分析
2.3. 物种聚类分析
-
随着分子生物学特别是DNA测序技术的快速发展,基于DNA条形码技术进行物种鉴别已成为植物分类学、系统与进化生物学、植物资源学等学科最活跃的研究领域和新的发展方向[11-12]. DNA条形码(DNA barcode)是一种基于DNA分子进化原理,利用短的DNA片段和现代分子系统学的原理和方法对“传统物种”在分子水平进行身份鉴定的最新物种生物学技术[13-14]. DNA条形码技术与传统的物种鉴定方法相比,具有准确性高(DNA序列信息可以避免形态变异或趋同导致的物种鉴定误差)、效率高(通过建立数据库,可一次性快速鉴定大量标本)、不受被鉴定对象的环境和个体发育及鉴定专家个人因素影响(物种的身份是通过实验技术来鉴定的,不受专家个人因素的影响)等优点[15]. DNA条形码技术自2003年诞生以来,已在动、植物物种鉴定中得到了广泛应用[16-17],并在动物的物种鉴定与分类中取得了很大成功.
本研究运用ITS2条形码序列对常见药用植物栝楼及混淆品进行DNA条形码鉴定,K-2P距离图表明栝楼及混淆品各物种间有较大的种间差异,而各物种种内变异较小,满足种间大于种内变异的要求;在NJ和ML系统树中栝楼Trichosanthes kirilowii与其混淆品罗汉果Siraitia grosvenorii、湖北栝楼Trichosanthes hupehensis、川贵栝楼Trichosanthes crenulata、猫爪草Ranunculus fuegianus、番薯Ipomoea batatas、隔山消Cynanchum wilfordii和飞来鹤Cynanchum auriculatum各物种形成单系类群.因此,ITS2序列能将药用植物栝楼及混淆品有效地分开,达到预期鉴定效果,对今后深入研究药用植物的遗传多样性产生和分化、生态环境的适应性及杂交育种中的作用也具有重要的理论指导意义.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: