-
沉香为瑞香科植物白木香Aquilaria sinensis(Lour.) Gilg含有树脂的干燥木材,具有温中止呕、纳气平喘、行气止痛的显著功效[1].沉香不仅可用作中药,还可作为一种天然名贵的香料,提取沉香精油[2].沉香精油的主要成分为倍半萜类、2-(2-苯乙基)色酮类、芳香族类等,其中倍半萜类化合物和芳香族类化合物决定了沉香精油的香气和功效,色酮类化合物是沉香精油鉴别和品质评价的重要特征成分[3-5].
沉香精油提取方法种类繁多,包括水蒸气提取法、溶剂萃取法、超临界萃取法、亚临界萃取法等[6-7].国内外很多学者也对沉香精油提取进行了研究. Tsan等[8]研究了超声辅助水蒸馏法提取沉香精油的效果,发现相对于传统的水蒸馏法,该法得率高,耗时少,提取率可达1.169%. Apibalsri等[9]研究了亚临界水连续萃取沉香精油的效果,利用响应面法对工艺参数进行了优化,在207 ℃,3.7 MPa,萃取剂流速为5.69 mL/min时,萃取效果最佳,与传统水蒸馏萃取相比,该法可以极大地减少提取时间.陈志雄等[10]对动态微波辅助法提取沉香精油的工艺进行了研究,从静态小试试验扩大到动态中试试验,并对试验参数进行了系统的优化,沉香精油得率为1.68%.邓红梅等[11]对超临界CO2萃取沉香精油的技术进行了研究,利用响应面法优化了工艺参数,在最优参数的条件下,提取率可达1.46%.有关沉香精油的提取研究多集中于某一种方法的参数优化,而有关多种方法的比较以及沉香精油品质系统评价的研究较少.在沉香精油提取的诸多方法中,传统的水蒸馏提取法等耗时长,提取率低,精油香气成分有损失[12];新兴的超临界萃取法、亚临界萃取法等设备造价高,成本高昂,限制了沉香精油的大规模生产[13-14],因此,溶剂萃取法有其应用的价值,而以乙醇为提取溶剂,绿色清洁,能够为沉香精油的品质安全提供保障.
本试验以西双版纳州蚂蚁结香的沉香木为原料,使用乙醇为提取溶剂,通过水浴回流提取法、索氏提取法、超声辅助萃取法、微波辅助萃取法4种提取方法制备沉香精油,采用气相色谱-质谱联用法(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)检测不同沉香精油样品的成分,结合提取率对4种提取方法进行比较,最终确定最优的提取方法;后续将对选择的最优方法开展工艺优化研究,为沉香精油的生产提供理论依据.
HTML
-
蚂蚁结香的沉香木,产于云南省西双版纳州;无水硫酸钠(分析纯),成都市科龙化工试剂厂;乙醇(分析纯),重庆川东化工有限公司;二氯甲烷(分析纯),成都市科隆化学品有限公司;乙酸苯乙酯(色谱纯),东京化成工业株式会社;正构烷烃混合标品(C5~C38),美国Supelco公司.
-
FA1004电子天平,上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;HWS-26电热恒温水浴锅,上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;MAS-Ⅱ微波反应发生器,上海新仪微波化学科技有限公司;JP-040S超声清洗器,深圳洁盟清洗设备有限公司;85-2数显恒温磁力搅拌器,金坛市易晨仪器制造有限公司;QP2010气相色谱-质谱联用仪,日本岛津公司.
-
取50 g经粉碎过40目筛的沉香木粉,加入500 mL 95%的乙醇,在80 ℃水浴下回流提取2 h,抽滤分离,真空减压回收溶剂至所剩溶剂约为提取所得浸膏的6倍,冷冻离心10 min (-18 ℃,4 000 r/min),取上清液,减压回收溶剂,加入无水硫酸钠干燥,过滤,得到沉香精油,称质量,平行试验3次,质量取平均值[14-15].
-
沉香精油得率=沉香精油质量(g)/原料质量(g)×100%
-
准确称取300 mg精油,置于色谱瓶中,加入1 mL二氯甲烷溶液,然后加入1 mL内标溶液,内标溶液为乙酸苯乙酯,用二氯甲烷配制成0.4 μg/mL的溶液.将上述色谱瓶放入超声萃取仪中,超声萃取20 min,取1 μL直接放入气质联用仪进样分析[15].
-
色谱条件:色谱柱:DB-5MS石英毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);柱箱温度:40 ℃;进样口温度:280 ℃;分流比:30:1;压力49.7 kPa;柱流量:1 mL/min;进样载气:He(99.9999%).升温程序:40 ℃保持2 min,以5 ℃/min升温至160 ℃,再以3 ℃/min升温至280 ℃,保持10 min.
质谱条件:电子电离源;电子能量:70 eV;离子源温度250 ℃;全扫描;质量扫描范围:40~400 amu.
定性定量分析:运用NIST 08s谱库检索GC-MS分析得到的数据,保留匹配度大于80的成分.通过各色谱峰的保留指数(RI)与文献中的保留指数对比定性,各组分的保留指数由其保留时间和相邻正构烷烃的保留时间计算得到[16].根据组分色谱峰面积与乙酸苯乙酯内标物的峰面积之比对沉香精油的特征性组分物质进行定量[17-18].本试验以乙酸苯乙酯内标是半定量的方式,各样品加入等量的乙酸苯乙酯,经过相同的处理方法,乙酸苯乙酯在色谱图上的出峰面积基本一致,使用内标定量法可以进行各样品间的质量浓度比较.
1.1. 材料与试剂
1.2. 仪器与设备
1.3. 方法
1.3.1. 沉香精油的提取方法比较
1.3.1.1. 水浴回流法提取沉香精油(以下简称“水浴回流”)
1.3.1.2. 索氏提取法提取沉香精油(以下简称“索氏提取”)
1.3.1.3. 超声辅助萃取法提取沉香精油(以下简称“超声辅助”)
1.3.1.4. 微波辅助萃取法提取沉香精油(以下简称“微波辅助”)
1.3.1.5. 沉香精油的得率
1.3.2. 沉香精油样品的制备与成分鉴定
1.3.2.1. 沉香精油样品的制备
1.3.2.2. GC-MS条件
-
4种方法所得沉香精油样品的得率见表 1.微波辅助萃取法制备的沉香精油得率明显高于其他方法,为1.32%,可能是因为微波辅助萃取全程保持在60 ℃温度以下,相对于水浴回流提取法和索氏提取法的高温条件,更大程度上避免了沉香精油有效成分的损失[16];微波相对于超声,对沉香的内部细胞组织破碎更充分,从而使得精油的浸出效率升高[17].
-
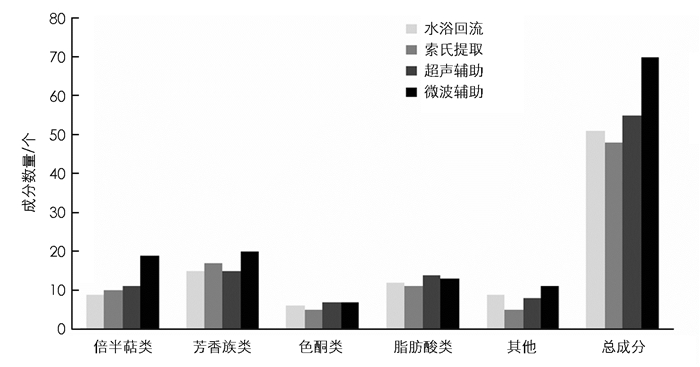
4种不同提取方法所得的沉香精油的样品,经GC-MC分析,共分离鉴定出98种物质,其中水浴回流提取法所得精油为51种,索氏提取法所得精油为48种,超声辅助萃取法所得精油为55种,微波辅助萃取法所得精油为70种. 4种方法共同鉴定出的成分为22种,结果见表 2. 22种共有成分中包括5种倍半萜类化合物、7种芳香族类化合物、3种色酮类化合物、5种脂肪酸类化合物、2种其他类化合物;其中质量浓度较高的10种物质分别为6,7-二甲氧基-2-苯乙基色酮、抗坏血酸二棕榈酸酯、4,4-二甲基-6-苄氧基-2-色酮、反油酸、巴伦西亚橘烯、苄基丙酮、愈创木醇、沉香螺醇、(+)-香橙烯、α-檀香醇.
-
见表 2和图 1,水浴回流提取法所得沉香精油样品的总成分数为51种,其中倍半萜类物质为9种,芳香族类物质为15种,色酮类物质为6种,脂肪酸类物质为12种,质量浓度较高的物质有2-甲基-4-苯乙基色酮(15.81%)、抗坏血酸二棕榈酸酯(8.64%)、6,7-二甲氧基-2-苯乙基色酮(7.81%)、反油酸(7.42%)、穿心莲内脂(4.42%);索氏提取法所得沉香精油样品的总成分数为48种,其中倍半萜类物质为10种,芳香族类物质为17种,色酮类物质为5种,脂肪酸类物质为11种,质量浓度较高的物质有6,7-二甲氧基-2-苯乙基色酮(7.24%)、抗坏血酸二棕榈酸酯(7.16%)、4,4-二甲基-6-苄氧基-2-色酮(6.56%)、反油酸(5.44%)、6,7-二甲氧基-2-乙基-4-苯基色酮(5.00%);超声辅助萃取法所得沉香精油样品的总成分数为55种,其中倍半萜类物质为11种,芳香族类物质为15种,色酮类物质为7种,脂肪酸类物质为14种,质量浓度较高的物质有2-甲基-4-苯乙基色酮(17.24%)、抗坏血酸二棕榈酸酯(8.32%)、6,7-二甲氧基-2-苯乙基色酮(7.60%)、反油酸(6.36%)、1-甲氧基-4-甲基-3-戊烯基苯(4.24%);微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油样品的总成分数为70种,其中倍半萜类物质为19种,芳香族类物质为20种,色酮类物质为7种,脂肪酸类物质为13种,质量浓度较高的物质有6,7-二甲氧基-2-苯乙基色酮(11.52%)、抗坏血酸二棕榈酸酯(8.96%)、4,4-二甲基-6-苄氧基-2-色酮(8.61%)、反油酸(8.00%)、(S)-(+)-2-(N,N-二苄基氨基)-4-甲基戊醇(5.22%).
微波辅助萃取法所得精油的总成分数量明显高于其他3种提取方法,增加的成分种类主要集中在倍半萜类和芳香族类等挥发性物质上,从而使得微波辅助萃取法提取的沉香精油的香气更加丰富,品质更好.
-
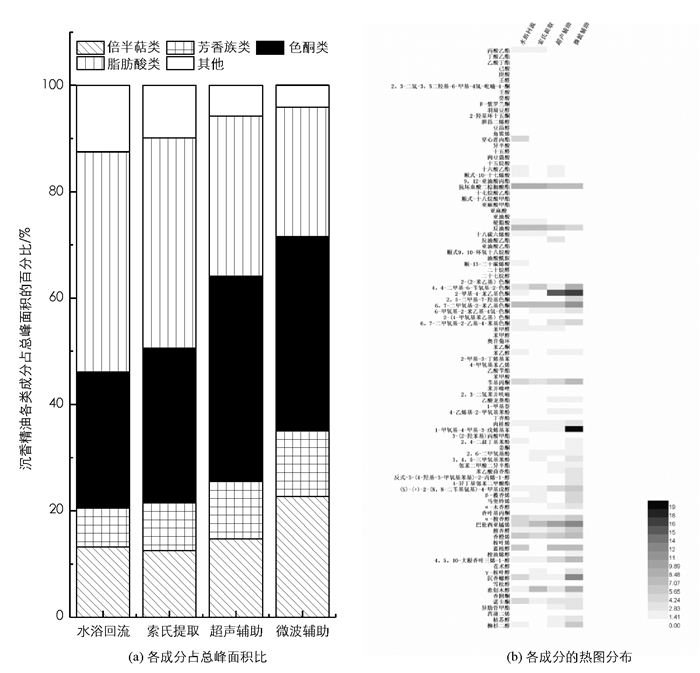
4种提取方法所得沉香精油样品主要由倍半萜类、芳香族类、色酮类、脂肪酸类等物质组成,但相对质量浓度间存在较明显的差异(图 2).
水浴回流提取法、索氏提取法、超声辅助萃取法和微波辅助萃取法所得到的沉香精油样品中倍半萜类化合物质量浓度分别为13.19%,12.51%,14.69%和22.29%.倍半萜类化合物既是沉香精油中重要的功效成分,又是沉香精油香气的重要来源,倍半萜类化合物质量浓度极大程度上决定了沉香精油的品质[19-21].微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油样品中倍半萜类化合物的相对质量浓度高于其他3种提取方法所得样品,而且检测出倍半萜化合物的种类为19种,也高于其他3种提取方法所得样品,因此,微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油的品质相对更好.
水浴回流提取法、索氏提取法、超声辅助萃取法、微波辅助萃取法所得到的沉香精油样品中芳香族类化合物的质量浓度分别为7.32%,8.99%,10.80%和12.36%.芳香族类化合物在沉香精油中所占比例较小,但却是沉香精油特殊香气的主要来源,因此可以作为沉香精油品质考察的一个重要指标[22].微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油样品中芳香族类化合物的质量浓度最高、种类最多,微波辅助萃取法相对较优于其他3种沉香精油提取方法.
色酮类化合物具有一定程度的抗过敏和神经保护方面的活性,是沉香精油鉴别和品质评价的重要特征成分[22-23].超声辅助萃取法(38.62%)和微波辅助萃取法(36.52%)所得到的沉香精油样品中色酮类化合物的质量浓度要高于水浴回流提取法(25.62%)和索氏提取法(29.12%)所得到的沉香精油样品,原因可能是后2种工艺在高温条件下进行,色酮类物质会受热分解,造成一定的损失[24].
脂肪酸类化合物可能是引起沉香精油酸败的原因之一,一般情况下,精油中相关物质的质量浓度越低说明精油的品质越好[23-24]. 4种提取方法所得沉香精油样品中,脂肪酸类化合物的质量浓度由少到多为:微波辅助萃取法、超声辅助萃取法、水浴回流提取法、索氏提取法,微波辅助萃取法脂肪酸的质量浓度为24.30%,较其他方法分别减少41.23%,38.45%和19.16%,说明微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油的品质相对优于其他提取方法.
图 2b热图是图 2a堆积图的形象直观反映,微波辅助萃取法所得精油样品在倍半萜类、芳香族类、色酮类物质区域颜色较深,在脂肪酸类、其他类物质区域颜色较浅,印证了微波辅助萃取法所得精油在品质上要优于其他提取方法.
-
在沉香精油研究领域,通过GM-MC技术与聚类分析等统计方法结合,发现沉香螺醇、γ-桉叶醇、愈创木醇、苍术醇、(+)-香橙烯和苄基丙酮与沉香精油的等级和品质具有重要的相关性,所以常常将它们作为沉香精油的重要特征性组分,用来评价沉香精油的品质[25-28].
表 3中,仅有微波辅助萃取法所得的沉香精油的样品中,沉香螺醇、γ-桉叶醇、愈创木醇、苍术醇、(+)-香橙烯、苄基丙酮6种特征性物质均有检出,而且除了苄基丙酮外,其他5种特征性物质的质量浓度,微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油的样品均要大于其他提取方法所得的样品,因此,微波辅助萃取法相对要优于其他沉香精油提取方法.
2.1. 沉香精油的得率比较
2.2. 沉香精油成分鉴定
2.3. 沉香精油成分种类的比较
2.4. 沉香精油成分组成的比较
2.5. 沉香精油特征性组分的质量浓度比较
-
在4种不同提取方法中,微波辅助萃取法所得沉香精油的提取率和物质种类最多,为1.32%和70种,其中反映精油品质的倍半萜类物质和芳香族物质分别为19种、20种,明显高于其他3种方法;4种方法所得精油的成分组成相似,均主要由倍半萜类、芳香族类、色酮类、脂肪酸类4类物质组成,但是质量浓度存在明显差别,其中微波辅助萃取法所得精油中倍半萜类和芳香族类物质的质量浓度最高,分别为22.29%,12.36%,脂肪酸类物质的质量浓度最低,为24.30%;超声辅助萃取法所得精油中色酮类物质的质量浓度最高,微波辅助萃取法次之,为36.52%;仅有微波辅助萃取法制备的沉香精油中6种特征性物质均有检出,其中沉香螺醇、愈创木醇、苍术醇、(+)-香橙烯、γ-桉叶醇的质量浓度最高,分别为1.53%,1.73%,0.19%,1.47%和1.69%.综上所述,微波辅助萃取法是4种方法中最优的沉香精油提取方法,具有提取率高、精油品质佳的优点.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: