-
广泛存在于真核细胞中的miRNA是一类长度约为18-25个核苷酸非编码的单链RNA分子,且在调控基因表达、细胞周期、生物体发育等方面起重要作用[1-2].为了更好研究miRNA与癌症的关系,需要对miRNA微阵列数据进行统计分析,而数据归一化是进行统计分析的必要步骤.由于miRNA微阵列数据存在系统误差,所以进行归一化处理的目的就是减小系统误差.本文就与胃癌相关的miRNA微阵列数据比较了6种不同的归一化方法.通过绘制MA图与箱线图来比较归一化方法对数据分布情况的影响,并且使用K-S检验和均方误差来综合衡量每种归一化方法.
HTML
-
本文数据取自于NCBI(National Center for Biotechnology Information:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE28700)[3]的GEO数据库中与胃癌有关的数据,其中包括22个正常样本和22个胃癌样本.实验组为胃癌样本,对照组为正常样本.把实验组miRNA的表达量用Ri(i=1,2,3,…,556)表示,对照组miRNA的表达量用Gi表示.把对数强度比,即log2(Ri/Gi),记为Mi;把平均对数强度,即log2
$\sqrt{R_{i}G_{i} }$ ,记为Ai.本文在RStudio中进行相关操作.我们将比较全局归一化[4]、局部加权回归方法[5]、分位数归一化[6]、修正均值归一化[7]、方差稳定归一化[8]以及尺度归一化[9]对miRNA微阵列数据的影响.本文使用MA图来比较6种归一化方法对数据分布的影响. MA图可以清楚看到系统误差的大小.如果MA图中的纵坐标M值集中分布在M=0附近,说明数据之间的差异较小[10].箱线图是利用数据中的5个统计量:最小值、第一、四分位数、中位数、第三、四分位数与最大值来描述数据的一种方法.我们可以从箱线图中粗略地看出数据是否具有对称性与分布的集中或离散等信息.
本文用K-S检验和均方误差来验证6种归一化方法的优良性. K-S检验是一种拟合优度检验. K-S统计量的值越小,归一化效果越好[11-12].均方误差是偏差平方与方差之和.较小的方差和偏差值表示更好的归一化,即均方误差越小,表明归一化方法的效果越好[13].
-
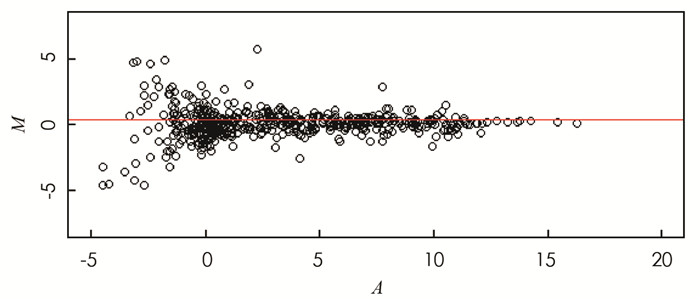
首先,给出未进行归一化的原始数据的MA图. 图 1中水平直线表示M的均值是0.14,偏离0.因此表明对数据进行归一化处理是必要的.
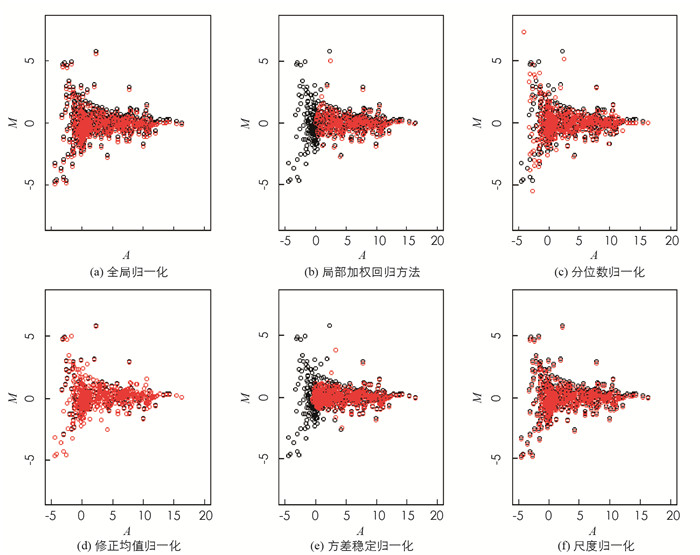
图 2分别显示了通过6种归一化方法变换后的数据的MA图,其中黑色表示未归一化的数据分布图,红色表示归一化后的数据分布图.由图 2可知:与未归一化相比,全局归一化将M的均值变为0;局部加权回归方法将MA图中的散点以M=0为中心基本呈对称分布;分位数归一化与尺度归一化使得M的均值明显减小且散点分布比较对称;修正均值归一化后的MA图与未归一化的MA图无明显变化;方差稳定归一化将比较离散的点集中在0附近.
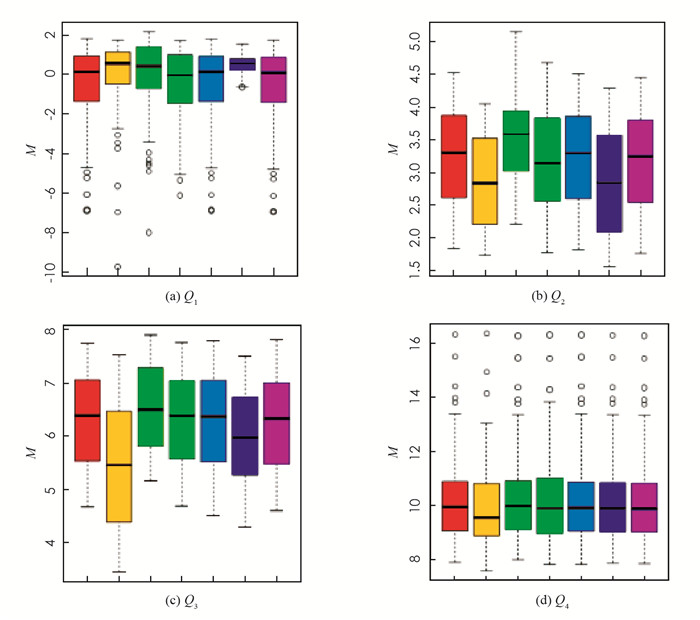
其次,利用四分位数将未归一化与归一化后的M值进行对比,即将M值分成4部分,分别用Q1表示最小值与第一四分位数之间的数据(图 3(a)),Q2表示第一四分位数与中位数之间的数据(图 3(b)),Q3表示中位数与第三四分位数之间的数据(图 3(c)),Q4表示第三四分位数与最大值之间的数据(图 3(d)).箱线图从左到右依次是:未归一化、全局归一化、局部加权回归方法、分位数归一化、修正均值归一化、方差稳定归一化和尺度归一化.从图 3(a),(b),(c)中可以看出,归一化后和原始数据的最小值、第一四分位数、中位数、第三四分位数以及最大值之间的波动较大.其中全局归一化方法与方差稳定归一化方法改变较大.但是在图 3(d)中,M值变大时,归一化后的最小值、第一四分位数、中位数、第三四分位数以及最大值均与原始数据比较接近,亦即数据越大,归一化方法对其影响越小.
-
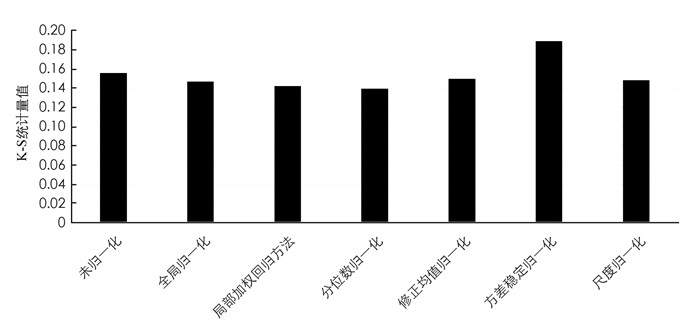
首先,用K-S检验来比较6种归一化方法.对于数据GSE28700,首先计算未归一化的M值,再分别计算用6种归一化方法作用后的M值.最后,用计算得到的M值进行K-S检验,得出K-S统计量值.由图 4可知,方差稳定归一化方法产生了较大的K-S统计量值.全局归一化、修正均值归一化与尺度归一化方法产生了低于未归一化的K-S统计量值,而分位数归一化与局部加权回归方法的K-S统计量值最低.从K-S检验的结果来看,局部加权回归方法和分位数归一化方法的K-S统计量值较小,但是相对于全局归一化、修正均值归一化以及尺度归一化这3种方法而言,K-S统计量值仅有稍微减少,优势并不显著.因此,下面采用均方误差来进一步衡量6种归一化方法.
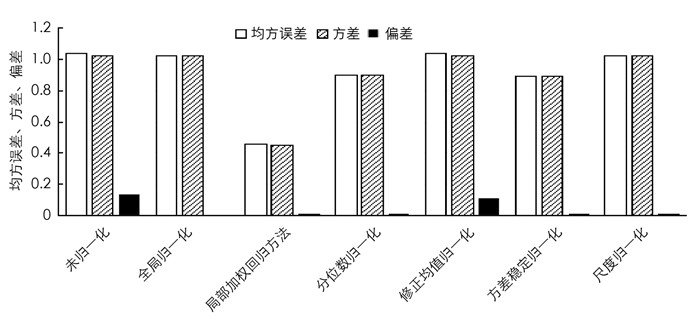
均方误差可以衡量不同归一化方法处理后的数据变化程度.从图 5可知:通过归一化方法变换之后,全局归一化方法消除了偏差,并且均方误差以及方差都有稍微的减小.全局归一化、修正均值归一化和尺度归一化方法产生了与未归一化相近的均方误差,而修正均值归一化方法还有较大的偏差.局部加权回归方法、分位数归一化以及方差稳定归一化方法与前面的3种相比,均方误差及方差值都明显减小,且偏差值都接近于0,其中局部加权回归方法产生了最小的均方误差及方差值.因此,从均方误差的比较结果来看,局部加权回归方法的归一化效果最好.
综合上述两种归一化方法的衡量准则可知,最适合miRNA微阵列数据的归一化方法为局部加权回归方法.
2.1. MA图与箱线图对归一化前后数据分布的呈现及对比
2.2. K-S检验和均方误差对归一化方法的衡量
-
数据归一化是miRNA微阵列数据分析中的一个关键步骤,而且miRNA微阵列数据对归一化方法的选择可能与miRNA表达的特点有关.为了探究适合miRNA微阵列数据的归一化方法,我们以与胃癌相关的数据GSE28700为例,比较了6种归一化方法对数据的影响.本文使用MA图和箱线图分别来比较归一化前后的数据分布情况,还使用了K-S检验和均方误差来衡量不同归一化方法的优良性.综合比较6种归一化方法的K-S统计量值和均方误差值发现:对于miRNA微阵列数据,局部加权回归方法的归一化效果最好,其次是分位数归一化方法.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: