-
教师是提高教育质量的关键。职业教育教师的专业化问题是职业教育的根本问题[1]。培养和发展“双师型”教师是职业教育教师专业发展的趋势。“双师型”教师是指兼具理论基础与实践能力的教师,其核心是教师教学能力[2]。欧盟职业培训发展中心将职业教育教师分为四类:普通学科教师、职业理论学科教师、学校实训基地或模拟教学环境的职业实践学科教师、公司培训者[3]。我国职业教育“双师型”教师多指职业理论学科教师和职业实践学科教师。信息时代对职业教育教师的教学能力提出了新要求,因此,分析职业教育教师教学能力的概念内涵和构成要素,建立信息时代职业教育教师教学能力的标准框架,就显得尤为必要。
全文HTML
-
在哲学层面,能力是人确定对象关系的手段、过程和结果,是置于主客体关系下的概念[4]。因此,在研究教学能力问题的同时要考虑师生关系问题[5],这也属于能力讨论范畴。基于主体能力理论,探寻教学研究能力与社会实践能力的关系可知:能力作用于实践,满足主体的需求;实践反作用于能力,促进主体的提升[6]。从管理学视角来看,能力也称为胜任力,指“一个人的潜在特征,该特征与个体在工作或其他情况下,参照标准的,有效和(或)卓越的绩效有因果关系”[7]。其观点强调了标准在能力界定上的重要作用以及个体绩效与其能力之间的因果联系,即标准发挥着度量和评估能力的功用。教学能力作为教师潜在的特征,由评价指标体系显示出来。从能力动态特征视角来看,能力重在内化与运用[8]11。从心理学视角来看,能力是一种符合活动需要并影响活动效果的个体心理特征,而教学能力是个体顺利完成教学活动的前提,并直接影响教学活动效率的心理特征,是在特定学科的教学活动中表现出来的一种特殊的职业能力[9]。目前, 研究者主要从心理认知和课程教学活动这两个视角对教学能力的概念内涵进行分析,并对教学能力的综合性、专业性和发展性等问题达成了共识。从心理认知视角来看,有研究者将教学能力分为技术层面和人格层面[10]。学界逐渐接受了教师的智力和教学能力是不同的观点,并把教学能力视为一种特殊能力[11]。这符合能力二因素论的观点,即能力是由基本因素和特殊因素共同组成的。基本因素反映着人的心理素质和个人潜质等,决定着人的综合素质是强还是弱;特殊因素体现着人在完成具有特定关系任务时所具备的一些素质[12]。从课程教学活动视角来看,研究者多依据教学过程和教学任务来讨论教学能力的构成,认为教学过程旨在完成预设的教学任务并确定学生应该达到的程度,且对教学进行逆向规划。有研究者将教学能力划分为传授知识、组织教学和处理人际关系三个维度[13],认为高校教师的教学能力构成除包含基本因素外,还应包括研究教育教学方法与探讨教学内在规律等方面的内容。博耶(Boyer)指出,应把大学教学提高到教学学术的水平,并开展专业研究和实践活动[14]。
-
职业教育与普通教育是两种不同的教育类型,信息时代的职业教育教师除了具备教学能力之外,还应承担起另外三种角色,即技师/工程师、数字公民和终身学习者。
-
相较于普通教育而言,职业教育教师教学能力结构研究更加关注行业能力,即社会能力、方法能力和专业能力[15]。目前,从师资队伍建设角度来分析“双师型”教师的研究较多,而从职业教育教师个体的角度来探讨“双师型”教师教学能力结构的研究并不多见。相较于公共课教师而言,专业课教师的职业属性更强,也更具有职业教育“双师型”教师的特征,因而职业教育教师教学能力的研究主要聚焦于专业课教师,国内外相关研究也多是从专业课教师视角切入。国内有学者认为职业教育“双师型”教师教学能力包括教学基础、专业实践、行业能力以及科研能力和素质这四个一级要素[16]。瓦吉兰(Wagiran)等人建立的职前职业教育教师教学能力模型,包括核心能力(core competence)、硬技能(hard skills)和软技能(soft skills)[17]。其中:核心能力主要指教师的教学知识、学科内容知识、技术知识;硬技能主要指教师的实际操作及专业理论课程教学能力、教师的实际操作及专业课程内容掌握水平;软技能主要指教师所具备的诚实可靠、遵守纪律、争当模范等品质。伊斯梅尔(Ismail)等人基于管理学胜任力视角、工作过程视角以及教学活动视角,采用焦点小组讨论的方式,构建了职业教育教师的教学能力框架,其框架包括三项一级维度(个人特质和专业水平、课程教学和培训、技术和创新)和与之对应的二级维度两个部分[18]。罗菲克(Rofiq)等人认为职前职业教育教师须具备教学(pedagogic)、专业(field of the expertise)、管理(managerial)、品格(personality)和社交(social)五个领域的能力[19]。迪普(Diep)等人从工作过程视角、心理学认知视角、胜任力视角和教学活动视角出发,构建了旨在满足可持续发展目标的职业教育教师教学能力框架,该框架共包括六个能力维度[20]。从哲学层面上社会实践与主体之间的辩证关系来看,职业教育教学活动的发生场域具有跨界性,即从院校延伸至企业、行业甚至整个社会,这对职业教育教师个体的素质和能力提出了更高的要求。
以服务发展为宗旨、以促进就业为导向的职业教育,须培养学生的职业技能和职业精神,使学生能够在专业、社会、个人等不同领域和情境中进行正确思考和选择、在行动中承担个人和社会责任。以校企合作为办学模式,以工学结合为培养模式,将学校单一形式的教与学发展为校企合作的教与学,这使得职业教育的教学结构和学习结构都发生了不同于普通教育的具有自身特点的深刻变化。“双高计划”是落实《国家职业教育改革实施方案》(简称《职教20条》)的重要举措,是职业教育“下好一盘大棋”的四大支柱之一,旨在集中力量建设一批引领改革、支撑发展、有中国特色、达到世界水平的高职学校和专业群,并且提出:“以‘四有’标准打造数量充足、专兼结合、结构合理的高水平双师队伍。”[21]由此可见,教师教学能力标准要特别强调行业权威性、国际影响力、解决实际问题能力、创新能力和技术技能性等[22]。
-
信息时代对身处其中的所有人都提出了新的要求,教师作为数字公民,也应具备相应的信息素养,尤其是要具备在信息化环境中不断优化自身教学的能力。移动互联、云计算、大数据、物联网、人工智能等层出不穷的新技术对职业教育产生了深远的影响[23]。信息技术的泛在化改变了个体的人际交流方式、工作生活内容、知识结构、信息获取途径、行为方式和思维习惯等。教师需要具备相应的信息素养,充分利用各类新技术,引导学生为迎接未来作准备。
在信息时代,人的发展与社会的发展,二者之间相互作用、相互促进的关系表现得更加明显。主要体现在:第一,劳动分工导致单一工种向复合工种转变;第二,技术进步导致简单职业向综合职业发展;第三,信息爆炸促进了学校教育向终身学习的转化[8]10。信息技术与教育教学的整合主要体现在工具手段层面的经验应用、逻辑系统层面的策略创新、人文价值层面的人性反思三个方面。职业教育要实现将技术发展所需的更高技能及知识与该技术所具备的功能更加有效地结合,就要构建新型的教学环境、运用新的教学方式、变革传统的教学结构等举措[8]32。过去的二十年,基于技术工具论的教师教学能力发展对提升教学质量的帮助较为有限,“教育+信息技术”的思维范式被束缚在狭窄的学科范畴中[5]。实践表明,教师的信息化教学能力不应受到技术工具论的裹挟,只有实现信息技术与教学的深度融合,才能整合并重组信息时代教师教学能力的相关构成要素。信息时代下,“教与学”的内涵与外延日益丰富多元,新技术、新模式重新定义了包括职业教育教师在内所有教师的教学能力的概念内涵。因此,职业教育教师信息化教学能力与职业教育教师教学能力,二者之间并非隶属关系,而是合二为一的融合关系。另外,信息时代既为教师国际间的沟通与协作提供了广阔的空间,也对教师的国际交流能力提出了更高的要求。
《职教20条》首次提出要“适应‘互联网+职业教育’的发展需求”,培养集“专业知识、职业技能和信息技术”于一身的高素质技能型人才,探索基于互联网认知规律的校企跨界合作、教学环境和工作场所结合、虚实环境相融合的新型职业教育教学方式[23-24]。因此,职业教育教师信息化教学能力的内涵理应包括信息化教学能力这个关键要素。教师的信息化教学能力有不同的名称,国内多用“信息化教学能力”“教育技术能力”等,而国外多使用“教师ICT能力”[25]。尽管名称不同,但其内涵特征具有一致性。特别是TPACK技术整合框架的提出,为更好地理解信息时代职业教育教师教学能力的内涵和构成提供了参考。
-
新科技革命和产业变革的浪潮奔腾而至,职业教育教师的教学知识、专业技能和信息素养等都面临着不断更新换代的挑战。很多曾经热门的专业,尤其是传统产业中的一些加工制造业,已经慢慢从一个专业萎缩成一门课程或者干脆消失,这对教师专业发展提出了巨大挑战。泰勒主义提出,大批量的生产方式强调员工的服从意识,每名员工只需熟悉一种技能即可,而以精益生产为代表的团队作业方式则强调每名员工都是多面手,员工要不断改进和提高现有技术和管理水平,发挥自身的最大潜能[26]12-13。基于此,职业教育教师需要不断增加自己的教学知识、提升自己的专业技能和信息素养。联合国教科文组织倡导将职业教育作为职业教育教师终身学习的一部分,学习与职业相关的知识和技能以及培养职业态度等,学习的范围涵盖与职业、生产和生计有关的教育、培训和技能发展等方面,其中,横向技能、公民技能、终身学习技能是职业教育的重要组成部分[27]。职业教育教师作为职业教育教学改革的核心,要将职业教育的终身学习理念投射到自身的专业发展上。
-
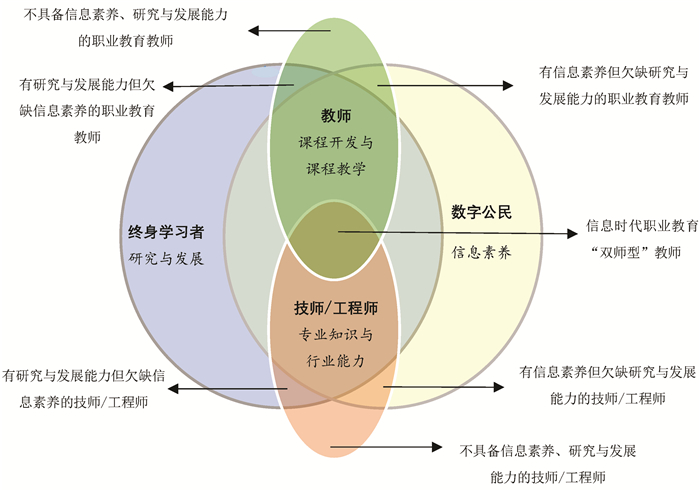
综上所述,信息时代职业教育教师需要兼具教师、技师/工程师、数字公民、终身学习者等多种角色特征,其相互间的关系,如图 1所示。由此,可把职业教育教师分为七类:一类是不具备信息素养、研究与发展能力的职业教育教师;二类是有研究与发展能力但欠缺信息素养的职业教育教师;三类是有信息素养但欠缺研究与发展能力的职业教育教师;四类是有研究与发展能力但欠缺信息素养的技师/工程师;五类是有信息素养但欠缺研究与发展能力的技师/工程师;六类是不具备信息素养、研究与发展能力的技师/工程师;七类是信息时代职业教育“双师型”教师。第七类是职业教育教师教学能力发展的目标与方向。
一. 具有技师/工程师特征的职业教育教师
二. 具有数字公民特征的职业教育教师
三. 具有终身学习者特征的职业教育教师
四. 信息时代职业教育“双师型”教师
-
国际K-12在线学习联盟(iNACOL)基于胜任力视角,将混合学习情境下中小学教师的教学能力分为心态、素质、适应性技能和技术技能[28]。我国《中小学教师信息技术应用能力标准(试行)》则基于课程教学活动视角,支持教师的教学工作及专业发展[29]。2005年,美国密歇根州立大学的米什拉(Mishra)和科勒(Kohler),在舒尔曼(Shulman)提出的教师知识结构的基础上,基于课程教学活动维度,构建了整合技术的学科教学知识(TPACK)体系[30]。该框架正在从中小学领域扩展至高等教育和职业教育领域。整体而言,中小学教师教学能力标准侧重于教师的师范属性。
-
国内外研究者对高校教师教学能力标准的研究主要从课程教学活动和心理认知两个角度展开。葛文双、韩锡斌将信息时代高校教师教学能力划分为信息技术融入教学的意识、信息技术融入教学的素养、信息技术融入教学的能力和信息技术融入教学的研究四个维度[31]。安吉丽(Angeli)等人将教学能力划分为主题识别、表征识别、教学策略识别、ICT工具识别、课堂技术融合策略识别[32]。陈(Chen)等人将信息化教学能力分为动机和价值观、对技术和方法的认知、对技术方法的运用、反思性评价[33]。博耶(Boyer)指出:应将大学教学上升到学术研究的高度;高校教师应当开展关于教学能力的专业研究和实践;教师的教学研究能力与学术研究能力同等重要[14]。
-
目前,常见的教师信息化教学能力标准有七个,分别是:美国国际教育技术协会(ISTE)2017版教育者标准[34];美国教育传播与技术协会(AECT)2012版教师教育技术能力标准[35];联合国ICT-CFT框架[36];IBSTPI面对面、在线和混合环境教师通用能力标准[37];我国中小学教师信息技术应用能力标准[38];我国师范生信息化教学能力标准[29];我国教育部在《职业院校数字校园建设规范》中提出的教师信息素养标准[39]。
尽管各标准的构成维度以及表述方式存在区别,但对教学能力的关注点是基本一致的,都主要聚焦于自主学习能力、交流能力、协作能力、创新能力、解决问题能力等方面。其中:ISTE教育者标准强调教师从理解学习者学习的视角来应用信息技术以优化教学,鼓励教师根据学生认知背景及学习特点的不同来设计多元化的学习环境和选择多元化的学习资源,体现了以学生为中心的建构主义教育理念;AECT标准与我国师范生信息化教学能力标准类似,都是以教育需求为导向,采取教师准入制度,对职前教师进行严格筛选,强调教学研究(研究创新)能力的重要性等。ISTE、AECT、ICT-CFT、IBSTPI、我国中小学教师信息技术应用能力标准、我国师范生信息化教学能力标准,均将教师信息技术应用能力与意识作为教师专业发展(教师学习)的基础而加以强调,并从信息技术赋能课程教学活动的视角来审视信息技术的设计、开发、应用、管理、评价等,尤其突出创新创造的重要性。ICT-CFT、我国中小学教师信息技术应用能力标准、我国师范生信息化教学能力标准,都有较为清晰一致的研究脉络,尤其是后两者,都基于我国国情进行了系统性的本土化科学论证。教育部发布的《职业院校数字校园规范》中将职业教育教师信息素养作为信息时代教学能力的关键要素,提出教师信息素养包含了意识与态度、知识与技能、应用与创新、研究与发展、社会责任等五个方面的内容。
-
国际培训、绩效、教学标准委员会的教师教学通用能力标准(IBSTPI)中提出,教学能力是制定教师能力标准的核心[37]。本文分析了五个具有代表性的职业教育教师教学能力标准,它们分别是澳大利亚职业教育教师专业能力标准(TAE10)[40]、英国职业教育师资培养专业标准[41]、欧盟职业教育教师专业能力标准框架[42]、德国教师教育中等专业科学与专业教学论内容上的各州共同要求[43]、我国中等职业学校教师专业标准(试行)[44]。
通过比较分析发现,以澳大利亚技术与继续教育体系(TAFE)为代表的职业教育教师教学能力标准侧重突出教师作为技师/工程师、终身学习者角色的特征[45],这与面向课堂教学活动的普通教育教师教学能力的要求有很大不同。英国职业教育师资培养的专业标准对教师本身的胜任力要求很高,对教师专业价值属性、知识理解与技能提出了要求。职业教育教师实际的工作场域复杂、多元,需要教师角色向技师/工程师、专业教学专家转化。欧盟职业教育教师专业能力标准框架以工作过程为导向,关注职业教育教师作为技师/工程师角色所发挥的功能,尤其是在工作关系网构建、团队合作、操作培训和学习管理等方面。德国职业教育教师标准结合了工作过程与教学活动两种视角,将职业教育教师界定为“介于理论与实践中间的熟练教学法专家”,强调了教师所具有的“双师”素质(兼具教师与工程师/技师角色)。我国中等职业学校教师专业标准从教师胜任力的视角出发,指向教师的专业理念、师德、专业知识与专业能力等方面,该标准对教师的个人品德修养、职业素质都提出了很高的要求,强调职业教育教师的知识结构要覆盖教育知识、课程教学知识、通识性知识以及相关的实践性知识等诸多方面。
-
综上所述,本文提出信息时代职业教育“双师型”教师教学能力标准框架。该框架分为两个维度,即教师教学能力的构成要素和教师教学能力的发展阶段。信息时代职业教育教师应兼具教师、技师/工程师、数字公民、终身学习者四种角色特征,再结合中小学教师教学能力标准、高校教师教学能力标准、教师信息化教学能力标准、职业院校教师教学能力标准等成果,将职业教育“双师型”教师教学能力的构成要素分为六个方面:课程开发、课程教学、专业知识、行业能力、信息素养、研究与发展能力。
课程开发也被称为课程设计或课程编制,指教学计划、教学大纲和教材的编写,并对教学计划、大纲和教材应达到的目标、选择的内容和评价的标准进行可行性研究[26]107。姜大源认为,职业教育课程属于工作过程系统化课程,对其开发可分为四个步骤:一是工作任务分析,即根据专业对应的工作岗位进行典型工作任务的分析;二是行动领域归纳,即根据能力的复杂程度,包括同类合并等措施,将典型工作任务整合形成相关的能力;三是学习领域转换,从这一步开始,要在目标中融入教育因素,所谓“学习领域”就是课程,“学习领域转换”就是构建课程体系;四是情境设计,即将学习领域分解为不同的主题学习单元[46]。基于此,王雯和韩锡斌提出了“互联网+职业教育”背景下职业院校混合课程开发的四个步骤:信息技术环境下的岗位分析、典型工作任务分析、工作过程课程开发和学习情境设计[47]。职业教育教师应具备基于上述步骤进行课程开发的能力。
课程教学是指根据一定的教育目的,以课程内容为中介,由有综合教学能力的教师“教”和学生的“学”共同构成的一种教育活动[48]。课程教学能力包括教学设计、教学实施、教学评价三种能力[49-51]。
专业知识指的是教师所教专业领域的知识,主要由专业理论知识、专业实践知识和专业反思知识构成[52]。
行业能力指的是教师所在行业的核心能力,包括行业沟通与合作能力、行业实践能力、行业服务能力[50]173-181。
信息素养指的是合理合法地利用各种信息工具,尤其是多媒体和网络技术,从而捕捉、获取、评估、应用、整合和创造信息,以实现某种特定目的的能力[53]。根据我国教育部发布的《职业院校数字校园规范》,信息素养主要包括意识与态度、知识与技能、应用与创新、研究与发展、社会责任等五个方面的内容[39]。
研究与发展能力指的是教师的科研能力、教学研究能力及专业发展能力。我国出台的《国家职业教育改革实施方案》[24]《中共中央国务院关于全面深化新时代教师队伍建设改革的意见》[54],以及《教育部山东省人民政府关于整省推进提质培优建设职业教育创新发展高地的意见》[55]等政策文件,均明确提出要提升职业教育教师的教学能力,尤其是教学研究能力与专业发展能力。
德国职业教育学家劳耐尔(Rauner)将职前职业教育教师的教学能力发展水平区分为新手、有进步的初学者、内行的行动者、熟练的专业人员和专家五个阶段,并据此划分了四个学习范畴[56]。国内也有一些研究者探讨了教师由非专业人员成长为专业人员的过程中,在不同时期所遭遇的不同问题或所关注的不同焦点[57-58]。教师职业本身具备一定的“工匠”属性,从职前培养强调见习实习到入职后实行“师徒制”,都需要教师“绝知此事要躬行”,这和职业教育人才培养的方式不谋而合。因此,本文基于劳耐尔(Rauner)的五个阶段和四个学习范畴[56],将信息时代职业教育“双师型”教师教学能力发展划分为四个阶段,即初学者→高级初学者→有能力者→熟练者→专家,并在表 1中标识出了这四个阶段教师应完成的学习任务,并有针对性地阐述了每个阶段职业教育教师的典型教学能力标准。
第一个学习阶段:初学者→高级初学者(完成职业定向性工作任务)。在学习之初,职业教育教师首先需要对信息时代职业教育教师教学能力构成要素及教师工作范围有一个初步的认识。教师不仅要认识和理解本职业(教师)的定位、与其他职业的关联以及工作范围,而且还要认识和理解在劳动分工结构中本职业的工作任务。初学者通过了解有关工作的结构、重点和内容等信息,来理解与本职业紧密相关的其他跨行业工作任务以及常规教学实践。初学者对职业领域内的入门和概括性知识进行学习是获取职业行动能力和教学设计能力的基础[59]。在教学能力提升的初始阶段,教师要参与以工作过程为导向的教学任务,这样他们就能够最快地实现从初学者向高级初学者的提升。在本阶段中,职业教育教师教学能力的课程开发、课程教学、研究与发展能力要素需要教师在外部指导下习得;专业知识与行业能力要素则需要教师具备处理该领域定向性与目的性任务的能力;信息素养要素需要教师将信息技术应用于教学的基本设计中,并基于信息化教学的基本理念来理解信息化教学特点。
第二个学习阶段:高级初学者→有能力者(完成程序性工作任务)。教师在了解了职业概况并获得初步技能后,就进入了第二个学习阶段,开始从事程序性的工作任务,以掌握与职业有关联的知识。程序性的工作任务就是指教师考虑教学内容的前后关联,以便系统地理解教学任务,从而建立一个整体化的职业观念。本阶段主要聚焦教师的知识内化与实践能力的提升,这与第一阶段的学习(主要侧重教师知识和技能习得)不同。在第二个学习阶段,教师须将所学的内容在教学实践中运用,这种基于工作场所的学习能够促进教师对职业关联性知识的理解与掌握。在教学实践中,基于职业教育课程实践的课程开发能力、基于教学实践的教学能力、研究与发展能力均建立在教师对信息时代职业教育教学有一定的前期积累基础之上,教师在此阶段可以较为独立地开展课程开发、课程教学及研究,而专业知识的获取在此阶段表现为教师对体系内若干项不同知识的整合和建立的关联。行业能力主要体现在教师完成行业工作任务的过程性行为和阶段性操作的熟练程度上。教师的信息素养基于第一阶段信息技术应用的学习,在第二个学习阶段更加突出对教学的优化,这是一个将信息技术与教学整合的过程。
第三个学习阶段:有能力者→熟练者(完成蕴含问题的特殊工作任务)。教师在掌握了完成程序性工作任务的能力以后,就进入了第三个学习阶段,即解决蕴含问题的特殊工作任务。每个职业归根到底都要在实践中学习,故而,在解决问题时,仅依靠已有的规则和方案是不够的。在教学中,往往会出现一些不符合常规和职业标准的情境,这是用熟知的方案无法解决的问题。蕴含问题的特殊工作任务往往包含一些新的问题,之前的工作经验无益于新问题的解决,这些新问题往往会集中出现在各种教学比赛中。为解决这些问题,教师迫切需要学习并掌握相关理论。因此,教师有必要首先分析工作任务,然后通过构建理论分析框架找出问题所在,最后设计出解决方案。完成该工作任务,除了要求掌握必要的教学理论知识外,还需要有一定的教学技巧和经验的积累,这是建立在第二个学习阶段基础上的。到了该阶段,教师通常已在实践教学中对程序性任务反复实施,对教学流程及各个优化环节已经熟稔于心,需要从经验获得到理论认识的进一步提升。教师要学习职业教育课程理论、教学理论、信息化教学理论等,从而更好地认识教育现象、解决教育问题,并在实践中强化自身综合运用专业知识的能力以及借助信息技术解决教学难题的能力。就教学能力构成要素中的研究与发展能力而言,教师需具备将理论与经验相结合的研究能力,从而解决真实的教学问题并达到创新的高度。
第四个学习阶段:熟练者→专家(完成无法预测结果的工作任务)。教师具备了完成蕴含问题的特殊工作任务的能力后,在理论和实践上均达到一定高度。这时,教师需要将自己的课程开发、课程教学案例整理后与同行分享,或者基于研究与创新成果来指导其他教师。该学习阶段是一个从实践到理论再到实践的过程,处于该阶段的教师在与其他教师的交流分享中,面临着更加多元、复杂、难以预测的局面,随着解决问题能力的不断提升,完成从熟练者型教师到专家型教师的跨越。该阶段,要求教师在课程开发、课程教学、信息素养、研究与发展能力等方面达到理论与实践的融会贯通,同时在专业知识与行业能力上,具有创造性地运用专业知识来系统分析无法预测结果的工作任务的能力,最终实现专家型教师角色的转变。
《职教20条》指出,我国进入新的发展阶段,产业升级和经济结构调整的步伐不断加快,各行各业对高素质技能型人才的需求越来越迫切,职业教育的重要地位和作用日益凸显,因此要多措并举打造“双师型”教师队伍。教育部等九部门印发的《职业教育提质培优行动计划(2020-2023年)》提出,鼓励职业学校利用现代信息技术推动人才培养模式的改革,职业教育要满足多样化学习需求,大力推进“互联网+”“智能+”等教育新形态,推动教育教学的变革与创新。基于上述发展要求,笔者提出了信息时代职业教育“双师型”教师教学能力的标准框架。后续研究将基于该标准框架进一步构建具体的指标体系和测量工具,为今后职业教育教师教学能力的评价和发展,以及职业院校“双师型”教师的聘任和业绩考核,提供参考。



 下载:
下载: