全文HTML
-
阅读理解指读者同时从文本中提取、建构意义的历程[1]。作为个体发展中的一项基本素质,阅读理解能力对学生的各学科学业成绩、学科素养都具有重要影响[2]。英文以及繁体中文的研究表明,正字法意识与阅读理解关系密切[3-4],正字法意识的发展对阅读理解能力具有促进作用。但国内的简体中文研究中,对二者之间关系仍然缺乏深入研究,无法回答正字法意识对阅读理解“如何起作用”以及起“多大作用”的关键问题,从而不利于有针对性的培养和干预工作的开展。因此,考虑到阅读理解在学业发展中的重要作用,有必要对阅读理解的影响因素及作用机制进行探讨,进而为培养小学生的阅读理解能力提供针对性建议。
-
在英文研究中,正字法意识是指能够掌握单词拼写规则和字母准行序列的正字法知识[5]。Badian提出的缺陷假设和Castles提出的双通道模型(The Dual-Route Cascaded model)都认为,正字法意识的缺陷是阅读障碍的核心缺陷之一[6-7]。正字法意识的缺陷使阅读障碍者常常无法立刻辨认一些应自动识别的单词(sight word),在阅读的流畅性和自动化的发展上也较缓慢[8]。在汉语研究中,彭聃龄等人认为,除独体字外,每个汉字均可以分成不同的部件,部件按照一定规则进行组合的方法为“正字法”,正字法意识是指关于汉字部件组合规则的意识[9]。在汉语阅读障碍的研究中,由于研究者对于正字法意识的考察方向不同,所以得出汉语阅读障碍是否存在正字法意识缺陷的结论也不同。沈丹丹、赵婧等以真假字和是非字的辨认对小学生的正字法意识进行考察,发现汉语阅读障碍者不存在正字法意识的缺陷[10-11];刘文理等、孟祥之等和王晓辰等从汉字偏旁部件的认知能力视角考察小学生的正字法意识,认为汉语阅读障碍儿童存在正字法意识的缺陷[12-14]。本研究综合现有研究对正字法意识的界定以及考察维度,将正字法意识界定为:以汉字的声旁确定发音、依据汉字形旁提取语义、能够整体把握汉字结构规则的意识。
早在20世纪80年代,正字法意识在熟练阅读者汉字识别中的作用就已在多个实验中得到证实[15-16]。李虹、彭虹等的研究表明,儿童正字法意识的发展要以一定的识字量为基础,阅读能力在发展的不同阶段,分别与正字法意识的不同方面密切相关[17]。廖晨惠等的实验研究表明,三年级识字困难学生的正字法意识与识字量呈显著相关,说明正字法意识是识字困难学生解码时依赖的主要线索[18]。同时,台湾学者的实证研究证明,关于正字法意识的教学确实能有效提升学生的识字能力[19-20]。由此得出,学生的正字法意识能够促进识字能力的发展,进而提高识字量。
-
学者Chall提出的阅读发展阶段(stages of reading development)理论[21]和Gunning提出的阅读发展理论[22]都将阅读的发展历程分为识字与理解两大部分,并以识字作为阅读理解的基础。
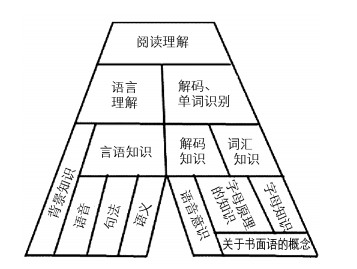
近30年来,识字的重要性得到广泛证实,识字量被认为是影响阅读者读写能力的最主要因素之一[23],丰富的词汇知识有助于儿童阅读能力的发展和学业成绩的提升[24]。Wren提出的阅读金字塔模型或“A”模型(见图 1)描述了个体掌握阅读理解的基本结构[25],即阅读理解主要由语言理解和解码构成。从Torgesen提出的阅读的简单方程:单词识别的流畅性和准确性*语言理解的知识*策略动机和兴趣=阅读理解[26],我们可以推断识字量会影响阅读理解能力的发展。
大量的实证研究也表明,识字量影响学生的阅读理解能力。早在1984年,Stanovich等人对低年级儿童的研究发现,儿童对字词的解码能力是预测阅读理解的最大变异量[27]。李虹等人研究发现,学前儿童汉字识别成绩能够独立解释阅读理解成绩的42%,说明学前期儿童阅读理解的能力主要取决于字词知识的获得量[28]。另一追踪研究显示,字词流畅性在小学低年级阶段对阅读理解的贡献大于句子流畅性[29]。有关对外汉语的研究也发现,字词知识和字词推理对阅读理解具有直接贡献[30]。
还有学者从识字能力落后来解释阅读障碍的形成历程,指出当识字自动化以后,阅读理解能力才得以发展[31]。Foorman等人提出,80%的学习障碍学生有阅读理解困难,其中90%来自识字困难,且缓慢的、不正确的识字表现是阅读理解能力低下的最佳预测变量[32]。综上所述,我们认为识字量能够正向预测小学生阅读理解能力的发展。
-
截至目前,关于正字法意识与阅读理解的相关研究较少。董琼等通过辨识真假字和是非字考察小学生的正字法意识,结果发现正字法意识与阅读理解未呈现出显著相关[33]。笔者认为,其原因在于对正字法意识的考察局限于汉字的组成成分和结构模式,并未涉及汉字的认知成分。而当前,已有少数台湾学者基于繁体中文,开展包含正字法认知成分的相关研究。如:吴敏而发现,儿童对于文字外表的整体认识及区分字和部首的能力有助于其日后阅读理解能力的提高[34];方金雅也发现,小学生的“汉字组字规则”“部首表义知识”“声旁表音知识”均随年级的增加而稳定成长,而且这些正字法知识与识字能力、语文阅读成绩有显著正相关[35];柯华威等的研究表明,正字法意识对阅读能力优秀学生的阅读理解有显著的解释量[36],并将三者关系表述为正字法意识影响识字的发展、识字和阅读理解互相影响[37]。
综上所述,目前汉语研究大多关注正字法意识与识字量的关系以及识字量与阅读理解的关系,关于正字法意识、识字量、阅读理解能力三者间的关系还不明晰,且现有正字法与阅读理解的关系均为台湾学者以繁体中文进行的研究,我们还不确定简体字与繁体字是否会对三者关系造成不同影响。因此,本研究试图在已有研究的基础上,验证汉语正字法意识与阅读理解的关系,并进一步考察识字量在其中发挥的中介作用,从而为制定有效的阅读训练策略提供依据。
一. 正字法意识对识字量有促进作用
二. 识字量能够预测阅读理解的发展
三. 正字法意识、识字量、阅读理解能力三者间关系有待探究
-
已有研究通过对左右结构的真字、假字和非字的词汇判断,发现小学低年级儿童接受假字为汉字的比例尚处于随机状态[38],二年级以上儿童已掌握了有关形旁、声旁组合的正字法规则[39],三年级儿童已对正字法敏感,六年级儿童对正字法的掌握已基本达到了大学生水准[40]。本研究结合前人的研究结果,选取已经基本掌握正字法的三年级小学生作为研究对象,在重庆市和黑龙江省选取4所学校的三年级学生(共计405名)作为研究被试。被试的母语均为汉语,无视觉和听力障碍,经监护人同意后参与研究。
-
综合前人研究,本研究借鉴Connie Ho等人编制的“香港阅读和书写学习困难测验卷”(Hong Kong Test of Specific Learning Difficulties in Reading and Writing,HKT-SpLD)[41],自编正字法意识测验卷,并根据“组字规则”“部首表义”“声旁表音”3个维度,发展出正反字判断任务、真假字判断任务、部件位置判断任务、部件组合任务和偏旁意识任务5项指标。其中,前4项主要考察小学生的“组字规则”意识,偏旁意识任务的两道题目分别考察“部首表义”和“声旁表音”意识。
依据各试题通过率计算出试题平均难度为0.32,适合三年级小学生使用。采用折半法计算出该测验内部一致性信度Cronbach α系数为0.61,符合统计学标准。效度检验方面,采用目前使用较为广泛的内容效度指数CVI(Content Validity Index)作为评价指标。评价本问卷内容效度的专家包括1位阅读障碍专家和4位教龄超过10年的资深小学语文教师。他们共同就试题条目与所属维度的关联性作出评价,并在4级评分的可选项“1=不相关,2=弱相关,3=较强相关,4=非常相关”中作出选择。通过分析,发现条目水平的CVI(item-level CVI,I-CVI),量表水平的CVI(scale-level CVI,S-CVI)均为1.00,具有较好的一致性,符合统计学标准[42]。
-
本研究阅读理解能力测验选用西南大学李欢、龙艳林等编制的“小学生阅读理解测验卷”。该测验依据阅读的理解成分编制题目,以字义搜寻、命题组合、形成命题、文义理解、推断、准确提取资讯、解释整合资讯、评价等为向度,测验内容为句子理解、段落理解、短文理解。折半法计算出该测验内部一致性信度Cronbach α系数为0.74,符合统计学标准。效度检验方面,采用目前使用较为广泛的内容效度指数CVI作为评价指标。其中,I-CVI和S-CVI均为1.00,具有较好的一致性;难度为0.57,区分度为0.41,均符合统计学要求。
-
识字量测验选用华东师范大学王孝玲、陶保平等编制“小学生识字量测试题库及评价量表”。编制者根据前期的大量调查和测试,得出各年级每个汉字的认识率(即某年级对某个字的正确作答数除以该年级总人数),并将其分为10组,其中第一组、第二组和第三组为高认识率(0.7~0.96),第四到第七组为中认识率(0.3~0.7),第八到第十组为低认识率(0.05~0.3)。该测验中,三年级试题的关联效度的信度在0.985~0.987之间,三年级试题信度在0.975~0.982之间,达到了标准化测试的优秀水准[43]。
-
测试在学生平时上课的教室进行。测验要求学生独立完成,学生答题完成后现场收回问卷。主试在进行测试之前准备好相关材料。作答时,主试提供作答样例,讲清作答方法和要求,学生独立答卷。
-
运用SPSS 25.0、Amos21.0和Excel软件进行统计分析,主要方法为相关分析、结构方程模型的建立和检验等。
一. 研究被试
二. 研究工具
1. 正字法意识测验
2. 阅读理解能力测验
3. 识字量测验
三. 研究程序
四. 数据管理与统计方法
-
本研究采用Pearson积差相关,对被试的正字法意识、识字量和阅读理解的得分正确率及其各维度间的关系进行统计分析,结果表明,正字法意识与阅读理解能力呈显著正相关(r=0.23,p < 0.01),正字法意识与识字量呈显著正相关(r=0.31,p < 0.01),识字量与阅读理解能力呈显著正相关(r=0.38,p < 0.01),详见表 1。
-
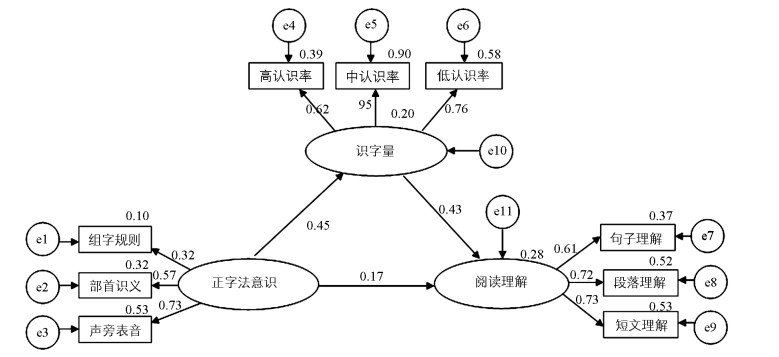
本研究运用结构方程模型,验证识字量在正字法意识与阅读理解能力中的中介作用。基于现有研究,以正字法意识各维度(组字规则、部首表义、声旁表音)为自变量,阅读理解为因变量,识字量为中介变量构建模型。拟合结果显示,模型的各指标均良好(如表 2所示),说明资料拟合验证了理论模型,可以进行下一步的中介作用分析。
基于模型的拟合结果,采用偏差校正的非参数百分位Bootstrap法,检验识字量在正字法意识与阅读理解能力中的中介效应。研究共重复抽样2 000次。结果表明,正字法意识对阅读理解能力有显著的正向预测作用(β=0.17,t=10.82,p < 0.001),其95%的置信区间为[0.08,0.39];正字法意识对识字量有显著的正向预测作用(β=0.45,t=10.29,p < 0.001),其95%的置信区间为[0.30,0.62];识字量对阅读理解能力有显著的正向预测作用(β=0.43,t=9.56,p < 0.001),其95%的置信区间为[0.24,0.61]。正字法意识通过识字量对阅读理解能力的中介效应大小为0.37,其95%的置信区间为[0.28,0.41],置信区间内不包含0,说明识字量的中介效应成立,它起部分中介作用,具体中介作用模型如图 2所示。由此可以说明,在正字法意识对阅读理解能力的影响机制中,既包括正字法意识对阅读理解能力的直接影响,又包括正字法意识通过识字量对阅读理解能力的间接影响。
一. 正字法意识、识字量与阅读理解能力的相关性分析
二. 识字量中介效应分析
-
本研究发现,正字法意识与阅读理解能力呈显著正相关,这一结果验证了本研究的假设,而且对周湾的研究结论[44]进行了补充。根据Wren提出的阅读金字塔模型或“A”模型以及阅读障碍的发生机制[25],可以推断出正字法意识影响阅读理解的原因。首先,由于学生对于正字法意识的知识缺乏,因此会出现无法根据形旁推测字本身的含义、无法通过声旁推测字的读音等状况[45];其次,在对字的理解存在困难的基础上,学生对于词组、句子、段落、短文,同样存在理解困难,即阅读理解困难,所以可以推测正字法对单词识别能力和阅读理解的发展起着至关重要的作用。另外,本研究发现,正字法意识对阅读理解能力的直接解释量较小。同样根据Wren提出的阅读金字塔模型或“A”模型以及阅读障碍的发生机制,可推断阅读理解是一个复杂的多因素影响的能力指标,涉及本研究关注的正字法意识、识字量以及本次实验未涉及的背景知识、阅读动机、阅读策略等多项因素,每一项因素的缺失都会影响阅读理解的程度[46]。由此,可解释为什么正字法意识在阅读理解能力的解释量中占比较小,但同时也说明正字法意识也是阅读理解能力不可或缺的一部分。
-
本研究发现,在正字法意识对阅读理解能力的影响中,识字量起着部分中介作用,这验证了本研究的假设,也与Chall与Gunning的阅读发展阶段理论[21-22]和Torgesen提出的阅读方程[26]契合:识字量能显著地预测阅读理解的成绩。正字法意识能够在一定程度上帮助儿童学习和记忆生字,并从记忆中提取学过的汉字从而帮助其学习和推测未学过的新字。但同时,正字法意识对识字的解释和预测量仅为43%,原因在于部首表义、声旁表音等正字法成分一般只适用于形声字,而形声字虽在汉字中占比达80%以上[47],但仍有一大部分汉字无法根据声旁和部首判断字音和字义。识字是阅读的基础,识字量的多少决定着阅读的长度和速度,影响着阅读理解的能力。识字量对阅读理解能力的解释量为45%,这同样说明影响阅读理解能力的因素较多,如语言理解、阅读动机等其他因素也发挥着十分显著的作用,这与前人的研究结果基本一致。
一. 正字法意识对阅读理解能力的直接效应
二. 识字量在正字法意识与阅读理解能力间的中介机制
-
据统计,《现代汉语通用字表》7 000个汉字中,形声字占到80%以上[47]。形声字由表义的形旁和表音的声旁构成,掌握部件对提高识字效率、增加识字量有着至关重要的作用。已有研究表明,提高正字法技能,要求教学中,教师要将儿童的注意力吸引到对汉字结构的把握上来[48]。第一,采用单字部件教学的方法,根据教材,按其功能,对单字组织偏旁、部首进行训练,指导学生分析字形结构、熟悉组字规则,从而通过记忆字形的方式提高学生的识记能力[49]。同时,教师可使用辅助教具,例如电脑动画拆解汉字的部件、投影拼字教具讲解部件书写等。第二,已有研究表明,部件位置不仅具有部件的相关属性(声旁的语音和形旁的语义),有时还具有部件的非相关属性(形旁的语音)[50]。因此,在教学过程中,对于复杂、难以直观理解的汉字,可以通过学习汉字部件常出现的位置进一步强化其音义的联结,或采用以文带字部件教学法、字族文识字法,辅以图片、音效,加强字形与字义的联系[51],从而提高学生的识字量。基于以上措施,在提升学生识字量的基础上,可以促进学生对词组、句子、段落、短文的理解。第三,声旁意识与阅读流畅性改善相关[52],因此应在教学中增加声旁表音的正字法意识相关训练,强化汉语的语音单元、声韵组合规律、形音联系[4],提升小学生阅读流畅性水平。将提升阅读准确性和阅读流畅性相结合,可有效促进小学生的阅读能力。
-
本研究结果表明,小学生的正字法意识对其阅读理解能力的解释量有限,这说明正字法意识不是提升小学生阅读理解能力的唯一途径。同时,阅读金字塔模型清晰地展示出阅读理解主要由背景知识、解码、单词识别(解码知识和词汇知识)构成[25]。但是,受英语阅读障碍干预研究的影响,汉语中关于语音意识的干预研究最多,而其他与阅读障碍密切相关的语素意识、阅读流畅性的干预较少[4]。因此,应基于汉字特点,注重语音、语素、流畅性等阅读相关技能,使用多种方式结合的教学策略进行阅读理解训练,全面促进小学生阅读能力的提升。
-
本研究证实识字量在正字法意识与阅读理解能力间起部分中介作用,但在研究对象、研究方法及研究内容上仍有一定的局限性。首先,在研究内容上,本研究从组字规则、部首表义、声旁表音3个维度测验小学三年级学生正字法意识,但不同年级学生的正字法意识发展规律以及组成维度还有待探究;其次,在研究方法上,已有研究证实阅读障碍儿童正字法意识与阅读流畅性呈显著正相关的同时性关系[10],因此未来研究可以尝试进行正字法意识对阅读流畅性、阅读准确性等相关阅读能力的跟踪研究,探讨正字法意识对相关阅读能力的纵向预测作用;最后,目前阅读障碍领域干预研究不足,建议通过集中正字法意识领域的相关研究,为今后阅读障碍领域制定详细具体的干预策略提供相应的理论依据。



 下载:
下载: