全文HTML
-
青少年体育是群众体育的“源头活水”,是竞技体育的“希望沃土”,更是体育产业的“未来蓝海”。[1]2007年中共中央、国务院颁布的《关于加强青少年体育增强青少年体质的意见》(中发[2007]7号),在青少年体育和青少年健身运动的开展中具有里程碑意义。这使得体育运动所承载的健康价值及其在关照、提高、监控人的生命质量方面的特殊护佑功能,得到了前所未有的发掘与认同。[2]但是,现实情况却不容乐观,我国青少年运动参与水平依然低下,运动健身氛围仍不够浓郁,体质健康状况令人担忧。
针对上述不利局面,国家和地方政府高度关注,颁布了一系列关于青少年体质健康教育促进的政策和文件。从政策文本的宏观层级来看,不乏国家级别的行政法规,部委、职能部门的指导性文件;从政策内容的微观层面来看,不仅包含青少年体质健康教育体系各中心节点的明确规定,而且还包括相关健身运动实施意见。然而,“高密集”政策和文件的颁布和实施并没有产生预想的成效。据2014年全国学生体质健康监测结果表明,肥胖、近视仍是困扰青少年健康成长的顽疾,更令人遗憾的是高血压、脂肪肝等疾病低龄化趋势愈加显著。[3]因此,从政策效能角度讲,无疑是政策本身或执行过程出现了“问题”。本研究旨在对近30年我国青少年体质健康教育政策的梳理与分析,明确政策的价值导向和共性特点,探讨政策本身的局限性和政策执行的瓶颈,提出青少年体质健康教育政策的优化策略和路径。进而为政策调整提供参考,有助于提升政策制定的科学性和实效性;有助于理清青少年体质羸弱的政策掣肘,为提升青少年体质健康水平提供政策保障和支撑;有助于体育教育工作者和青少年正确理解和把握政策精髓和本质要求,改进和提升政策执行的效果。
-
随着依法治国战略的确立和实施,青少年体质健康教育领域的法制化建设和法治化治理体系已初具规模,法治精神和理念已深入人心。在当前教育改革的大背景下,青少年体质健康教育工作紧紧围绕素质教育这一主题,突出“以人为本、健康第一”的教育理念,以学校体育为突破口,积极进行相关法律、法规、政策和文件的制定和细化落实工作。学校体育的目的、任务、地位及作用通过体育立法的形式得以明确;体育课程、课外体育锻炼、运动竞赛及训练等工作从政策制度上得以规范。可以说,当前青少年体质健康教育工作不仅具有厚重的政策和舆论优势,更令人欣慰的是相关政策文本的决策水平也越来越趋于科学和理性。近30年来,我国主要青少年体质健康教育政策见表 1。
-
党和国家领导人一贯重视和关切青少年体质健康教育工作。毛泽东同志在正式发表的第一篇学术论文《体育之研究》中,就为青少年体质健康教育工作指明了方向——欲图体育之效,非动其主观,促其对体育之自觉不可,并在建国之初提出了沿用至今的“健康第一”的教育方针。[4]邓小平、江泽民、胡锦涛同志也极为关注青少年的体质健康问题,对青少年体质健康教育工作做过很多重要批示。党的十八大以来,以习近平同志为核心的党中央将青少年体质健康提升到更为显著的位置,习近平同志个人也在各种公开场合表达了自己对足球运动的热爱,很好地推动和促进了“校园足球”的广泛开展,为青少年践行和实现“中国梦”奠定坚实的体质基础。
为了使党和国家领导人的重要指示和批示精神落到实处,中央政府相关职能部门积极行动起来,通过立法和制定政策、文件等形式,将青少年体质健康教育工作列入国家顶层政策设计的序列。2006年12月23日,在原国务委员陈至立同志的亲自安排和领导下,教育部、国家体育总局在北京联合召开了建国以来第一次“全国学校体育工作会议”,会议的主题是“关注亿万青少年学生身体健康”。2007年1月7日,原中共中央总书记胡锦涛同志针对当时我国青少年的体质健康问题,做出了重要批示:“增强青少年体质,促进青少年健康成长是关系国家和民族未来的大事,需要党委和政府高度重视,全社会要关心、支持”,并希望教育部、国家体育总局拿出具体可行的对策和方案。2007年5月7日,中共中央国务院下发了《关于加强青少年体育增强青少年体质的意见》,该文件作为建国以来青少年体质健康教育政策的最高规格文件之一,成为这一时期及未来一段时间的重要纲领性文件。2011年3月,政府工作报告第一次对青少年体质健康教育工作提出明确、具体的要求:“保证中小学生每天一小时校园体育活动”。2012年10月,国务院办公厅转发教育部等部门《关于进一步加强学校体育工作若干意见的通知》,通知要求:明确加强青少年体质健康教育的总体思路和主要目标,落实学校体育的重点任务,加强对学校体育的组织领导,建立健全青少年体质健康监测评价机制。[5]2013年11月,党的十八届三中全会审议通过了《中共中央关于全面深化改革若干重大问题的决定》,该决定明确指出:各级政府要强化体育课和课外锻炼,促进青少年身心健康、体魄强健,这是党中央对学生体质和青少年体质健康教育工作的重大决策。[6]2016年4月,国务院办公厅发布《关于强化学校体育促进学生身心健康全面发展的意见》,该意见对青少年体质健康教育工作提出更为全面而长远的要求,指出学校体育要以“天天锻炼、健康成长、终身受益”为目标。2016年10月,中共中央国务院下发了《“健康中国2030”规划纲要》,纲要明确指出以学校体育为突破口,建立学校健康教育推进机制。
-
健身运动无疑是提高青少年健康水平的必要选择。首先,青少年正处于人生的起步和快速发展时期,他们思想活跃、性格冲动、乐于冒险、精力旺盛,体育运动显然是他们乐于接受的、能够充分展示自我能力的最佳方式。其次,由于体育运动中的大部分项目是集体项目,在此类项目运动中所培养的集体意识、团队精神和相互协作的心向,则能够有效地提升青少年的心理承受能力,也为他们以后走向社会、适应社会提供了必要的积累和准备。因此,以科学有效的体育教学方式,为青少年学生提供丰富多彩的体育健身指导,增强其健康素养,[7]将是完成青少年体质健康教育工作使命的重要途径。
通过对表 1中所涉及的相关重要政策文本的研读,我们不难发现,学校体育教学是青少年体质健康教育政策一直关切和突出的主线与核心内容。相关实证研究表明:青少年体质健康教育政策文本涉及主题内容最多的是体育教学,占政策主题总量的17.4%;体育教学的标准、大纲、方案、教科书等学习类政策工具占整体政策工具体系的33.8%,位居第一。[8]基于上述分析,我们认为青少年体质健康教育政策符合教育规律,政策演进主题鲜明,能够为青少年体质健康状况的改善提供正确的方向指引和政策保障。虽然,目前政策实施的效果还有不尽人意的地方,但那只是政策执行和发展中的细节问题和阶段性矛盾,不存在大政方针上的错误和偏差。
-
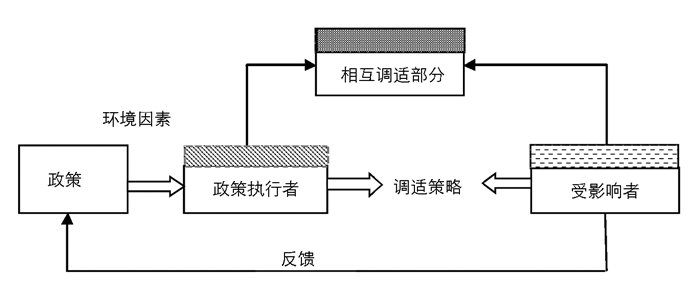
1976年,美国学者M.麦克拉夫林(M.Mclaughlin)在其代表作《互相调适的政策实施》中提出“互适模型”(见图 1)。该理论模型指出,公共政策的执行过程会受到政治、经济、文化等环境因素的影响,政策执行者和受影响者双方基于政策上的共同利益诉求,通过平等的对话,经过说明、协商甚至妥协等双向交流过程,达成一个双方共同认可的政策执行方式,同时,政策执行者的目标和手段并非一成不变,会随着环境因素和受影响者的需求和观点的变化而改变,这是一个动态调节、相互适应的过程。[9]
近30年,特别是近10年来,系列青少年体质健康教育政策的实施与执行过程,都具有一个共同的特点就是渐进调节、互适推进。这种政策执行方式也很好地顺应和契合了M.麦克拉夫林的互适模型所表达的核心理念和思想。例如,体育新课程标准研制组通过对实验区进行分层,在不同的实验区试点实施,根据师生的反馈信息,修订和完善体育新课标,进而在全国范围内进行推广实施。体育新课标的“新”主要体现在对新时代教育要求的适应、对学生需求变化的满足以及对旧教学大纲的局部超越。当然,体育新课标的执行过程并没有否定和抛弃体育大纲的精华之处,而是在发扬和继承的基础上,紧密结合经济、社会和教育发展的时代要求,政策执行者与教师、学生等受众群体之间通过平等的对话和交流,双方的需求和观点不断契合的政策互适过程。著名体育学者杨文轩教授在标准修订过程中也明确指出,要在不断的实践、调试、完善、发展和积淀中,促进新体育课程建设。[10]
一. 党和国家领导人高度重视,顶层设计优势凸显
二. 学校体育教学是政策演进的主旋律
三. 渐进调适是政策演进的方式
-
政策受影响者是否支持政策的实施,并不取决于对政策愿景的期望,而在于对自身利益得失的现实判断。如果政策受影响者遵循政策规范,付出成本过高,或者融入政策改革会使自身的既得利益受损,消极适应政策甚至抵制政策执行的现象就不足为奇,政策愿景自然无法实现。在现行的升学选拔机制中,文化课成绩是首要考量的因素,体育成绩占比很小,甚至在高考中没有实质性权重。因此,政策受影响者对高考文化课成绩的利益诉求远远超越了对体质健康教育的价值认同。学校、家庭、教师、家长、学生等构成了青少年体质健康教育政策受影响者群体。对于学校而言,减少学生体育活动时间,延长学生学习时间,高考成绩提高,升学率提升就会得到上级教育主管部门的肯定,受到家长和学生的认可和赞誉。反之,学校积极落实青少年体质健康教育政策,学生体质增强,综合素质得以提升,但升学率会受到影响,主管部门、家长和学生对学校的认可度必然降低。对于上述两种政策执行的认同,更多学校会出于近期利益考量,而选择前者。就家长而言,特别是农村家长投资子女教育的主要目的是为了让子女通过高考改变命运,他们认为良好的身体素质在高考中并派不上用场,体育在文化课成绩面前微不足道,自然不情愿也不支持子女参与到以“维系人类健康,满足人类精神文化需求,使人类充分享受自由和幸福”[11]的体育活动中。对于青少年体质健康教育工作者,尤其一线体育教师而言,新政策的实施过程充满着不确定性、否定性甚至巨大的挑战,这就意味着墨守成规的做法已不适应新的政策要求,轻松的工作氛围需要不断创新。如果教师在观念上对政策的解读和接受程度不到位,陈旧的行为惯性就难以改变,对政策执行抱以怀疑、拖延甚至排斥而安于现状的态度就会成为常态。
可见,青少年体质健康教育政策受影响者的多元价值诉求和政策愿景形成了某种错位。造成这种错位的根本原因在于政策主体范畴狭隘,政策受影响者得不到主体性尊重,不能平等地参与到政策的制定和执行过程之中,处于被动接受行政命令和被管理的“弱势群体”地位,以致于受影响者的多元价值诉求得不到重视和彰显。因此,受影响者在主体地位缺失的政策环境下,局部利益、短期利益、直接利益就成为其首要考量的对象,这种单向度的利益考量必然会使丰富的体质健康教育政策内涵和愿景,在具体的执行中发生某种质变和方向上的偏离。
-
政策的现实性、前瞻性和系统性是政策演变永恒的主题。政策研究的现实意义是当遇到社会问题或危机时,通过制定和执行新的政策,协调不同群体的利益关系,发挥资源整合的合力作用,解决矛盾。因此,政策编制与执行的首要考量是政策本身的现实性,即问题导向性,政策的目的、可行性、合理性等现实因素直接关系到政策执行的效果。我国青少年体质健康教育政策的编制和执行一直坚持问题导向原则,从解决现实实际问题出发,整合资源,化解危机和矛盾。
同时,政策编制应该具有一定的前瞻性,能够预料政策执行可能产生的新问题,预知事物未来的发展趋向。目前,我国青少年体质健康教育政策的前瞻性欠佳,相关政策文本的内容表述重复现象严重,政策演变体现出善后补救式政策规律,政策的时效性和持久性大打折扣。据相关研究统计,近30年有关青少年体质健康教育的法律、法规、文件有60余件,平均每年2件,多数新出台的政策存在着内容重复的现象。[8]比如,2007年5月7日,中共中央国务院下发的《关于加强青少年体育增强青少年体质的意见》和2012年10月22日,国务院办公厅转发教育部等部门《关于进一步加强学校体育工作若干意见的通知》以及2016年4月21日,国务院办公厅下发的《关于强化学校体育促进学生身心健康全面发展的意见》等文件在课堂教学、课外活动等环节存在着重复性表述。受迫于现实危机而急于问题解决的青少年体质健康教育政策,虽然对解决某些现实问题非常有效,但并未充分考虑青少年体质健康教育系统发展的内生动力与外在环境,缺乏对青少年体质健康教育趋势准确而科学地研判,致使政策的制定缺乏战略性和前瞻性规划。
青少年体质健康教育政策体系是一个复杂的系统,不仅包括体育课堂教学、课余训练与竞赛、课外体育活动等众多构成要素,而且也涵盖了诸如政策间的兼容互补、要素间的协调统一、系统与外部环境间的能动适应等复杂的非线性关系。基于青少年体质健康教育政策体系的系统性考虑,该政策体系的顺利实施需要完整的理念和系统的思维,在与社会经济、文化和教育等外部环境高度契合的基础上,不同政策之间需要内在的逻辑衔接和相互配合补充,形成“协调增益”之效。国办发[2016]27号文件《国务院办公厅关于强化学校体育促进学生身心健康全面发展的意见》(以下简称《意见》)规定“进一步完善政府主导、部门协作、社会参与的青少年体质健康教育机制,基本形成体系健全、制度完善、充满活力、注重实效的中国特色青少年体质健康教育发展格局。”[12]可以看出,青少年体质健康教育政策已经拓展为关联社会多个方面的政策系统,既要有教育行政部门的指导、学校管理者的实施、体育教师和学生的落实,也要有学生家长的参与,广泛联系到了社会的方方面面。因此,《意见》的顺利实施需要多方政策执行主体的团结协作,需要相关配套政策的支持和落实,仅仅依靠政策本身不可能解决系统的问题。令人遗憾的是,目前青少年体质健康教育政策并未形成一种合理的配套政策体系,体育师资配套、职能部门责权划分、问责地方等方面的政策均没有明确规定,使得青少年体质健康教育工作者在实际工作中缺乏强有力的配套政策支持。[13]
-
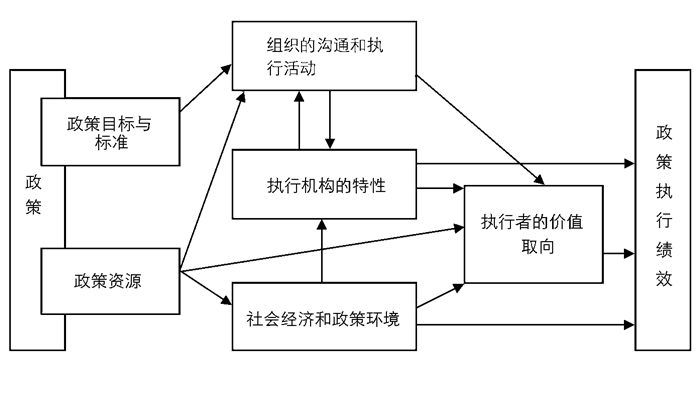
美国政策学家范·米特(D.S.Vanmeter)和范·霍恩(C.E.Vanhorn)以公共行政学为理论基础,遵照行政组织的层级原则,设计提出了米特-霍恩政策执行系统模型(如图 2)。[14]该模型指出影响政策决策成功转化为政策效果的因素,主要由6个变量组成,即“政策标准与目标”、“政策资源”、“组织间沟通与执行活动”、“执行机构的特性”、“社会经济和政治环境”、“执行人员的价值取向”。[15]其中,“组织间沟通和执行活动”这一变量可以左右政策执行者的意向,搭建政策与执行之间的关联,进而深刻影响政策执行与监督机制的建立。依据该模型对照我国青少年体质健康教育政策执行中的“组织间沟通和执行活动”,会发现体质健康教育政策的多元执行主体间存在着沟通不畅、合作机制欠缺的短板,以致于陷入政策执行机制和监督机制不能很好建立并发挥实效的窘境。
从政策执行角度讲,教育、体育、卫生、人社、财政、共青团等多个部门构成了青少年体质健康教育政策的具体执行主体。纵观各相关政策文本,我们会发现,文本中并没有明确划分各相关职能部门的职权和职责,相应的事权关系和边界界定更无从谈起。这就造成了职能部门间权责不明,沟通与合作机制缺乏,政策执行机制不健全以及执行效率低下的困境。长期以来,教育和体育部门主要负责青少年体质健康教育政策的落实与执行工作,但并没有被赋予处理和协调本部门以外相关事务和职能部门的权力,有悖于责权对等的组织设计原则,造成了青少年体质健康教育政策执行的“无奈”和“纵深”不足。[16]教育和体育部门在推动和执行青少年体质健康教育政策中,常常会掣肘于学校体育经费问题与当地财务部门意见不一,体育教师编制与人社部门意见不一,政策执行部门能够调动的资源非常有限。[17]同时,因职能部门间责权不明,事权关系和管理边界划分模糊,也造成了青少年体质健康教育政策执行的评价、考核和奖惩机制无法建立。
从政策监督角度讲,我国青少年体质健康教育政策执行缺乏常态化、制度化、多层次的有效监督。政策执行中更多地注重形式建设,以“运动”方式轰轰烈烈组织的会议和活动不少,但缺乏对学校体育常态工作的有力推进和监管。[11]青少年体质健康教育政策执行的事前防御、事中控制、事后反馈等制度化监督机制有待完善和规范。长期以来,青少年体质健康教育政策执行的监测和督导工作主要由教育行政部门来承担。其监督形式主要表现为听学校汇报、查阅文字材料和实地考察固定而流程式的“三部曲”。教育行政部门对于政策执行反馈信息的获取,过分依赖于学校单方面汇报,故此学校多在文字和数据上挖空心思,对政策执行中的问题多轻描淡写,真正的问题往往不能被发现,这就加剧了政策执行信息的不对称和失真的风险,大大增加了政策监控的难度。另外一个政策监督不足的原因是监督机构的独立性问题。教育行政部门的督导检查组要么是其下属的职能科室,要么由兄弟院校同行专家临时组建。监督的主体和客体之间存在着复杂、密切的共生关系,甚至有着相互制约的利害关系。督导检查组真正的监管和督查职能在这些错综复杂的关系中难以发挥作用。
-
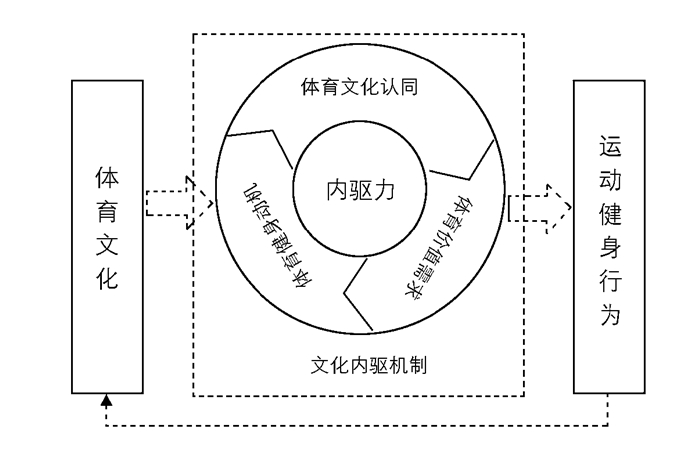
体育政策文化溢出效应过程图(见图 3)诠释了青少年体质健康教育政策演进的文化内在驱动机制和体育政策文化效应溢出的全过程。一方面,青少年的体育文化认同、体育价值需求和体育健身动机等内部心理机制的形成与发展是体质健康教育政策演进的文化内在驱动力,其中,体育文化认同为政策演进提供了起源动力,体育价值需求为政策效果提供了生成动力,体育健身动机为政策的文化效应溢出提供了行为催化。另一方面,青少年学生只有在体育文化的无形熏陶中,才会形成体育健身文化认同,产生体育健身价值需求,进而在体育健身动机的驱使下,自觉参加健身运动,把体育内化为生命与生活的一部分。
然而,近30年颁布的系列青少年体质健康教育政策,并未在体育健身文化塑造和健身价值需求引导等方面引起足够重视,甚至成为严重缺失和被遗忘的重要内容。致使政策演进缺乏文化认同、价值需求和心理动机等内在驱动力的推动和促进,使得政策的贯彻与落实成为“空中楼阁”,政策在实践中表现出空洞化、形式化、表面化,最终导致体质健康教育政策对提升学校体育工作水平和增强青少年健康素质的效果甚微。因此,今后如何推动青少年体质健康教育政策的体育文化建设,提升政策的体育文化溢出效应并有效形成文化内驱力,将成为实现和提升政策效益的根本所在。
一. 政策受影响者的利益诉求偏离政策愿景
二. 政策的前瞻性和系统性欠佳
三. 政策执行机制不健全,监督机制待加强
四. 政策的体育文化溢出效应严重缺失
-
在政策制定过程中,政策制定主体间应通过积极而有效的沟通,有效消除部门壁垒,加强协调与配合,同时调动广大政策受影响者积极性,参与到政策文本的起草、制定和修改等工作。这样不仅有利于建立一个良好的多元价值诉求和利益表达机制,而且有利于形成部门高效协同、全社会共同参与的青少年体质健康教育政策制定格局。在美国,联邦政府通过经济手段宏观干预《不让一个孩子掉队法》的实施,地方相关职能部门通过制定具体落实政策以获得较多的政府资金支持,这样联邦政府与地方职能部门就形成了高效的协调与配合机制。[18]在英国,青少年体质健康教育政策制定主体通过建立合作伙伴关系和创新角色定位(合作伙伴发展管理者、青少年体质健康教育协调员、联络教师等),形成工作网络,实现主体之间的有效合作。[19]由此可见,西方发达国家青少年体质健康教育政策的制定中,中央与地方、职能部门与职能部门、职能部门与社会组织之间能够建立起跨界、联动、高效的合作机制,共同促进青少年运动参与行为,增强青少年体质健康水平是政策制定的主要特色和亮点。这些成功的经验与做法是值得我们学习和借鉴的地方。
另外,要解决好青少年体质健康教育政策与其他教育政策的互适和协同发展问题。目前,该领域最为主要,也是迫切需要我们解决的一个问题是高考人才选拔政策与青少年体质健康教育政策之间存在隔阂。体育成绩在高考中得不到体现和重视,两种不同的价值诉求和利益导向造成政策间的不协调,在“高考政策指挥棒”下,必然导致体质健康教育政策的愿景偏离或异化。因此,做好政策体系规划,凸显政策的前瞻性,解决和处理好政策间的协同配合问题,消除彼此隔膜与相关掣肘,形成系统性的政策体系来引领青少年体质健康教育的良性发展尤为重要。
-
青少年体质健康教育政策的执行主体应明晰各自的权责关系,由教育和体育部门牵头,其他相关职能部门积极配合的组织构架下,构建联动执行机制,调动多方资源,充分发挥合力作用,形成科学的政策执行机制和格局。具体而言,在中央层面建立“青少年体质健康教育政策执行委员会”,统筹不同层级政府和部级相关职能部门之间的协作与配合,宏观调控青少年体质健康教育政策执行的治理工作。在地方政府层面设立多部门协同的“青少年体质健康教育政策执行联席会议”制度,主要负责青少年体质健康教育政策、文件和方案的细化落实与推进工作,建立高效的青少年体质健康教育政策跨界性合作执行机制,保障多元政策执行主体的参与和互动,最大限度降低因部门狭隘利益产生的不利影响,有效凝聚政策执行合力。上述两种纵向和横向政策执行制度的建立,不仅有利于划清各执行主体的职权与职责界限,而且有利于建立科学合理的政策执行评价与奖惩制度。
政策会随着行动者的意图和目的而不断变革,不可避免地在社会互动中产生变异,忠实实施仅存理论可能。[20]因此,建立科学合理的政策监督与问责机制是提高政策执行效力的关键环节。建立具有独立地位的政策监督机构,并赋予其对称的职权和职责,增强监督的有效性与权威性。同时,建立对青少年体质健康教育政策执行情况的常态化、制度化监督机制,形成“监督—反馈—执行—再监督”的政策良性运转闭路,有效杜绝政策执行中的怠慢、偏离、敷衍、抵制现象。另外,加大对政策执行主体的问责力度,不仅要对学校校长问责,更要对各级地方政府和相关职能部门党政一把手问责,通过“督学”、“督政”等手段,确保政策执行在良性的轨道上顺利运行。
-
青少年的广泛认同和支持,是落实青少年体质健康教育政策和开展青少年体质健康促进工作的前提条件。青少年若不能在内在心理上形成积极、稳定的体育文化认同与健身动机,就无法从根本上转变对体质健康教育的轻视和抵制。西方发达国家,多通过体育文化渗透和健康教育引导促进青少年的运动参与。20世纪初,法国在“身体运动创造体育价值”的文化理念下,有效促进了人们对体育的理解、认同和热爱,使体育生活化的价值观念深入人心。[21]2012年,英国颁布实施的“让运动成为生活习惯”的教育政策,非常注重体育健身文化的打造,该政策不仅有力促进了青少年体育的快速发展,而且有效提升了青少年对体育价值的认同度和运动参与的热爱度。[22]西方发达国家的成功经验告诉我们,要改变青少年体质健康教育的被动局面和切实提高政策效果的根本途径是提升青少年的体育文化认同度。具体而言,通过加强健康教育政策的体育文化建设,提升政策的体育文化溢出效应,营造浓郁的体育健身文化氛围,使青少年在内部心理上产生体育文化认同,形成体育价值需求,进而萌发运动参与动机,最终形成体育健身的核心内驱力。在该体育文化内驱力量的推动下,促成青少年运动参与行为的发生,同时青少年在运动实践中通过亲身的体验与感悟会形成更高层次的体育文化认同。这一过程是一个循环往复、渐进量变到跃迁质变的演进过程,最终实现青少年体质健康教育政策实施效果的递增与叠加。
一. 加强政策制定主体之间的沟通与协作,优化政策体系
二. 健全政策执行机制,完善政策监督机制
三. 提升政策的文化溢出效应,提高青少年的体育文化认同度
-
青少年体质健康教育政策的演进和执行过程是一项复杂而艰巨的系统工程。近30年以来,我国针对青少年体质健康问题出台的一系列健康教育促进政策,取得了一定的成效,但同时也出现了令人尴尬的“阿喀琉斯之踵”。因此,今后青少年体质健康教育政策的发展,应在积极汲取和借鉴国内外先进做法和成功经验的基础上,进行青少年体质健康教育政策的优化与提升。其优化的现实路径是加强政策制定主体之间的沟通与协作,优化政策体系;关键路径是健全政策执行机制,完善政策监督机制;根本路径是提升政策的文化溢出效应,提高青少年的体育文化认同度。唯有如此,才能进一步做好青少年体质健康教育工作,从根本上扭转青少年体质羸弱的被动局面。



 下载:
下载: