-
半夏Pinellia ternatat (Thunb.) Breit属于天南星科半夏属,块茎可入药,具有燥湿化痰,降逆止呕,消痞散结的功效[1].但是药用植物的药用成分含量低一直是困扰人们的一大难题,而添加外源物质是解决这一问题的有效途径.外源物质包括营养元素、渗透调节物质、前体物、植物生长调节剂、诱导子、信号分子等[2],添加前体物和诱导子是目前提高有效成分常用且有效的方法[3].诱导子是一种能引起植物过敏反应的物质,其与植物相互作用时能选择性、快速、高度专一地诱导植物特定基因的表达,从而积累特定的次生代谢产物[4]. NO不仅参与植物种子萌发、叶片伸展、根系生长、器官衰老等多种代谢过程[5-9],还可诱导植物次生代谢产物的合成[10]. ASA作为水杨酸(SA)的衍生物正逐渐被人们重视.张秀省等[11]研究发现,2 mg/L ASA处理长春花植株显著提高了长春花中长春质碱、总生物碱、长春碱的含量.前体物是指某一代谢中间体前一段的物质,添加前体物质会影响植物组织和细胞生长及次生代谢产物的合成[3]. Phe,Asp作为植物代谢中重要的氨基酸常被用于提高植物次生代谢产物的合成,李琰[12]在雷公藤的培养基中添加天冬氨酸、酪氨酸、精氨酸、丝氨酸、苯丙氨酸、蛋氨酸和半胱氨酸,发现均能不同程度地促进内酯醇的合成.
目前的研究主要集中在半夏再生体系的建立及外源物质对其生理生长的影响,而外源物质对其次生代谢产物、氮代谢过程的影响及两者之间的关系却鲜有报道.因此,研究外源物质对半夏有效成分含量与氮代谢关键酶活性的关系具有重要意义.本研究以半夏愈伤组织为材料,通过添加适宜浓度的单一或两两复合外源物Phe,Asp,SNP,ASA于培养基中来研究外源物质对半夏愈伤组织中氮代谢相关酶及有效成分的影响,以期从氮代谢方面探讨外源物质对半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷的调控机理,为提高半夏愈伤组织中有效成分含量提供参考.
全文HTML
-
以半夏幼嫩叶柄为外植体,0.1% HgCl2消毒10 min后用无菌水冲洗数遍,然后切成约0.5 cm的小段于愈伤组织诱导培养基(MS+0.5 mg/L 2,4-D+1.5 mg/L KT+1.0 mg/L IAA,3.0%蔗糖,0.7%琼脂,pH=5.8) 中.诱导出愈伤组织后每30 d于继代培养基(MS+2.0 mg/L 2,4-D+1.0 mg/L KT+1.0 mg/L IAA,3.0蔗糖,0.7%琼脂,pH=5.8) 中继代1次,继而作为实验材料.
根据预实验于继代培养基中添加不同质量浓度及组合的外源物质,分别为0 mg/L (CK),50 mg/L Phe(T1),150 mg/L Asp(T2),1 mg/L SNP(T3),1 mg/LASA(T4),50 mg/L Phe+150 mg/L Asp(T5),50 mg/L Phe+1 mg/L ASA(T6),150 mg/L Asp+1 mg/L ASA(T7),1 mg/L SNP+1 mg/L ASA(T8),50 mg/L Phe+1 mg/L SNP(T9),1 mg/L SNP+150 mg/L Asp(T10). 30 d后测定各项指标,3次重复.
-
GOGAT,GDH酶液提取参照Zhao等[13]的方法,略有改动:精确称取半夏愈伤组织1 g后用8 mL 50 mmol/L的Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH=8.0) 冰浴研磨,随后4 ℃、10 000 r/min离心30 min,取上清,上清液即为酶提取液. GOGAT活性测定参照王小纯等[14]的方法,每分钟反应混合液减少1 μmol NADH为一个酶活单位. GDH活性测定参照Loulakis等[15]的方法,以每分钟于30 ℃下氧化或还原1 μmol的辅酶(NADH或NAD+)定义为一个酶活单位;GOT酶提取液的提取:精确称取半夏愈伤组织0.4 g后用2.0 mL 0.25 mol/ L的Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH=7.2) 冰浴研磨,然后4 ℃、10 000 r/min离心30 min,取上清,上清液则为酶提取液,酶活性测定参照吴良欢等[16]的方法,一个GOT活性单位定义为每克植物鲜样在1 h内生成丙酮酸的微摩尔数. PAL的活性测定参照孙健玲等[17]的文献,以每分钟0.01 OD值为一个酶活力单位(U).
-
采用李合生[18]的考马斯亮蓝G250比色法,以牛血清蛋白为标准品.
-
总生物碱测定方法参照于超等[19]的方法.
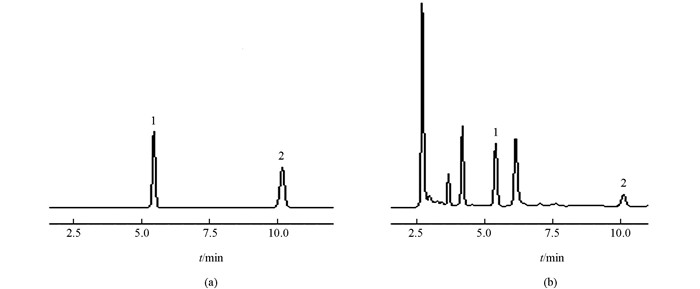
鸟苷、腺苷样品制备采用超声提取法:将半夏愈伤组织烘干至恒定质量后研碎过50目筛,精密称取0.3 g粉末加3 mL 30%甲醇后称质量,超声提取30 min后用30%甲醇补足至超声之前的质量,5 000 r/min离心10 min,取上清稀释3倍后经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后备用.含量测定采用HPLC法[20]:色谱条件为Xtimate C18色谱柱,流动相为甲醇:水=15:85,流速1.0 mL/min,检测波长254 nm,柱温30 ℃,进样量20 μL.
-
所有指标均重复测定3次,数据采用SPSS 11.5进行统计分析和方差检验,结果以平均值±标准误差表示.
1.1. 愈伤组织的诱导及处理
1.2. 测定方法
1.2.1. 氮代谢关键酶及PAL活性测定
1.2.2. 可溶性蛋白含量测定
1.2.3. 总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷含量测定
1.3. 数据处理
-
由图 2可知,与对照相比,单独(T1-T4) 添加时T1,T3,T4处理均可显著提高半夏愈伤组织中GOGAT的活性,提高幅度分别为57.1%,78.0%,62.7%.同时,T1-T4处理明显提高GDH,GOT的活性,其中T3,T4处理效果最佳,GDH的活性分别较对照提高了77.4%,68.2%,GOT的活性分别较对照增加42.4%,52.0%;复合(T5-T10) 添加时,T6,T7,T9处理可显著提高GOGAT的活性,而T8和T10处理却抑制了GOGAT的活性;T5-T9均显著提高了半夏愈伤组织中GDH和GOT的活性,其中T7处理效果最佳,GDH,GOT的活性分别较对照提高了87.4%,106.3%.
如图 2所示,与对照相比,T1-T4处理均能提高半夏愈伤组织中PAL的活性,其中T1,T3处理达到显著水平,分别较对照提高了26.9%,28.9%;T5-T10处理中,除T10处理抑制PAL活性外,其他各处理组均促进PAL活性的提高,其中T7处理与其他处理的差异均具有统计学意义,较对照增加了63.9%.
-
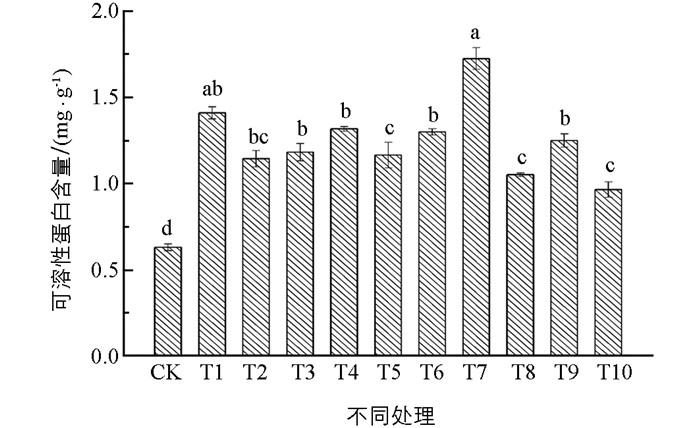
如图 3所示,在T1-T4处理中,与对照相比4种物质均可促进半夏愈伤组织中可溶性蛋白含量的积累且差异均具有统计学意义,其中T1处理效果最明显;在T5-T10处理中,与对照相比可溶性蛋白含量均有增加且差异具有统计学意义,其中T7处理效果最明显,比对照提高了107.9%;综合T1-T10处理组,最佳复合处理组(T7) 效果好于最优单独处理组(T1),但是两者之间差异不具有统计学意义.
-
如表 1所示,单独添加外源物(T1-T4) 均促进了半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的合成且与对照组的差异具有统计学意义,其中T1和T3处理效果最佳,分别提高了125.%和124.24%;T1,T2,T4处理均显著提高了鸟苷的含量,其中T4处理效果最佳,较对照提高了106.7%,而T3处理却降低了鸟苷含量;T1处理显著提高了腺苷的含量,提高幅度为85.7%.
两两复合添加时,T5-T9处理显著提高了半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱含量,其中T7处理时升高幅度最大,而T10处理却抑制了总生物碱的积累;T5,T7,T10处理对于鸟苷含量的提高均具有显著性,但T8处理抑制了鸟苷的积累;T5,T6处理可显著提高腺苷的积累,分别比对照升高了85.7%,128.6%,而T7,T8,T10处理降低了腺苷积累.
在单独处理时,T1处理对总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷的积累效果最好;复合处理时,T7处理对总生物碱含量和鸟苷含量提高幅度最大,T6处理对腺苷含量提高幅度最大,而T7对总生物碱含量和鸟苷含量的提高幅度大于T1,T6对腺苷含量提高幅度大于T1,所以复合处理效果更好.
2.1. 不同处理对半夏愈伤组织中氮代谢相关酶及PAL活性的影响
2.2. 不同处理对半夏愈伤组织中可溶性蛋白含量的影响
2.3. 不同处理对半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷含量的影响
-
植物细胞培养基中添加前体物是提高次生代谢产物产量的有效途径. Carrier等[21]用银杏细胞中棚皮素的前体物黄烷酮、苯丙氨酸饲喂银杏细胞后发现,前体物的添加可使有效成分的含量增加8~10倍.前体物氨基酸进入植物体内后,可通过转氨基作用、脱氨基作用加以同化[22]而被植物利用.在本实验中,适宜质量浓度的Phe和Asp均促进了半夏愈伤组织中氮代谢相关酶活性的提高及可溶性蛋白、总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷含量的积累.可能是因为Phe通过PAL的催化作用生成反式肉桂酸,而PAL作用释放的NH4+又经过同化过程[23],这一过程刺激了氮代谢过程中相关酶活性的增加.也有可能是因为氮代谢底物的增加导致氮代谢相关酶活性的增加[24],从而加速了氮代谢的效率.氮代谢期间合成的天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸及肉桂酸为半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的合成提供了大量底物.同时Phe和Asp本身就是半夏有效成分合成的底物,底物的增多也会大大提高有效成分合成的效率.
-
诱导子除了通过诱导次生代谢关键酶的基因表达提高其活性,还通过调节氮代谢中某些酶的活性为次生代谢产物的生成提供能量和前体,如张少颖等[25]发现SNP浸种能促进玉米幼苗叶片NR活性的提高.本研究发现,向培养基中添加外源NO的供体SNP后,半夏愈伤组织体内GOGAT,GDH,GOT等酶活性显著高于对照,可能是外源NO提高了植物细胞中NR的活性[26],将植物吸收的NO3-还原成NH4+,NH4+的增多促使GOGAT,GDH,GOT等活性增强,加速无机氮向有机氮的同化及转化.由此推断,SNP可能通过提高植物氮代谢相关酶活性来提高半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的含量.但SNP的添加却抑制了鸟苷及腺苷的合成,可能是因为SNP对其合成过程中其他途径的关键酶产生了抑制作用,这还有待于研究.
ASA是SA的衍生物,在植物体内可调节多种生理过程[27-28].有研究表明,外源物质ASA可提高植物体内SA水平,并通过SA的生理效应实现其生理功能[29]. SA能激活磷脂酶催化质膜磷酸水解产生第二信使或增加次生代谢合成途径中参与次生代谢物合成酶的活性[30].本研究发现,添加适宜质量浓度的ASA提高了半夏愈伤组织细胞中GOGAT,GDH,GOT的活性,可能是因为SA促进了NR活性的提高[31],使细胞快速将NO3-转化为NH4+,然后通过GS/OGAT循环有效固定NH4+,为合成前体物质Phe提供氨基.也有可能是SA同时提高了NR和GS活性以及转氨酶的活性[32],从而加速了无机氮的吸收、同化及转运、合成游离氨基酸及可溶性蛋白,并产生能量. ASA的添加提高了半夏愈伤组织中PAL的活性,可能诱导了PAL酶基因活性的表达,提高了PAL的数量及活性[33].研究发现,添加诱导子ASA后,GOGAT,GDH,GOT,PAL酶活性与总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷含量呈一定的正相关,猜测ASA可能通过提高氮代谢及次生代谢相关酶的活性,直接或间接提供半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷合成所需的底物及能量来提高半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷的含量.
-
两种或多种能提高次生代谢物产率的条件联合作用会对次生代谢物产量的提高发挥协同或加和作用.曲均革等[34]探索前体物苯丙氨酸和诱导子茉莉酸甲酯及光照等因素联合作用下对葡萄细胞产生花青素的影响,得出结论是几种因素协同作用使鲜细胞花青素含量提高2.7倍,产量提高3.4倍,比单独加入时效果显著得多.本研究发现,复合添加与单独添加相比,不同复合组合添加对氮代谢相关酶活性及有效成分积累的影响效果不同,有的甚至出现了抑制现象.比如SNP与ASA、Asp组合,可能是因为质量浓度不合适或者没有协同作用,也可能是加入的时间不合适,这些都有待于进一步研究.而ASA与Asp、phe组合却能显著提高氮代谢相关酶活性及有效成分含量,且与单独添加相比差异具有统计学意义.可能是因为前体物的加入为半夏细胞氮代谢及次生代谢提供了底物,而诱导子进一步提高了GOGAT,GDH,GOT等氮代谢酶及PAL酶活性,加速了无机氮的同化及转化,为半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷积累提供了更多的底物及能量.
综合所有处理可以看出,单一处理对氮代谢关键酶、有效成分含量及两者之间的关系影响较为清楚,氮代谢关键酶的变化与有效成分的含量呈正相关.但对于复合添加,两者之间的关系较为复杂,氮代谢关键酶活性的变化与有效成分含量的变化无明显线性相关,这可能是因为复合添加对外援物质加入的质量浓度及时间要求不同,这些都有待于进一步研究.
本研究结果表明,适宜质量浓度的SNP,ASA,Phe,Asp单一或两两复合添加调控半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷合成与其体内氮代谢有关.一方面调节GOGAT,GDH和GOT的活性,通过提高GOGAT,GDH等酶的活性促进无机氮向有机氮转化,提高GOT的活性促进谷氨酸转移为其他氨基酸,进而合成蛋白质和其他含氮类化合物,为总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷合成提供底物及能量;另一方面通过提高PAL活性,加速苯丙烷类物质代谢,促进总生物碱的合成.单独添加时,添加phe对氮代谢相关酶活性的提高及有效成分含量的积累效果最好;复合添加1 mg/L ASA和150 mg/L Asp诱导GOGAT,GDH,GOT,PAL的活性提高和可溶性蛋白含量的增加效果最好,此时半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷含量最高.



 下载:
下载: