-
半夏 Pinellia ternata 为天南星科半夏属多年生宿根草本植物, 块茎可入药, 是一味传统的中药材.其性温、味辛[1-2].生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷是其主要有效成分, 药理作用强, 具有镇咳祛痰、健脾胃、止呕吐、降压降脂、抗心律失常、抗坏血栓及抗肿瘤等功效[3-6].通过植物组织培养技术对半夏进行组织培养来生产有效成分, 而添加特定的外源物质来提高植物体内次生代谢物是目前提高植物次生代谢物的有效办法[7-12].本文以三叶半夏愈伤组织为材料, 用不同质量浓度诱导子硝普钠(SNP), 乙酰水杨酸(ASA)和前体物苯丙氨酸(Phe), 天冬氨酸(Asp)来诱导半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的合成, 筛选出促进半夏愈伤组织次生代谢物积累的外源添加物及最适质量浓度, 为半夏的工业化生产提供参考.
全文HTML
-
半夏愈伤组织由本实验室以三叶半夏叶柄为外植体诱导而来, 选取继代4次生长均一的稳定体系.培养条件为MS+2.0 mg/L 2, 4-D+1.0 mg/L KT+1.0 mg/L IAA+ 3.0%蔗糖+ 0.7%琼脂, pH值为5.8~6.0(灭菌前), 温度(25±1) ℃, 暗培养, 培养周期为30 d.
-
前体物为Phe和Asp, 添加的质量浓度梯度分别为0 mg/L, 25 mg/L, 50 mg/L, 100 mg/L, 150 mg/L; 诱导子SNP添加的质量浓度梯度为0 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L, 0.5 mg/L, 1 mg/L, 5 mg/L; 诱导子ASA添加的质量浓度梯度为0 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L, 0.5 mg/L, 1 mg/L, 3 mg/L.
将半夏愈伤组织接种于添加有诱导子的固体培养基, 并立即置于培养箱中暗处理30 d.对照为不添加任何诱导子.
-
将培养30 d的愈伤组织取出, 洗去培养基后用吸水纸吸干水分, 放于天平上称鲜质量, 计算半夏愈伤组织的相对生长速率.
R=(m2-m1)/m1×100
式中:R为相对生长率; m1为接种鲜质量(g); m2为收获鲜质量(g).
-
取出培养30 d后的各处理组半夏愈伤组织, 用水洗净培养基后放入烘箱中先于80 ℃烘2 h, 之后于60 ℃下烘干, 磨碎后过60目筛, 其粉末用于生物碱测定.测定方法参照于超等[13]的紫外分光光度计法.
-
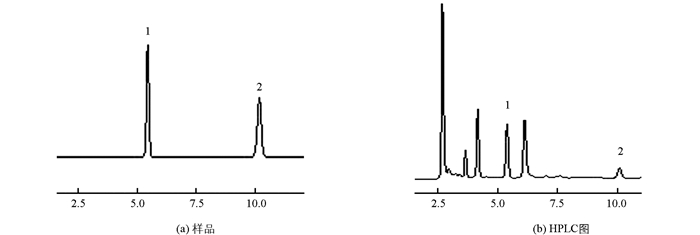
色谱条件:参照张敏等[14]的文献略有改动, Xtimate C18色谱柱(4.60 mm×250 mm, 5 μm), 流动相为甲醇:水=15:85, 流速为1.0 mL/min, 检测波长为254 nm, 柱温30 ℃, 进样量20 μL.鸟苷和腺苷的色谱峰分离良好, 鸟苷保留时间约为5.5 min, 腺苷保留时间约为10 min.
样品制备:将半夏愈伤组织烘干至恒质量, 研碎过60目筛, 取各处理组样品粉沫0.3 g加入30%甲醇3 mL后称质量, 超声提取30 min, 用30%甲醇补足质量后于离心机5 000 r/min离心10 min, 提取上清液再稀释3倍, 过0.22 μm微孔滤膜后进样.
鸟苷、腺苷标准品及样品色谱图见图 1.
数据均采用SPSS 11.5进行统计分析.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 添加前体和诱导子试验设计
1.2.2. 半夏愈伤组织生长测定
1.2.3. 总生物碱含量测定
1.2.4. 鸟苷、腺苷的测定
-
不同质量浓度的Phe对半夏愈伤组织的生长均有抑制作用.当Phe质量浓度为25 mg/L和50 mg/L时, 半夏愈伤组织相对生长速率分别比对照降低22.8%和7.9%, 但是与对照差异不显著, 高质量浓度Phe则显著抑制其生长.
Phe在0 mg/L~150 mg/L质量浓度范围内, 总生物碱含量呈先增加后降低的趋势, 其中50 mg/L时达到最大, 比对照增加了99%, 其后随着Phe质量浓度的升高而下降.
鸟苷在Phe质量浓度为0 mg/L~50 mg/L时逐渐升高, 50 mg/L时达到最大, 在半夏体内鸟苷百分比为0.041%, 其后逐渐降低, 在150 mg/L时最小, 比对照降低了46.7%, 说明低质量浓度Phe促进鸟苷的合成, 而高质量浓度Phe会抑制鸟苷的积累.
在Phe质量浓度为0 mg/L~100 mg/L范围内, 均促进半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的积累, 其中50 mg/L时效果最显著, 与对照相比增幅为112.5%, 呈显著性差异, 当Phe质量浓度为150 mg/L时, 则抑制了腺苷的积累(表 1).
-
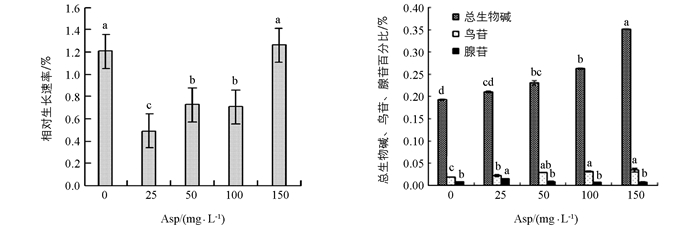
在0 mg/L~100 mg/L范围内的Asp均抑制半夏愈伤组织生长, 且随着质量浓度升高, 其抑制作用逐渐减弱, 在Asp质量浓度为150 mg/L时, 反而促进了半夏愈伤组织生物量的增加, 但与对照差异不显著.
不同质量浓度Asp的加入均有利于半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的积累, 与对照相比分别提高了9.9%, 23.4%, 36.5%, 82.8%.
在培养基中添加质量浓度为0 mg/L~150 mg/L的Asp后, 半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷百分比提高, 且呈逐渐上升趋势, 其中添加150 mg/L Asp使鸟苷达到最大值, 与对照相比增加了90%.
在0 mg/L~25 mg/L Asp范围内, 半夏愈伤组织体内腺苷迅速增加, 当质量浓度为25 mg/L时达到最大值, 比对照提高了87.5%, 25 mg/L~150 mg/L范围内的Asp抑制其体内腺苷的合成, 分别比对照降低了25%, 12.5%, 但是差异不显著.
-
在试验质量浓度范围内, SNP的添加均有利于半夏愈伤组织的生长, 且随着质量浓度的增加, 其相对生长速率逐渐增大, 当SNP质量浓度为5 mg/L时, 与对照相比增幅为173.5%, 呈极显著差异.
不同质量浓度SNP的加入, 均促进了半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的积累, 整体呈先上升后下降的趋势, 其中SNP质量浓度为1 mg/L时达到最大值, 比对照增加了92.7%.
SNP对半夏细胞内鸟苷的积累为低质量浓度时促进, 高质量浓度时抑制.在0 mg/L~0.1 mg/L质量浓度范围内, 半夏细胞内鸟苷百分比增加, 且SNP质量浓度在0.1 mg/L时达到最大, 比对照增加了10%, 其后随着培养基中SNP质量浓度升高, 半夏细胞内鸟苷的合成开始受到抑制, 且质量浓度越大抑制作用越强.
不同质量浓度SNP的添加均抑制半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的积累(表 2).
-
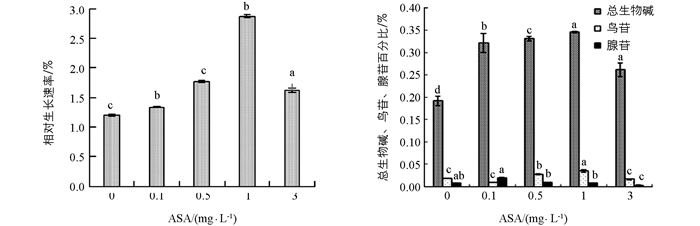
添加不同质量浓度的ASA于半夏愈伤组织培养基中均可促进半夏愈伤组织生长, 但随着ASA质量浓度的升高, 其相对生长速率呈先增加后降低的趋势, 分别比对照增加了10.4%, 46.7%, 138.4%, 34.7%.
对于总生物碱, 当ASA质量浓度为0 mg/L~1 mg/L时, 总生物碱的合成量逐渐增加, 在1 mg/L时达到最大, 与对照相比增幅为80.2%.随后开始下降, 但在ASA质量浓度为3 mg/L时, 仍高于对照组.
当ASA质量浓度较低时促进半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷的积累, 质量浓度较高时则抑制鸟苷的合成, 其中ASA质量浓度为1 mg/L时合成量最高, 比对照增加了93.3%.
ASA对半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的影响与鸟苷类似, 在ASA质量浓度低时促进, 质量浓度高时抑制.在0 mg/L~0.1 mg/L时, 半夏愈伤组织腺苷合成量增加, 在0.1 mg/L时最高, 比对照增加了150%, 但当ASA质量浓度高于0.1 mg/L后, 腺苷含量迅速降低, 当ASA质量浓度为3 mg/L时, 半夏愈伤组织中腺苷比对照降低了62.5%(图 3).
2.1. Phe对半夏愈伤组织生长及体内总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的影响
2.2. Asp对半夏愈伤组织生长及体内总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的影响
2.3. SNP对半夏愈伤组织生长及体内总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的影响
2.4. ASA对半夏愈伤组织生长及体内总生物碱、鸟苷及腺苷的影响
-
生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷是半夏的主要有效成分.Phe作为一种体内必需的氨基酸及前体物质, 可能通过多种代谢通路直接或间接地调控了半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷的合成, Asp是腺苷的直接前体物质[15-19].本研究结果表明, 低质量浓度的Phe促进半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷的合成, 其中50 mg/L Phe效果最好, 较高Phe质量浓度的添加则抑制其总生物碱、鸟苷和腺苷的积累.低质量浓度Asp的添加有利于半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的积累, 高质量浓度时则抑制腺苷的合成.
一氧化氮(NO)是一种新型的植物信号分子, 目前已证实是参与植物细胞次生代谢产物合成调控的必需信号分子之一[20].本研究发现, 试验质量浓度范围内的SNP均可促进半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的积累, 其中SNP为1 mg/L时效果最明显; SNP对半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷的积累具有低质量浓度时促进, 高质量浓度时抑制的现象; 不同质量浓度SNP均抑制半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的积累, 说明外源NO参与了半夏愈伤组织次生代谢的调控.
ASA在植物体内具有提高植物抗性, 改善果实口感, 提高果实品质等多方面的功能[21-22], 近年来亦被用于植物次生代谢的调控.在本试验中, 不同质量浓度的ASA对半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱均有促进作用, 以1 mg/L ASA对其促进效果最明显, 为对照的180.2%.半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷和腺苷的合成均表现为低质量浓度ASA时被促进, 而高质量浓度ASA时被抑制, 其中鸟苷在1 mg/L ASA时达到最大, 腺苷在0.1 mg/L ASA时处于峰值, 说明了ASA有利于半夏中总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷的合成, 但是诱导不同次生代谢物合成所需的ASA质量浓度不同.
在试验质量浓度范围内, 前体物Phe, Asp的添加均抑制半夏愈伤组织生长, 而诱导子SNP, ASA的添加促进半夏愈伤组织的生长; Phe在低质量浓度时促进半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的积累, 高质量浓度时则抑制其合成, 不同质量浓度的Asp, SNP, ASA添加均可促进半夏愈伤组织中总生物碱的积累; 低质量浓度Phe和ASA的添加可促进半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷的合成, 而高质量浓度Phe和ASA的添加则会抑制鸟苷的积累, 不同质量浓度Asp, ASA对半夏愈伤组织中鸟苷的合成均起促进作用; 除不同质量浓度SNP的添加抑制半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的积累外, Phe, Asp, ASA对半夏愈伤组织中腺苷的合成均具有低质量浓度时促进, 高质量浓度时抑制的现象.说明不同外源添加物对半夏愈伤组织生长及总生物碱、鸟苷、腺苷的作用效果与添加物的种类质量浓度有关.



 下载:
下载: