-
犬弓首蛔虫病是由弓首科(Toxocaridae)弓首属(Toxocara)的犬弓首蛔虫(T. canis)寄生于犬及犬科动物的小肠而引起的一种人兽共患寄生虫病,动物通过摄入其感染性虫卵或幼虫而感染.当人体感染时,幼虫通常在人体内不能发育为成虫,而是移行到各个器官和组织中[1],引起内脏幼虫移行症(visceral larva migrans,VLM)、眼睛幼虫移行症(ocular larva migrans,OLM)、神经弓首蛔虫病(neurological toxocariasis,NT)和隐性弓首蛔虫病(covert toxocariasis,CT)等[2],造成组织和器官损害,严重影响人类健康.
腺苷三磷酸结合盒转运蛋白(ATP-Binding Cassette transporters,ABC转运蛋白)是以ATP为驱动能的一类跨膜糖蛋白,负责转运内源性和异源性的生物大分子及小分子化合物,包括糖、氨基酸、多肽、细胞代谢产物、金属离子和药物等[3]. ABC转运蛋白在维持渗透压稳定、营养吸收、多药耐药、抗原加工、细胞分裂、孢子形成、繁殖等[4-6]诸多生物学过程中发挥重要作用.
已报道的寄生虫ABC转运蛋白基因有65种[7],对其功能的研究主要集中在ABC转运蛋白的耐药性方面[8],尽管已经对蠕虫ABC转运蛋白的功能和分子特征进行了研究,但是对犬弓首蛔虫ABC转运蛋白的研究还未见报道.本研究拟对犬弓首蛔虫ABC转运蛋白全长基因(Tc-abcg-5)进行克隆及序列分析,以期为ABCG5转运蛋白的功能研究奠定基础.
全文HTML
-
T. canis采自西南大学荣昌校区动物医院患病犬,经形态学鉴定后用液氮速冻并保存.
Taq DNA聚合酶、pMD19-T(simple)Vector、PrimeScriptTM反转录试剂盒购自TaKaRa公司;EasyPure©胶回收试剂盒、DH5α购自TransGen Biotech公司;Trizol试剂购自Invitrogen公司.
-
根据T.canis基因组数据(GenBank:KHN79547),用Primer Premier(Version5.0)软件设计引物,引物由南京金斯瑞生物科技有限公司合成,序列如表 1所示.
-
采用Trizol试剂提取T. canis成虫的总RNA.采用核酸蛋白检测仪检测总RNA的浓度和纯度.以提取的T. canis总RNA为模板,按反转录试剂盒说明合成cDNA.
-
以合成的T. canis cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增.扩增体系为25 μL:10×PCR buffer(不含Mg2+)2.0 μL、Mg2+(25 mmol/L)2.5 μL、dNTPs(2.5 mmol/L)2.0 μL、上游引物(10 μmol/L)0.5 μL、下游引物(10 μmol/L)0.5 μL、cDNA 1.0 μL、rTaq酶0.5 μL、dd H2O 16.0 μL. PCR反应条件为94 ℃预变性3 min,94 ℃变性30 s,52 ℃复性30 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35个循环;最后72 ℃延伸5 min.扩增产物经1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并按DNA胶回收试剂盒说明回收目的PCR产物.
-
将回收的目的PCR产物与pMD19-T(simple)Vector载体连接,将上述连接产物转化至DH5α感受态细胞,涂布于含Amp+(100 mg/mL),X-Gal(20 mg/mL)和IPTG(24 mg/mL)的LB琼脂平板中,置恒温箱37 ℃培养12~14 h.
-
将经菌液PCR鉴定为阳性的重组菌液送南京金斯瑞生物科技有限公司测序.将测得的序列利用DNAStar 5.0等软件,分别从核酸和氨基酸水平对该基因进行生物学分析.利用SMART和InterProScan(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)预测功能结构域.应用MUSCLE,Clustal Omega和MAFFT软件进行多重序列比对,用MEGA 5.0软件中的邻接法(Neighbour-joining,NJ法)[9]构建系统进化树,进化树的可靠性用Bootstrap进行分析,共1 000个重复.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 引物的设计与合成
1.2.2. 总RNA的提取与cDNA的合成
1.2.3. Tc-abcg-5基因的PCR扩增
1.2.4. Tc-abcg-5基因的克隆
1.2.5. 测序及序列分析
-
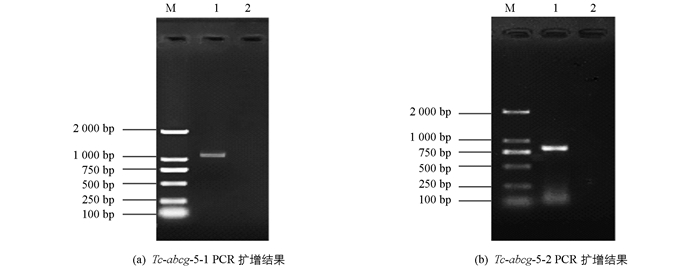
扩增产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,Tc-abcg-5-1在约1 100 bp处可见相应条带,Tc-abcg-5-2在约900 bp处可见相应条带,与理论大小相符;阴性对照没有条带出现(图 1).
-
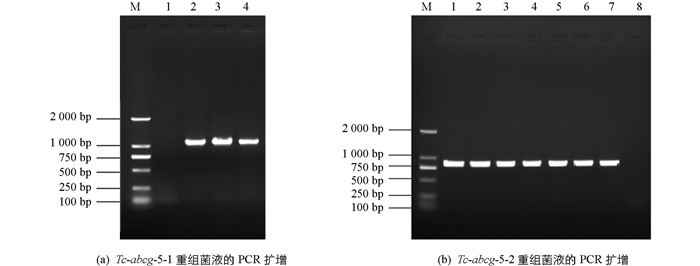
阳性克隆的重组菌液经PCR扩增后进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测.结果显示Tc-abcg-5-1在约1 100 bp处有特异目的条带,Tc-abcg-5-2在约900 bp处有特异目的条带;阴性对照没有条带出现(图 2).
-
将经过菌液PCR鉴定为阳性的重组菌液送至南京金斯瑞生物科技有限公司进行序列测定,结果显示Tc-abcg-5基因的完整编码区序列为1 902 bp,编码633个氨基酸,命名为TcABCG5蛋白.利用SMART对TcABCG5蛋白的功能结构域分析发现,ABCG5蛋白包含1个ABC转运蛋白结构域(第43-188位)和6个跨膜区(分别位于第350-372位,第387-409位,第422-453位,第468-490位,第497-514位,第600-622位)(图 3),同时还发现该蛋白含有高度保守的Walker A模体(特征氨基酸序列为GxxxxGK[S/T],x代表任意氨基酸)和Walker B模体(特征氨基酸序列为hhhh[D/E],h表示任意疏水性氨基酸残基)(图 3). GO注释显示ABCG5具有ATP结合(GO:0005524)和ATP酶活性(GO:0016887).
-
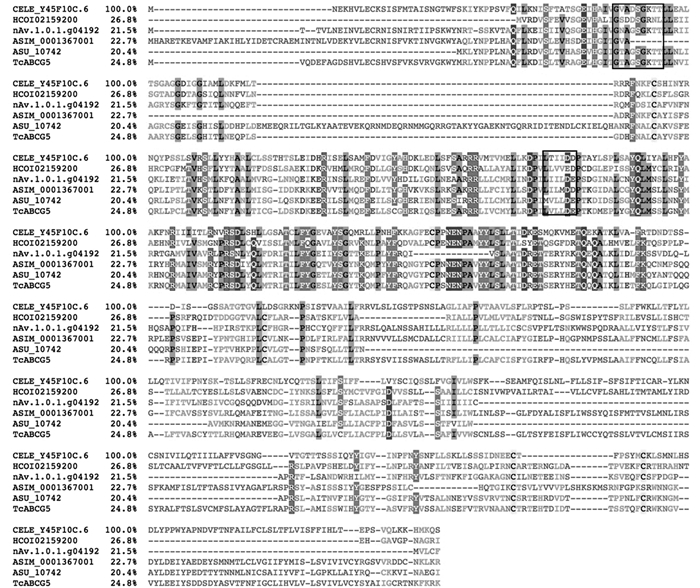
通过文献[10]检索,将TcABCG5蛋白氨基酸序列与5个线虫的ABCG5蛋白氨基酸序列进行多重序列比对,这些序列分别是秀丽隐杆线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans;序列号:Y45F10C.6)、捻转血矛线虫(Haemonchus contortus;序列号:HCOI02159200)、魏氏棘唇线虫(Acanthocheilonema viteae;序列号:nAv.1.0.1.g04192)、单一异尖线虫(Anisakis simplex;序列号:ASIM0001367001)和猪蛔虫(Ascaris suum;序列号:ASU10742).结果发现,TcABCG5的Walker A和Walker B模体与这5个线虫的Walker A和Walker B模体高度保守(图 4).
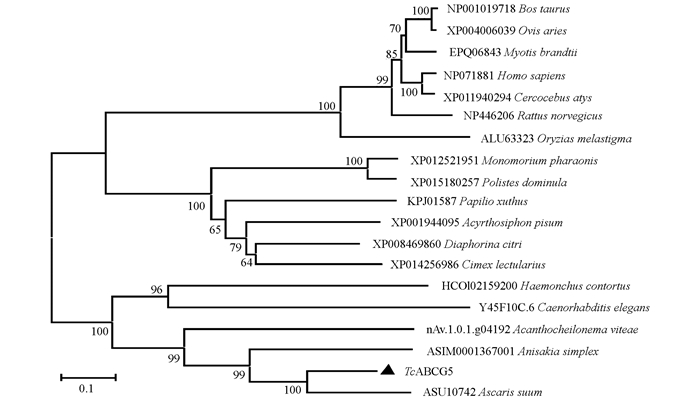
将Tc-abcg-5编码的氨基酸序列与WormBase ParaSite和GenBank中收录的秀丽隐杆线虫(C. elegans;序列号:Y45F10C.6)、捻转血矛线虫(H. contortus;序列号:HCOI02159200)、魏氏棘唇线虫(A. viteae;序列号:nAv.1.0.1.g04192)、单一异尖线虫(A. simplex;序列号:ASIM0001367001)、猪蛔虫(A. suum;序列号:ASU10742)、人(Homo sapiens;GenBank No. NP071881)、褐家鼠(Rattus norvegicus;GenBank No. NP446206)、牛(Bos taurus;GenBank No. NP001019718)、绵羊(Ovis aries;GenBank No. XP004006039)、布氏鼠耳蝠(Myotis brandtii;GenBank No. EPQ06843)、白眉猴(Cercocebus atys;GenBank No. XP011940294)、黑点青鳉(Oryzias melastigma;GenBank No. ALU63323)、柑橘木虱(Diaphorina citri;GenBank No. XP008469860)、柑橘凤蝶(Papilio xuthus;GenBank No. KPJ01587)、豌豆蚜(Acyrthosiphon pisum;GenBank No. XP001944095)、温带臭虫(Cimex lectularius;GenBank No. XP014256986)、法老蚁(Monomorium pharaonis;GenBank No. XP012521951)和造纸胡峰(Polistes dominula;GenBank No. XP015180257)进行多重序列比对后构建进化树.结果显示TcABCG5与猪蛔虫(序列号:ASU10742)的ABCG5位于同一分支,其进化关系较近,与哺乳动物(牛、绵羊、布氏鼠耳蝠、人、白眉猴和褐家鼠)的进化关系较远(图 5).
2.1. PCR扩增结果
2.2. 重组质粒的菌液PCR鉴定
2.3. 测序结果及分析
2.4. 多重序列比对及种系发育进化树分析
-
典型的ABC转运蛋白结构包含高度疏水的跨膜结构域(transmembrane domains,TMD)和核苷酸结合域(nucleotide-binding domains,NBD)两部分.根据这2个结构域数目的不同,ABC转运蛋白又分为全转运子或半转运子.全转运子的核心结构通常由4个结构域组成,包括2个核苷酸结合域和2个跨膜结构域[11],而半转运子只含有1个核苷酸结合域和1个跨膜结构域.本研究发现TcABCG5为半转运子,其2个亚基的排列顺序为NBD-TMD. NBD由高度保守的Walker A和Walker B组成,其具有结合和水解ATP的作用[12].而TMD通常由6个α螺旋构成[13],它们形成1个跨膜通道以实现底物分子的跨膜运输,同时还参与底物的识别过程[14].从这些保守的结构域推测TcABCG蛋白同样具有转运底物的功能.
ABC转运蛋白在原核和真核生物中高度保守,根据ABC转运蛋白保守区序列的同源性,将其分为8个亚型(ABCA-ABCH)[15].研究发现存在于人类基因组中的ABC转运蛋白成员有48个[16];在拟南芥基因组中有129个ABC转运蛋白基因,而在水稻基因组中只有128个[17];存在于寄生虫中的ABC转运蛋白有65种;在原生动物嗜热四膜虫中鉴定出了165个ABC转运蛋白基因;在大肠杆菌基因组中至少发现有100个ABC转运蛋白基因,而白念珠菌只有28个;在酵母菌中有31个ABC转运蛋白基因. ABC转运蛋白主要负责转运各种生物大分子及小分子化合物,广泛参与生物生命活动中的许多过程.
ABC转运蛋白在代谢调节、维持渗透压稳定、多药耐药和繁殖等各种生物学过程中发挥着重要作用.在哺乳动物中,ABCB1参与保护细胞免受有毒物质的侵害;ABCG2除了在维持细胞自身稳定及机体正常生理功能等方面起着重要的作用外,还参与肿瘤干细胞多药抗性的形成[18].植物ABC转运蛋白参与植物体内激素、脂质、金属离子、次生代谢物和外源物质的运输,同时还参与植物体内离子通道的调控[19].在微生物中,ABC转运蛋白主要参与细菌耐药性的产生和次生代谢产物积累.而在寄生虫ABC转运蛋白的研究中,除了发现ABC转运蛋白在耐药性方面有重要作用外,还发现ABC转运蛋白在孢子形成和繁殖等生物学过程中发挥重要作用. Tran等[20]在对恶性疟原虫的研究中发现ABC转运蛋白G家族与恶性疟原虫雌性配子体的生殖过程有关;Kusel等[21]发现ABC转运蛋白在血吸虫的虫卵产生、代谢调节、药物和其他有毒物质的排泄、以及与宿主的相互作用中发挥重要作用.而TcABCG5在T. canis的生长、发育、繁殖等生物学过程中是否也具有同样的生理功能,有待后续进一步的试验研究.



 下载:
下载: