-
不可压缩流体是流体力学中的一个重要问题,广泛用于天气、海洋以及血液循环等方面. Navier-Stokes方程正好为描述这种流体运动规律提供了一种数学模型.近几十年来,很多作者研究了Navier-Stokes方程的有限元解法[1-3].本文考虑的是非定常Navier-Stokes方程的有限元算子分裂算法.算子分裂方法主要思想是在时间上分为若干步,使得不同的算子出现在不同的方程中,从而降低难度.该方法最开始由文献[2-3]提出,已经用于空间离散、有限差分和谱方法中.文献[4]给出的算子分裂方法是将非线性项和不可压缩性项分开处理.本文在文献[4]的基础上给出稳定化的有限元算子分裂算法,该方法主要分为两步:第一步是线性椭圆型问题,可看作是线性化的Burger's问题;第二步是一般的Stokes问题.通过理论推导,给出了速度的误差估计和收敛精度,并用数值实验验证了方法的正确性.相比标准的有限元方法,我们的方法得到的误差估计更小.
全文HTML
-
考虑下面的Navier-Stokes方程:
其中:Ω是在
$ \mathbb{R}^2$ 上具有利普希茨连续边界的有界区域,u(x,t)∈$ \mathbb{R}$ d表示速度矢量,p(x,t)∈$ \mathbb{R}$ 是压力,f(x,t)是流体驱动的体积力,ν>0为流体粘性系数, u0是使得∇·u=0的初始速度,并且${\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}_t} = \frac{{\partial u}}{{\partial t}} $ .对于上面给出的Navier-Stokes方程,我们引入下面的希尔伯特空间:
其中:(·,·)表示空间L2(Ω)2或L2(Ω)的标准内积,(∇u,∇u)和‖∇u‖0为空间V的一般标量和范数.在这篇文章中,我们用字母C表示一个与时间步长和网格参数无关的正数.
设u和p满足下面的条件:
(R1) u∈C0(0,T;H)∩L∞(0,T;H2(Ω)),∇p∈L∞(0,T;L2(Ω)).
(R2a) ut∈L2(0,T;L2(Ω)).
(R2b) ut∈L2(0,T;H01(Ω)).
(R3) ∫0T t‖utt(t)‖-12dt≤C.
(R4) ∫0T‖utt(t)‖V′2dt≤C.
定义三线性项c(·,·,·)为c(u,v,w)=((u·∇)v,w),∀u∈H1(Ω),v∈H1(Ω),w∈H01(Ω),它有如下的性质:
并且定义:
-
步骤一 寻找解
${\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}} $ 使得步骤二 根据(5)式解得的
${\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}} $ 求解un+1和pn+1使得其中δt是时间步长,满足0<δt<1,tn=nδt,n=0,1,…,N-1,和
$ N = \left[ {\frac{T}{{\delta t}}} \right]$ . -
对于方程(5)-(9)的有限元离散,我们假设Tμ={K}(μ=h)是准均匀的三角形网格剖分并且网格尺寸0<μ<1.定义数值格式中出现的亚格子模型为:
其中α>0是稳定化参数,根据算子Πh的定义,下列关系式成立:
我们定义R0={v∈L2(Ω):v|K∈P0,∀K∈Tμ(Ω)},Lμ=R02×2,L=L2(Ω)2×2,其中P0是常量元素K的空间,那么标准的L2-正交投影Πμ:L→Lμ有如下性质:
下面给出亚格子稳定化的有限元算子分裂算法:
步骤一 对于给定的uhn∈Vh使得对于所有的vhn∈Vh,有
步骤二 寻找解uhn+1∈Vh和phn+1∈Qh使得对于所有的(vh,qh)∈Vh×Qh有
上述提到的方法中,步骤二可以看作是一般的Stokes问题.其中有限元空间Vh⊂H01(Ω),Qh⊂L02(Ω)且Vh和Qh要求满足下面的条件:
(H1) 存在与h无关的β>0,使得对于所有的h>0有:
其中Bh:Vh→Qh′和Bht:Qh→Vh′定义如下:
(H2) 存在与h无关的γ>0,使得对于所有的v∈Hr(Ω)和q∈Hs(Ω)以及任意的h>0有:
(H3) 存在与δt和h无关的C>0,使得:
2.1. 时间离散的算子分裂方法
2.2. 亚格子稳定化的有限元方法
-
定义速度误差函数为:
定理1[4] 假设(R1),(R2b),(R3)和(R4)成立,那么对
$ N = 0, \cdots , \left[ {\frac{T}{{\delta t}}} \right] - 1$ ,和足够小的δt,有下面的估计: -
设有限元解
$ ({\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}_h}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}, \mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}_h^{n + 1}, \mathit{\boldsymbol{p}}_h^{n + 1})$ 是半离散分步解$ ({\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}}, {\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}^{n + 1}}, {\mathit{\boldsymbol{p}}^{n + 1}})$ 的逼近解,我们定义如下误差:引入与有限元空间有关的误差函数:
引理1[4] 设Vh和Qh满足inf-sup条件(H1),则对于u∈V满足:
定理2 设(R1),(R2b),(R3),(H1)和(H3)成立,那么对于
$ N = 0, \cdots , \left[ {\frac{T}{{\delta t}}} \right] - 1$ 和足够小的δt和h,满足:证 让(5)式和(14)式与vh做内积,且让两式相减得:∀(vh,qh)∈Vh×Qh,
对于任意给定的(vh,wh,qh)∈Vh×ker(Bh)×Qh,由(15)式可得:
下面对(22)式右端各项估计:
因为∇·un+1=0且wh∈ker(Bh).
对于三线性项有:
在(25)式中右端第一项为0,对其余各项估计:
由定理1可知,
$ {\left\| {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{e}}_c}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}} \right\|_1} \le C\delta {t^{\frac{1}{2}}}$ ,且由(R1)可得:同理,可得:
将(23),(24),(26),(27),(28)式代入(22)式,并且两边同时取下确界可得:
然后将(29)式两端从0加到N-1,当时间足够小时,得:
对于足够小的δt和h,由离散的Gronwall引理,(H3)和三角不等式得证定理2成立.
结合定理1和定理2,我们可估计
推论 设(R1),(R2b),(R3),(H1),(H2)和(H3)成立,设对于所有的
$n = 0, \cdots , \left[ {\frac{T}{{\delta t}}} \right] - 1 $ ,un+1,$ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{u}}^{n + \frac{1}{2}}}$ ∈Hk(Ω)和pn+1∈Hk-1(Ω)且一致有界,那么对于$n = 0, \cdots , \left[ {\frac{T}{{\delta t}}} \right] - 1 $ ,以及足够小的δt>0和h,有如下估计:
3.1. 速度的半离散误差估计
3.2. 全离散解的误差估计
-
利用FreeFem++软件[11]进行一些实验验证理论预测的正确性.
-
选择Navier-Stokes方程的精确解为:
其中解的区域Ω=[0, 1]×[0, 1]⊂
$ \mathbb{R}$ 2,在这个问题中P1b-P1元用于空间离散,并且取ν=1.0×10-7,T=0.1,α=0.1 h. 表 1给出了数值结果.从表 1可知:我们的方法对空间和时间离散是一阶收敛的,同时数值结果也表明我们的理论预测是正确的.为了对比我们现在的方法和标准的有限元方法,当网格尺寸$ h = \frac{1}{{128}}$ ,时间步长$\mathit{\Delta }t = \frac{1}{{800}} $ 时,我们分别计算ν=1,0.1,0.01,0.001时方程的解.从表 2可以看出我们的有限元算子分裂算法得到的误差估计更小. -
考虑一个定义在Ω=[0,2.2]×[0,0.41]上的圆柱绕流问题,其中圆心为(x,y)=(0.2,0.2),半径为0.05,取入流速度为
并且在其他边界上满足无滑边界条件.
在这个问题中,Hood-Taylor元用于空间离散,粘性系数ν=0.001,网格大小为
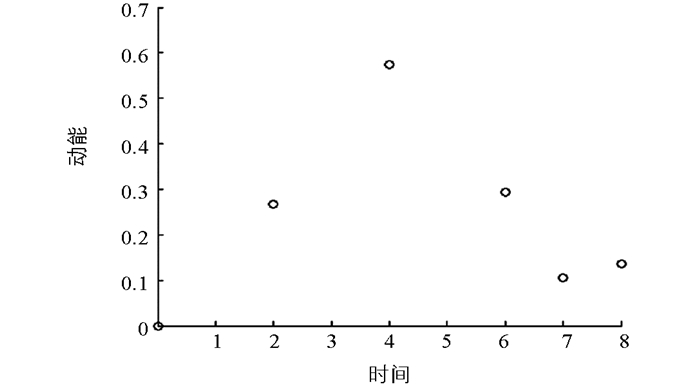
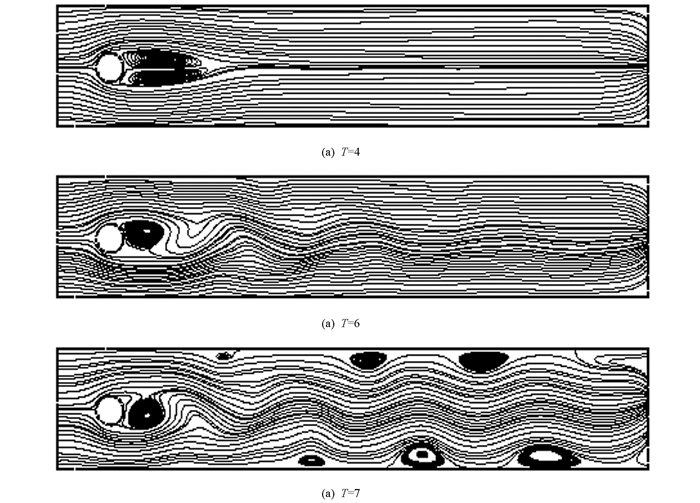
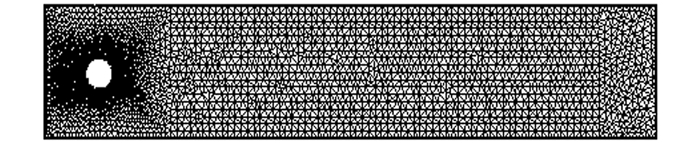
$ h = \frac{1}{{32}}$ ,稳定化参数α=0.1h2,时间步长Δt=0.001,分别取得最后时刻T=4,6,7. 图 1给出了区域Ω的网格剖分,图 2描述了算法关于动能和时间T的关系,图 3对比了不同时刻的流线图.
4.1. 解析解
4.2. 圆柱绕流
-
本文主要结合亚格子稳定模型和有限元算子分裂算法,理论上给出了全离散速度的误差估计,并用数值实验验证了理论的正确性和方法的有效性.对比标准的有限元方法,我们的方法得到的误差估计更小.



 下载:
下载: