-
辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)属于茄科(Solanaceae)辣椒属(Capsicum)植物,是一类重要的蔬菜作物和经济作物.病毒病是影响辣椒生产的一类重要病害,感病植株表现出叶片畸形、斑驳、花叶和植株矮化等症状,造成辣椒产量下降,品质降低,严重制约辣椒产业发展[1-2].目前,世界上已有60多种植物病毒可侵染辣椒[3],在我国辣椒上检测到的病毒有33种,归属于10个科12个属[4].其中,已报道有6种烟草花叶病毒属(Tobamovirus)病毒侵染辣椒,分别为烟草花叶病毒(Tobacco mosaic virus,TMV)、番茄花叶病毒(Tomato mosaic virus,ToMV)[1]、辣椒轻斑驳病毒(Pepper mild mottle virus,PMMoV)[5]、烟草轻型绿花叶病毒(Tobacco mild green mosaic virus,TMGMV)[6]、番茄斑驳花叶病毒(Tomato mottle mosaic virus,ToMMV)[7-8]和油菜花叶病毒(Youcai mosaic virus,YoMV)[9].
烟草轻型绿花叶病毒(Tobacco mild green mosaic virus,TMGMV),属于烟草花叶病毒属(Tobamovirus)成员,最早在烟草(Nicotiana gluanca)上发现. TMGMV除危害烟草外,还可以侵染辣椒[6]、番茄[10]和南瓜[11]等多种作物及杂草,其在辣椒上发生和危害较为严重. TMGMV侵染辣椒后引起叶片褪绿、黄化及坏死,且在病果上有明显的褪绿条纹等症状.在我国,TMGMV危害辣椒的报道最早于2005年出现在台湾地区;2013年在厦门出现[6];2015年在江苏出现;2016年在山东大面积发生,严重影响了辣椒的产量[12].这些报道表明该病在我国呈现扩散态势,是当前我国辣椒生产上的潜在危害病毒之一.
本实验室在前期工作中,从重庆北碚、石柱和潼南等地区采集了表现出花叶、卷曲、斑驳、黄化的辣椒样品,通过高通量测序方法检测到了黄瓜花叶病毒(Cucumber mosaic virus,CMV)、蚕豆萎蔫病毒2号(Broad bean wilt virus 2,BBWV-2)、辣椒潜隐病毒2号(Pepper cryptic virus 2,PCV-2)、辣椒脉斑驳病毒(Chilli veinal mottle virus,ChiVMV)、甜椒脉斑驳病毒(Pepper veinal mottle virus,PVMV)、TMV、PMMoV和TMGMV等8种病毒.虽然在我国已经报道了TMGMV在辣椒上发生危害,但在重庆地区还未见报道.因此,本研究在前期工作的基础上,利用RT-PCR方法对重庆辣椒上的TMGMV进行测定,分析其检出率;通过分段扩增方法获得其基因组全序列,并与国内外报道的TMGMV全序列进行同源性比较,以期明确重庆不同地区TMGMV的发生情况及其与国内外其他分离物间的进化关系.
全文HTML
-
疑似感染病毒的辣椒样品于2016年6月采自重庆北碚、潼南、石柱和九龙坡4个区县,共29份,保存于-80 ℃冰箱.
-
克隆载体pGEM-T Easy Vector,美国Promega公司;大肠杆菌Escherichia coli Trans5α,北京全式金生物技术有限公司.
-
Trizol,Invitrogen公司;反转录试剂盒、连接酶,TaKaRa公司;HiFi Taq DNA聚合酶,北京全式金生物技术有限公司;DNA回收试剂盒和质料提取试剂盒,北京天根生化科技公司.
-
用于检测TMGMV的引物依据文献[6]报道的序列;根据GenBank中TMGMV的基因组全长序列,比对分析后设计分段扩增TMGMV全基因组引物(表 1).
-
总RNA的提取参考Trizol RNA (TaKaRa)取说明书,最后每份RNA加入30 μL的RNase-free ddH2O溶解RNA,-80 ℃保存,备用.
以提取样品总RNA为模板,利用反转录试剂盒(PrimeScript RT reagent Kit,TaKaRa)合成cDNA.反应体系为:5×PrimeScript Buffer 2 μL,Oligo dT Primer 0.5 μL,Random 6 mers 0.5 μL,PrimeScript RT Enzyme Mix I 0.5 μL,总RNA 2 μL,加RNase-free ddH2O至10 μL.反应程序为:37 ℃ 30 min,85 ℃ 20 s. cDNA保存于-20 ℃,备用.
-
以合成的cDNA为模版进行PCR扩增,反应体系为:10×HiFi buffer (Mg2+) 2.5 μL,dNTPs (2.5mM) 2.0 μL,primer F(10 μM) 0.3 μL,primer F(10 μM) 0.3 μL,cDNA 1 μL,HiFi Taq (500 U) 0.2 μL加ddH2O至25 μL. PCR反应程序:94 ℃预变性3 min,94 ℃变性30 s,退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1 000 bp/min,循环35次,72 ℃延伸10 min.取5 μL PCR产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测.
PCR产物纯化参考天根DNA纯化回收试剂盒(Universal DNA Purification Kit,TIANGEN)进行PCR产物回收,最后用30 μL ddH2O溶解DNA,12 000 r/min离心2 min,收集DNA溶液. DNA回收产物保存于-20 ℃,备用.
-
参考T载体快速连接试剂盒(pGEM-T Easy Vector System I,Promega)和本实验室体系[13]进行回收的DNA片段连接.反应体系为:2×Ligation Buffer 5 μL,pGEM-T载体1 μL,DNA片段3 μL,T4 DNA Ligase(3 U/μL)1 μL.置室温反应2 h或4 ℃反应8 h.将重组质粒转化至大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,培养后经蓝白斑筛选,挑选白色单克隆菌落至LB液体培养基(含100 μg/mL Amp)中培养4~6 h后PCR检测阳性克隆用于测序.
-
菌液经过PCR鉴定为阳性克隆后委托华大基因科技有限公司进行序列测定.利用DNAStar[14]软件对所获得的基因序列进行处理,利用BLAST程序进行序列相似性搜索,并用DNAStar MegAlign程序的Clustal W方法与GenBank已登录的病毒核苷酸序列进行多序列比较分析,采用MEGA 5.0[15-16]的邻接法(neighbor joining,NJ)构建进化树,重复次数设置为1 000次.
1.1. 材料
1.1.1. 毒源
1.1.2. 载体和菌株
1.1.3. 主要试剂
1.1.4. 引物
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 植物总RNA提取及cDNA合成
1.2.2. RT-PCR及DNA纯化
1.2.3. T载体连接、转化及检测
1.2.4. 序列测定与分析
-
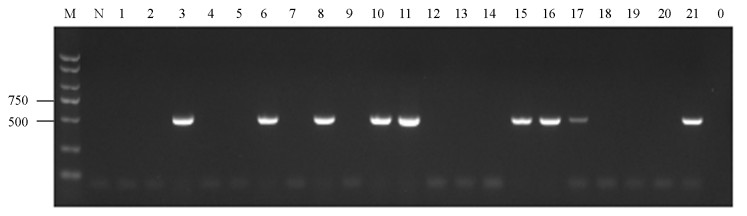
对采集自重庆4个区县的29份辣椒疑似病毒病害样品进行总RNA抽提,反转录合成cDNA,利用TMGMV CP基因特异性引物进行PCR扩增,获得目的大小的PCR产物(图 1).阳性结果分析发现共有9个样品检测到TMGMV,检出率为31.03%,表明TMGMV在重庆北碚、九龙坡、潼南和石柱均有发生(表 2).进一步分析发现,从石柱采集的5份样品中检测到TMGMV的样品有3份,检出率高达60.00%;潼南TMGMV检出率为40.00%;九龙坡TMGMV检出率为30.00%;而北碚9份样品中仅有1份样品检测到TMGMV,检出率最低,为11.11%(表 2).
-
采用RT-PCR方法成功克隆重庆辣椒上TMGMV CP基因,通过连接pGEM-T载体,转化大肠杆菌、菌液PCR检测,DNA测序等过程,获得重庆地区分离物TMGMV CP基因全序列,命名为TMGMV-CQ.对已获得的分离物与GenBank中19个TMGMV分离物的CP基因进行系统进化树分析(图 2).结果表明,这20个TMGMV分离物主要聚为3支.其中,巴拿马辣椒分离物(EU934035)与西班牙等欧洲分离物聚为一支(group Ⅰ);TMGMV-CQ与2个韩国分离物(AF103782和AF103783)、美国烟草分离物(AF131908)、美国鲸鱼花分离物(EF469769)和2个中国辣椒分离物(KM596785、JX534224)聚为一支(group Ⅱ);韩国矮牵牛分离物(AM262165)、美国烟草分离物(AF132907)、中国台湾辣椒分离物(DQ821941)和日本烟草分离物(AB078435)聚为一支(group Ⅲ),系统进化分析结果表明TMGMV分离物间的亲缘关系具有一定的地理相关性. TMGMV-CQ与厦门辣椒分离物(JX534224)聚集在同一个小分支,表明两者的亲缘关系最近.
-
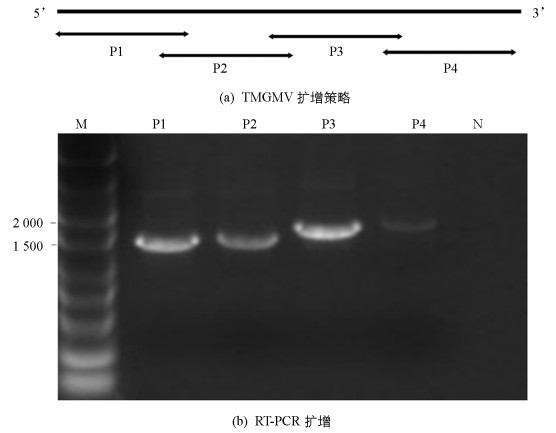
将GenBank中TMGMV的基因组全长序列经过序列比对,根据其保守序列设计分段扩增TMGMV基因组全长的引物(表 1),采用分段扩增再拼接的方法,分成4个片段进行扩增(图 3a).对采自重庆潼南的辣椒样品(编号TN29)进行TMGMV基因组分段扩增,获得大小约为1.6 kb,1.6 kb,1.8 kb和1.9 kb的4个片段(图 3b),分别连接pGEM-T载体,转化大肠杆菌、菌液PCR检测,DNA测序等过程.测序结果获得了TMGMV-TN29基因组片段分别为1 588 nt,1 648 nt,1 852 nt和1 915 nt.这4个片段经过DNAStar的Segman程序拼接,最终得到TMGMV-TN29基因组全长序列为6 356 nt,其5’和3’末端分别有71 nt和210 nt的非编码区(Untranslated Regions,UTR),包括4个开放阅读框(Open Reading Frame,ORF),分别编码1.83×105/1.26×105的复制相关蛋白,2.8×104的移动蛋白(Movement protein,MP)和1.7×104的外壳蛋白(Coat protein,CP)(图 4).
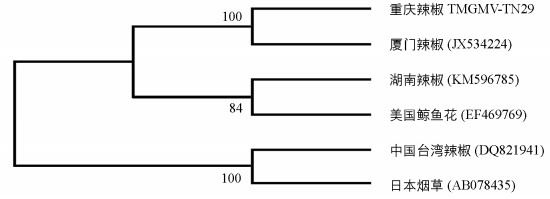
将TMGMV-TN29分离物与已报道的其他TMGMV全基因序列进行同源性分析表明,TMGMV各分离物之间的同源性在97.00%~99.7%之间.序列分析结果表明,TMGMV-TN29与厦门辣椒分离物Xiamen(JX534224)基因组核苷酸序列及其编码的氨基酸序列的相似性都为最高(表 3).系统进化树显示TMGMV-CQ分离物与厦门辣椒分离物Xiamen(JX534224)聚为一组,表明这两者的亲缘关系最近(图 5).
2.1. TMGMV在重庆辣椒上的发生情况
2.2. 重庆辣椒上TMGMV CP克隆及序列分析
2.3. 重庆辣椒上TMGMV全基因组序列分析
-
虽然在重庆辣椒上检测到了CMV,TMV,TuMV,ToMV,BBWV-2,PCV-2和TSWV等病毒[17-21],但还未见TMGMV侵染重庆辣椒的报道.近年来,TMGMV在我国各地报道不断增多,为明确重庆辣椒是否受TMGMV侵染,本研究从重庆4个不同辣椒种植区采集了29份疑似病毒病样品,经RT-PCR及克隆测序发现,这4个地区均有TMGMV发生,且发病率介于11.11%~60.00%之间.石柱是重庆重要的辣椒生产地[22],TMGMV检出率高达60.00%,值得植保工作者注意.本文首次在重庆辣椒上检测到TMGMV,说明TMGMV在重庆辣椒上也存在,可能是其早就侵入重庆而未被发现,或近几年来才扩散到重庆.鉴于TMGMV在我国辣椒上流行的风险,有必要对TMGMV发生情况加以监测.
TMGMV最早在烟草上发现,属Tobamovirus成员.本研究首次从重庆辣椒上检测并克隆了TMGMV的全基因组序列,共包含6 356 nt,由4个开放阅读框组成,ORF1和ORF2分别编码1.83×105,1.2×105复制酶相关蛋白,ORF3编码运动相关蛋白,ORF4编码外壳蛋白,具有Tobamovirus病毒特征.大多数的Tobamovirus病毒能通过种子传播,近年来随着贸易的发展,我国各地辣椒种植地区对辣椒种子的引进和交换也越来越频繁. 2013年厦门出入境检验检疫局从进境辣椒种子中检测到TMGMV,说明该病毒有较高的传入风险.根据以往的报道结果显示Tobamovirus病毒进化缓慢,基因组通常比较保守[23-24],而目前对TMGMV亲缘关系的研究集中在CP ORF水平,为更全面地了解TMGMV遗传结构,本研究对重庆地区侵染辣椒的TMGMV测定了其全基因组序列,进一步发现TMGMV重庆辣椒分离物TMGMV-TN29与厦门辣椒分离物Xiamen(JX534224)的基因组核苷酸序列相似性高达99.75%,基于基因组全长的进化树分析也表明,TMGMV-TN29与Xiamen(JX534224)的亲缘关系较近,由此推测它们可能来源于同一个进化祖先.



 下载:
下载: