-
磷对能量转运和生物生长有重要作用,而且也是广泛使用的营养元素之一.然而,含磷产品的过量消费不可避免地会造成大量污染物,引起水体富营养化[1].因此,研究简单、高效去除磷的方法有重要意义.吸附技术因其简单、高效及成本低已成为一种广泛使用的除磷方法[2].金属有机框架(metal organic framework,MOF)是一类多孔材料,是由有机配体与无机金属离子或金属离子簇自组装而成的配位聚合物[3],具有高孔隙率、低密度及大比表面积等特点,可直接吸附水中的各种有机污染物[4],但鲜见其用于废水除磷的研究报道.本研究使用2-氨基对苯二甲酸作为配体,合成双金属Fe-Zr MOF,探讨其吸附去除水中磷酸盐的特性,研究结果可为除磷吸附剂的筛选奠定基础.
全文HTML
-
紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-2450,岛津苏州);pH计(PHS-3D,上海精密科学仪器有限公司). FeCl3·6H2O,ZrCl4及N,N´-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)购自Sigma-Aldrich(上海,中国);2-氨基对苯二甲酸NH2BDC购自TCI化成工业发展有限公司(中国上海);磷酸二氢钾、钼酸铵、抗坏血酸及酒石酸锑钾购自成都化学工业有限公司(成都,中国).其他化学试剂,如乙醇、HCl和NaOH均购自重庆市钛新化工有限公司(重庆,中国).
-
将1 mmol FeCl3·6H2O (0.271 g)、1 mmol ZrCl4 (0.233 g)和2 mmol (0.362 g) NH2BDC溶于40 mL DMF中,然后再加入0.2 g PVP,搅拌至完全溶解后,超声30 min,将混合溶液转移至反应釜中,加热至150 ℃反应24 h后,冷却至室温,用DMF和乙醇交替洗涤3次后,在90 ℃下干燥12 h,即得Fe-Zr MOF材料.分别按照n(Fe3+):n(NH2BDC)=1:1,n(Zr4+):n(NH2BDC)=1:1的比例将混合物溶解在20 mL DMF中(不添加PVP),其余步骤同合成Fe-Zr MOF一样,即可得到Fe-MOF和Zr-MOF.
-
本实验采用恒温震荡摇床在25 ℃ 180 r/min进行吸附去除磷实验,pH值用0.1 mol/L NaOH或0.1 mol/L HCl进行调节.磷酸盐质量浓度用钼酸铵分光光度法进行测定[4].吸附量按方程(1)计算:
式中q为吸附量(mg/g);C0为初始磷酸盐质量浓度(mg/L);Ct为t时刻反应后磷酸盐的质量浓度(mg/L);V为溶液体积(L);m代表吸附剂的量(g).
吸附剂用量优化实验条件:Fe-Zr MOF吸附剂量从1 mg到40 mg,50 mL KH2PO4溶液(50 mg/L),pH=7.0,温度为25 ℃,吸附时间为24 h.
pH值的优化实验条件:pH值优化范围从3.0到10.0,2 mg吸附剂,50 mL KH2PO4溶液(50 mg/L),温度25 ℃,吸附时间24 h.
吸附动力学实验方法:将一系列50 mg/L磷酸盐溶液(50 mL)调至pH=7.0,加入2 mg Fe-Zr MOF,放入振荡器中反应30 min至30 h,将实验数据用准一级动力学和准二级动力学模型进行拟合[5]:
式中qe和qt分别为平衡吸附量和t时刻的吸附量(mg/g),k1为准一级动力学常数(1/h),k2为准二级动力学常数(g/mg·h).
吸附等温线实验方法:将2 mg Fe-Zr MOF加入50 mL不同质量浓度(5~200 mg/L)的磷酸盐溶液(pH=7.0)中,然后在25 ℃以180 r/min摇动24 h,取上清液测定磷酸盐浓度,将实验数据用Langmuir(方程4)和Freundlich等温线(方程5)模型模拟[6]:
式中Ce(mg/L)是磷酸盐的平衡质量浓度,qe(mg/g)是平衡吸附量,qmax是最大吸附容量(mg/g),KL(L/mg)和KF(mg/g)分别是Langmuir常数和Freundlich常数. n是Freundlich指数.
1.1. 仪器及试剂
1.2. Fe-Zr MOF的合成
1.3. 实验方法
-
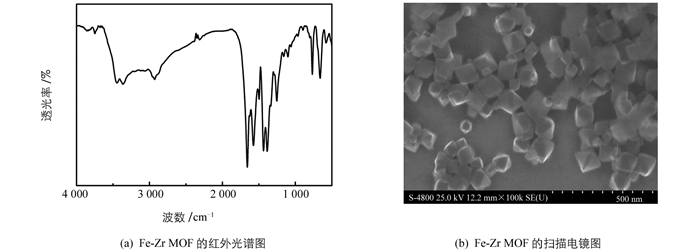
用溶剂热法合成了Fe-Zr MOF,图 1(a)是其红外光谱图,其中3 443 cm-1和3 363 cm-1是—NH2的对称和不对称伸缩振动峰,1 656 cm-1是N—H的弯曲振动峰[7],1 020,963和893 cm-1是Fe-OH的伸缩振动峰[8],767,660,579,482 cm-1是Zr—O键的特征振动峰[9],说明Fe-Zr MOF合成成功. 图 1(b)是扫描电镜,可以看出材料是八面体结构,表面比较光滑.
-
在相同条件下试验了Fe-MOF、Zr-MOF及Fe-Zr MOF对磷酸盐的吸附量,结果表明,它们对磷酸盐的吸附量分别为(107.16±5.23)、(91.17±2.33)、(222.35±2.00) mg/g.可见,Fe-Zr双金属有机框架材料的吸附量均显著大于Fe-MOF及Zr-MOF的吸附量,而且大于两者之和,表现出协同效应.
-
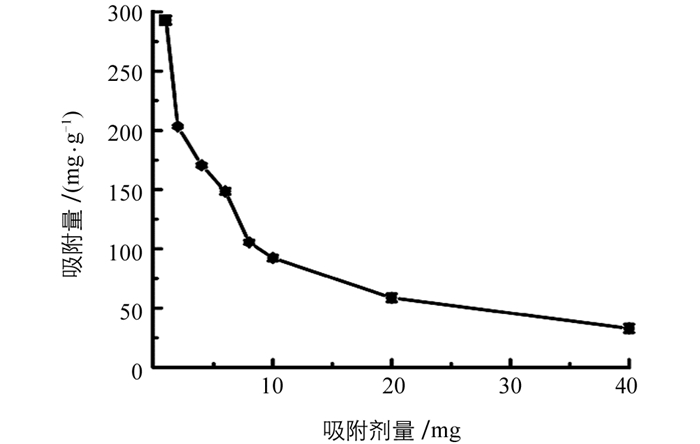
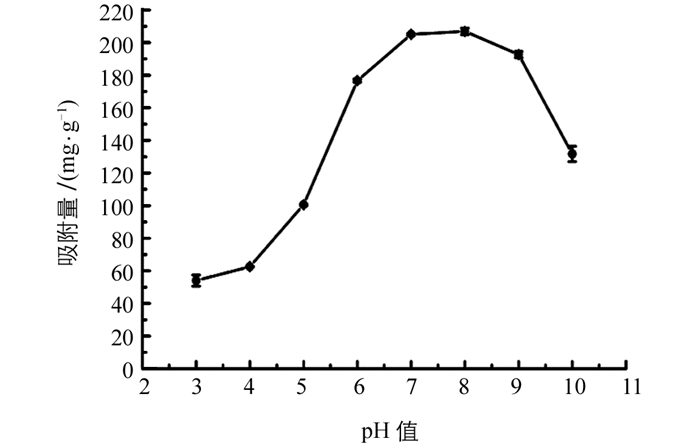
吸附剂量影响的结果列于图 2,随着吸附剂量从1 mg增加到40 mg,吸附量从293 mg/g减小到33 mg/g,这是由于在低剂量吸附剂下,吸附位点被磷酸盐快速占据并且达到饱和,相反,吸附剂用量越大,吸附过程中未被磷酸盐占据的位点越多,导致吸附能力降低.为保持较高吸附量,选择2 mg Fe-Zr MOF进行进一步实验.试验了初始pH值对磷酸盐吸附的影响,结果列于图 3.可见,随着pH值从3增加到7,吸附量逐渐增加,当pH值从7增加到8时,吸附量保持相对恒定;pH值大于8时,吸附量降低.选择pH=7进行后续实验.
-
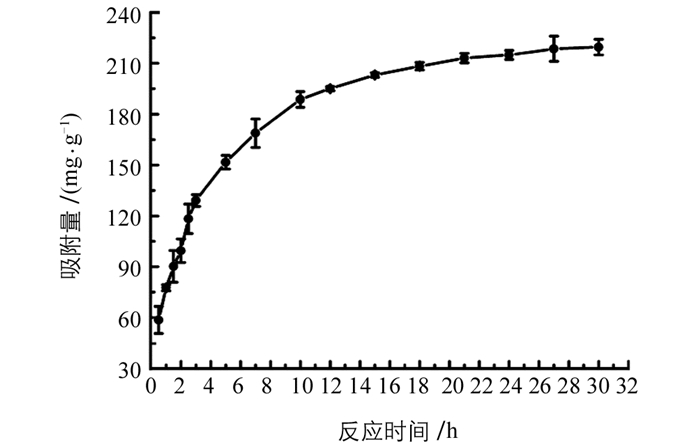
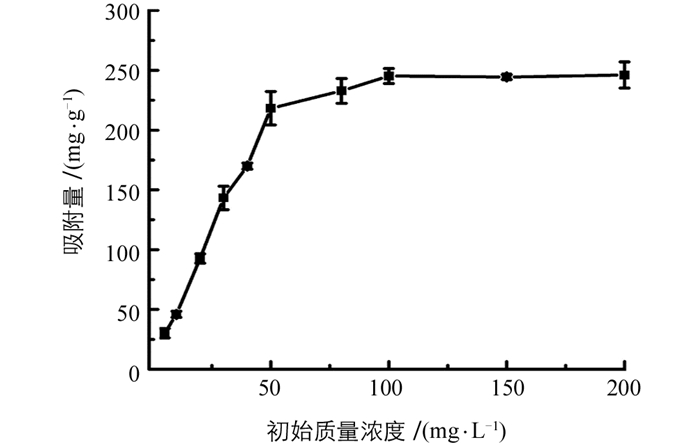
图 4所示为吸附时间对Fe-Zr MOF吸附去除磷酸盐的影响,可见,吸附时间从30 min到10 h,吸附量显著增加,超过10 h后吸附量增加缓慢,为保证吸附达到平衡,实验选择24 h为吸附时间.根据方程(2)及方程(3)对实验数据进行拟合,结果表明,准一级及准二级动力学模型得到的qe分别为153.27及238.09 mg/g,相关系数r2分别为0.996 1及0.999 0;可见准二级动力学模型得到的qe与实验值219.53 mg/g更接近,而且相关系数更大,表明吸附更符合准二级动力学模型,表明Fe-Zr MOF吸附磷酸盐是化学吸附过程. 图 5所示是吸附等温线图,可见,随着磷酸盐质量浓度从5 mg/L增加到100 mg/L,吸附量从30 mg/g增加到245 mg/g;当磷酸盐质量浓度从100 mg/L到200 mg/L时,吸附量基本保持恒定,这是由于在低磷酸盐质量浓度时,Fe-Zr MOF吸附剂上的活性位点充足,吸附量随磷酸盐质量浓度增加而快速增加;当磷酸盐质量浓度较大时,吸附剂的位点被大量占据,吸附量呈缓慢增加趋势,直至吸附剂的位点完全占据达到平衡.根据方程(4)及方程(5)对实验数据进行拟合,结果表明,Langmuir模型(r2=0.980 8)拟合效果要好于Freundlich模型(r2=0.877 3),表明Fe-Zr MOF吸附磷酸盐是一个单分子吸附过程,计算得到的最大吸附量为285.7 mg/g.
-
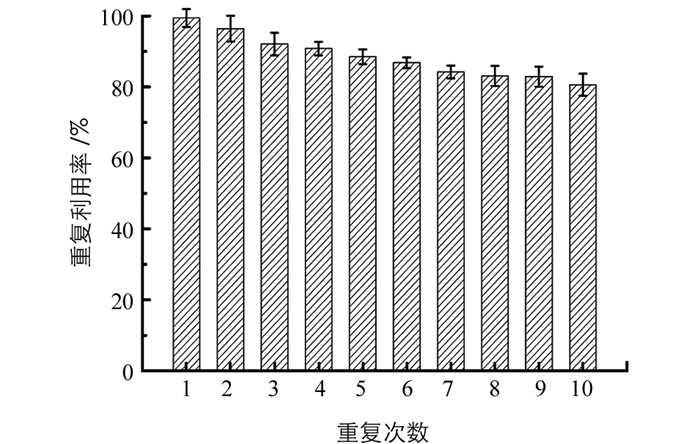
将吸附了磷酸盐的Fe-Zr MOF用0.1 mol/L的NaOH作为洗脱剂,超声解吸30 min,进行抽滤、洗涤及烘干后,即完成Fe-Zr MOF的再生,并将该再生材料用于磷酸盐的吸附,以考察其重复利用性能.结果见图 6,可见,材料在吸附-解吸重复使用10次之后,对磷酸盐的吸附量为最初吸附量的80.6%,表明Fe-Zr双金属-有机框架材料的重复利用性能良好,可以用于水中磷酸盐的去除.



 下载:
下载: