-
随着社会快速发展,城市化水平也日渐提高,人们对城市绿地的关注也随之提升.城市绿地对改善城市环境、维护城市生态系统平衡起着重要的作用,城市绿地中植物物种多样性直接影响城市绿地系统的稳定性[1-2].木本植物作为城市绿地系统的重要组成部分,是构成城市植物物种多样性的基础[3].目前,国内外学者在城市绿地木本植物物种多样性方面做了大量的研究工作,包括城市化对植物物种多样性的影响作用[4]、城市植物物种多样性调查[5-7]、不同类型城市绿地木本植物物种多样性分析等[8].城市化易造成本土植物物种的丢失和外来物种的增加,目前,城市化驱动木本植物物种多样性变化多以理论研究为主,缺少定量的分析[9].因此,探讨城市化背景下木本植物物种多样性成为目前相关研究的热点之一.
通过对东营市建成区内3个城区进行木本植物物种的抽样调查,对植物种类组成和多样性指数进行分析,总结当前东营市城市绿地建设存在的主要问题,并提出建议,为东营市环境生态建设、绿地系统规划建设、区域植物种群分布等工作的设计规划与建设方案提供信息化、数据化的参考,促进东营市城市绿化建设水平的提升.
全文HTML
-
研究区域为东营市建成区,其位于山东省东营市中心部,辖区地理坐标为东经118°07′-119°10′,北纬36°55′-38°10′.建成区总面积96.84 km2,划分为3个行政区域:西城区面积为39.82 km2,东城区面积为27.99 km2,经济技术开发区面积为29.03 km2.城区人口为80万人,气候是季风型大陆性气候区,年均气温12.4 ℃,年均风速为3.3 m/s,年均降雨量约553.9 mm,无霜期206 d.土壤以褐土、砂姜黑土、潮土和盐土为主.据统计,截至2017年,东营市绿地率为42.89%.
-
本次调查于2017年4月-10月进行,在对东营市建成区(包括东城区、西城区、技术开发区)绿地全面调查的基础上,根据绿地规模和植被分布等特点,选择具有代表性的绿地包括公园绿地、带状绿地、街旁绿地、居住绿地、公共设施绿地和道路绿地等共计117处,样方分布情况为:东城区222个,西城区208个,技术开发区70个,共计500个样方,合计面积0.2 km2.
-
调查采用典型取样法[10],道路绿地和带状绿地设置10 m×40 m的样方,其余绿地设置20 m×20 m的样方,样方面积均为400 m2.拍摄区域照片,画出平面图.所用工具包括三维激光测距仪、胸径尺、花杆、卷尺和相机等.调查中乔木指胸径(主干离地表面1.3 m处的直径)大于4 cm的树种;灌木指胸径小于4 cm的小乔木和高度高于1.5 m的树种(包含修剪成球形或柱形的造型植物)[11].
-
记录调查时间、天气、样地面积、位置、周围环境、群落结构以及各层片的高度和盖度等相关信息;乔木进行每株调查,记录其名称、数量、胸径、冠径、树高、冠下高、生长势、色彩和树冠形态等;灌木记录名称、数量(丛数)或面积、盖度、高度、生长势和色彩等.
-
将调查得到的原始数据按不同城区,分乔木、灌木两类进行处理,计算物种的频度、相对多度、相对显著度或相对盖度、相对重要值、优势度指数和物种多样性指数等,并用Excel和SPSS 20.0软件对其进行相关性分析.
式中:ni为每一个种的重要值,N为全部种的重要值.
物种丰富度指区域内物种的数量,采用Margalef物种丰富度指数.物种多样性指数是体现物种数量、结构和分布均匀程度的综合量化指标,通常采用Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson多样性指数、Pielou均匀度指数[12].各指数分别为:
Margalef物种丰富度指数
Shannon-Wiener多样性指数
Simpson多样性指数
Pielou均匀度指数
式中:Pi为种i的株数占样地所有树种总株数的比例,n为所有物种个体数之和,S为种数[13].
1.1. 研究区域概况
1.2. 研究方法
1.2.1. 调查时间和范围
1.2.2. 调查方法
1.2.3. 调查内容
1.3. 数据分析与处理
-
样地调查结果表明:东营市城市绿地木本植物共计166种,隶属于47科80属,其中乔木103种,隶属于29科47属;灌木63种,隶属于25科37属.乔木与灌木树种的比例为1:0.61.从样地内植物的数量上来看,乔木13 125株,灌木7 391株,其数量比为1:0.56.
常绿植物32种,落叶植物134种,常绿与落叶植物的物种比例为1:4.2.和东营市相似纬度地区比较,小于大连常绿、落叶树种比1:3.5[14],大于安国市的常绿、落叶树种比1:10.6[15],常绿、落叶树种比例适中.样地中木本植物数量共计20 516株,其中常绿植物6 765株,落叶植物13 751株,其数量比为1:2.03.
调查区域内乡土树种46种,外来树种120种,比例为1:3.植物种类数量占有率较多的科为蔷薇科(Rosaceae)10属46种,其次为木犀科(Oleaceae)4属14种;柏科(Cupressaceae)2属6种;豆科(Leguminosae)8属12种;松科(Pinaceae) 4属11种;榆科(Ulmaceae)3属8种;忍冬科(Caprifoliaceae)3属5种;杨柳科(Salicaceae)2属9种;桑科(Moraceae)3属3种;楝科(Meliaceae)2属2种;其余科均为1属.从表 1可以看出,东营市建成区不同城区的木本植物组成存在较大差异,植物物种的科、属、种数从多到少排序均为:东城区、西城区、技术开发区.东城区的植物物种相对丰富.乔灌比方面,技术开发区的灌木层植物种类少,常绿落叶比方面,东城区常绿树种少.
-
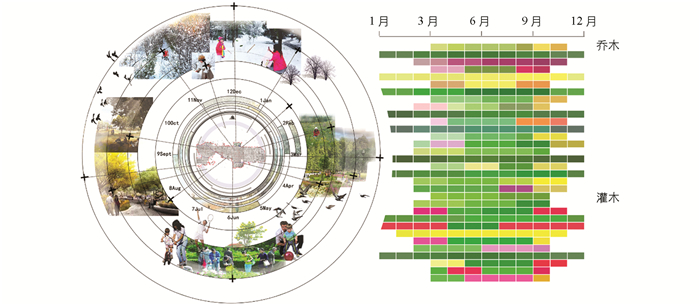
物种的频度是指物种在样方内出现的频率,体现了物种在群落中的密度和分布情况.东营市绿地不同木本植物种类间频度差异很大,从表 2中可知,应用频度在5%以上的只有32种,占全部树种的19.27%,其中乔木23种,灌木9种,大部分木本植物的应用频度很低.乔木中只有白蜡的应用频度达到40%以上,这与白蜡是东营市的市树有关.根据木本植物的应用频度在5%以上的树种数量分析,城市木本植物的主要色彩见图 1,主要以绿色为主,秋叶色彩主要有黄色、褐(橙)色以及红色三大类.秋色叶树种共有10种,彩色叶树种共有4种,种类较少,观赏期集中在3,4,9,10月.应用频度特别低但观赏价值很高的如金钟连翘(Forsythia × intermedia)、紫丁香(Syringa oblata)、紫穗槐(Amorpha fruticosa)、红王子锦带(Weigela florida cv. ‘Red Prince’)等植物,其频度仅为1%左右,导致部分绿地的景观效果较差.
-
木本植物的相对重要值体现其物种优势.以每个城区木本植物物种相对重要值总和达到80%为依据,列出排序在前列的植物表.从表 3可看出乔木的优势比较明显,重要值高的树种共39种,其中乔木25种,灌木14种. 3个城区中优势树种数量比从大到小为:东城区、西城区、技术开发区,表明东城区树种应用较多,树木优势种也较多.
-
从各城区的绿地木本植物优势种的集中程度上来看,乔木层物种分布较均匀;灌木层优势度指数高,均匀度低(表 4). 3个城区中乔木层的优势度指数为东城区和技术开发区相等,均大于西城区,可知乔木层在西城区优势种集中程度较弱;灌木层优势度指数从大到小为:技术开发区、东城区、西城区,表明灌木层在技术开发区的优势度指数最高,优势种集中,存在单一灌木树种应用集中和普遍的现象.
-
东营市3个城区中木本植物的物种丰富度结果见表 5,乔木层的丰富度指数大于灌木层.不同城区木本植物物种丰富度存在差异,从大到小排序为:东城区、西城区、技术开发区.根据SPSS 20.0对数据用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),不同城区木本植物物种丰富度存在显著性差异,在显著水平0.05条件下,东城区和西城区的差异不具有统计学意义;但东城区与技术开发区以及西城区和技术开发区的差异均具有统计学意义.表明技术开发区在绿地分布和植物物种种类、数量方面和其他城区相比有明显区别,存在很大的提升空间.
-
物种多样性指数对群落稳定性和健康性有重要作用,Shannon-Wiener指数表示物种出现的紊乱性和不确定性. Simpson多样性指数即优势度指数的反面,物种集中性高,多样性程度低.物种均匀度能够表示物种群落或生境中物种组成的均匀程度[16].
东营市城市绿地中乔木层的多样性指数均高于灌木层.不同城区木本植物多样性指数存在一定差异,3个城区木本植物Simpson多样性指数均在0.5以上,其从大到小排序为:东城区、西城区、技术开发区;Shannon-Wiener指数从大到小排序为:东城区、西城区、技术开发区;Pielou均匀度从大到小排序为:技术开发区、西城区、东城区(表 6).这表明东城区的物种多样性最高,物种数量多但分布不均匀.
由表 7可看出,Shannon-Wiener多样性指数与Simpson多样性指数相关系数为1,呈极显著正相关趋势;Shannon-Wiener多样性指数与Pielou均匀度、Simpson多样性指数与Pielou均匀度相关性系数均为-1,呈极显著负相关趋势.三者在东城区、西城区的总体趋势基本一致,但是与技术开发区的多样性指数有差异,其与技术开发区的植物数量较少有相关性,或存在一定的偶然因素.
2.1. 木本植物物种统计分析
2.1.1. 物种组成统计
2.1.2. 物种应用频度及色彩
2.2. 木本植物重要值和优势度分析
2.2.1. 植物物种重要值
2.2.2. 优势度指数
2.3. 木本植物物种多样性基本特征分析
2.3.1. 植物物种丰富度
2.3.2. 植物物种多样性指数
-
在城市园林中,乔木层与灌木层植物种类比例保持在1:3~1:6之间较为适宜[17],调查区域中绿地木本植物乔灌木树种比例为1:0.61,灌木层植物种类过少,达不到绿化种植合理指标.陈自新等提出绿地中乔、灌木数量的合理指标为1:6[18],调查区域中乔灌木数量比例为1:0.56,和合理搭配指标差距过大.应重点增加灌木种类和数量,并优化乔木和灌木的种类比例.
有些研究表明,城市绿地中植物的常绿树与落叶树的数量比例为2:3比较适宜[18],调查区域中常绿落叶树种数量比为1:2.03,应用的常绿树种数量较少,应增加常绿树种的数量,提升常绿乔木在城市绿地中的数量比例.
-
东营市的城市绿地木本植物在生长习性和观赏性方面资源有限.据调查,乡土树种和经过长年驯化适应当地气候的栽培种使用频度较高,但乡土树种种类应用少,与外来树种比为1:3. 《东营市城市绿地系统规划2018-2035年》提出在城市绿化建设中应多运用乡土树种,同时在绿地建设中,应加强同纬度耐盐碱植物的引种试种工作并注重盐生及耐盐碱植物的运用.通过选育适合本地的物种,丰富本地区的新物种,从而降低建设成本.并且注意防止盲目引进和滥栽滥伐,应加强利用东营市的乡土植物资源,形成具有东营市滨海特色的园林风貌.东营市乡土植物可选乔木有:蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)、朴树(Celtis sinensis)、臭椿、元宝枫(Acer truncatum)、沙枣(Elaeagnus angustifolia)、大叶白蜡(Fraxinus rhynchophylla)等;可选灌木种类有:紫穗槐、锦鸡儿(Caragana sinica)、荆条(Vitex negundo var. heterophylla)、鸡桑(Morus australis)、扁担木(Grewia biloba var. parviflora)等.
-
园林应用的常绿树种和彩色观赏树种较少,色彩多以绿色为主,有部分黄色、粉色、紫色等树种,但数量较少.根据植物不同的观赏特性,可选用观花的植物如麻叶绣线菊(Spiraea cantoniensis)、红花碧桃(Amygdalus persica var.persica f.rubro-plena)、珍珠梅(Sorbaria sorbifolia)、合欢(Albizia julibrissin)、月季(Rosa chinensis)等;观叶的植物如美人梅(Prunus × blireana cv. ‘Meiren’)、鸡爪槭(Acer palmatum)、乌桕(Sapium sebiferum)、梧桐(Firmiana platanifolia)、金叶榆(Ulmus pumila cv.‘Jinye’)等;观果的植物如白杜(Euonymus maackii)、西府海棠(Malus × micromalus)、白梨(Pyrus bretschneideri)、沙枣(Elaeagnus angustifolia)等;观枝干的植物如红瑞木(Swida alba)、白皮松(Pinus bungeana)、龙爪槐(Sophora japonica f. pendula)等.
-
在城市绿地木本植物重要值较高的树种中,乔木层多于灌木层,乔木层物种组成较复杂,生态能力高于灌木层,但种植较分散;而灌木层优势度指数高,优势种突出,种植集中化明显.各城区应增加重要值较高的灌木层树种种类和数量.
在绿化建设中,个别乡土树种占比过高,容易出现“百路一树”的雷同景观.其原因与东营市土壤结构性质有关,应增加重要值低但长势好、观赏佳的树木.并引种驯化新树种使其适应当地环境,提升整体木本植物优势度.
西城区的优势种集中程度较弱、分布分散;其他城区优势种分布相对集中.在西城区可实施近自然模式[19],应用重要值低但长势佳的树种如英桐(Platanus acerifolia)、樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)、山杨(Populus davidiana)、榆叶梅(Prunus triloba)等,提升物种优势度,同时完善了生态系统结构.技术开发区存在单一树种群植的现象,在植物选择方面,增加重要值较高的木本植物种类和数量使其优势度提升.形成以植被系统稳定性、生物多样性和多功能性为目标的具有景观效果的近自然绿地[20].
-
东营市3个城区木本植物物种多样性差异较大.这与城区的建设年限、种植结构、养护管理不同有关.也与城市化导致的外来物种增多,乡土树种减少,广适性物种逐渐增加有关.
东城区绿地规模较大,其木本植物物种丰富度和多样性指数较高,在绿地生态环境质量、木本植物多样性、乔灌木复层种植、彩色观赏树种搭配等方面较好.但相比于乔木层,灌木层的丰富度和多样性较低,可增加灌木层植物种类和数量进行改善.
西城区是旧城区,绿地植物多以乡土树种为骨干树,乔木层植物分布较分散、物种丰富度低;灌木层植物长势较差,多以自然式为主,人工痕迹较少,景观效果不佳.可在原基础上进行改造,增加重要值较高、观赏性较强的树种种类和数量,形成景观协调、开放互通、生态多样的绿地景观.
由于开发晚,技术开发区的绿地面积小、分布散乱,造成物种多样性指数偏低、均匀度指数偏高,同时,灌木层植物丰富度低,个别树种单一均等化种植,集中性强,抗病虫害能力弱,使本区域的整体生态与景观功能较弱.可适当增加人工绿地如植物专类园,形成植物的引种驯化基地,加大植物育种工作,丰富植物生物多样性的同时提高绿化效益.
为提升城市绿地多样性水平,减少各城区植物物种多样性差异,使其均衡化发展,达到最佳综合效益,提出3点措施:第一,针对东营市木本植物物种多样性水平的调研结果,建议将所有绿地进行串联,形成踏脚石、廊道结构以体现滨海油田城市特色的绿地网络,促进植物自身传播降低管理成本,优化城市植物物种多样性布局,加强植物物种多样性保护,增加植物物种丰富度,提高生态系统的稳定性,为动植物的迁徙提供连续的生态空间.第二,针对各城区木本植物物种多样性差异较大的结果,建议在植物选择方面要关注植物自身特性,因地制宜,以近自然模式进行植物造景,关注植物的美景度和生态效益,提升各城区植物物种多样性水平.第三,针对滨海油田城市的特殊土壤导致的植物选择问题,建议进行土壤改良,降低土壤盐分含量,提高绿化树种的多样性.
3.1. 优化城市绿地木本植物应用
3.1.1. 增加灌木及常绿木本植物种类与数量
3.1.2. 增加乡土木本植物种类与数量
3.1.3. 增加彩色观赏木本植物种类和数量
3.2. 提高城市绿地优势植物物种的种类和数量
3.3. 提升城市绿地木本植物物种多样性水平
-
本文以东营市建成区为例,调查木本植物种类构成与分布,探讨木本植物物种多样性特征以及物种多样性与城区分布之间的关系,明确城市化对物种多样性的潜在问题.结果表明,在滨海城市园林绿化表现优良的树种未能充分利用;乡土树种较少,引进外来树种应用状况不佳;新建城区的绿地树种多样性有待提高.因此,东营市应注重加强植物的引种驯化工作,完善物种应用数据库,改良土壤,提高乡土树种比例、扩大种植范围.以丰富城市绿化树种多样性,优化植物复层结构,建立绿地网络模式.力求形成多样化、自然化、稳定化、平衡化的绿地系统,为东营市绿化树种选择和配置提供参考依据,为形成滨海盐生植物特色构建理论基础,营造高质量的绿地生态环境,实现生态园林城市的综合效益.



 下载:
下载: