-
铬及其化合物是重要的化工原料,广泛用于制革、电镀和颜料生产等.由于其具有致癌、致突变性质,这些工业排放的含铬Cr(Ⅵ)废液对环境和人类健康产生了严重威胁.为此,建立了多种技术方法用于去除Cr(Ⅵ),如化学还原、离子交换和吸附法[1-3]等.吸附法具有简单、易操作、成本低等优点,受到广泛关注.目前,基于微生物细胞[4]、壳聚糖[5]和农业副产物[6]的生物吸附剂已用于Cr(Ⅵ)去除,具有成本低、无毒和来源丰富等优点.壳聚糖(CTS)是一种很有潜力的生物吸附剂,因为CTS易生物降解,而且其分子链中含有丰富的功能基团(—NH2和—OH)等[7].然而,未修饰的CTS难以从废水中分离出来,因此,多种磁性CTS吸附剂应运而生,已用于去除Cr(Ⅵ)[7-8].然而在多数情况下,这些MCTS合成过程复杂,至少包括三步:首先合成磁性Fe3O4纳米颗粒,其次对其表面进行修饰,最后再将CTS嫁接在其表面.而且,已经报道的MCTS对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量有限,如Hu等[9]用乙二胺修饰的交联CTS对Cr(Ⅵ)的最大吸附容量仅为51.81 mg/g,为改善其吸附容量,王文凤等通过一步热溶剂法简单快速地合成了200 nm左右的MCTS微球,该微球对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附容量可达129.6 mg/g,而且吸附在10 min内达到平衡[10].聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)是具有支链结构的阳离子聚电解质,其分子链上富含大量氨基,在较宽的pH值范围内都可以质子化带正电荷,可与带负电荷的阴离子通过静电作用实现去除.本研究先通过一步热溶剂法合成纳米颗粒MCTS,再通过交联法将PEI修饰在其表面,从而进一步提高吸附剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附能力.
全文HTML
-
所有化学试剂的使用都没有经过进一步的纯化.脱乙酰度为91.1%的CTS(平均分子量为3.0×105 g/mol)购自南通兴成生物制品厂.聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)(Mw,18000)购自上海Sigma-Aldrich有限公司. NaAc购买于科龙化学试剂有限公司.其他试剂,如乙二醇、丙酮、乙醇等均购自重庆化学试剂有限公司. UV-2450型紫外-可见分光光度计(岛津公司,苏州);ZHWY-2102C型恒温振荡培养箱(上海智城仪器制造有限公司,上海).
-
将2 g FeCl3·6H2O溶于60 mL乙二醇中,加入4 g NaAc后,磁力搅拌使其完全溶解后,再加入CTS 4 g,并搅拌12 h,之后将混合溶液转移至反应釜中加热到200 ℃,并在该温度下反应8 h后冷却至室温得到黑色材料,依次用去离子水和乙醇洗3遍,分离后的材料在60 ℃下干燥即得MCTS.为制备PEI-MCTS,将0.3 g MCTS加入到50 mL PEI溶液中,超声20 min后,在室温和300 r/min机械搅拌条件下逐滴加入25 mL体积分数为5%的戊二醛水溶液,继续搅拌30 min后,用超纯水冲洗材料直至上清液清澈,固体材料在50 ℃下干燥,即得PEI-MCTS.
-
在一系列100 mL锥形瓶中,分别加入50 mL Cr(Ⅵ)溶液和5 mg吸附剂,置于摇床中以180 r/min转速摇一段吋间,吸附完成后,磁性分离,取上清液测定Cr(Ⅵ)的质量浓度.每一组实验均设置平行样,所有结果取两个平行样的平均值. Cr(Vl)溶液初始pH值用稀NaOH溶液或稀HCl溶液调节.上清液中Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法测定.计算吸附容量:
式中,qe为吸附容量(mg/g);Co和Ce分别为Cr(Ⅵ)的初始质量浓度和平衡质量浓度(mg/L);V(mL)是Cr(Ⅵ)溶液的体积;m(mg)是PEI-MCTS的质量(g).
1.1. 仪器及试剂
1.2. PEI-MCTS的制备
1.3. 吸附实验
-
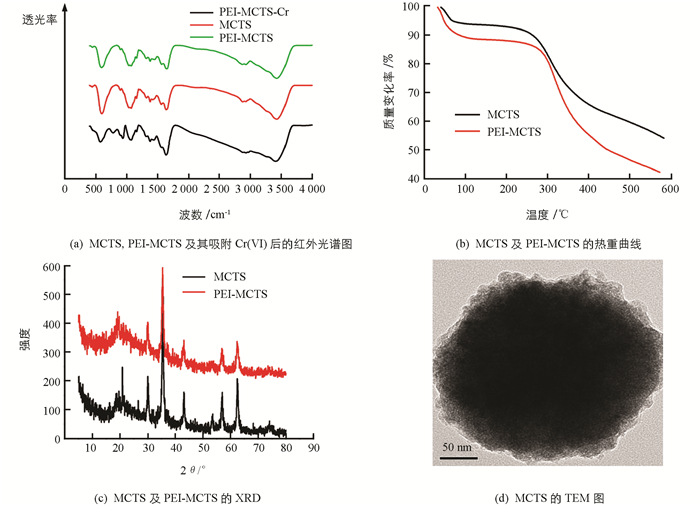
图 1(a)是MCTS、PEI-MCTS及其吸附Cr(Ⅵ)后的红外光谱图,可见MCTS和PEI-MCTS中呈现CTS的主要特征峰:3430 cm-1(—OH,—NH2的伸缩振动峰)[11]、2 878 cm-1(—CH伸缩振动)、1 657 cm-1(—NH2弯曲振动)、1 379 cm-1(—CH弯曲振动)、1 081 cm-1(C3处C—O伸缩振动) [12],而550 cm-1处为Fe3O4中Fe—O振动峰[13],说明MCTS合成成功.吸附Cr(Ⅵ)后,PEI-MCTS的—NH2伸缩振动峰偏移至3 408 cm-1,表明氨基参与了Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附.另外,在777 cm-1和934 cm-1处出现了新峰,分别对应Cr—O和Cr = O的吸收峰[14],进一步表明Cr(Ⅵ)成功吸附在PEI-MCTS上.
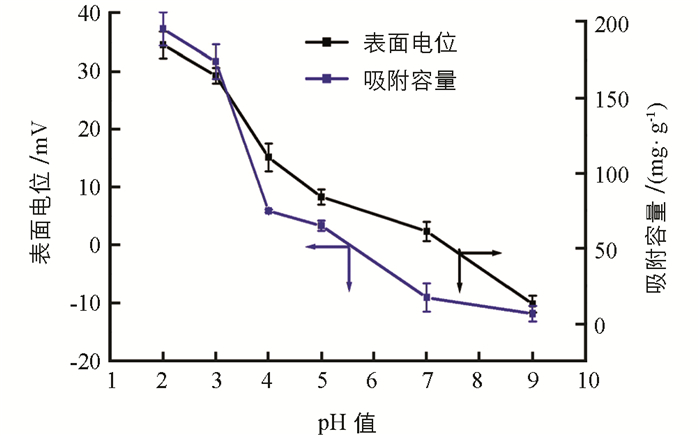
从热重曲线可以看出(图 1(b)),温度100 ℃下,MCTS,及PEI-MCTS的质量分别下降了6%和12%,这是材料中水蒸发的原因.当温度从100 ℃升高到250 ℃时,材料无明显质量损失,继续升高温度至600 ℃时,材料质量损失明显,这是由于CTS和PEI热解所致,表明PEI成功修饰到CTS上. XRD结果表明(图 1(c)),MCTS及PEI-MCTS呈现Fe3O4的(220)、(311)、(400),(422)、(511)和(440)面的衍射峰,但PEI-MCTS的特征峰比MCTS的特征峰弱,这是由于引入PEI的缘故.另外,在20°处有一个明显的衍射峰,其来自CTS. 图 1(d)为MCTS的TEM图,可以看出,MCTS呈球形,颗粒粒径大小在200 nm左右.从图 2可知,随着pH值升高,PEI-MCTS表面的电位逐渐下降,在酸性条件下材料有较高的zeta电位.这是因为酸性条件下,材料表面的氨基会被质子化从而得到较高的电位.
-
实验研究了初始pH值对Cr(Ⅵ)吸附的影响,从图 2可见,酸性条件下材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除能力明显优于碱性条件.这是因为在酸性条件下,材料表面的—NH2会被质子化形成带正电荷的—NH3+,其会与阴离子Cr(Ⅵ)(当pH值低于6.8时,HCrO4-是Cr(Ⅵ)的主要存在形式;当pH值高于6.8时,HCrO4-会完全转化为CrO42-)发生静电吸附作用,实现对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除.
-
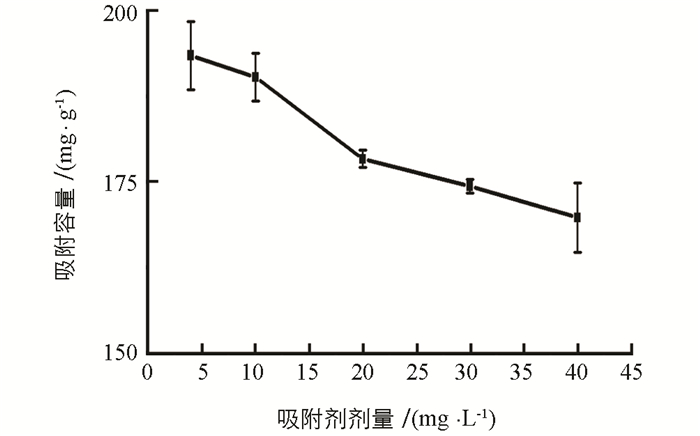
实验研究了0,5,10,20,30,40及50 g/L PEI质量浓度的影响,结果表明,得到的PEI-MCTS对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量分别为115.45,177.28,190.91,192.45,190.21,191.78及190.34 mg/g,可见,Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量随PEI质量浓度的增加而增加,但PEI质量浓度超过20 g/L时,吸附容量变化较小.实验选择20 g/L PEI进行MCTS的功能化.考察了吸附剂用量的影响(图 3),Cr(Ⅵ)吸附容量随吸附剂用量增加而降低,为确保材料对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量,实验选择其剂量为5 mg/L.
-
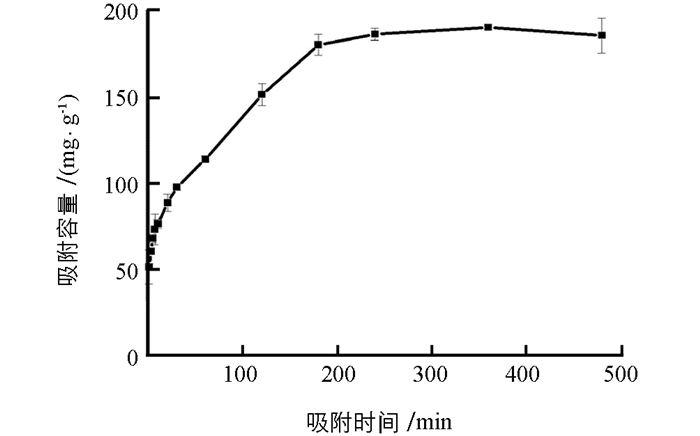
图 4所示为吸附时间对PEI-MCTS去除Cr(Ⅵ)的影响,可见,PEI-MCTS吸附Cr(Ⅵ)在3 h之前随时间增加,吸附容量显著增加,超过3 h后吸附达到平衡,实验选择吸附时间为3 h.用吸附准一级和准二级动力学模型对实验数据进行拟合:
其中:qe和qt分别代表平衡时的吸附容量和时间为t时的吸附容量. k1(min-1)和k2(g (mg·min)-1)分别是准一级和准二级速率常数.拟合结果表明,准二级动力学模型得到的qe为192.08 mg/g,非常接近实验值190.54 mg/g,而且r2>0.99,表明吸附更符合准二级动力学模型,说明PEI-MCTS吸附Cr(Ⅵ)一个化学吸附过程.
-
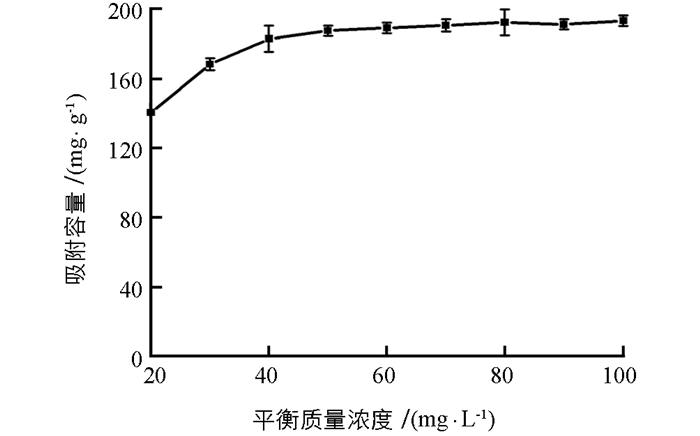
吸附等温线列于图 5,可见,Cr(Ⅵ)吸附容量在其初始质量浓度为70 mg/L达到平衡.分别用Langmuir(方程3)和Freundlich(方程4)对实验数据进行拟合:
式中:Ce(mg/L)代表吸附平衡时Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度,qe(mg/g)是吸附平衡时Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量,b(L/mg)是和吸附能量相关的Langmuir常数,qmax(mg/g)表示是最大吸附容量. K和n表示Freundlich吸附常数. Langmuir模型(r2=0.995 8)拟合效果要好于Freundlich模型(r2=0.876 4),这说明该吸附是一个单分子吸附过程,对Cr(Ⅵ)的最大吸附容量为193.57 mg/g.
-
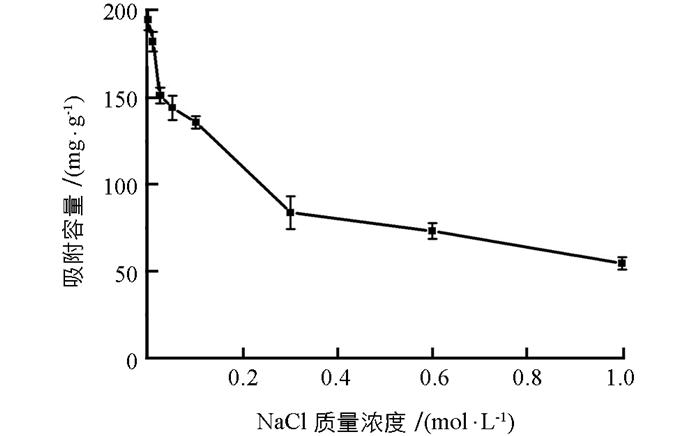
实验研究了不同浓度NaCl (0~1 mol/L)对PEI-MCTS吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的影响.结果见图 6,可见,NaCl对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附有非常显著的影响.在考察的浓度范围内,随着NaCl浓度升高吸附容量迅速下降,例如当NaCl浓度从0 mol/L升到0.1 mol/L时,吸附容量从194.72 mg/g降到135.80 mg/g.这可能是因为NaCl中的Cl-与Cr(Ⅵ)产生了竞争吸附.
-
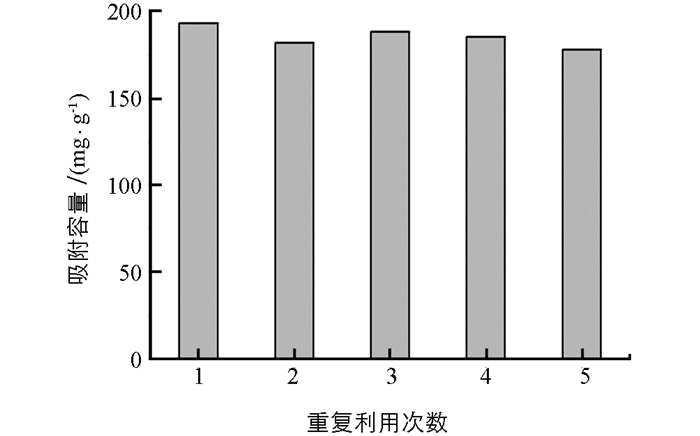
用0.5 mol/L NaOH作为洗脱剂,对吸附Cr(Ⅵ)后的PEI-MCTS材料进行再生后用于Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附,以考察其重复利用性能,结果见图 7.可见,材料在重复使用5次之后,对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附容量是第一次吸附容量的95%,显示了材料良好的重复利用性能.



 下载:
下载: