-
草地贪夜蛾(Spodoptera frugiperda),别名伪黏虫、秋行军虫、秋黏虫,隶属鳞翅目Lepidoptera,夜蛾科Noctuidae,灰翅夜蛾属Spodoptera,是一种原产于美洲热带和亚热带地区的重要农业入侵害虫,具有迁飞性、杂食性和暴发性等特点[1-4].草地贪夜蛾飞行能力强,迁移扩散速度快,能快速、大范围扩散蔓延,造成粮食作物的严重损害[5-6]. 2019年1月11日,我国云南省普洱市江城县首次发现草地贪夜蛾入侵,而后其迅速向邻近省份扩散,快速迁飞到长江中下游、黄淮、华东、东北和西北等地[7].截至2019年5月10日,草地贪夜蛾已扩散至全国13个省261个县(市、区),而截至2019年7月5日,草地贪夜蛾已蔓延至全国20个省市(自治区)1 128个县(市、区)[8],造成了我国农业生产的巨大经济损失[9].
昆虫肠道作为昆虫的一个重要器官,多种复杂的微生物定殖于此,构成了一个相对稳定的肠道微生态系统,该系统在宿主的营养消化、免疫防御、信息素合成等多个方面起着重要的作用[10-12].目前,在常见昆虫中已经发现的肠道微生物包括细菌、真菌和古细菌,其中昆虫肠道细菌菌群研究报道较多,而对肠道真菌的研究报道较少.本课题组在前期对草地贪夜蛾肠道优势细菌研究的基础上[13-15],以重庆巫山地区玉米田及重庆江津地区高粱田中的草地贪夜蛾幼虫为样本,通过传统培养法以及rDNA ITS测序对草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌进行初步分离鉴定,以期为后续深入研究草地贪夜蛾肠道微生态与宿主间关系奠定基础.
全文HTML
-
草地贪夜蛾幼虫采自重庆巫山玉米田及重庆江津高粱田中.
-
马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(PDA);ITS1,ITS4引物,r Taq PCR酶(上海生工生物工程股份有限公司).
-
选取不同来源地的草地贪夜蛾幼虫新鲜粪便样品作为实验材料,在超净工作台上进行分离操作.取草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便置于无菌1.5 mL EP管中,向离心管中加入1 mL灭菌PBS缓冲液,高速涡旋震荡,混匀备用.
取20 μL氨苄青霉素及卡那抗生素均匀涂布于PDA平板上,晾干.再分别取20 μL上述粪便悬浊液涂布于处理后的PDA平板上,放置于30 ℃恒温培养箱中倒置培养.待菌落长出后,初步根据菌落形态、大小和颜色等特征选取单菌落,从菌落边缘挑取少量,再次转接至PDA培养基平板上,多次纯化,由此获得菌株纯培养物.
-
将分离纯化的菌株接种到PDA平板中央,置于30 ℃恒温条件下培养,定期观察菌落生长情况,记录其颜色及形态,并在光学显微镜下观察菌株形态,参照《酵母菌的特征与鉴定手册》[16]、《真菌鉴定手册》[17]等对分离到的菌株进行初步鉴定.
-
使用CTAB法[18]提取菌株的基因组DNA,DNA用NanoDrop ND-2000仪器测定浓度,-20 ℃储存用于后续实验.
采用真菌通用引物ITS1(5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′)和ITS4(5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′)进行ITS序列扩增.反应体系:模板DNA 2.5 μL,引物ITS1/ITS4各1 μL,r Taq酶12.5 μL,无菌水补足至25 μL.反应程序为:94 ℃预变性10 min;94 ℃变性30 s,51 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min.将扩增产物送往上海生工生物工程股份有限公司测序.将所得基因序列与GenBank数据库中保存的基因序列进行比对,得到与目的菌株具有同源性的多株菌株相应序列.从中选择下载同源性较高的序列,使用MEGA5.2软件,运用NJ法进行1 000次步长计算,构建系统发育进化树.
1.1. 供试昆虫
1.2. 供试培养基与主要试剂
1.3. 草地贪夜蛾幼虫肠道真菌的分离
1.4. 肠道真菌的形态学鉴定
1.5. 肠道真菌的分子学鉴定
-
将来自重庆巫山玉米田及重庆江津高粱田的不同草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便匀浆,均匀涂布于PDA平板上,分离获得草地贪夜蛾幼虫肠道菌株.从重庆巫山玉米地草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便样品中分离纯化得到7株真菌,分别编号WSF-1到WSF-7.从重庆江津高粱地草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便样品中分离纯化得到3株真菌,编号为JSF-1到JSF-3.
-
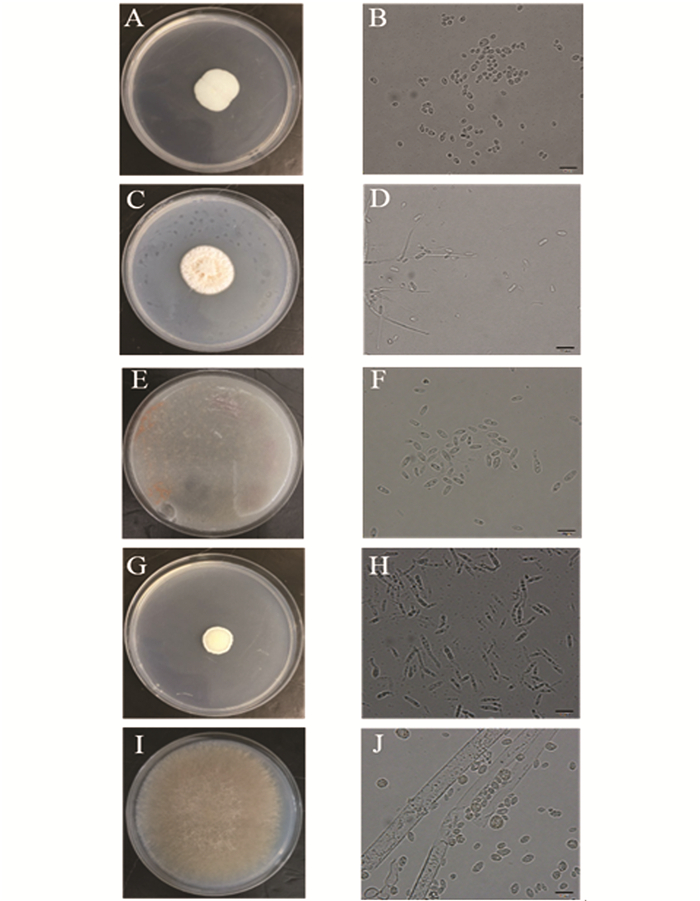
通过菌株形态学观察,从来自重庆巫山玉米田及重庆江津高粱地的不同草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便样品中共得到5个属的肠道真菌菌株,其中菌株WSF-1,WSF-4和JSF-3归类于念珠菌属(Candida),菌株WSF-2,WSF-3,WSF-5和WSF-6归类于帚枝霉属(Sarocladium),菌株WSF-7属于掷孢酵母属(Sporobolomyces),菌株JSF-1属于莫氏黑粉菌属(Moesziomyces),菌株JSF-2属于毛霉属(Mucor).各属的菌落与细胞形态观察如图 1所示.
1) 念珠菌属(Candida):图 1(A),菌落较小,生长速度慢,呈乳白色奶油状,不透明,边缘不整齐,中间有凸起. 图 1(B),单细胞,出芽生殖,可形成假菌丝,营养细胞呈球形或卵形.
2) 帚枝霉属(Sarocladium):图 1(C),菌落生长迅速,呈橙红色. 图 1(D),分生孢子梗简单,偶尔分枝.分生孢子分为黏性头,圆柱形或椭圆形,透明.
3) 掷孢酵母属(Sporobolomyces):图 1(E),菌落呈圆形凸起、表面光滑、湿润黏稠、边缘齐整,粉红色. 图 1(F),菌体细胞呈现大小不等的椭圆形,形成肾形的掷孢子,有明显的出芽生殖特征,与普通酵母相似.
4) 莫氏黑粉菌属(Moesziomyces):图 1(G),菌落较小,正面呈淡黄色不透明状,背面呈鹅黄色,酵母样形态. 图 1(H),菌落干燥,有明显的皱褶,边缘不整齐.双核菌丝,冬孢子球呈球形、卵形.
5) 毛霉属(Mucor):图 1(I),菌落形态较大,质地疏松,外观干燥,不透明,疏松绒毛状,菌落与培养基间的连接紧密. 图 1(J),其具有发达的菌丝体,菌丝无隔多核.菌丝初期白色,后变为灰白色.无假根和匍匐枝形成,孢子囊球形,成熟后易破裂,散发出大量的孢子囊孢子.
-
将分离纯化得到的菌株采用CTAB法提取DNA进行PCR扩增,扩增产物测序后在GenBank中进行BLAST同源性检索,选取相关序列通过Mega 5.2,使用N-J进行1 000次步长计算,构建系统发育树(图 2).结果表明,草地贪夜蛾肠道分离的可培养真菌在进化树上形成不同的分支,物种丰富度较低.在基于ITS rDNA序列片段构建的系统发育进化树中,菌株WSF-1,JSF-3与KT876709.1 Candida intermedia聚为同一分支;菌株WSF-4与KP131721.1 Candida intermedia聚为同一分支;菌株WSF-2,WSF-3,WSF-5和WSF-6与GQ167229.1 Sarocladium zeae,KT878336.1 Sarocladium zeae聚为同一分支;WSF-7与MK592826.1 Sporobolomyces carnicolor,LC191346.1 Sporobolomyces carnicolor聚为同一分支;JSF-1与LC368626.1 Moesziomyces antarcticus聚为同一分支;JSF-2与MG583964.1 Mucor irregularis聚为同一分支.与形态学鉴定结果相结合,将菌株WSF-1,WSF-4和JSF-3归类于念珠菌属(Candida),菌株WSF-2,WSF-3,WSF-5和WSF-6归类于帚枝霉属(Sarocladium),菌株WSF-7归类于掷孢酵母属(Sporobolomyces),菌株JSF-1归类于莫氏黑粉菌属(Moesziomyces),菌株JSF-2归类于毛霉属(Mucor).
2.1. 草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌的分离纯化
2.2. 肠道真菌的形态学鉴定
2.3. 肠道真菌的分子生物学鉴定
-
本实验通过分离培养重庆不同地区、不同食物的草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌,结合形态学观察及rDNA ITS测序完成属水平的鉴定,共分离得到10个真菌分离株,其中分离自重庆巫山玉米田草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌归为3个属,分别为念珠菌属(Candida)、掷孢酵母属(Sporobolomyces)和帚枝霉属(Sarocladium);分离自重庆江津高粱地草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌归为3个属,分别为念珠菌属(Candida)、莫氏黑粉菌属(Moesziomyces)和毛霉属(Mucor).将测序得到的草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌ITS序列进行系统进化分析,草地贪夜蛾肠道分离的可培养真菌在进化树上形成了不同的分支,物种丰富度较低.念珠菌属在两地草地贪夜蛾幼虫粪便样品中均分离得到,可以推测念珠菌属可能是定殖于草地贪夜蛾肠道的菌群.同时,课题组发现同种昆虫的肠道微生物种类和丰度出现了差异,可能是由于食物和地域的不同所致[19-20].
昆虫肠道内环境里存在着真菌菌群,在漫长的进化过程中两者逐渐形成了复杂而密切的关系,进一步探究两者间的进化关系,有利于防治昆虫病害,也有利于从昆虫肠道这一特殊环境中获得特殊功能的菌种资源[13, 21].例如,念珠菌属作为重要的昆虫肠道共生菌,从甲虫等昆虫的肠道中常分离到新种[22-23],Candida intermedia可以产生抑制灰霉病菌菌丝生长和分生孢子萌发的挥发性物质,具有抗菌活性成分,可作为生防因子防治草莓灰霉病、番茄灰霉病等植物病害[24];帚枝霉属曾从白蚁肠道中分离得到,能水解纤维素和木聚糖[25],也是一种植物病原菌,会引起水稻叶鞘腐败病、茎节腐烂病等病害,造成严重的损失[26-27];掷孢酵母属在自然环境中分布广泛,常见于空气、植物的叶片等处,且适应能力较强,应用广泛,是真菌中最普遍的石油烃降解菌之一,有利于污水治理[28];Moesziomyces antarcticus最初从南极洲Vanda湖中沉积物样品中分离得到,研究表明其可降解部分塑料,是一种重要的糖脂表面活性剂甘露糖赤藓糖醇脂质(MELs)的重要生产者[29];毛霉属在土壤、粪便及空气等环境中广泛存在,菌丝致密、柔软,有利于腐乳形成皮膜,同时能产生高活力蛋白酶,能保证大豆蛋白质的适度分解等,在腐乳生产中占据重要的地位[30].
研究发现,邵明伟[31]从蜻蜓目蜻蜓肠道内分离出曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.),弯孢霉属(Curvularia sp.),芽枝霉属(Cladosporium sp.),刺孢壳属(Chaetomella sp.),镰刀菌属(Fusarium sp.),青霉属(Peuicillium sp.)和茎点霉属(Phoma sp.);陈君芝等[32]从直翅目中华剑角蝗中分离出青霉属(Peuicillium sp.),曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.),镰刀菌属(Fusarium sp.),从赤壳属(Nectria sp.),茎点霉属(Phoma sp.),刺盘孢属(Colletotrichum sp.),节菱孢属(Arthrinium sp.)和隔孢伏革属(Peuiophora sp.);俞和韦等[33]从鳞翅目贡嘎蝠蛾幼虫肠道分离出隐球酵母(Cryptococcus magnus),丝孢酵母(Trichosporon porosum)和地丝霉属(Geomyces sp.).这些肠道真菌菌株未从本次研究中分离获得,且不同物种的昆虫肠道真菌分离鉴定情况也有所不同,表明不同昆虫的肠道真菌群落组成具有特异性.
本课题组首次在国内报道了重庆地区玉米田及高粱田中草地贪夜蛾的肠道真菌分离株,初步探究了地域、食物对草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌菌群组成的影响,实验证明草地贪夜蛾肠道真菌组成会受到环境因素的影响,为后续研究奠定了基础.目前,对于肠道真菌与昆虫相互作用的研究还较少.本实验中分离到的真菌对草地贪夜蛾肠道内微生态的作用以及是否与草地贪夜蛾幼虫的生长发育有关,还有待进一步分析.近几年来,随着宏基因组等非培养法的应用,更加有利于深入了解肠道微生物的结构组成,探究肠道微生物的种群结构及多样性特征,将传统培养技术与新技术相结合,为实现草地贪夜蛾生物防治提供了更好的方法.



 下载:
下载:
