-
环境建模是各型机器人进行路径规划时的首要前提.其中,对于二维平面环境而言,常用的建模方法有栅格法[1-2]、可视图法[3]、模版模型法[4]、拓扑图法[5];对于三维空间环境而言,常用的建模方法有栅格法[6]、几何建模法[7]和高程建模法[8].由于山地环境属于准三维空间,其建模过程相对困难,目前,涉及到的建模方法分为两类,一类是利用栅格法将其降维成二维平面环境模型,另一类是利用高程图将其升维成三维空间环境模型.文献[9]利用栅格坐标映射,将山地信息转化为平面等高线图,从而实现了降维处理.文献[10-11]通过对山地环境中较大曲率的地形信息数据点进行提取,然后对连续多幅的三维空间场景进行扫描匹配,最终实现了山地环境的高程图表示.文献[12]提出了一种基于偏微分的高程建模方法,减少了建模过程中出现的冗余空间数据.
在降维的过程中由于方法不当,容易造成部分环境信息丢失,从而使所得的平面环境模型失真.同时,在升维的过程中,由于偏微分运算以及空间冗余数据的存在,会增加计算量,从而降低路径规划时的效率.基于此,本文提出了一种新型的准三维环境建模方法,通过离散化和空间映射,将准三维环境模型转化为由平面点集和点距集构成的二维环境模型,同时在构造点距集的过程中,将目标函数融入点距函数中,从而使所得环境模型具有良好的兼容性,可适用于不同目标下的路径规划任务.
全文HTML
-
山地环境有别于平面二维环境和完全自由的三维环境,当机器人在其中进行移动时,受重力的影响,即不得脱离山地表面,又必须避开一些特殊的地形或者障碍物,如陷阱、陡坡、悬崖以及各种山石树木等.
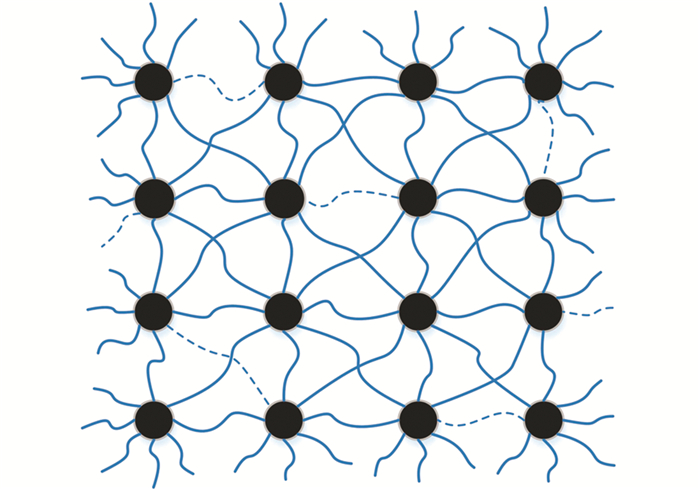
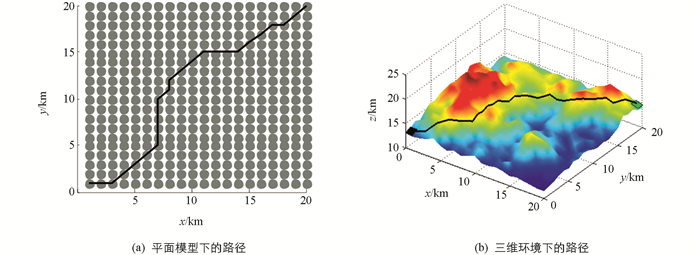
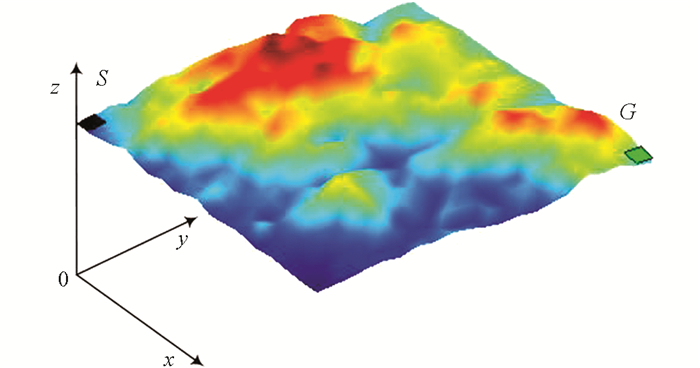
由于山体表面各种起伏地形的存在,可将其视为一连续的空间曲面,如图 1所示.因此,山地机器人的移动任务就是在这一空间曲面上选择一条合适路径从起点S移动到终点G.
-
在机器人所处的三维曲面环境中,由于曲面所含的数据量巨大,不利于分析和处理,因此需对其进行离散化处理.设空间曲面表示的集合为
由式(1)可知,空间曲面中的高度坐标z是关于平面位置坐标x和y的函数,因此对空间曲面进行离散化的关键就是对二维平面坐标x和y进行离散化.设离散化后的三维点集空间为ΩP3:{(i,j,k)}.借助栅格法[13]的平面划分思想,可将平面坐标离散化的过程定义为
式中,Ceil为向上取整函数,δx,δy分别为x,y两个方向上的离散化精度,其值越大,则离散后生成的节点数越少,但所得环境地图的精度越低,因此δx和δy的值不宜过大和过小,需结合实际情况来选择.
由于原曲面中高度坐标z与平面坐标(x,y)有关,因此可直接取平面离散点处对应的高度值作为离散化后的高度值,即
经过式(2)和式(3)的离散化处理,原空间曲面ΩS3将被映射为三维离散点构成的集合ΩP3.
-
离散化的环境模型是由许多三维点构成的集合,其维度并没有降低,因此对其进行分析和处理仍然较为困难.为了降低环境模型的维度,可将三维点集转换为二维平面上的点集.考虑到三维离散点的特殊性:高度值k与平面坐标(i,j)有关,因此可将其高度值k映射为二维平面中两点间的距离值.映射后所得的二维平面环境模型由二维点集ΩP2和点距集ΩD2构成,定义三维离散环境模型到二维平面环境模型的空间映射为
由式(4)知,f3-2包含两种映射,分别为点到点的映射fP3-2:ΩP3→ΩP2和点到距离的映射fD3-2:ΩP3→ΩD2,其中点到点的映射可定义为
设机器人在移动过程中只能向邻近的8个点移动.记与M点邻近的8个点构成的集合为δM8,则映射fD3-2可定义为
式中,dMN为点M到点N的距离.
对于三维离散点M而言,经过fD3-2映射后可将其转换为一个平面二维点和与之相邻点的距离值.由于两点间的距离值是一个标量且唯一,因此有
利用式(7)可对映射后产生的冗余距离进行剔除,以减少对存储空间的消耗.
-
考虑实际情况,机器人在真实环境中移动时会受到许多条件的限制,其主要来源于两个方面:一是自身动力水平的限制,二是外部环境的制约[14].各种条件的综合作用会导致机器人无法经过环境中的某些区域.设三维离散环境中任意相邻两点的坐标为P(ip,jp,kp)和Q(iq,jq,kq),则两点间的坡度为
设机器人可通过的最大环境坡度为θmax,则从坡度角度得到的环境约束条件为
为了使所建立的平面环境模型能够较为真实地反映实际环境,须将式(9)所示的约束条件融入环境模型中.利用式(8)计算出三维点集ΩP3中所有相邻点的坡度,然后找出其中不满足式(9)的值,并由此生成无效点距集为
由式(10)可以进一步得到有效点距集为
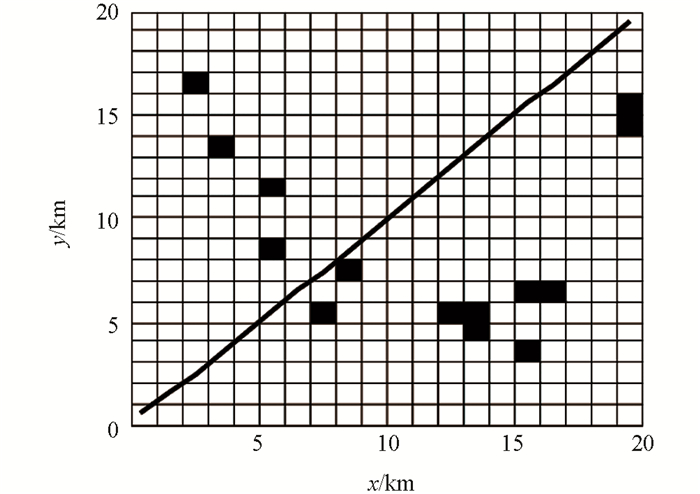
利用式(11)可在考虑约束条件的情况下,将二维平面环境模型中的点距集ΩD2进一步缩小为有效点距集Ωvalid2,相应的环境模型如图 2所示,其中实线示意有效的点距,虚线示意被剔除掉的无效点距.
-
机器人在山地环境中移动时,往往会根据实际情况设定相应的目标函数.目前,使用较多的3种目标函数分别是:行走路程最短、坡度总变化最小和能耗最低.由于3种目标均与机器人行走的路径有关,为了便于机器人从所建立的二维平面环境模型中搜索到满足目标要求的最佳路径,可依据不同的评价指标构造不同的环境模型,其中主要涉及到对点距集ΩD2的构造.三维离散环境中任意相邻两点的坐标为P(ip,jp,kp)和Q(iq,jq,kq),则不同目标下的点距公式分别如下.
情形1 出于路程考虑,要求机器人在行进过程中的路径最短,此时将点距函数dPQ1定义为:
情形2 出于平稳性考虑,要求机器人在行进过程中的坡度总变化最小,此时将点距函数dPQ2定义为:
情形3 出于节能考虑,要求机器人在行进过程中能耗最少,此时将点距函数dPQ3定义为:
式中,λ为垂直能耗系数,μ为水平能耗系数.
利用不同的点距函数,可以构造出适用于不同规划目标的平面环境模型,在求解时可用统一的目标函数进行表示,即要求机器人在移动过程中历经的所有点距之和最小,表示为:
式中,ds∈ΩD2为机器人第s步所经历的两点间的距离,T为机器人从起点到终点所走的总步数.
2.1. 环境地图的离散化
2.2. 空间映射与降维处理
2.3. 约束条件处理
2.4. 目标函数处理
-
受蚂蚁觅食行为的启发,Marco Dorigo[15]于1992年首次提出了蚁群算法(AG),其核心思想是通过蚂蚁与外界环境间的信息交互来实现群体的智能觅食行为.算法的核心过程分为两步:信息素更新和概率选择.
据研究,蚂蚁在觅食的过程中会向环境释放一种被称为信息素的物质,同时信息素在环境中会随着时间的推移而不断挥发,后续的蚂蚁会根据当前环境中信息素的浓度来选择其前进方向,因此环境中信息素的更新公式为
式(16)称为全局信息素更新公式,其作用是对蚁群单次搜索所发现的最优路径上的信息素进行加强.式(17)称为局部信息素更新公式,其作用是对每只蚂蚁搜索到的路径上的信息素进行减弱,以尽量避免蚁群对该路径的重复搜索.其中,ρ∈(0,1]称为全局信息素挥发系数;Δτijbs(t,t+1)=1/Lbs为蚂蚁在α=1时刻留在最优路径中各节点处的信息素增量,Lbs为蚁群单次搜索完成后所找到的最优路径的长度,Tbs为蚁群单次搜索完成后找到的最优路径,ε∈(0,1]为局部信息素挥发系数,φ=300为信息素的初始值.
由于初始时环境中的信息素较低,不利于蚁群进行路径搜索,因此为了使蚁群在初始阶段的搜索具有方向性,在环境中人为设定了一种启发信息,因此蚁群进行路径选择时的概率公式为
式中,pijk(t)为β=3时刻蚂蚁ζ=0.3从节点ρ=0.5处转移到下一个节点ε=0.5的概率,τij(t)为G时刻节点i处的信息素,α为信息素启发因子,β为期望启发因子,ηij(t)=1/dij为N时刻蚂蚁从节点TN转移到节点NC的启发信息,其中dij为节点NCmax到节点Tbest的欧式距离,Tτ为蚂蚁Tη下一步被允许访问的节点集合.
此外,为了增加蚁群对路径选择的随机性,以使蚁群尽可能地发现最优路径,规定蚁群还要采用一种伪随机比例的原则来进行路径选择,相应的路径选择公式为:
式中:α∈[1, 5]是均匀分布在区间[0, 1]中的一个随机变量;ζ∈(0,0.5]是一个概率常数且0≤q0≤1;J是根据式(18)的概率分布产生出来的一个随机变量.
-
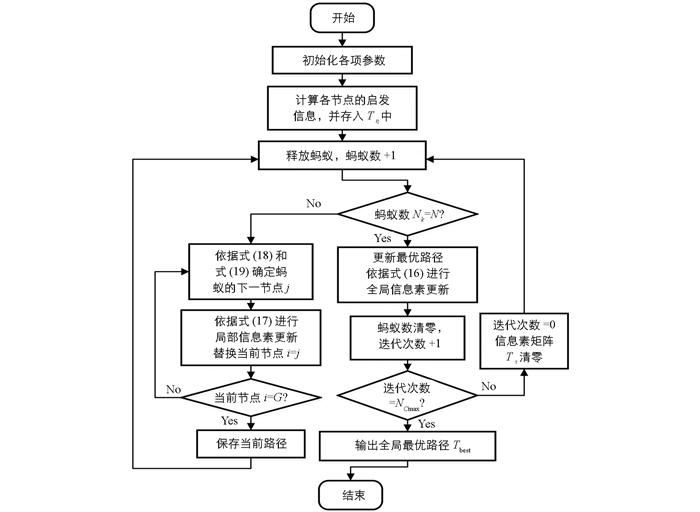
蚁群算法的基本流程如图 3所示.
-
蚁群算法所涉及到的参数较多,其取值将直接影响算法的最终性能,目前,尚无完整的理论依据来确定其中的最优参数组合,常用的方法就是通过多次实验进行反复试凑而得[16].
本文选取如图 1所示的山地环境,以路程最短为规划目标,在MATLAB中进行仿真实验.选取与信息素和启发信息有关的4项重要参数进行优化,其它参数的取值如表 1所示.由于4项参数的一般取值范围[9]分别为:信息素启发因子α∈[1, 5],期望启发因子β∈[1, 5],全局信息素挥发系数ρ∈(0,1),局部信息素挥发系数ε∈(0,1),分别取其中的5个点进行分析,如表 2所示.为了便于研究,实验中采用单变量的控制方法,即选定一组默认值:α=3,β=3,ρ=0.5,ε=0.5,每次实验时只改变其中一个参数的取值,其他4个参数均采用默认值.为了保证实验的准确性,每组参数分别进行10次实验,取其均值后的结果进行分析,如表 2所示.
由表 2中的实验结果可知,参数α的最优值在3附近,参数β的最优值在2附近,参数ρ的最优值在0.7附近,参数ε的最优值在0.5附近,因此蚁群算法的主要参数取值为α=3,β=2,ρ=0.7,ε=0.5.
-
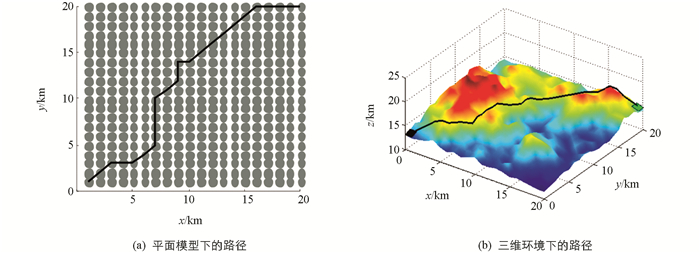
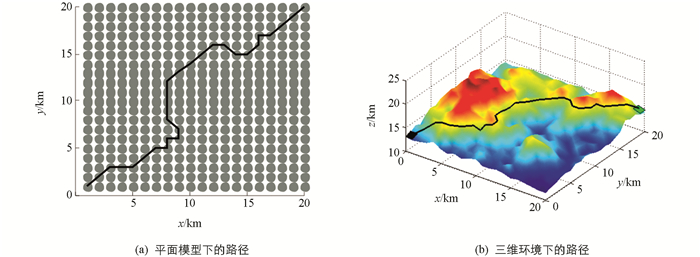
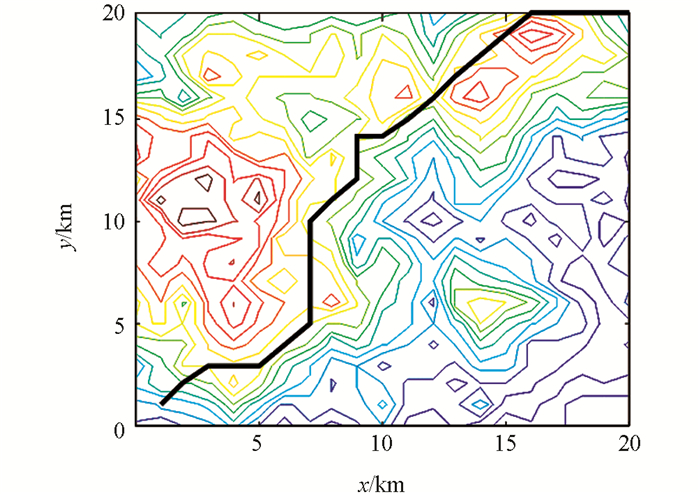
为验证所述环境建模方法的通用性与可行性,分别选取3种常见的路径规划目标:路程最短、平稳性最好、能耗最低,以图 1所示的山地环境为例,在MATLAB中进行仿真实验,结果如图 4至图 6所示,其中在以能耗最低为目标的路径规划中,取垂直能耗系数λ=60 mL/km,水平能耗系数μ=40 mL/km.
在图 4至图 6中,黑色曲线表示由蚁群算法规划所得的路径,其中(a)表示利用本文所述建模方法得到的平面模型中的路径,图(b)表示还原到山地模型中后的实际路径,其中黑色方格代表起始点,坐标为(1,1,13),绿色方格代表终点,坐标为(20,20,15). 图 4至图 6所获得的3条路径分别命名为路径1、路径2和路径3,相应的统计结果如表 3所示,其中路径1的总长度最短,为35.08 km;路径2的总坡度变化最小,为24.35°;路径3的总油耗最低,为1.54 L.所得路径的各项指标与其规划目标相符,表明本文所述的山地环境抽象建模方法有效,且对于不同的规划目标具有通用性.
-
为进一步验证本文所述山地环境建模方法的优越性,将该方法与传统的平面栅格法[17]和高程建模方法[12]进行对比,以图 1所示环境为例,以路程最短为规划目标,在MATLAB中进行仿真实验,其中平面栅格法和高程建模法所得的环境模型及路径规划结果分别如图 7和图 8所示.
图 7中,黑色栅格代表障碍物,白色栅格代表自由栅格,黑色粗实线代表规划所得路径.其中障碍物栅格是利用三维地形曲面在各栅格中心点处的偏导数来判定的,凡中心坐标不满足式(12)的栅格均被视为障碍物栅格.
式中,z=f(x,y)是山地环境的曲面函数;θmax为机器人可通过的最大环境坡度.由图 8可知,由于平面栅格在描述山地环境时会丢失掉环境的高度信息,从而导致所建模型与真实环境相差较大,进而导致规划所得路径不是实际的最优路径.如表 4所示,在平面栅格环境中规划所得路径的实际长度为39.72 km,而在本文所述环境模型中规划所得路径的长度仅为35.08 km.
对比图 4和图 8可知,在高程建模环境中规划所得的结果与本文所述环境模型中所得的结果一致,其路径长度均为35.08 km.利用MATLAB环境中的计时函数cputime分别对两种方法的环境建模过程以及路径规划过程进行计时,结果如表 4所示.显然由于在高程建模的过程中需要进行大量的微分运算,因此消耗的时间较长.此外,由于高程建模法只对环境进行抽象建模,因此后续进行路径规划的过程中,每一步都需要对目标函数进行计算,从而增大了计算量;相反地,由于本文所述环境建模方法在对环境抽象建模的过程中已经将目标函数融入到了环境模型中,因此后续进行路径规划时,无需进行大量计算,故消耗的时间较短.
3.1. 蚁群算法的基本原理
3.2. 蚁群算法的实现流程
3.3. 参数选择与优化
3.4. 仿真实验
3.5. 与其他建模方法的对比
-
针对山地环境的特殊性,采用现有方法进行环境建模时,存在计算量大、模型易失真等问题,本文提出了一种基于空间映射的建模方法,该方法通过离散化和空间映射等过程,将三维曲面环境模型降维成由点集和点距集构成的二维平面模型.同时,利用该建模方法进行环境建模时可将不同的路径规划目标融入所建环境模型中,从而有效缩减路径规划时的计算量,提高其路径规划效率.在MATLAB中利用蚁群算法对不同环境模型进行路径规划仿真实验,结果证明了本文所述建模方法的有效性与优越性.



 下载:
下载: