-
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):

-
近年来,在光热治疗领域,许多能有效吸收近红外光的光热剂被逐渐发掘出来,铜基二元/三元硫属化合物即是其中极具代表性的一类[1-4],它们在近红外区具有较强的局部表面等离子体激元共振吸收,这一特点使其具有优异的光热转换能力[5-9]. 由于铜原子的缺失,Cu2-xE(E=S,Se,Te,0≤x≤1)系列化合物也有着较强的等离子体激元共振吸收和优异的光热性能[10],通过改变x的具体数值可以调节其等离子体激元共振吸收性质[11-13].
基于此,本研究构建了基于Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX的光热/化学动力学/化学治疗三模式乏氧治疗体系. 在整个体系中,光热剂Cu2-xSe纳米粒子产生的高热不仅发挥了其本身光热治疗的作用,而且还同肿瘤微环境的酸性pH共同促进了MIL-100(Fe)芬顿反应的进行以及药物阿霉素的释放,提高了治疗效率. 更重要的一点是,光热、化学动力学以及化学治疗都是不依赖氧气的治疗方式,因此本研究构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX在乏氧肿瘤治疗领域有着一定的潜在应用价值.
全文HTML
-
仪器:Rigaku D/max-TTR-Ⅲ衍射仪(Cu-Kα辐射λ=0.154 05 nm),FEI Tecnai G2 S-Twin透射电子显微镜,Leica SP8设备,表面分析系统(Thermofisher Escalab Xi+).
试剂:CuCl(AR),NH2-PEG(2000)-NH2(AR),EDC(AR),NHS(AR),PVP(AR),FeCl3(AR),H3BTC(AR)以及油胺、十八烯、无水乙醇均为分析级,未进一步纯化而直接用于实验过程.
-
取10 mmol硒粉与10 mL油胺于三颈瓶中,将此溶液加热至140 ℃,打开真空泵,使瓶内保持真空状态30 min以除去溶液中的低沸点溶剂杂质,接着关闭真空泵,通入氮气,继续将溶液加热至320 ℃,在氮气环境中反应30 min制得Se-OAm前驱体[14].
-
根据文献[15]合成了Cu2-xSe纳米粒子. 取0.5 mmol氯化亚铜、8mL十八烯和2mL油胺于四颈瓶中,将此溶液加热至140 ℃,打开真空泵,使瓶内保持真空状态30 min以除去低沸点溶剂杂质,接着关闭真空泵,通入氮气,将溶液加热至200 ℃时立即用注射器将Se—OAm前驱体快速注入到四颈瓶中,接着将温度升至220 ℃并保持1 h. 反应后的溶液用乙醇、环己烷洗涤数次,即得到沉淀的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子.
-
室温下,在烧杯中将合成的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子分散在30 mg聚乙烯吡咯烷酮的三氯甲烷溶液中并搅拌12 h,然后离心收集沉淀得到聚乙烯吡咯烷酮修饰的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子. 接着将所得粒子分散在乙醇中,加入一定量的氯化铁,搅拌30 min后再逐滴加入与氯化铁等质量的量的均苯三甲酸,反应24 h,产物用乙醇离心洗涤数次除去过量的反应物,收集沉淀得到核-壳结构的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)纳米材料.
-
将制备的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)溶于磷酸盐缓冲溶液,加入一定量的阿霉素,室温下避光搅拌24 h后离心洗涤除去过量的阿霉素,所得沉淀即为产物Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX. 通过测定上层清液中阿霉素在480 nm处的紫外吸收强度以及阿霉素的标准曲线来计算其担载量[16-17].
1.1. 实验仪器与试剂
1.2. Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)的合成
1.2.1. 硒-油胺(Se-OAm)前驱体的合成
1.2.2. Cu2-xSe纳米粒子的合成
1.2.3. Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)核-壳材料的合成
1.2.4. 在Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)上负载阿霉素
-
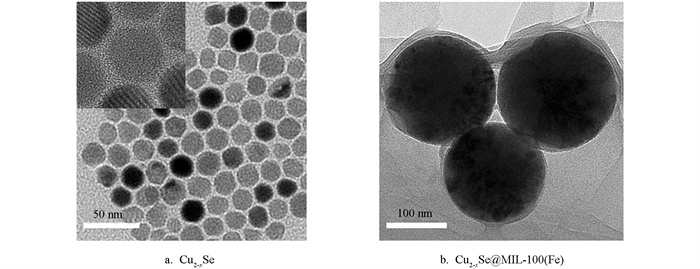
图 1是合成的Cu2-xSe和Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)纳米粒子的透射电子显微镜(TEM)图片. 由图 1a可知,通过两步高温热解法在油性溶剂中制备出的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子呈现出清晰、均匀的球形形貌且粒径大小为20 nm左右. 而从图 1a中的HRTEM图可以清晰地看到晶体的晶格条纹,证明了Cu2-xSe材料良好的结晶性. 然后在三氯甲烷中将得到的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子连接上聚乙烯吡咯烷酮进行转水修饰,紧接着在乙醇中通过该粒子和氯化铁、均苯三甲酸的一步反应包覆上金属有机骨架MIL-100(Fe)壳层,所得的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe) 粒子形貌见图 1b. 从图 1b中可以看出,Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)粒子的形貌依旧保持了球形且有着明显的内核-外壳结构,直径增至140 nm左右. 内核直径相对于图 1a的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子直径明显变大,可能是由于纳米粒子发生了聚沉.
图 2是制备的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子的XRD图. 经过与标准卡片(JCPDS No. 06-0680)比对可知,所得材料的图谱能与其标准图谱的特征衍射峰匹配吻合,主要特征峰对应的晶面有(111)、(220)、(311)和(422). 图 3是制备的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX纳米粒子在纯水和磷酸缓冲溶液(PBS)中的动力学光散射粒径分布图. 从图 3可以看出,Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX纳米粒子的粒径与之前透射图(图 1b)中观察到的基本一致,且在水和磷酸缓冲溶液中均能稳定分布,这为该粒子后续在水溶液和生物体环境中的分散及应用提供了基础.
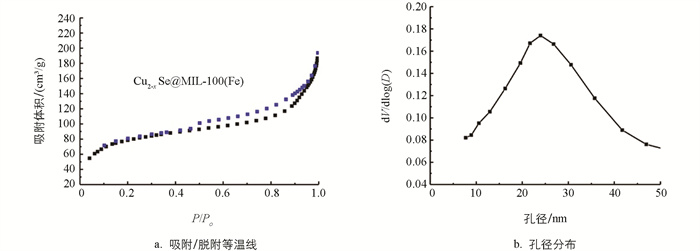
图 4是Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)纳米粒子的N2吸附/脱附等温线和相应的孔径分布图. 由图 4可知,其等温线是典型的Ⅳ型等温线且其孔道大小为25 nm,表明体系中存在着丰富的介孔孔道,同时经测定可知样品的比表面积为256.65 m2/g. 体系较大的比表面积和孔道直径保证了后续抗癌药物阿霉素的担载.
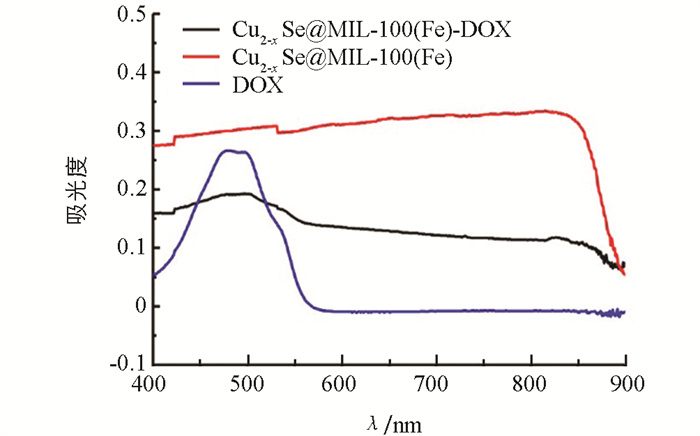
图 5是制备过程中各个样品的Zeta电位变化图. 由图 5可知,在油胺/十八烯中合成的Cu2-xSe纳米粒子表面带负电荷(-12.3 mV),在溶液中修饰上聚乙烯吡咯烷酮并包覆MIL-100(Fe)壳层后电荷转正(+9.2 mV). Zeta电位绝对值越大,体系的稳定性越高,粒子不容易发生聚沉. 因此,根据Zeta电位的数值变化可以分析解释透射图(图 1)中内核粒子粒径增大的原因. 在溶液中修饰上聚乙烯吡咯烷酮即转水修饰后,Cu2-xSe粒子的电位明显降低,从而体系变得不稳定,粒子发生聚沉致使粒径变大. 图 6是各样品的紫外-可见吸收光谱图,从图 6中可以看出在Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX的吸收曲线中出现了DOX的特征吸收峰(480 nm附近),表明材料中成功负载上了抗肿瘤药物阿霉素[18-19].
-
配制了一系列梯度质量浓度(80,40,20,10,5,0 μg/mL)的阿霉素溶液并检测了其在480 nm特征波长处的吸光度,经线性拟合得到其标准曲线(图 7a),图 7中阿霉素的紫外-可见吸光度(Y)与其浓度(X)的线性关系为Y=25.294X+0.025. 根据产物Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX的紫外-可见吸收曲线以及朗伯-比尔定律可以估算出阿霉素的担载率为40.3%. 紧接着,探究了在不同pH值和光照条件下材料中阿霉素在溶液中的释放曲线. 如图 7b所示,在pH=7.4的磷酸缓冲溶液中,当1 064 nm激光的功率设置为0,0.4,0.8 W/cm2时,阿霉素的释放率分别为12.1%,21.3%,42.7%. 可以看到,随着激光功率的增大,阿霉素的释放量明显增加,这主要是因为激光功率的增大使得体系的光热温度提高,高热促进了阿霉素的释放. 而从图 7c可知,当磷酸缓冲溶液的pH调节为5.5时,在激光功率为0,0.4,0.8 W/cm2时,阿霉素的释放率分别增加到了39.1%,48.1%,73.3%. 相比于中性环境,酸性pH下DOX的释放率更高. 利用这一点,在肿瘤治疗领域可以依赖肿瘤微酸性的环境促进药物的定向释放、增强治疗效果. 综上可知,Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX体系实现了酸性pH/光热的双响应释放,因此可以有效地发挥药物治疗作用.
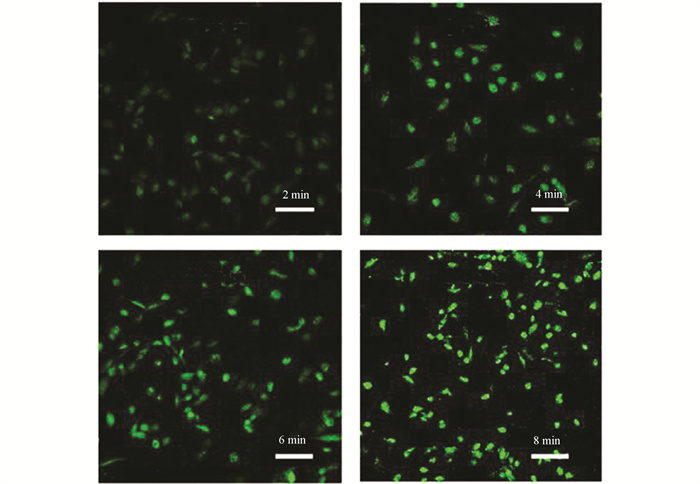
考虑到羟基自由基寿命短、化学活性高的特点,使用电子顺磁共振法(EPR)检测了原位羟基自由基的生成[20-21]. 将制备的材料与适量的过氧化氢混合,用相应的磷酸缓冲溶液调节溶液的pH值至5.5或7.4,再加入与材料等体积的捕获剂5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯烷-N-氧化物,用1 064 nm激光照射1 min后进行检测即可得到相应的图谱. 图 8是在不同条件下测出的电子顺磁共振谱图. 由图 8可知,所有谱图中均出现了羟基自由基的四重特征信号峰,且在光照和酸性条件下材料的信号峰最强,即生成的羟基自由基最多最快. 与阿霉素的pH/光热的双响应释放一样,酸性pH与高热的双重刺激也促进了芬顿反应的进行,有利于体系利用酸性的肿瘤微环境发展化学动力学治疗. 用2',7'-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)表征了材料生成活性氧的能力,使用共聚焦显微镜观察细胞. 如图 9所示,随着时间的延长(2,4,6,8 min),绿色荧光逐渐增强,即材料生成的活性氧越来越多. 以上结果表明,本研究所构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX材料有潜力在肿瘤微环境的条件下有效地生成活性氧.
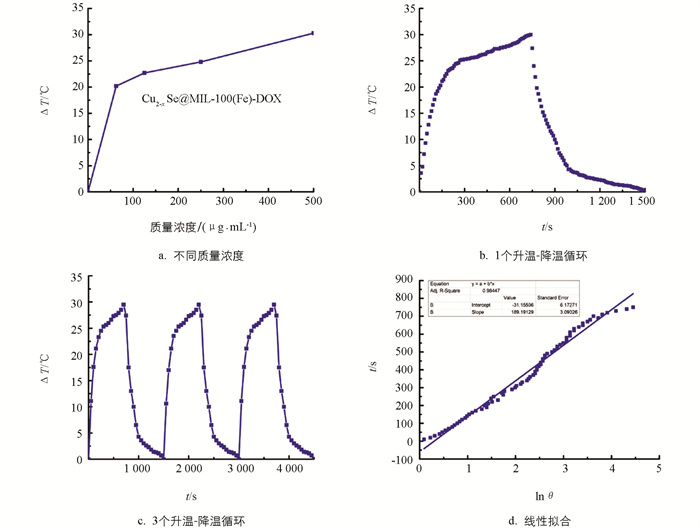
通过一系列实验深入探究了Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX材料的光热转换能力. 图 10a是不同质量浓度(500,250,125,62.5,0 μg/mL)的材料被1 064 nm激光照射500 s后的温度变化图. 从图 10中可以发现材料的质量浓度越高,其能达到的最终温度也越高,材料质量浓度为500 μg/mL时最终温度可达到50 ℃,这完全满足了生物应用中光热治疗的要求. 图 10b与图 10c分别是1个和3个循环周期内的温度变化图. 以1 500 s为一个循环周期,持续用激光照射材料的水溶液750 s后关掉激光器让材料自然冷却,期间始终用热红外成像仪监测材料的温度变化并且每10 s记录1次温度值,循环3次. 实验结果表明,几个循环周期内材料的光热温度值和变化趋势并没有明显的变化,即Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX材料具有良好的光热稳定性. 根据循环曲线中的冷却部分可以得到相应的-lnθ值,将其与温度进行线性拟合可以得到图 8d,其斜率值189.19为系统的时间常数τ_(s)的数值. 据此,计算出材料Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX的光热转换效率η为51.21%[22-23]. 如图 11所示,用1 064 nm激光分别辐照水和Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX材料的水溶液5 min,每隔1 min用红外热成像仪拍照记录一次溶液的温度. 从红外热成像图片中可以直观地观察到材料的温度颜色从一开始的淡黄泛红到变红到最终呈白热化的状态,而作为对照组的溶剂水的颜色则一直保持着淡蓝色的室温状态. 实验结果进一步证明了本研究构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX具有优异的光热转换能力.
-
实验结果表明本研究所构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX体系具有良好的载药性能、活性氧生成能力以及光热转换能力. 于是我们进一步对材料的生物应用进行了探究. 为了确保材料在生物应用时安全无害,首先进行了生物相容性实验. 将不同质量浓度(500,250,125,62.5,31.3,15.6,7.8 μg/mL)的材料与L929成纤维细胞共同培养处理24 h后经酶标仪测定得各组细胞的存活率数值(图 12a),每组细胞(包括材料质量浓度高达500 μg/mL的培养细胞)的存活率均在90%以上,据此判断材料具有良好的生物相容性. 紧接着我们探究了材料对海拉肿瘤细胞的毒性,将海拉细胞分为不同组,设置其中一组为对照组,其余组细胞分别用光照、纯阿霉素、Cu2-xSe+光照、Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)+光照、Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX+光照处理,经过同样的MTT处理得到相应的细胞存活率数值(图 12b). 从图 12b的柱状图可知,对照组和1 064 nm光照组的细胞存活率均在90%以上,可见近红外光照对细胞基本没有损伤. 而纯阿霉素(500 μg/mL)处理的细胞存活率降至60%左右,表明阿霉素是一种有效的抗癌药物. Cu2-xSe+光照、Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)+光照、Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX+光照处理的细胞存活率在材料质量浓度为500 μg/mL时分别降低至60%,43%,20%左右. 依次递增的抗肿瘤细胞能力可分别归因于逐步引入的光热、化学动力学和药物治疗.
为了更直观地观察抗肿瘤效果,使用碘化丙啶对细胞进行染色(红色标记死细胞),用共聚焦显微镜观察细胞样品,结果见图 13.
可以直观地看到,Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX+光照培养组的红色细胞数量最多,意味着被杀死的肿瘤细胞最多;而Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)+光照和Cu2-xSe+光照组死亡的红色细胞数量分别次之,该实验结果与上述MTT毒性实验结果一致. 以上细胞实验结果表明所构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX体系可以有效地发挥光热、化学动力学和药物治疗的三模式协同治疗作用,在肿瘤治疗领域具有一定的应用前景[24-25].
2.1. 形貌、物相和元素分析
2.2. 性能分析
2.3. 体外抗癌性能研究
-
本研究构建的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX复合材料体系的光热转换温度高达50 ℃,可用于光热治疗. 经转水修饰后在乙醇溶液中一步合成的Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)核壳材料的比表面积为256.65 m2/g,使得抗癌药物阿霉素的担载率达到40.3%;体外细胞实验表明材料的生物相容性较好,材料质量浓度为500 μg/mL时,细胞的存活率高达90%;材料质量浓度为500 μg/mL时,Cu2-xSe-AIPH+NIR组癌细胞存活率可降至20%. 因此,本研究所得Cu2-xSe@MIL-100(Fe)-DOX材料可以有效地发挥光热、化学动力学和药物治疗的三模式协同治疗作用,在肿瘤治疗领域具有潜在的应用价值.



 下载:
下载: