-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
水库消落带又称涨落区或涨落带,是河流或水库季节性的水位涨落而使周边的土地周期性地水淹-落干-水淹的特殊区域[1]. 消落带作为水陆衔接带,是重要的缓冲带和过滤带,但对环境变化特别敏感,容易受到干扰. 植被作为消落带湿地生态系统结构和功能的核心,可为库岸生态系统提供多种生态功能[2-3]. 作为世界上大型水利枢纽之一,三峡水库采取“冬蓄夏排”的水位调度方式,在水库两岸145~175 m高程形成了反季节、涨落幅度达30 m的大面积消落带[4]. 三峡库区消落带作为水、陆生态系统之间物质运输、能量交换和信息传递的活跃地带,具有典型的生态脆弱性特征[5]. 由于三峡水库周期性、高强度以及反季节的长时间蓄水使库区消落带生境恶化,引发了一系列的生态环境问题,如群落结构单一化、生物多样性降低、土地退化、景观恶化以及土壤侵蚀严重等[6-7],对库区生态安全造成极大威胁.
消落带极易受到水淹的影响[8-9]. 三峡水库的水文节律影响着消落带植物群落的分布和演替,导致消落带新形成的湿地植物群落物种数量降低[10]. 与建坝前相比,三峡库区消落带植被生物量和物种多样性持续下降,乔木和灌木等木本植物几乎消失,一年生和多年生草本植物成为消落区最常见的植物种类[11]. Yang等[12]分别在2001年和2009年对三峡大坝建立前后的消落带植被进行调查,发现维管束植物下降了43%,优势植物群落类型明显改变,一年生植物逐渐取得优势. 已有研究表明,水淹深度、持续时间和频率都会影响库区消落带的植物群落,水库消落带低高程植物群落受到水淹胁迫的影响,而高高程植物群落则受到水淹和干旱胁迫的共同影响[13]. 与此同时,土壤、地形等环境因子也可能主导消落带的植被分布格局,但因二者作用机理有所不同,还可能会产生耦合效应,因此消落带植被与环境之间的关系及其复杂[14-15]. 目前关于三峡库区消落带植物群落特征与环境因子之间相关性已有研究,对于揭示库区消落带植物群落初期演替具有一定的参考价值. 但随着水库运行时间的增长,消落带的植物群落仍然处于动态变化之中,与环境因子之间的关系有待于进一步研究.
三峡库区周期性水位涨落,伴随着水淹时间的延长,库区消落带植被的物种组成、物种多样性和空间分布还处在不断变化之中. 本文选取具有典型代表性特征的三峡库区忠县消落带为研究对象,在三峡水库高水位运行10年后对当地消落带不同高程区域的植物群落及其环境因子进行重点研究. 通过比较不同高程的物种丰富度和多样性的差异,应用双向聚类法划分不同的群落类型,并分析物种多样性与环境因子之间的关系,从而为三峡库区消落带植被保护及修复提供一定的科学依据.
全文HTML
-
忠县位于重庆市中部(东经107°32′~108°14′,北纬30°03′~30°53′),东西长66.45 km,南北宽60.15 km,面积达2 187 km2. 忠县属暖湿亚热带东南季风区山地气候,植被类型为亚热带常绿阔叶林. 一年四季分明,降水充沛,气候垂直差异较大. 日照充足,日照率为26%,日照时数长达1 204.7 h. 年降雨量1 192.8 mm,相对湿度81.1%. 全县常见的土壤有水稻土、冲积土、紫色土和黄壤土[16].
忠县位于三峡库区腹心地带,消落带面积约32 km2,约占库区总面积的11%. 土壤类型以水稻土和紫色土为主,消落带植被退化,水土流失较为严重;主要土地利用类型为农业用地、林业用地、荒地滩涂用地等[17]. 忠县消落带经历多次高水位水淹后原有的乔灌木基本消失,只有一些人工乔木(如落羽杉、池杉)在165 m高程以上存活. 目前,忠县消落带的优势植物以一年生草本植物为主,包括苍耳、狼杷草、草木犀;同时还分布有一些多年生草本植物,如狗牙根、牛鞭草、香附子等.
-
于2019年7月,在三峡库区消落带处于低水位运行期间,采用样带法和样方法结合对忠县消落带的植物群落进行调查. 为了解不同水淹强度对植物群落组成和多样性的影响,根据忠县消落带的水位变化特征,将其划分为3个高程段,即低高程区(145~155 m)、中高程区(155~165 m)和高高程区(165~175 m),然后在各高程段平行于河道方向设置长100 m和宽20 m的调查样带. 在样带内以50 m为间隔设置3个大小为2 m×2 m样方,记录样方中的物种组成、高度和盖度,以及样方的高程(Ele)和坡向(Aspect)等环境因子. 本次共调查132个样方,其中低高程带46个,中高程带37个,高高程带49个.
-
样方调查结束后,用环刀取0~20 cm表层土壤测定容重(BD). 采用五点取样法取土样,混合均匀后用四分法取1 kg用于土壤理化性质的测定. 土壤含水量的测定采用烘干法(SWC);采用酸度计法测定土壤的pH值;采用重铬酸钾容量法-稀释热法测定有机质(SOM);采用间断化学分析仪(Clever Chem Anna,德国)测定速效磷(AP)、铵态氮(NH4+-N)和硝态氮(NO3--N)[16-18]. 年平均温度(T)从当地的气象局网站获得(http://data.cma.cn/).
-
考虑到忠县消落带内植被多以草本植物为主,故采用相对盖度(Relative Cover,RC)和相对高度(Relative Height,RH)作为重要值(Importance Value,IV)的计算依据[19].
选取总重要值大于1的物种作为群落的主要优势物种[20].
-
为了确定不同水淹强度对植物群落物种多样性的影响,本研究选取了Patrick丰富度指数(R)、Shannon-Wiener指数(H)、Simpson多样性指数(D)和Pielou均匀度指数(E)表征群落物种多样性.
Patrick丰富度指数(R)
Shannon-Wiener指数(H)
Simpson多样性指数(D)
Pielou均匀度指数(E)
S为出现在样方中的物种数,Pi为物种i的重要值(IV).
-
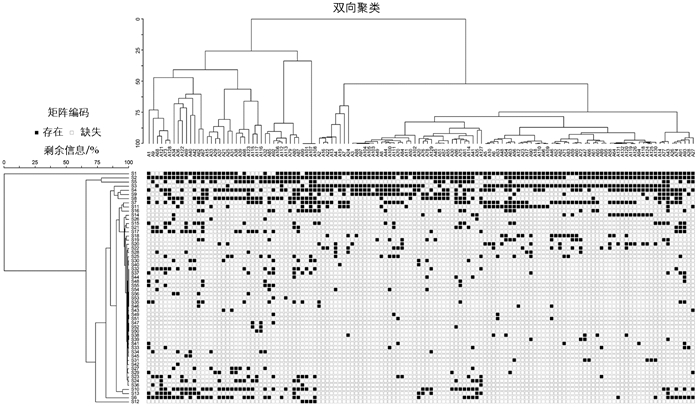
双向聚类分析可以直观反应群落和群落中各物种之间的相似程度,采用PC-ORD 5.0软件中的双向聚类分析方法对群落及群落中的物种进行数量分析. 为了降低稀有物种对分类结果的影响,只保留了物种重要值大于0.1的56个物种进行双向聚类分析,以43.50%为阈值对群落进行划分[21].
-
采用非参数检验中的Kruskal-Wallis H检验法对不同高程植物群落物种多样性指数进行检验,数据分析在SPSS 23.0,Excel 2016中进行. 在Canoco 5.0中采用冗余分析揭示植物群落组成和环境因子的关系,采用Origin 8.5制图.
1.1. 研究区概况
1.2. 研究方法
1.2.1. 样方调查
1.2.2. 土壤取样
1.3. 物种重要值和多样性指数的计算
1.3.1. 重要值的计算
1.3.2. 多样性指数的计算
1.4. 植物群落类型划分
1.5. 数据分析
-
在本研究调查的忠县消落带中,共记录到维管植物96种,隶属于34科80属. 其中菊科(Compositae)11属15种,禾本科(Gramineae)12属14种,豆科(Leguminosae)6属7种,伞形科(Umbelliferae)5属6种,蓼科(Polygonaceae)2属6种,唇形科(Labiatae)4属4种,苋科(Amaranthaceae)3属4种,茄科(Solanaceae)、大戟科(Euphorbiaceae)和玄参科(Scrophulariaceae)各3属3种,荨麻科(Urticaceae)、桑科(Moraceae)、毛茛科(Ranunculaceae)各2属2种,莎草科(Cyperaceae)和鸭跖草科(Commelinaceae)各1属2种,其余19科为单属单种. 总体而言,菊科、禾本科、豆科、蓼科、伞形科、唇形科和苋科是该区域的优势科,占总体的64.84%.
如表 1所示,主要优势种在不同高程的重要值存在差异. 狗牙根(Cynodom dactylon)在低高程(IV=23.48)、中高程(IV=15.50)和高高程(IV=9.42)的重要值均明显高于其他物种,且从高到低依次为低高程、中高程、高高程;苍耳(Xanthium strumarium)、狼杷草(Bidens tripartita)、牛鞭草(Hemarthria sibirica)、喜旱莲子草(Alternanthera philoxeroides)和野黍(Eriochloa villosa)等物种的重要值随高程的增加呈上升趋势,而苦蘵(Physalis angulata)、酸模叶蓼(Polygonum lapathifolium)、西来稗(Echinochloa crusgalli var. zelayensis)、马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis)和稗(Echinochloa crusgalli)等物种的重要值随高程的增加呈下降趋势;落羽杉(Taxodium distichum)和小蓬草(Erigeron canadensis)则只出现在高高程区域,草木犀(Melilotus officinalis)和藿香蓟(Ageratum conyzoides)只出现在中高程区域,旋鳞莎草(Cyperus michelianus)只出现在低高程区域.
-
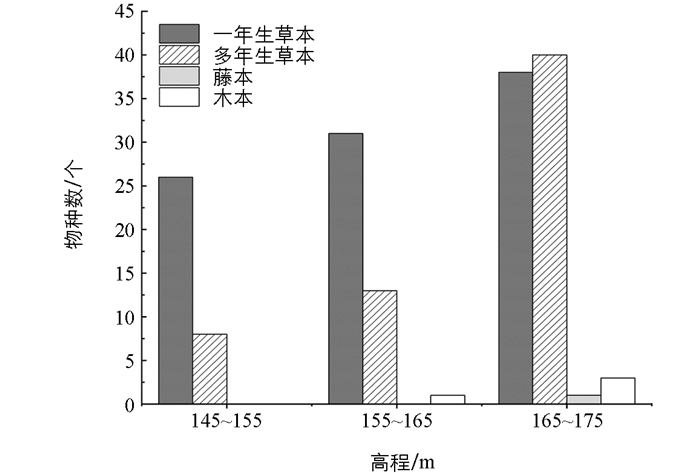
根据《中国植物志》(http://www.iplant.cn/frps)将研究区植物划分为4种生活型(图 1). 结果发现该区域的植物群落组成中草本植物占据绝对优势,占95.83%,其中一年生草本植物51种(53.12%),多年生草本植物41种(42.71%),藤本1种(1.04%),木本3种(3.13%). 不同高程段的植物组成结构存在差异,145~155 m高程段有34种(35.42%),其中一年生草本植物26种(27.08%),多年生草本植物8种(8.33%). 155~165 m高程段有45种(46.88%),其中一年生草本植物32种(33.33%),多年生草本植物12种(12.50%),木本植物1种(1.04%). 165~175 m高程段有79种(82.29%),其中一年生草本植物38种(39.58%),多年生草本植物38种(39.58%),木本植物3种(3.13%).
-
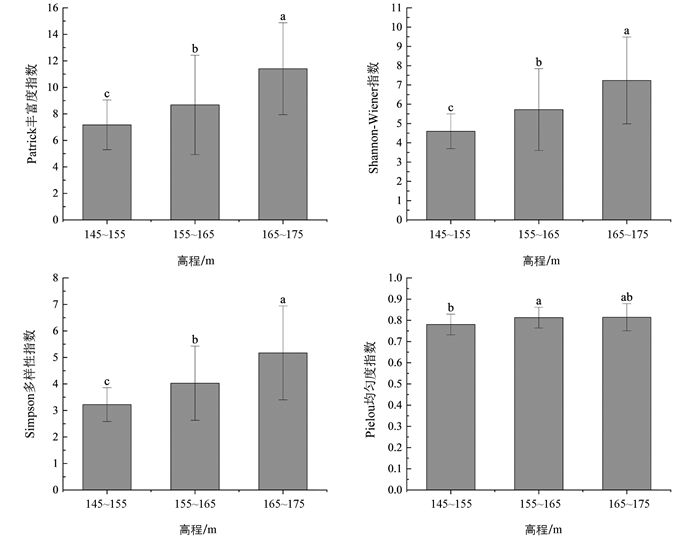
试验结果可以看出,不同高程梯度下的植物群落物种多样性指数差异有统计学意义(p<0.05). Patrick丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener指数和Simpson多样性指数随着高程的升高显著上升;中高程的Pielou均匀度指数高于低高程且差异有统计学意义,与高高程之间差异无统计学意义(图 2).
-
根据双向聚类分析共划分出5种不同的植物群落类型,以群落中的优势物种对群落进行命名(图 3).
1) 草木犀(M. officinalis)-狗牙根(C. dactylon)群落. 优势物种为草木犀(M. officinalis)和狗牙根(C. dactylon),伴生种为狗尾草(S. viridis)、野黍(E. villosa)和苍耳(X. sibiricum)等. 该类群包括13个样方,样方分布在165~175 m高程,为消落带的高高程区域.
2) 苍耳(X. sibiricum)-狗牙根(C. dactylon)-喜旱莲子草(A. philoxeroides)群落. 优势物种为苍耳(X. sibiricum)、狗牙根(C. dactylon)、喜旱莲子草(A. philoxeroides),伴生种为草木犀(M. officinalis)、狼杷草(B. tripartita)、牛鞭草(H. altissima)等. 该类群包括14个样方,样方分布在165~175 m高程,为消落带的高高程区域.
3) 牛鞭草(H. altissima)-苍耳(X. sibiricum)-狗牙根(C. dactylon)群落. 优势物种为牛鞭草(H. altissima)、苍耳(X. sibiricum)、狗牙根(C. dactylon),伴生种为喜旱莲子草(A. philoxeroides)、草木犀(M. officinalis)、狼杷草(B. tripartita)等. 该类群包括9个样方,样方分布在165~175 m高程,为消落带的高高程区域.
4) 落羽杉(T. distichum)-狼杷草(B. tripartita)-苍耳(X. sibiricum)群落. 优势物种为落羽杉(T. distichum)、狼杷草(B. tripartita)、苍耳(X. sibiricum),伴生种为喜旱莲子草(A. philoxeroides)、野黍(E. villosa)、酸模叶蓼(P. lapathifolium)等. 该类群包括4个样方,样方分布在165~175 m高程,为消落带的高高程区域.
5) 狗牙根(C. dactylon)群落. 优势物种为狗牙根(C. dactylon)、苍耳(X. sibiricum)、苦蘵(P. angulata),伴生种为狼杷草(B. tripartita)、香附子(Cyperus rotundus)、酸模叶蓼(P. lapathifolium)等. 该类群包括91个样方,主要分布在145~175 m高程梯度,在消落带不同高程区域均有分布.
-
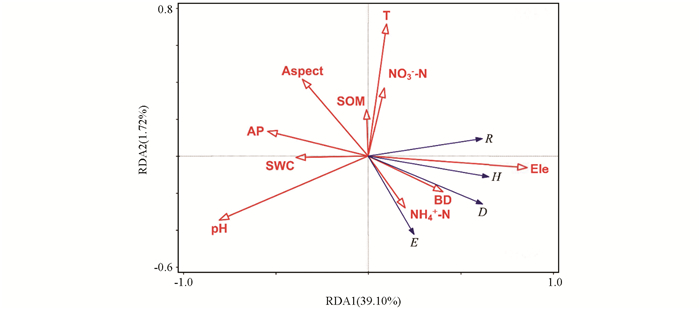
RDA分析结果表明,环境因子能够解释40.82%的植物群落多样性变化. 高程、土壤pH值、土壤铵态氮含量及坡向对忠县消落带植物群落多样性解释度最大,依次为28.80%,5.60%,2.60%,2.20%;且高程、坡向及土壤pH值、土壤铵态氮对植物群落多样性有显著影响(p<0.05),其余土壤养分对植被变化的解释度较小(表 2). 因此影响忠县消落带物种多样性的主要因子为高程、土壤pH值、土壤铵态氮及坡向(图 4).
2.1. 物种组成与物种重要值
2.2. 物种生活型特征
2.3. 忠县消落带植物群落物种多样性
2.4. 基于双向聚类分析的植物群落类型划分
2.5. 环境因子与忠县消落带物种多样性之间的关系
-
本研究发现,忠县消落带物种组成以菊科和禾本科植物为主,菊科和禾本科为该区的优势科,这与郭燕等[22]和童笑笑等[23]在三峡库区消落带研究所获得的结果一致. 禾本科植物能适应各种不同的环境,其根系较为发达,耐水淹能力较强,能适应库区的水位变动;菊科植物生活周期短,能避开不良环境,具有快速繁殖及多样的营养繁殖方式等,能让其较好地适应消落带环境[21-22]. 多年生草本植物狗牙根在研究区分布广泛,其重要值在不同高程区域皆为最高,这可能是因为狗牙根在水淹期间,其根部通气组织形成,根系生物量增加,繁殖速度快,水位下降后能很快萌发[19, 24]. 本研究表明,忠县消落带一年生草本植物为56种,占58.3%,是该地区的优势生活型. 一年生草本植物快速生长发育有可能是植物对环境剧烈变化不可预测的生态适应性结果;三峡水库消落带干湿交替的恶劣环境,导致了一年生植物的生长优势[21]. 张爱英等[25]和王业春等[26]对三峡库区忠县消落带物种组成进行研究发现,该地区一年生草本植物所占比例增加,多年生草本、木本植物所占比例下降,灌木基本消失[27]. 长期的淹水提高了一年生草本植物的比例,其之所以能在长期水淹的环境中存活,原因是一年生草本植物生活周期短,在出露时间短的低高程地区也能完成从萌发到开花结果的过程,即快速萌发、早期定居,进而提高植物的竞争优势[28]. 种子萌发时期与库区每年的落干周期之间的关系会影响现存植物群落的分布及其与各自种子库的相似性. 三峡库区消落带高高程区域的落干期早于中低高程,使得高高程区域的种子有更多的时间萌发、生长并完成生命周期,而萌发较晚或生命周期长于库区落干期的植物将被淘汰或被限制只能生活在高高程[29]. 此外,Lu等[11]研究发现忠县消落带处于群落演替的早期,地上植被中的大部分一年生植物都可以通过种子库进行恢复,也是一年生植物占优势的原因之一.
-
消落带植物群落物种多样性受高程及环境变量的影响[28]. 本研究中,忠县消落带植物群落Patrick丰富度指数、Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson多样性指数和Pielou均匀度指数均随着高程的上升而逐渐增加,表明随着高程的上升,植物群落中的物种数增多,群落物种多样性和优势物种数量增加,群落内物种分布也更均匀[23]. 除Pielou均匀度指数外,各高程之间物种多样性差异有统计学意义,这与前人的研究结果较为一致. 刘维暐等[8]对三峡水库干流和主要支流消落带的植被物种分布进行调查发现,不同高程间α多样性差异有统计学意义;柯智溢等[30]也发现消落带植物物种多样性随高程升高呈现上升趋势;造成这种差异的原因可能与不同高程淹水时间、深度不同有关. 低高程地区(145~155 m)位于消落带下部,其淹水时间长,大多数物种难以生存,形成了以狗牙根等耐淹物种为主的单优群落,故其多样性最低. 高高程区域(165~175 m)受到的水淹胁迫较小,植物生长更为容易,同时高高程地区受人为干扰强,土壤养分较高,且种子飘落更多,所以物种多样性更高[21]. 中高程地区(155~165 m)物种多样性较高高程较低则可能与其坡度较陡、水分截留困难有关[31]. 而有研究者在香溪河消落带的研究表明,植物群落物种多样性随高程的升高先增加后减少,即中度淹水区域多样性指数最大,符合中度干扰理论[32-33]. 三峡水库区域大,各地的原生植被组成、地形、调查的时间和方法等都会对调查结果产生一定影响[34]. 同时,消落带的植物群落仍处于演替的初级阶段[22],并未完全达到稳定状态,且大多数研究范围较小,因此后续研究还需要长期、大范围的动态监测[30].
-
根据双向聚类分类结果,忠县消落带优势群落为狗牙根群落,与整个三峡库区丰富的植被类型相比,消落带植被具有物种较少、群落组成简单、以草本植物为主等特征. 狗牙根群落在消落带不同高程均有分布(145~175 m),为忠县消落带优势群落,这与张爱英等[35]在忠县消落带的研究结果相似. 狗牙根的根系和通气组织较为发达,在水淹胁迫下,狗牙根通过加速根系生长、优先分配植株的分蘖和地下生物量等适应性机制,使其能够在水淹环境下生存和为脱离水淹胁迫后的快速生长提供营养和能量储备[36-37]. 苍耳-狗牙根-喜旱莲子草群落、草木犀-狗牙根群落、牛鞭草-苍耳-狗牙根群落主要分布在高高程区域(165~175 m). 苍耳种子产量较高,其具有较强的耐水淹能力,即使是在原位水淹半年以上,绝大多数的苍耳种子仍然具有较高的活力,但苍耳植株并不耐淹,短期水淹会导致植株死亡,也是苍耳优势群落只存在于高高程区域的原因之一[38]. 牛鞭草为耐水淹的中生物种,对水分的需求不是太强烈,草木犀则为旱生的一年生植物,二者形成的群落往往分布在消落带高高程区域[39]. 落羽杉-狼杷草-苍耳群落出现在高高程区域主要是因为本研究课题组前期(2012年)在忠县石宝镇共和村汝溪河消落带植被修复示范基地内进行了落羽杉人工林重建,现已成林,林下伴生着狼杷草、苍耳等一年生植物,表明落羽杉可用于三峡库区消落带高高程区域的人工植被修复[40]. 忠县消落带经过多年的高水位蓄水,优势物种逐渐由荩草(Arthraxon hispidus)、白茅(Imperata cylindrica)等物种转变为狗牙根、苍耳等[25],这些现存植物经过了长期自然筛选后存活率较高,能适应三峡库区消落带的特殊环境. 消落带植物群落构建是一个长期并处于动态变化的过程,需要长期的定位监测,只有这样才能深入揭示库区消落带自然植物群落及其环境因子的变化机制[21, 41].
-
河岸带土壤具有特殊的质地、结构及养分特征[42-43],消落带植物对于维持消落带生态系统的稳定性起到重要的作用. 群落物种多样性是反映植物群落结构复杂程度的重要指标之一[44],探讨其与环境因子的关系对于了解消落带生态系统的过程与功能有着重要意义. 消落带的土壤会受到植物生长的影响,而土壤养分含量及高程、坡向等地形因素也会显著影响植物群落的空间分布[45-46]. 植物的生长与土壤条件密不可分,土壤状况影响着植物群落的生物量分配和物种多样性[47]. 罗琰等[48]通过研究辉河湿地消落带的植物多样性,发现其主要影响因子为土壤全氮含量、全磷含量和含水量;而本研究发现影响三峡库区忠县消落带植物群落物种多样性的土壤因子主要为铵态氮和pH值. 氮是植物生长发育过程所必须的大量元素之一,可以限制生态系统的初级生产力,是调节生态系统结构及其功能的关键元素[49-50]. 前人研究发现,氮养分的提高有利于群落物种丰富度的增加,对于促进湿地植被的恢复具有重要意义,这与本研究中土壤铵态氮与植物多样性的显著相关结果较为一致. 土壤pH值是反映土壤化学性质的综合指标之一,对土壤养分有效性影响较大. Zhang等[51]研究也发现,土壤pH值对河岸带植被物种组成有重要影响. 已有学者对澎溪河消落带植被进行的调查发现,与水淹有关的环境因子如高程、淹水时间和淹水深度等也会影响植被物种多样性[23],本研究结果与之相似. 本研究中,对忠县消落带植被物种多样性影响最大的因子是高程因素. 高程作为综合性环境因子,其变化会引起温度、湿度、光照及水淹时间、水淹深度等多种环境因子的变化,能够显著影响消落带植物的分布,在消落带植物群落空间格局形成过程中起着主导作用[21]. 地形因子中的坡向对忠县消落带植物群落物种多样性也存在显著影响,不同坡向可能具有不同的生境条件,其引起的光照、温度、水分等自然因素的差异会对植被的空间分布格局造成一定的影响[52].
3.1. 不同高程植物群落组成与生活型分布差异
3.2. 不同强度的水淹对消落带植物群落物种多样性的影响
3.3. 研究区消落带的典型植物群落类型
3.4. 环境因子与消落带物种多样性之间的关系
-
三峡库区经历多年周期性水位涨落后,忠县消落带的植物群落特征发生了较大变化. 本研究发现忠县消落带以一年生和多年生草本植物为主,乔木和藤本植物只在高高程区域零星分布,菊科和禾本科植物在消落带占有优势,消落带的植物群落物种多样性随高程上升而逐渐增加. 双向聚类分析表明狗牙根群落在各高程区域均有分布,而高高程区域植物群落分部主要为苍耳-狗牙根-喜旱莲子草群落、草木犀-狗牙根群落和牛鞭草-苍耳-狗牙根群落. 高程因素是影响消落带物种空间分布和物种多样性最重要的因素,此外土壤pH值、土壤铵态氮含量及坡向也会产生一定的影响. 三峡库区消落带的植物群落和环境条件仍然随三峡水库的运行处于动态变化之中,多位点、长时间的定位监测可以更好地揭示植物群与环境因子之间的时空变化规律,这也是未来的研究方向.



 下载:
下载: