-
推进新型工业化、城镇化、信息化、农业现代化及绿色化的协同发展符合社会可持续发展的基本要求,是促进区域社会转型发展和改善人民生活的必由之路.党的十八大提出,我国城市化发展过程中要重点把握由“四化同步”到“五化协同”的转变,提出要坚持绿色化发展这一历史性命题.党的十九大对此进行了补充,提出要坚持走新型工业化、城镇化道路并指出建设生态文明是中华民族永续发展的千年大计,将绿色发展提升到一个新的高度,以应对随着社会经济发展、环境恶化、资源枯竭等日益凸显的问题.随着社会经济的发展和2015年4月《京津冀协同发展规划》的实施,京津冀地区城市之间的社会经济、生态环境及人民生活之间的联系日趋紧密,探讨城市的“五化”耦合协调时空分异及影响因素已经成为实现京津冀城市群一体化发展过程中的热点问题.当前,业内学者关于“五化”的相关研究主要集中于“五化”协调发展时空格局[1]、影响因素[2]、时空演变[3-4]、发展效率[5]、综合评价[6]、进展与反思[7]、机理与测度[8]等方面;研究方法多为单一的协同发展指数及协同发展效率、耦合协调模型、VAR模型、偏最小二乘路径模型、灰色关联分析模型、地理加权回归分析等,鲜有利用耦合协调模型与地理探测器相结合分析“五化”时空分异及影响因子的案例;研究尺度多集中于全国、地区、省域、单个城市以及县域,针对城市群尺度的相关研究比较少见,尤其是京津冀这种对全国经济具重大研究意义的典型城市群.研究从京津冀一体化及协同发展角度出发,以京津冀城市群为研究对象,对2006年、2011年和2016年城市“五化”综合发展指数、耦合度、协调度时空分异格局及影响因素进行分析,旨在为不同城市群的差异化发展政策的制定提供支撑,促进区域一体化的发展.
全文HTML
-
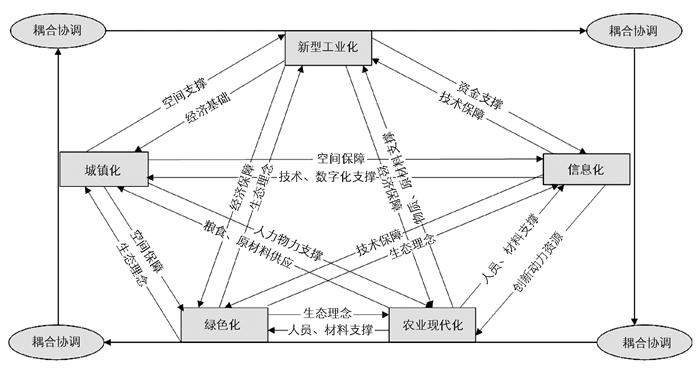
“五化”包括新型工业化、城镇化、信息化、农业现代化及绿色化5个模块,涉及社会生活的方方面面,彼此之间相互联系、相互制约并互动发展,单一化的变动发展,都会对其他各化产生联动影响,即牵一发而动全身,但城市间的社会经济状态不同,各化之间发展差异较大,并不一定具有耦合协调发展的特征,因此探讨“五化”的耦合协调发展机理至关重要.具体“五化”的协调机制及各自内涵如下:新型工业化是基础和动力,指科技含量高、经济效益好、资源消耗低、环境污染少、人力资源优势得到充分发挥的工业化,可以为其他各化提供其发展所需要的产业支持及物质保障,反过来拉动新型农业化的发展[9].城镇化是空间载体[10],指为其余各化提供活动载体和相关的高素质人力及物力保障,反过来推动农村的城镇化.农业现代化是重要保障,指使用现代化的工业技术设备,利用信息化手段在绿色化理念的指导下的现代化农业发展过程,可以为其他各化的发展提供充足的粮食和原材料[11].信息化是重要的推动力,指以现代通信、网络、数据库技术为基础,培育、发展以智能化工具为代表的新的生产力并使之造福于社会的历史过程,可以优化产业结构,为其余各化的发展提供信息化和智能化的指导,推动数字化、信息化、高科技城市的发展.绿色化是指向标和引导力,指以一种低消耗、高科技、生态化的理念、产业结构和生活方式,为其余各化的发展提供理念支撑与引导[8].具体“五化”之间的耦合协调发展机理如图 1所示.
-
“五化”各指标因素间相互联系、相互影响且密不可分,某一因素变化会影响整个“五化”的发展.在白雪、顾先问等人研究成果的基础上[12-13],考虑到指标的全面性、可比性、可获取性和科学性等原则,基于“五化”耦合协调发展的内涵,确定京津冀“五化”耦合协调综合评价指标体系由新型工业化发展指数、城镇化发展指数、信息化发展指数、农业现代化发展指数和绿色化发展指数5大准则层31个指标组成.
-
研究对象为京津冀城市群中的13个城市,具体包括北京、天津、石家庄、唐山、张家口、秦皇岛、邯郸、沧州、承德、衡水、邢台、廊坊和保定,以2006,2011和2016年为研究时间点,所需研究数据主要来源于2007年、2012年和2017年《中国城市统计年鉴》《河北省经济年鉴》《北京市统计年鉴》和《天津市统计年鉴》,部分年份数据如农业机械动力水平和化肥使用情况等采用《中国区域经济统计年鉴》进行补充.
-
采用极差法对原数据进行标准化,运用熵值法确定指标权重,求取工业化发展指数U(g)、城镇化发展指数U(c)、信息化发展指数U(x)、农业现代化发展指数U(n)和绿色化发展指数U(l),表达式分别为:
式中:αi,βi,θi,γi,πi为权重;gi,ci,xi,ni,li为各指标对应的标准化值;m为指标的总数.
将各准则层指数进行加权求平均后,得到“五化”发展的综合指数T,表达式为:
-
物理学上“耦合”指两个或两上以上系统或运动方式间通过各种相互作用而彼此影响以至联合起来的现象,可较全面地反映子系统间的耦合程度[14-15].考虑到此模型具有无法判断耦合是否为良性的局限性,即当各系统综合发展水平都处于较低水平时,仍然能够得到较高的耦合度[16],采用耦合协调度来量化系统间的耦合协调情况.根据“五化”的指标数据特征,借鉴何太蓉、徐维祥、王侠等人的研究成果[17-19],确定“五化”耦合度C及协调度D的计算模型,以更好地反映各系统间不同的耦合协调发展程度,表达式为:
式中:C为耦合度;D为协调度.
-
地理探测器是一种通过探测要素空间分层异质性来揭示其背后驱动力的方法,而空间分层异质性是指层内方差之和小于层间总方差的现象[20].地理探测器中因子探测器可以探测因变量的空间分异性以及自变量对因变量的解释力;交互探测器用来解释影响因子具有独立作用还是交互作用,能够同时分析两个或者多个变量之间的交互作用对因变量影响.本研究选择因子探测器和交互探测器对“五化”的影响因子进行分析,其中因子探测分析大小用q值来衡量,一般来说,q在(0,1)之间,q值越大,影响因子对“五化”的作用强度越大;交互探测器大小则用表达式进行判断,若P(x1∩x2)<min(P(x1),P(x2)),代表因子x1和x2交互后非线性减弱;若min(P(x1),P(x2))<P(x1∩x2)<max(P(x1),P(x2)),代表x1和x2交互后单线性减弱;若P(x1∩x2)>max(P(x1)+P(x2)),代表x1和x2交互后双线性加强;若P(x1∩x2)=P(x1)+P(x2),代表x1和x2交互后非线性加强;若P(x1∩x2)>P(x1)+P(x2),代表因子x1和x2相互独立[21].因子探测器的详细表达式为:
式中:q代表因子影响力,取值范围为[0, 1],q值越大,说明变量Y(即“五化”)的空间分异性越明显;如果分层由自变量X生成,则q越大表明自变量X对属性Y的解释力越强,反之则越弱;h(h=1,…I)为变量Y或者因子X的分层;Nh和N分别为层h和全区的单元数;σh2和σ2分别是层h和全区Y值的方差;SSW和SST分别为层内方差之和和全区总方差[20].
2.1. 指标体系构建
2.2. 数据来源
2.3. 研究方法
2.3.1. “五化”综合指数
2.3.2. “五化”耦合度及协调度
2.3.3. 地理探测器
-
根据公式1测算得到“五化”各指标的发展指数(表 2).从“五化”发展指数来看,京津冀各市的城镇化、农业化和信息化发展指数随时间整体呈现缓慢上升趋势,工业化、绿色化发展指数则呈现下降趋势. 2006年、2011年和2016年城镇化和信息化发展指数较高的均为北京和天津;工业化发展指数较高的为天津、北京和唐山;农业化发展指数较高的为石家庄、邯郸、保定、邢台等地;绿色化发展指数较高的为北京、天津等地.具体来看,2006-2011年,城镇化和工业化发展指数呈现上升趋势,绿色化、农业化和信息化发展指数呈现下降趋势;2011-2016年,除工业化发展指数有所下降外,其余发展指数均呈现上升趋势.从“五化”发展指数均值来看,均随时间呈现“先下降后上升”的发展趋势.其中,农业化发展指数均值在历年均处于最高水平,其次为绿色化发展指数均值,信息化发展指数均值最低,表明当前京津冀地区各市总体上仍以农业化发展为主,同时注重绿色化的发展,但对高新技术产业的支持和资金投入力度还不够,进而影响了城镇化和工业化发展指数均值,未来仍需大力发展信息化产业,以提高区域的“五化”整体发展水平.
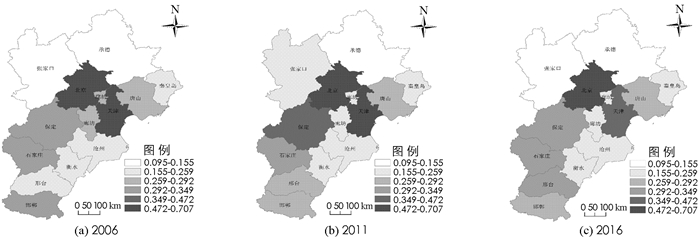
根据公式2测算得到京津冀各市历年的“五化”综合发展指数,结合GIS绘制成图 2.具体来看,①综合发展指数最低阶段[0.095,0.155]. 2006年和2016年均为张家口和承德;2011年仅承德1市,表明处于该阶段的城市“五化”发展水平处于低水平阶段且数量较为稳定,且集中分布于京津冀的北部地区,未来仍有一定的发展空间. ②综合发展指数较低阶段(0.155,0.259]. 2006年为秦皇岛、沧州、衡水和邢台;2011年变为秦皇岛、沧州、衡水、廊坊和张家口,原有的邢台在石家庄等地辐射带动下,向高一级跃进,廊坊则受沧州等低值区影响,“五化”综合发展水平下降至该阶段,而张家口则受北京的影响,“五化”综合发展水平提高,发展至该阶段;2016年,张家口“五化”综合发展水平下降,发展为低一级类型阶段,其余城市未发生变化. ③综合发展指数偏低阶段(0.259,0.292]. 2006年为唐山和廊坊;2011年分布范围扩大,为唐山、邢台和邯郸,原有的廊坊“五化”综合发展水平有所下降,发展为低一级类型;2016年仅有唐山和邯郸,原有的邢台“五化”综合水平随时间呈逐步上升趋势,发展为高一级类型. ④综合发展指数一般阶段(0.292,0.349]. 2006年为保定、石家庄和邯郸;2011年分布范围缩小,仅有石家庄,原有保定在北京辐射带动下,向高一级跃进,而邯郸则受周边低值区域影响,发展为综合发展指数偏低阶段;2016年为保定、石家庄和邢台,其中保定的“五化”发展水平在2011年基础上有所下降,重新发展至该阶段,邢台则在石家庄影响下“五化”水平有所提高,上升至该阶段. ⑤综合发展指数偏高阶段(0.349,0.472]. 2006年为零;2011年仅有保定,表明保定随时间发展“五化”综合发展水平有所提升,且处于偏高水平;2016年分布范围向东北部移动,仅有天津,原有保定在周边低值区域影响下,“五化”发展水平有所下降,发展为综合发展指数一般阶段. ⑥综合发展指数较高阶段(0.472,0.707]. 2006年有北京和天津;2011年没有变化;2016年仅有北京,表明北京和天津的“五化”综合发展水平一直处于京津冀地区最高水平,但天津随时间发展“五化”水平略有下降.整体来看,北京、石家庄、唐山和承德随时间“五化”发展趋于稳定状态,秦皇岛、沧州、衡水、邢台趋于上升状态,天津、邯郸和廊坊趋于下降状态,而张家口和保定则呈现趋于先上升后下降的状态.
受政策实施和经济发展速度的影响,2006-2011年,“五化”综合发展指数呈现快速上升趋势;2011-2016年,呈缓慢下降趋势.整体上看,2006年、2011年和2016年,“五化”综合指数越大,其位置分布越靠近北京和天津;反之,其位置越靠近边缘地区.受北京、天津的辐射带动影响,京津冀“五化”综合发展指数整体较高,大致呈由中心的北京、天津向四周逐渐扩散降低的趋势;同时,“五化”综合发展指数随时间呈现波动变化特征,其中京津冀西南部城市波动变化较大,东北部城市则相对平稳.原因在于:①受传统发展模式制约,北京、天津地区侧重于信息化与城市化的发展,唐山侧重于工业化的发展,承德和秦皇岛侧重于绿色化发展,邢台等市则侧重于农业发展,因而导致不同城市综合发展水平出现一定差异;②随着国家政策的不断调整和京津冀一体化战略实施的进一步深入,城市之间经济社会联系不断增强,但北京和天津社会经济发展水平和政策优势突出,其他城市优势相对较弱,区域差异依然存在;③传统发展方式中对于农业现代化发展的重视度不足,加上城市化发展水平的差异,导致各市的“五化”综合发展水平有所不同.
-
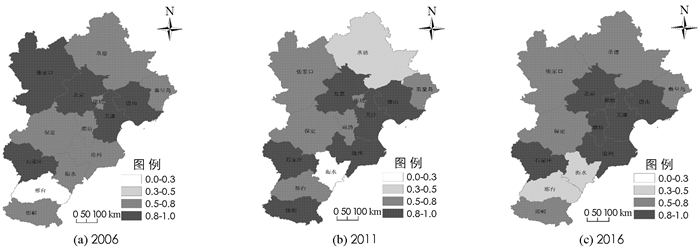
根据耦合度测算结果,结合自然断点分级法,将“五化”耦合度划分为低水平耦合阶段、颉颃阶段、磨合阶段和高水平耦合阶段四个阶段,见图 3. ①低水平耦合阶段(0 < C≤0.3),2006年仅有邢台;2011年变为衡水,原来的邢台市“五化”之间联系度加强,向较高一级发展;2016年处于此阶段城市消失. ②颉颃阶段(0.3 < C≤0.5),2006年为零;2011年仅有承德,表明承德地区“五化”耦合度处于较低水平,距高耦合水平阶段还有一定差距;2016年变为衡水和邢台,表明这2市的耦合度水平随时间不断增强,原有承德在周边高耦合区域的辐射带动下,耦合度增强,发展为磨合阶段. ③磨合阶段(0.5 < C≤0.8),2006年有7个,分别为秦皇岛、承德、廊坊、保定、沧州、衡水和邯郸,分布范围较大;2011年有5个,分别为张家口、保定、廊坊、秦皇岛和邢台,分布范围发生变化,分布重心向西部移动;2016年有5个,分别为秦皇岛、承德、张家口、保定和邯郸,分布重心向京津冀城市群的北部、西部和南部地区分散. ④高水平耦合阶段(0.8 < C≤1),2006年有5个,分别为张家口、北京、天津、唐山和石家庄,表明这些地区耦合度均处于区域最高水平;2011年有6个,分别为北京、天津、唐山、石家庄、沧州和邯郸;2016年为北京、天津、唐山、石家庄、廊坊和沧州,分布重心不断向北京和天津移动.综上可知,2006-2016年京津冀“五化”整体处于较高水平的耦合阶段,耦合状态在波动变化中不断趋于优化,处于高水平耦合阶段城市逐渐增多,低水平耦合阶段城市逐渐减少最终消失.从空间上看,高值耦合区域分布范围逐渐扩大且随时间逐渐趋于集中分布,最终汇集于北京和天津周边,并以此为中心向四周逐渐呈环形减弱趋势;从时间上看,耦合度随时间不断趋于优化,区域整体耦合度不断增强.总体上看,在京津冀一体化和协同发展政策支持下,各城市“五化”系统彼此之间互动磨合和适应程度不断加强.
-
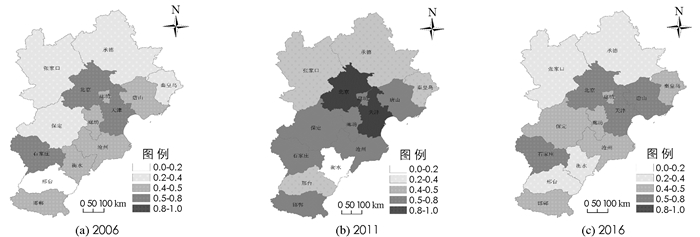
根据协调度测算结果,借鉴王琦等人的研究成果[18],采用自然断点分级法将“五化”协调度划分为5个阶段,见图 4. ①严重失调阶段(0 < D≤0.2). 2006年仅有邢台;2011年变为衡水,原来的邢台市由于“五化”各要素间的关联度日益增强,发展为中度失调阶段;2016年处于此阶段城市消失. ②中度失调阶段(0.2 < D≤0.4). 2006年处于该阶段的城市有4个,分别为张家口、承德、秦皇岛和保定;2011年分别为张家口、承德、秦皇岛和邢台;2016年分别为张家口、承德、邢台和衡水,分布范围逐渐向南北方向移动,原来的秦皇岛“五化”之间联系度增强,发展为基本协调水平阶段,而衡水则在石家庄等地带动下,上升到该阶段. ③基本协调阶段(0.4 < D≤0.5). 2006年为唐山、廊坊、沧州、衡水和邯郸;2011年为廊坊、沧州、保定和邯郸;2016年增加了秦皇岛,表明秦皇岛协调度相较2011年有所提升,“五化”之间的联系度加强. ④中度协调阶段(0.5 < D≤0.8). 2006年为北京、天津和石家庄;2011年增加保定、廊坊、沧州、邯郸和唐山,北京和天津向高一级跃进;2016年与2011年相比变化较大而与2006年相近(增加了唐山),表明该阶段处于不断波动发展状态,但石家庄一直较稳定. ⑤高度协调阶段(0.8 < D≤1).仅2011年包含北京和天津,目前未有城市处于该阶段.
整体来看,处于协调阶段的城市大致可细分为以下两类:①优质协调区.以北京和天津等城市为首,该类型区处于京津冀的核心区域,各种设施条件优越,“五化”的各指标发展指数及综合发展指数均相对较高. ②一般协调区.以保定、沧州、邯郸等京津周边城市为首,该类型区处于京津周边环线及京津冀的南部地区,受京津地区的辐射带动作用,“五化”发展水平随时间不断提高,但整体发展指数偏低.
据以上分析可知,京津冀“五化”协调水平随时间不断向高协调阶段转化,但均未达到高度协调水平阶段,以基本协调和中度协调为主,且处于失调阶段的城市占比较大,未来城市各系统之间协调发展水平还有较大的提升空间.在空间上看,处于协调阶段的城市多集中于中部和东部地区,而南部、北部及西部地区城市多处于不协调阶段,差距较大;在时间上看,京津冀各市的“五化”协调度逐渐向高协调类型转变,处于高协调阶段的城市数量逐渐增加,而处于失调阶段的城市逐渐减少甚至消失.
3.1. 京津冀“五化”综合发展指数时空格局演变
3.2. 京津冀“五化”耦合度时空变化
3.3. 京津冀“五化”协调度时空变化
-
在不同的时间节点,京津冀城市群的发展水平不同,为了更加客观、有效地反映现阶段的“五化”发展状况,选取最能反映当前情况的2016年为研究时点,采用地理探测器中的因子探测器和交互探测器来探测因子的显著性,并衡量各影响因子对“五化”的影响强度以及各因子的交互影响程度.根据京津冀“五化”的实际发展程度,选取11个指标作为综合性影响因子,具体包括:产业结构(X1)、人均固定资产投资额(X2)、教育支出水平(X3)、科研经费支出水平(X4)、人均GDP(X5)、城乡收入比(X6)、人均公园绿地面积(X7)、当年实际使用外资金额(X8)、公路客运量(X9)、居民人民币储蓄存款余额(X10)和人口密度(X11).
从表 3的因子探测结果来看,京津冀“五化”的主导因子及因子解释力差距较大.整体来看,所有影响因子的值均有统计学意义,但是各因子影响程度具有较大的差异,具体因子影响力q值从大到小依次为:当年实际使用外资金额、人均公园绿地面积、居民人民币储蓄存款余额/人均GDP、科研经费支出水平、公路客运量、教育支出水平、城乡收入比、人口密度、人均固定资产投资额、产业结构.其中当年实际使用外资金额对“五化”的综合影响程度显著区别于其他因子,q值显著水平高达0.714,该因子可直观反映该城市的经济发展水平,使用金额数量越大,城市经济发展形式越好,“五化”发展水平也越好,因此为主导影响因子;人均公园绿地面积、居民人民币储蓄存款余额、人均GDP、科研经费支出水平、公路客运量和教育支出水平的因子解释力q值也高达0.5以上,分别为0.646,0.609,0.600,0.539和0.538,这些因子涉及绿化、居民生活、科技水平、教育能力及交通等各个方面,可以较为全面地反映一个城市的综合发展水平,对于“五化”的发展具有重要促进作用,属于高水平影响因子;而人口密度、人均固定资产投资额和产业结构对“五化”的影响程度则处于较低水平,值均处于0.5以下,分别为0.427,0.397和0.299,由于京津冀各城市人口悬殊,产业结构发展中各有侧重,且除北京、天津的经济发展水平和科研能力较高外,其余城市发展程度差异较大,因此这些影响因素对“五化”的综合影响力较弱,属于一般影响因子.综上分析可知,经济、科研、绿化、交通和教育等方面因子对“五化”产生的影响力较大,而人口和产业结构的影响力则较弱,且主要受京津冀区域整体社会经济发展状态和劳动力状态的影响.
从表 4的交互探测结果来看,各影响因子对“五化”的耦合协调发展均存在交互作用,任意两个因子交互后的影响力均具有双因子增强或者非线性增强的特征,表明在任意两因子综合作用下,城市“五化”内部发展差异减小,交互因子影响力显著增强,即经济、科研、绿化、交通和教育等方面的综合作用与“五化”发展之间的联系要优于单项因子的独立作用.当年实际使用外资金额作为主导影响因子,与其他因子交互后解释力持续增强,优于单项因子解释力水平,表明任一因子在资金的支撑下,影响力增强,印证了经济因素是保证“五化”协调发展的重要动力源泉;产业结构与人口密度作为一般性影响因子,与其他因子交互后影响力显著增强,印证了产业结构和人口密度影响因子对“五化”发展的至不可或缺性.其中,影响力最强的为当年实际使用外资金额和人均固定资产投资交互因子,交互影响值达到0.987;其次为实际使用外资金额和人均GDP交互因子,交互影响值达到0.980,说明经济性因子对“五化”的影响最大.综上可知,所选影响因子对“五化”发展均存在明显的交互作用,未来要在经济又好又快发展的背景下,发挥高水平影响因子的主导作用,同时注重与各一般性及低水平影响因子之间的融合,增强因子间的综合影响力水平,逐步提高“五化”综合协调发展水平.
-
1) 结合“五化”数据特征和GIS分析得到,京津冀“五化”各指标发展指数和综合指数区域差异性较大,但随时间均呈现缓慢上升趋势且差距逐渐缩小,其中北京和天津等经济发展中心地区各指标发展指数和综合指数均处于区域最高水平,并以此为中心向四周呈梯度衰减趋势.
2) 通过耦合度和协调度测算结果可知,京津冀“五化”耦合度整体处于较高水平阶段,北部城市耦合度高于南部,且随时间不断优化;协调度整体处于高度协调水平以下,相对较低,在空间上呈由东部向西部逐渐降低趋势,未来还有一定的提升空间.
3) 通过地理探测器中的因子探测器和交互探测器分析可知,选取的11个综合因子对“五化”的综合影响力差异有统计学意义,且任意两因子交互后影响力显著增强.总体来看,经济类影响因子对“五化”影响程度较大,其他因子的影响则相对较弱,其中当年实际使用外资金额影响程度最大,属于主导因子,而人口密度和产业结构等指标影响程度最小,属于一般影响因子;各因子的交互作用反映了京津冀城市群“五化”发展影响因素的综合性和多样性.
-
研究侧重于“五化”的耦合协调及时空分异和影响因子的分析,可为京津冀城市群的一体化发展提供新的分析思路,但仅选取了2006年、2011年和2016年作为研究时点,未来可适当完善时间序列,采用面板数据进行研究;研究区域集中于京津冀城市群,未来会进一步细化到市区和县域等微观单元;由于篇幅限制,仅对“五化”内涵及发展的机理进行了简单叙述,未就此展开深入剖析,未来会针对此问题作进一步探究.
针对京津冀地区“五化”的科研创新能力整体较弱,产业结构水平不尽合理,区域差异较大,协调水平不高等问题,未来要在京津冀协同发展战略布局背景下,继续增加科研技术投入,进一步加大高素质创新人才引进力度,优化调整产业利用布局与结构,加强地区之间的交流,保障就业,促进人居和谐及区域一体化发展水平,增强区域的全面、可持续发展能力;完善相关政策,坚持协调发展及内部优化策略,以京津地区为中心,扩散“五化”的整体影响力,为“五化”的协调发展提供强劲动力,进而提高区域整体竞争力.



 下载:
下载: