-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
近年来,锌指核酸酶(ZFNs)、转录激活物样效应器核酸酶(TALENs)、聚集的规则间隔短回文重复序列/CRISPR相关蛋白9(CRISPR/Cas9)等基因编辑技术在动植物中得到了快速的发展[1]. CRISPR/Cas9由于其高效性、简便性以及低成本等优点迅速成为最受欢迎的基因编辑技术之一,该技术不仅在生物学方面起着革命性的突破作用,在人类疾病防治和动植物育种方面也具有较大潜力[2-3]. 随着其重要性的增加,CRISPR/Cas9系统先后在拟南芥、烟草、高粱、水稻、黄豆、玉米和其他植物中建立起来[4-7]. CRISPR/Cas9的递送方法主要是基于传统的遗传转化(比如农杆菌)致使外源DNA片段插入到靶标宿主的基因组上[8]. 由于缺乏有效的方法,很多植物难于进行遗传转化. 尽管通过杂交选择后代的方法可以分离转基因元件,但在基因编辑过程中涉及的转基因未来仍可能会引发公众和监管部门的注意[9]. 为了克服监管障碍,Woo等[10]在体外将Cas9蛋白和gRNA复合物进行组装后,利用聚乙二醇将其转染到原生质体中,从而在拟南芥、烟草、莴苣和水稻的再生植株中实现靶向突变. 该策略在玉米和小麦中也展现了很高的效率和更低的脱靶[11-12],然而,该方法的前提必须是要分离获得靶标植物的原生质体,否则该策略就不能进行. 目前该方法在大部分的非模式植物中基本上还没有成功,而病毒递送CRISPR元件也许是一个比较好的方法,原因如下:1) 病毒不会整合到宿主植物基因组中,因此其产生的是非转基因植物[13];2) RNA病毒能高量表达外源蛋白[14];3) 马铃薯病毒X(PVX)能从一个细胞移动到另外一个细胞,从而系统感染植物[15]. 由于大部分的病毒载体只能运载较小的蛋白,比如锌指核酸酶[16]等,而来源于金黄色葡萄球菌的SaCas9(3.1kb)由于其太大,因此不能直接在植物病毒中表达. 有研究报道,可以将Cas9分成两段在病毒载体中独立表达,然后采用多种系统将分段的Cas9连接起来,从而行使完整Cas9的编辑作用,这些系统包括:1) sgRNA作为支架用于Cas9组装;2) 雷帕霉素控制的FKBP/FRB系统;3) 光调控的磁性系统;4) 内含肽[17-19]. Moretti等[20]采用腺相关病毒载体(rAAV)运载内含肽介导的Cas9,成功在杜兴氏肌肉萎缩症模型猪中进行体细胞基因编辑,有效改善了骨骼肌和心肌衰竭.
本研究我们开发了一个内含肽介导的片段化Cas9系统,用于植物的基因编辑. 将SaCas9基因分割成3个部分,通过内含肽DnaB或DnaE将其进行组合,并采用马铃薯病毒X载体进行递送,使其能系统感染烟草.
HTML
-
研究使用的HEK293FT,是一种人胚胎肾细胞系,保存于西南大学前沿交叉学科研究院生物学研究中心. 在37 ℃条件下,用Dulbecco改良的Eagle氏培养基、约5%的CO2和10%的胎牛血清(合格,Invitrogen)培养细胞. 植物材料使用栽培烟草红花大金元,在烟草的4片真叶期用于瞬时转染.
-
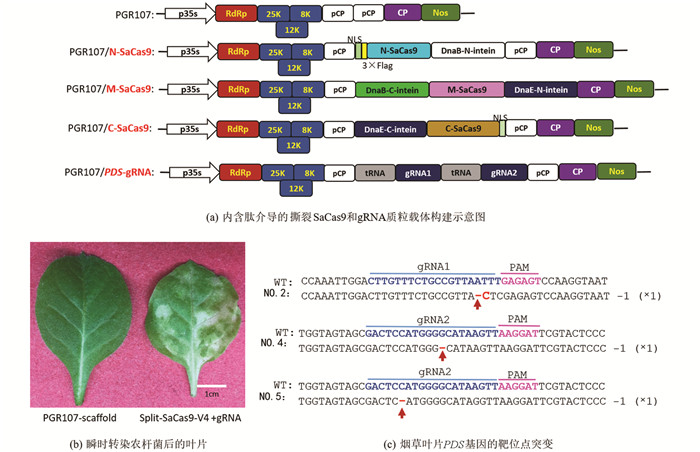
利用化学方法合成EF1a启动子后,采用Nco I,Sal I和Xho I酶切连接的方法将EF1a启动子插入到PUC-V4-N-SaCas9载体上,以形成含有SV40终止子的EF1a-V4-N载体. 在金斯瑞生物科技公司化学合成gRNA-T4S和12个内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9(V1-N-SaCas9,V1-M-SaCas9,V1-C-SaCas9,V2-N-SaCas9,V2-M-SaCas9,V2-C-SaCas9,V3-N-SaCas9,V3-M-SaCas9,V3-C-SaCas9,V4-N-SaCas9,V4-M-SaCas9,V4-C-SaCas9),并通过Nco I和Sal I将其插入到EF1a-V4-N载体,以构建EF1a-V1/V2/V3/V4-N/M/C-SaCas9载体. 采用Cla I和Sal I将内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9克隆到马铃薯病毒X载体(PGR107)上,以形成PGR107-V4的4个系列载体:PGR107-V4-N-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-M-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-C-SaCas9和PGR107-gRNA-T4S.
-
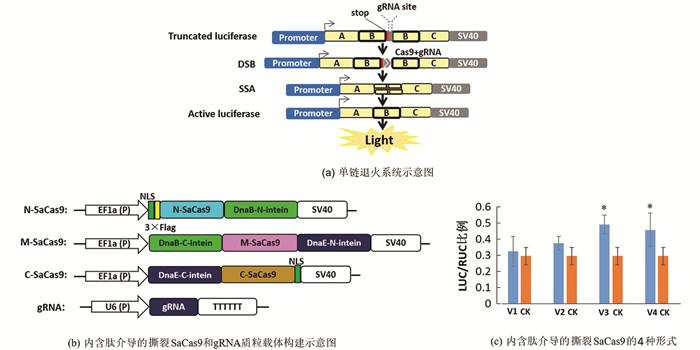
基于Huang等[21]描述的方法构建单链退火系统(SSA). 在SSA中,采用人巨细胞病毒启动子启动荧光素酶(LUC)的表达[21]. 将荧光素酶切分成3个部分,分别命名为LUC-A (317 bp),LUC-B (871 bp)和LUC-C (465 bp). 将终止子(TGA)和gRNA靶位点置放于2个LUC-B之间,从而将LUC分成2个部分. 当Cas9和gRNA加入到SSA中,gRNA会引导Cas9去切割DNA,从而形成双链缺口,2个LUC-B可基于SSA形成完整的荧光素酶,用pRL-TK载体表达海肾萤光素酶(RUC)作为对照组. 将HEK293FT细胞置放在有培养基的24孔板中,加入300 ng内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9(EF1a-Vx-N-SaCas9,EF1a-Vx-M-SaCas9和EF1a-Vx-C- SaCas9),300 ng的EF1a-gRNA,150 ng的SSA质粒和50 ng海肾萤光素酶质粒,利用脂质体2000将其共转染到细胞中. 48 h后,收集细胞,基于操作手册采用双荧光素酶检测系统测定萤光素酶(LUC)和海肾荧光素酶(RUC)的活性. 每个实验重复3次.
-
基于Pandey等[22]的方法进行少许修改,进行病毒感染的瞬时侵染实验,主要包括以下步骤:将4种质粒(PGR107-V4-N-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-M-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-C-SaCas9和PGR107-gRNA-T4S)转化到农杆菌GV3101菌株中,挑取阳性克隆子在含有卡那霉素(50 mg/L)和利福平(25 mg/L)的酵母抽提物牛肉培养基中28 ℃生长16 h;通过离心的方式收集农杆菌细胞,并将其利用侵染溶液(含10 mmol/L MES,10 mmol/L MgCl2和200 μmol/L乙酰丁香酮)重悬,使农杆菌细胞的光密度在1.6~2.0范围内;将4种农杆菌按照1∶1∶1∶1的比例进行混合,并将其放置在25 ℃培养箱中静置4~6 h;使用注射器针头将上述混合的重新悬浮的农杆菌渗透到植株叶片的远轴表面.
-
将农杆菌注射到烟草叶片15 d后,收集新长出的叶片以及注射的叶片,采用EasyPure Plant Genomic DNA Kit提取烟草叶片的DNA,并以此为模板,设计引物进行PCR扩增,采用PEASY-T5进行TA克隆,最后在华大基因公司进行Sanger测序. 通过序列分析,以判定DNA的突变形式和突变效率.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 载体构建
1.3. 单链退火系统的构建和荧光素酶活性检测
1.4. 病毒侵染
1.5. DNA提取和突变检测
-
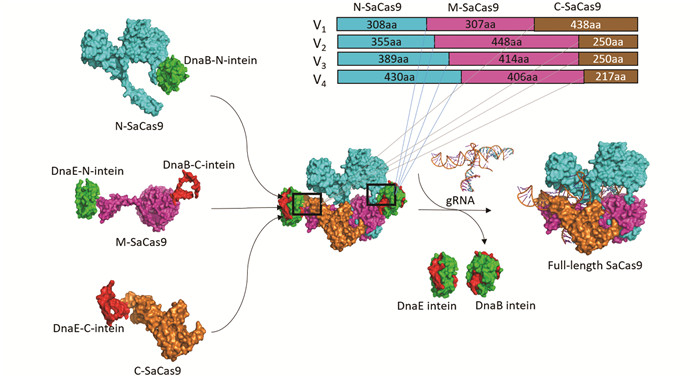
当植物病毒载体运送外源DNA时,外源DNA的大小和蛋白表达的稳定性呈现出负相关[23]. SaCas9基因的大小是3.1 kb,我们将SaCas9的编码序列分成3部分以适应马铃薯病毒X载体(PGR107)的运载能力. 内含肽介导蛋白表达的方法被应用于体内重新产生全长的SaCas9蛋白. 基于SaCas9蛋白的晶体结构鉴定了7个可能的潜在切割位点[24],从而形成了4个N端形式,称为N1-308,N1-355,N1-389和N1-430,4个中间体形式,称为M309-615,M356-803,M390-803和M431-836,3个C端形式,称为C616-1053,C804-1053和C837-1053. 内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9是由N端、M端和C端的SaCas9,经由内含肽DnaB或DnaE连接而来(图 1). 为了确保内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9具有核酸酶的活性,将SaCas9设计了4种形式(V1,V2,V3和V4). V1采用SaCas91-308,SaCas9309-615和SaCas9616-1053作为撕裂Cas9,形成的3种融合结构称为V1-N-SaCas9,V1-M-SaCas9和V1-C-SaCas9;V2采用SaCas91-355,SaCas9356-803和SaCas9804-1053作为撕裂Cas9,形成的3种融合结构称为V2-N-SaCas9,V2-M-SaCas9和V2-C-SaCas9;V3采用SaCas91-389,SaCas9390-803和SaCas9804-1053作为撕裂Cas9,形成的3种融合结构称为V3-N-SaCas9,V3-M-SaCas9和V3-C-SaCas9;V4采用SaCas91-430,SaCas9431-836和SaCas9837-1053作为撕裂Cas9,形成的3种融合结构称为V4-N-SaCas9,V4-M-SaCas9和V4-C-SaCas9.
-
为了高效测试内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9是否具有活性,我们构建了单链退火系统(SSA),将荧光素酶基因分成3个部分,包括A,B和C区域(图 2). 将终止子和gRNA靶位点放于2个B区域之间. 如果添加的Cas9蛋白具有活性,Cas9能将gRNA靶位点切割形成双链缺口,基于SSA修复机制,荧光素酶的B区域将被修复,形成一个完整的荧光素酶基因,因此荧光素酶的活性就能被检测到(图 2a). 在该实验中,内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9的4种形式(SaCas9-V1/V2/V3/V4)和gRNA在载体中分别被组装起来(图 2b). gRNA,EF1a-N/M/C-SaCas9和SSA载体同时转染到HEK293FT哺乳动物细胞中,48 h后检测荧光素酶的活性. 结果表明在4种测试形式中,有2种形式(V3和V4)的LUC/RUC的比例显著高于对照组(只有SSA和pRL-TK载体)(图 2c). 该结果表明了内含肽DnaB和DnaE能高效介导全长Cas9蛋白的形成. V1和V2不能使3部分的SaCas9片段形成全长SaCas9的原因可能是第306号、315号、或第613号氨基酸残基起了十分重要的作用. 此外,SSA活性暗示了重新形成的Cas9蛋白保留了基因编辑的活性,基于此,选择V4用于后续研究.
-
为了进一步检测内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9是否能在植物中有效引起突变,构建了V4形式的撕裂SaCas9到PGR107载体中,CP启动子控制了撕裂SaCas9的表达,gRNA也在CP启动子中表达. 应用tRNA系统构建了2个gRNA靶向PDS基因(图 3a). 将4种含有PGR107-V4-N-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-M-SaCas9,PGR107-V4-C-SaCas9和PGR107-gRNA-T4S质粒的农杆菌侵染处于4~6叶期的烟草叶片中,15 d后,在烟草叶片上出现了白化的表型(图 3b),而在对照组(只有PGR107载体)中,没有出现白化的表型. 为了探究白化表型是否是由于植物病毒载体表达的撕裂SaCas9引起的,收集了5个植株新发育的叶片,进行DNA提取、PCR扩增、TA克隆和Sanger测序,序列分析表明在2号植株中在gRNA位点1上有单碱基的删除和替换,在第4号和第5号植株上出现了单碱基的删除(图 3c). 以上结果暗示由于移码突变,PDS基因不能被翻译成正确的蛋白,从而使烟草叶片变为白色,而经由内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9引起PDS突变的频率较低,在1.25%~5.00%之间(表 1). 该结果可能是因为SaCas9被分成了3个部分,而仅有少部分形成了全长SaCas9分子.
2.1. 内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9系统的设计
2.2. 内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9在SSA中有活性
2.3. 内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9能通过马铃薯病毒X递送到烟草中有效靶向PDS基因
-
在本研究中,我们构建了内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9载体. 采用SSA系统,在一种哺乳动物细胞系中证实了内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9活性. 采用瞬时侵染的方法,发现马铃薯病毒X载体(PGR107)能运载撕裂SaCas9,SaCas9能在新长出的叶片中表达,并能实现靶向编辑烟草的内源基因.
目前已经开发了两种非转基因的基因组编辑策略,以推广和应用基因组编辑方法产生新的植物:1) 从大肠杆菌中纯化到核酸酶(Cas9,Cpf1)和gRNA在体外进行组装,将该复合物通过聚乙二醇或是基因枪递送到原生质中,之后由原生质体再生形成非转基因的小苗[11-12];2) 通过植物病毒载体瞬时表达锌指核酸酶[16]. 以上两种方法与传统RNA引导的核酸内切酶(RGEN)相比,能得到非转基因植株,但外源DNA不会插入到宿主基因组中. 由于第1种方法效率高、时间少、脱靶率低,已经成功应用到一些双子叶(拟南芥、烟草、莴苣、马铃薯和牵牛花)和单子叶植物(水稻、玉米和小麦)中[10-12, 23, 25-26]. 在RNA引导的核酸内切酶复合体方法中用到的原生质体分离、转染以及再生步骤,则会阻止该方法在其他植物中的应用和延伸. 由于便携的操作和不需要原生质体,Marton等[16]采用TRV成功在烟草和牵牛花中表达了锌指核酸酶,并获得了可以遗传的基因编辑植株.
马铃薯病毒X是一种单链病毒,不能被整合到宿主基因组DNA中[23]. 此外,马铃薯病毒X在多个组织中可以高量表达,且能系统感染,所以该病毒被应用于基因功能研究以降低基因的表达量或是在植物中表达具有商业价值的蛋白[15, 22]. 在本研究中,采用马铃薯病毒X表达SaCas9蛋白,可获得非转基因的编辑烟草植株.
本研究采用内含肽介导的撕裂SaCas9蛋白成功在烟草叶片中编辑了PDS基因,然而该系统的编辑效率不是很高,主要的原因可能是SaCas9被分成了3个部分,而3个部分比2个部分组装形成全长SaCas9的概率低,因此探寻更小的Cas9[27]或是运载能力更大的载体,或许能提高撕裂SaCas9的效率. 如果该系统的效率能得到提升,那么其可能在植物基因功能研究上成为一个简单且有效的基因编辑方法.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: