-
MYB类转录因子与植物生长发育、生理代谢、逆境响应等过程有关,是植物中最大的转录因子家族之一,包含众多成员[1-3]. MYB类转录因子具有高度保守的MYB结构域,因MYB结构域的数量差异,被分为R1-MYB,R2R3-MYB,R1R2R3-MYB和4R等不同的亚类[3].在这些类别中,一般植物含有R2R3-MYB数量较多,且研究较为深入.如在模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中,有64个R1-MYB类基因,126个R2R3-MYB类基因,5个R1R2R3-MYB类基因,1个4R-MYB类基因[4-5].水稻(Oryza.sativa)中有70个R1-MYB类基因,109个R2R3-MYB类基因,5个R1R2R3-MYB类基因,1个4R-MYB类基因[4].不同类别的MYB在功能上具有一定差异,因此,对植物MYB进行相关研究应首先分析其属类关系. R1-MYB也参与调控植株的逆境响应过程,如过表达羊草(Leymus chinensis)R1-MYB可改善转基因拟南芥的耐盐性[6];麻风树(Jatropha curca)R1-MYB(JcR1MYB1)能在根中高水平表达,且受聚乙二醇,NaCl,低温以及脱落酸(ABA),茉莉酮酸,乙烯等处理诱导而上调表达,过表达JcR1MYB1的转基因烟草具有较好的耐盐能力[7];西红柿(Solanum lycopersicum)R1-MYB在盐胁迫下与气孔开闭相关[8],但目前对R1-MYB的研究相对较少.
核桃(Juglans regia)属多年生落叶乔木,是中国重要的“木本粮油”战略树种,也是我国扶贫攻坚项目的重要树种.核桃产业在推动区域经济发展上具有重要作用,而核桃产业的健康快速发展与核桃的产量和质量息息相关.但近年来由于全球环境的变化,环境因子特别是西北地区夏秋核桃成熟期严重的高温干旱等气候现象,严重影响着核桃产业的发展.因此,选育抗逆优良核桃品种、掌握核桃抗逆适应机制,对深入了解核桃的适应性具有重要指导作用.而这关键的技术之一就是筛选鉴定核桃抗逆相关基因并对其进行功能机制分析.鉴于此,本研究我们克隆获得1条核桃的R1-MYB(JrEFM1),对其基本生物学信息、启动子及逆境处理下的表达进行分析,探讨该基因的逆境响应潜力,为后续深入开展核桃逆境适应分子机制研究提供候选基因.
HTML
-
本研究以2年生‘香玲’核桃嫁接苗为试验材料.分别对核桃进行5 ℃(低温),45 ℃(高温),干旱(20%PEG6000),0.1 mmol/L ABA,2 mg/L水杨酸(SA)以及100 mg/L茉莉酸(JA)胁迫处理0,3,6,12,24 h,0 h为对照.分别收集各处理时间点的根和叶,液氮速冻后保存于-80℃冰箱备用.干旱,SA,ABA及JA胁迫均使用浇灌根部的方法进行处理,且在胁迫时间内植株托盘有足够溶液保证处于胁迫状态.每个处理重复3次,每次重复处理包含6棵植株.
-
以“MYB transcription factor”为关键词在‘香玲’核桃转录组中查找相关基因,经BLAST比对分析,获得若干MYB基因,选择其中1条R1-MYB(命名为JrEFM1)进行分析.用ORF finder(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)确定JrEFM1的开放读码框(ORF),根据ORF两端序列设计引物JrEFM1-F和JrEFM1-R(表 1),进行PCR扩增.扩增产物经纯化后与pMD-18-T连接并转化大肠杆菌DH5ɑ感受态细胞,挑取阳性克隆进行菌液PCR及测序确认.利用Expasy ProtParam(http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)对确认的JrEFM1序列特征进行分析.利用BLASTP(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast)进行序列同源性搜索;利用Clustal 3.0软件对不同物种的R1-MYB进行进化分析.使用plantCARE(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)及PLACE(https://sogo.dna.affrc.go.jp/cgi-bin/sogo.cgi?lang=en&pj=640&action=page&page=newplace)分析该基因启动子中含有的顺式作用元件.
-
采用CTAB法提取各样品总RNA,经DNA消化酶处理后采用PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit(CWBIO,康为世纪,中国)反转录为cDNA,稀释10倍作为实时荧光定量RT-PCR(qRT-PCR)的模板,18S rRNA基因为内参基因[9-10],引物见表 1. qRT-PCR使用SYBR Green Real time PCR Master mix(CWBIO)进行. qRT-PCR定量引物为JrEFM1-DL-F和JrEFM1-DL-R(表 1).定量反应使用Applied Biosystems生产的StepOneTM Real-Time PCR System进行.反应程序为94 ℃预变性30 s;94 ℃变性12 s,60 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,45个循环;81 ℃读板1 s,每个样品重复3次.采用2-△△Ct法对定量结果进行相对分析[11],相对表达水平为相对于内参基因及对照的表达值.
1.1. 材料及处理
1.2. JrEFM1的克隆与分析
1.3. JrEFM1的表达分析
-
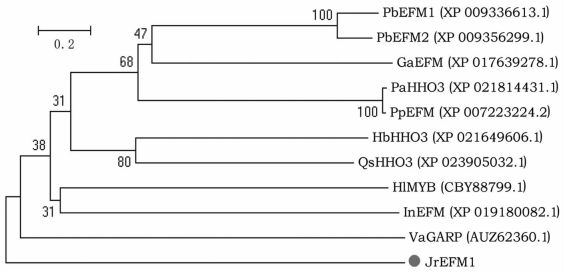
以核桃cDNA为模板,通过核桃转录组查找及PCR验证获得1条R1-MYB基因,即JrEFM1.经分析发现JrEFM1基因ORF长1 320 bp(图 1),相对分子质量为48.322 kDa,编码的蛋白包含439个氨基酸(图 2),理论等电点为9.26. BLAST分析发现该基因具有1个Myb_DNA-bing(Accession pfam00249)保守结构域,含有myb_SHAQKYF,PLN03162结构,表明JrEFM1为R1-MYB[12].经BLASTP同源搜索及TAIR网查找获得不同植物的MYB蛋白,与JrEFM1蛋白进行进化分析,发现JrEFM1蛋白与葡萄(Vitis amurensis)VaGARP进化关系较近(图 3),推测JrEFM1蛋白与这些同源蛋白具有相似功能.
-
从NCBI数据库中获得JrEHM1起始密码子上游1 578 bp的DNA序列进行启动子生物信息学分析,PlantCare及PLACE预测显示,JrEHM1启动子中除了TATA-box,CAAT-box等常见元件外,还包含与逆境响应及激素调控相关的顺式作用元件,如干旱胁迫(MBS),热激响应(HSE),ABA,SA,玉米素(O2-site),赤霉素响应(GARE-motif)等(表 2),推测其具有调控JrEHM1参与逆境刺激的能力.
-
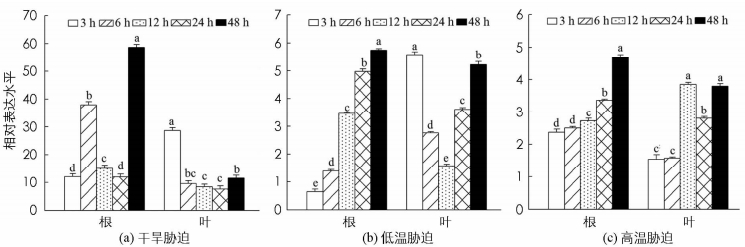
对基因进行逆境胁迫下的表达分析,有利于快速了解其响应逆境的潜在功能.对核桃进行不同逆境处理后,通过qRT-PCR技术分析JrEFM1在干旱、低温及热激胁迫下的表达水平,有利于预测JrEFM1响应干旱、低温及高温胁迫的功能.结果显示,JrEFM1能被干旱、低温及高温胁迫不同程度地诱导;不同胁迫时间下,在叶和根中的表达水平存在明显差异;在同一时间点,JrEFM1在根和叶中的转录水平具有差异,表明JrEFM1在干旱、低温及高温胁迫响应中具有时间表达及组织表达特异性(图 4).从具体表达水平上看,干旱胁迫能诱导JrEFM1在根和叶中高水平表达,其在根中胁迫48 h的表达最大,为对照的58.62倍;在叶中,JrEFM1的表达水平较根中低,最大值出现在3 h,为对照的28.64倍(图 4a).低温胁迫下,JrEFM1在根的表达随胁迫时间延长变大,到48 h时达最大,为对照的5.74倍;在叶中,JrEFM1的表达在3~12 h逐渐下降,在12~48 h逐渐升高,最低值为对照的1.58倍(图 4b).高温胁迫下,根中JrEFM1的表达随时间延长逐渐增大,为对照的2.37~4.68倍;在叶中,其转录水平为对照的1.53~3.79倍(图 4c).
-
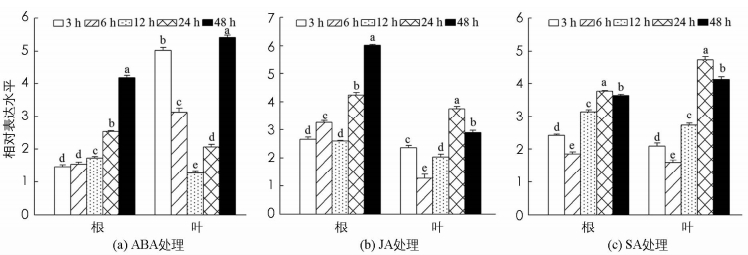
通常情况下,在逆境响应中,很多基因表达与相关激素信号通路相关.因此,对核桃材料进行不同的激素处理后分析JrEFM1的表达情况,有利于了解JrEFM1响应激素调控的功能.结果显示,在ABA,SA和JA处理下,JrEFM1在根和叶中都被明显诱导,且也体现了时空表达特性和组织表达特性(图 5). ABA处理下,JrEFM1在根和叶中的表达趋势与低温胁迫下的表达相似,即在根中随着时间延长逐渐增大,为对照的1.46~4.18倍;在叶中则先降低后增加,12 h表达水平最低,为对照的1.27倍;最大值出现在48 h,为对照的5.41倍(图 5a). JA处理下,根和叶中的表达趋势差异较大;根中的最大表达为对照的6.02倍;在叶中的转录水平,为对照的1.27~3.75倍(图 5b). SA处理下,JrEFM1在根和叶中的表达趋势随时间变化相似,在6 h和24 h分别达到最低和最高水平;最大值分别为对照的3.77,4.75倍(图 5c).
2.1. JrEFM1全长cDNA序列分析
2.2. JrEFM1启动子分析
2.3. JrEFM1响应非生物胁迫的表达模式
2.4. JrEFM1响应外源激素刺激的表达模式
-
转录调控是植物逆境响应相关基因表达的最主要调控方式,转录因子在其中起着重要作用.植株的抗逆性是数量性状,涉及大量相关基因的协调作用,其分子调控机制十分复杂;而在基因的表达调控过程中,转录因子起到关键作用[13].核桃是我国主要经济树种之一,在推动区域经济发展上具有重要作用.核桃同其他植物一样,在受到外界干旱、盐碱、重金属、异常温度、病虫害等不良刺激时,相关转录因子会对胁迫产生应答反应[13],以降低或消除给植株带来的危害.在诸多转录因子家族中,MYB类转录因子是植物中最大的转录因子家族之一.且大量研究表明,MYB在植株逆境调控中具有重要作用.如小麦(Triticum aestivum)R2M3-MYB亚家族基因TaMyb1D在烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)植物中的过表达增强了烟草对干旱和氧化胁迫的耐受性,表明TaMyb1D作为苯丙素代谢的负调控因子,是植物对干旱和氧化胁迫耐受性的正调控因子[1].苹果(Malus×domestica)MdMYB88和MdMYB124作为冷激结构蛋白3(COLD SHOCK DOMAIN PROTEIN 3,MdCSP3)和生物钟相关基因1(CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1,MdCCA1)的直接调节因子,且能促进冷胁迫响应的H2O2解毒[14].番茄ARS1基因能被盐胁迫诱导,其表达可有效改善植株的耐盐性[8].因此,挖掘核桃MYB转录因子进行逆境响应分析,具有重要的研究前景和意义.在前期研究中,我们克隆获得了一些核桃逆境响应相关调控因子,其中包括MYB.本研究我们对其中的R1-MYB类基因JrEFM1进行分析,发现该蛋白在进化上与葡萄、番薯等的MYB相近,推测其可能与这些蛋白具有相似功能.
启动子是研究基因功能的重要组成部分,通常包含多种不同的顺式作用元件,与基因功能调节有关.如核桃JrVHAG1基因上游启动子中包含了MYB,LTR,ARE等与逆境响应相关的元件,经酵母单杂交试验调取获得上游能识别其中MYB元件的JrMYB2转录因子,参与JrVHAG1的Cd胁迫响应调控[15].柽柳TheIF1A启动子包含WRKY,MYB,DOF等与逆境响应相关的元件,经分析发现,上游调控因子Dof等基因通过识别这些元件来调控TheIF1A响应盐和干旱等胁迫[16].玉米ZmCIPK10和ZmZIP71基因启动子序列中含有ABA,SA,低温等相关顺式作用元件,与盐、干旱、低温胁迫下ZmCIPK10和ZmZIP71的表达相关[17-18].本研究我们鉴定获得的JrEFM1上游1 578 bp启动子中也含有SA,O2-site,MBS,HSE等顺式作用元件,预测该启动子也能调控JrEFM1参与植物生长发育及逆境响应过程.考虑到西北地区核桃生产受到高温和干旱等不良气候因子的严重制约,研究JrEFM1响应温度变化和干旱胁迫的潜在功能,有助于为核桃抗旱抵寒热相关生产管理及育种提供有效的基因资源和指导作用.因此,对核桃进行干旱、低温、高温等胁迫处理,分析根和叶中JrEFM1的表达水平,发现JrEFM1能被干旱、低温、高温不同程度地诱导,且体现出组织特异性(图 4).这与其他逆境响应相关基因在不同组织中的表达特性具有相似性.如柽柳HSP家族基因在不同时间的盐、旱等胁迫处理下,表现出了明显的根、茎、叶组织表达差异性[19].核桃WRKY转录因子JrWRKY2和JrWRKY7在盐害、干旱、冷害、ABA等处理下也表现出胁迫时间及根、叶差异表达[10].核桃JrHSP20-1在不同温度胁迫下的表达也具有组织差异性[17].可见,逆境响应相关基因的时空表达及组织表达特性普遍存在.表明JrEFM1在不同胁迫下的诱导表达与逆境响应调控具有重要关系.
MYB类转录因子在调控植株逆境响应中主要涉及激素信号通路.如拟南芥AtMyb7在种子发芽中起着关键作用.在ABA和高盐胁迫条件下,AtMyb7植株显示出比野生型植株更低的发芽率[18].与WT相比,过表达OsMYBR1的转基因植物表现出对干旱胁迫的更大耐受性和降低对ABA的敏感性,表明OsMYBR1参与介导植物对ABA和干旱的反应[20].在荞麦中,FtMYB13,FtMYB14,FtMYB15和FtMYB16为JA诱导型MYB,它们直接抑制荞麦中的芦丁生物合成. FtMYB13能与JA信号传导的关键阻遏物FtJAZ1特异性地相互作用[21].小麦MYB基因TaPIMP1受ABA和SA调控;TaPIMP1表达不足的转基因小麦在ABA和SA处理后表现出胁迫应答基因的诱导受损,表明TaPIMP1作为一种正向分子连接体,通过调节小麦ABA和SA信号途径中与胁迫相关的基因调控抗旱性[22].因此,本研究也分析了在不同激素(ABA,SA,JA)处理下JrEFM1的表达,发现该基因可被ABA,SA,JA显著诱导,并体现出组织特异性(图 5).由此可见,JrEFM1调控植物逆境响应也极可能与ABA,JA及SA等信号通路相关.在后续研究中,我们将通过过量表达等方法全面分析JrEFM1的逆境响应功能机制.








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: