-
非均匀有理B样条曲线经国际标准化组织认定,成为描述自由曲线/曲面的一种标准形式[1-2].传统CNC系统的直线和圆弧插补导致低加工效率和二次插补精度丢失等问题,对数控技术的发展造成阻碍[3-4],NURBS曲线实时插补技术有效地解决了以上问题,其优点是对接参数曲线进行插补,取代了原始系统使用小线段来逼近原有曲线的方法,大大提高了加工效率和插补精度[5-7].但是,NURBS曲线没有明确弧长与曲线的参数关系,无法在线实时调节速度带[8].因此,对于有效和稳定的NURBS插补器的研究对数控技术具有重要意义.
根据NURBS插补算法可知,速度是插补运算中的重要参数,速度大小影响着每一插补周期的弧长,从而在插补时间一定的情况下影响着插补精度.加工过程中,效率与工艺都对速度提出了要求.目前,已经有了关于NURBS曲线插补器的相关研究.文献[8]提出了基于分段进给率规划的NURBS插补算法,将NURBS曲线划分为曲线分段,并在这些分段中规划进给速率,然后处理相邻分段离散点的进给速率转换,并根据进给速率确定插值,缺点是计算复杂度高,不易操作.文献[9]提出用于5轴机床生成轴插补命令的刀具中心点(TCP)进给率调度算法,该算法不仅考虑TCP速度、加速度和加加速度的约束,而且还考虑每个块连接处每个轴的速度差异,但是没有考虑机床加减速限制.文献[10]提出了一种新的机器人轨迹规划算法,该算法采用非均匀有理B样条(NURBS)曲线插值,总轨迹规划过程分为2个阶段:使用NURBS曲线拟合阶段和轨迹插值阶段,该方法没有考虑机床加减速限制.文献[11]设计了有效的速度规划算法,提高了算法效率,得到了满足加速度与弦长误差的光滑速度曲线.文献[12]根据前瞻算法,设计出自适应前瞻NURBS插补算法,但是该算法复杂,实时性难以保证.
本文设计了离散比例积分器在线速度规划算法.根据积分器对阶跃输入的积分作用,在开始阶段对速度曲线进行积分得到实际速度;当实际速度曲线等于最大速度时,积分器关闭,刀具轨迹以最大速度运行;当到达根据最大速度计算的时间时,速度输入为零,此时开启积分器,实际输出速度会按照积分常数进行递减,直至速度为零.由于速度曲线的对称性,因此2次开启积分器的时间间隔一致,且能保证速度为零时到达轨迹终点.
HTML
-
k次NURBS曲线表示为
式(1)中n+1为控制顶点数,Pi为控制顶点,wi为权因子,Ni(u)为基函数.
根据DeBoor-Cox递推公式得出Ni,p(u)表达式为
根据递推公式,其对参数的微分分为一阶和二阶微分,其中一阶微分为
其二阶微分为
式(3)、式(4)中:X′,Y′,Z′表示X,Y,Z对参数的一阶微分,X″,Y″,Z″表示X,Y,Z对参数的二阶微分.
因为NURBS给出了自由曲线的确定数学表达形式,所以对应于每一确定的参数ui,都对应着曲线上已确定的点Ci.因此,插补算法可以通过计算给定插补周期后的曲线参数,得出刀具下一插补周期需要到达的点.
针对NURBS曲线没有明确的弧长与曲线参数关系,导致难以对其进行在线实时调节速度的问题,本文提出一种基于离散比例积分器的在线速度规划算法.该方法首先采用数值方法计算NURBS曲线的弧长,计算出在给定速度下的运行时间,然后根据积分器的信号转换功能以及加减速的对称性,完成对NURBS曲线插补的在线速度规划.采用离散比例积分器的速度规划方法能够实现实时控制起始段、结束段的轨迹速度,保证系统加速度不超出机床要求.
-
根据采样插补算法原理,每一插补周期计算出机床刀具的目标点,然后输送给电机,使刀具按轨迹要求进行行走.由于NURBS曲线没有精确的弧长与参数函数,采用数值算法难以保证实时性.因此,采用二阶泰勒展开,对下一插补周期的参数进行估计,其表达式为
式(5)中T为插补周期,ui为第i时刻曲线参数,ui+1为第i+1时刻曲线参数,
$\frac{{{\rm{d}}u}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}$ 为参数对时间的一阶导数,$\frac{{{{\rm{d}}^2}u}}{{{\rm{d}}{t^2}}}$ 为参数对时间的二阶导数,ε为曲线参数的高阶无穷小量.根据链式法则,进一步求出式(7)中
$\dot s$ 表示轨迹速度,${\ddot s}$ 表示轨迹加速度,σ为曲线弧微分,其表达式为σ-1为曲线弧微分对参数的一阶导数,其表达式为
虽然二阶泰勒展开依然是估算,但是对于连续曲线,在插补周期很短的情况下,其精度能够满足要求.
根据插补公式,当插补周期固定时,通过ui点的曲线特征及其速度与加速度,即可求出ui+1点曲线参数,进而通过NURBS方程求出Ci+1.
根据加工过程与效率要求得出带加工轨迹的线速度为F;根据机床性能要求得出加工过程待加工轨迹的加速度为A.设待加工轨迹为L,其弧长为s,则以速度F加工L所用时间为T.
由于初始与结束状态时,机床的速度都为零,当以速度F开始加工和结束时,需要机床提供很大的加速度,超出机床的动力性能.因此,需要对初始段与结束段的速度进行规划,使其满足机床动力性能要求.
-
当一阶跃信号输入到积分器后,其输出为一斜坡信号.因此在输入速度后设置一比例积分器,输入的速度信号为从零突变到F的阶跃信号,而输出则为按一定斜率从零增长的斜坡信号.斜率可以通过适当调整比例系数获得,且其斜率为加速度.
由于有最大速度限制,速度不能无限增加,因此比例积分器不能一直开启,使速度无限增加,当速度达到最大值时,关闭比例积分器,按最大速度进行输出.
开始阶段的速度规划图如如图 1所示:
如何让轨迹平稳准确地到达终点,一直是轨迹速度规划的一个难点.本文采用比例积分器的方法对速度进行规划,能够很好地解决末尾结束时对速度的要求.根据加减速的对称性,若开始段与结束段采用相同的比例因子,则开始段与结束段的弧长位移和运行时间都相同.记录开始阶段加速运行时间,即为结束时速度停止时间.由于开始阶段速度低于F,轨迹速度按一定加速度加速,因此按积分器处理后速度运行的轨迹位移比没有积分器运行的位移小一半.根据加减速的对称性,末位减速度与初始加速度轨迹位移相等,则对起始阶段少运行的位移进行了补偿.
对开始与结束设置相同的比例积分器,即比例积分器的参数相同、运行时间相同,即可实现平稳准确地到达轨迹终点的目的.
结束具体实现过程为:根据整体轨迹长度与设计轨迹速度,计算出输入最大速度的时间T0.当轨迹运行到时间T时,改变输入速度方向,同时开启积分器,直至速度减为零,关闭积分器和速度输入,加工完成.
结束阶段的速度规划如图 2所示.
-
根据速度规划算法,需要计算曲线弧长.由于NURBS曲线没有解析弧长公式,无法直接得到NURBS曲线弧长,因此采用Simpson数值积分公式求取NURBS曲线弧长,并通过迭代,直至积分稳定. Simpson求积公式为
式(11)中,a与b为积分曲线起始点与终点,h=b-a为参数长度,c=(a+b)/2为参数中点.曲线分段段数为
每段采用Simpson求积公式,最终弧长为
根据给定的误差要求ε,不断缩短h,直至误差满足要求
式(14)中h1和h2为相邻2次迭代弧长计算所选步长.
NURBS为参数曲线,其被积函数为
相较于传统S型插补法和改进曲率约束算法,本文速度规划算法能有效地满足系统约束,保证机床平稳运行,在插补精度、插补实时性及速度波动率性能方面都要优于其他2种算法.
2.1. NURBS曲线插补算法
2.2. 比例积分速度规划算法
2.3. NURBS曲线弧长计算
-
为了说明本文方法的有效性,采用matlab对该方法进行了在线实时仿真.所选的运动学参数如表 1、表 2所示.
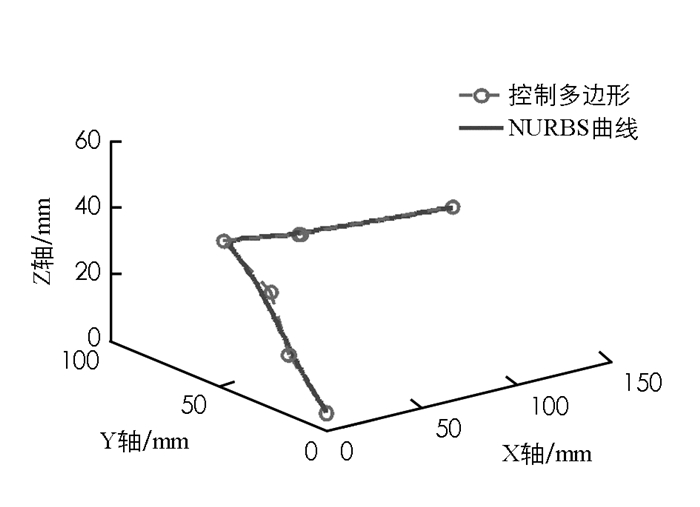
仿真所用曲线为3次NURBS曲线,所选控制顶点数为7个.其具体参数如表 2所示.
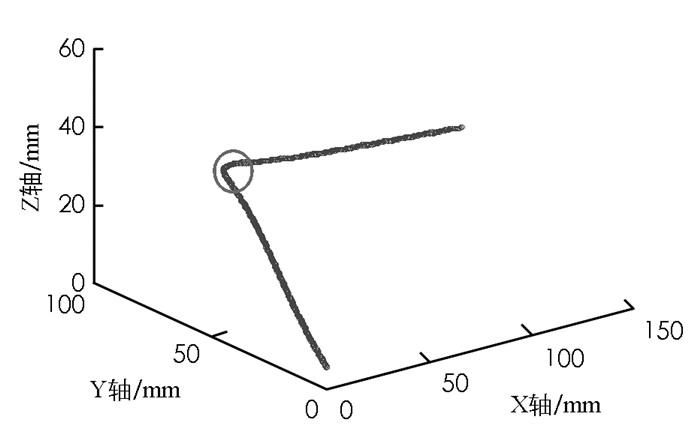
NURBS曲线如图 3所示.
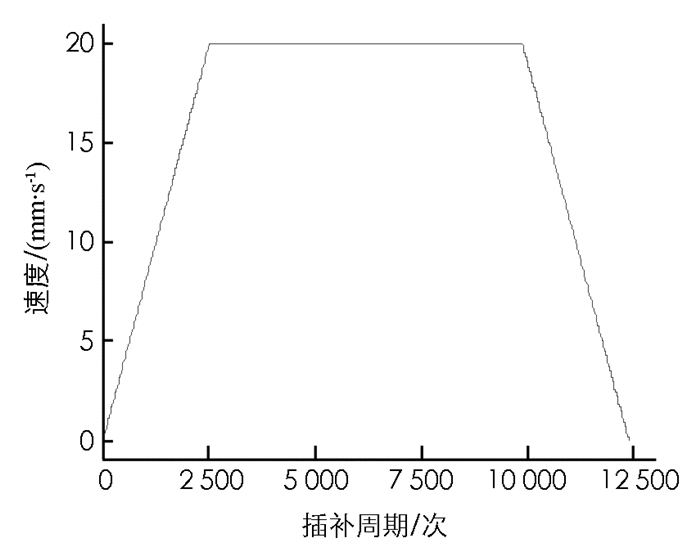
根据上述选择的插补方式及其速度规划方法,得出仿真结果.其速度曲线如图 4所示.
NURBS曲线插补图如图 5所示.
由仿真分析得出,通过在线比例积分器的方法,很好地实现了在线实时计算速度的目的.由图 4可以看出,在开始阶段与结束阶段都能够实现很好的匀加减速过程,减少了开始阶段与结束阶段的冲击. 图 5为插补点图,通过图 6可以看出,插补算法能够很好地实现插补过程.通过对结尾处的观察,可以看出插补算法很好地实现了到达结尾的目的.结合速度图 4,可以看出到达结尾处的速度为零,充分验证了本文所提算法的正确性与有效性.
为了证明本文算法的先进性,将本文算法与其他算法进行比较,分别从插补精度、插补实时性及速度波动率3个性能方面进行比较,实验结果如表 3所示.
从表 3数据可以看出,本文算法在插补误差、插补实时性和速度波动率性能方面优于传统S型规划法与改进曲率约束的算法,说明本文算法能够降低插补误差和速度波动率,同时完成实时插补,表明本文方法具有有效性和先进性.
-
本文提出了NURBS曲线插补的离散比例积分器速度规划算法.该方法在初始阶段开启比例积分器,将突变的速度转换成斜坡递增速度,当速度达到最大值时,关闭比例积分器,以最大速度进行输出.当输入速度结束时,由于比例积分器的存在,输出速度不能突变为零,而是按照一定斜率慢慢递减,减少了冲击.由于加减速的对称性,保证了速度为零时到达曲线终点.实验结果表明,本文算法能够实现自动加减速,准确到达终点且算法简洁,满足实时插补对运算复杂度的要求.另外,与其他算法的对比实验得出,本文算法性能优于传统S型规划法与改进曲率约束算法,说明了本文方法的有效性和先进性.下一步研究工作需拓展离散比例积分功能,使其能够在线调节系统加加速度,满足机床加加速度的限制要求.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: