-
水痘(varicella)是一种由水痘-带状疱疹病毒引起的急性传染病,对水痘传播动力学模型的研究最早见于文献[1],之后有许多学者在此基础上构建了新的模型[2-7],对水痘的传播进行预测. 文献[8]利用传染病模型评价水痘爆发疫情的控制效果. 文献[9]根据水痘在人群中的传播特征建立了流行病模型,得出了模型平衡点的稳定性. 鉴于双线性发生率[9-10]和标准发生率[11]具有局限性,在模型中考虑非线性发生率[12-14]具有很重要的现实意义. 由于水痘的潜伏期较长,因此在模型中考虑潜伏期时滞就显得尤为重要,但前期相关文献研究中很少有包含潜伏期时滞的水痘传播动力学模型的研究. 针对上述问题,本文在文献[9]的基础上,将总人口分为5个仓室,分别是:S为易感者,V为接种疫苗者,E为潜伏者,I为染病者,R为恢复者,在模型中引入潜伏期时滞并考虑一般发生率,建立如下具有一般发生率和潜伏期时滞的水痘传播动力学模型
其中:A为人口的常数输入率,μ是自然死亡率,ε为易感人群的疫苗接种率,β反映了疫苗接种者V免疫的有效性(β∈[0, 1]),σ为疫苗接种成功率,τ表示潜伏期时滞,γ代表染病者的恢复率.
系统(1)满足初始条件:
其中φ =(φ1(θ),φ2(θ),φ3(θ),φ4(θ),φ5(θ))T∈C,C表示从[-τ,0]到
$\mathbb{R} _{+}^5$ 的Banach空间C([-τ,0],$\mathbb{R} _{+}^5$ )上的连续函数空间,$\mathbb{R} _{+}^5$ ={(S,V,E,I,R):S≥0,V≥0,E≥0,I≥0,R≥0}.关于系统(1)中的f(I)有如下假设:
(H1)
$f(0)=0; f(I)>0, \forall I>0; f^{\prime}(I)>0, \forall I \geqslant 0; \lim\limits _{I \rightarrow \infty} f^{\prime}(I) < \infty$ ..(H2) If′(I)-f(I)≤0;f″(I)≤0,I>0且f′(I)≥0,即0≤f′(I)≤f′(0).
(H3) 当I∈(0,I*)时,
$\frac{I}{I^*} \leqslant \frac{f(I)}{f\left(I^*\right)}$ ;当I>I*时,$\frac{I}{I^*}>\frac{f(I)}{f\left(I^*\right)}$ .由于系统(1)中的第1,2,4个方程与E和R无关,故我们可以研究以下约化系统:
HTML
-
引理1 在初始条件(2)的情况下,系统(3)的解(S(t),V(t),I(t))始终非负且有界.
证 1) 利用反证法证明非负性. 假设存在时间t1>0使得S(t)第一次到达0,即S(t1)=0,则
所以对于充分小的ε>0,当t∈(t1-ε,t1)时,S(t) < 0,这与在(0,t1)上S(t)>0矛盾. 类似地,可证得V(t)>0,I(t)>0.
2) 有界性. 令N(t)=S(t)+V(t)+eμτI(t+τ),则
从而有
引理1证毕.
由引理1知,系统(3)的可行域为
本文将在可行域Ω内研究系统(3)的动力学性态.
令系统(3)的右端为0,易知系统(3)总存在无病平衡点
基于下一代矩阵的方法[15],可以得到系统(3)的基本再生数为:
引理2 当R0>1时,系统(3)存在唯一的地方病平衡点E*=(S*,V*,I*).
证 令系统(3)的右端等于0,可以得到如下方程组:
解方程组(4)得
把式(5)代入方程组(4)的第三个方程得
令
则有
由条件(H2)可知,φ′(I) < 0. 故由根的存在性定理可知,当R0>1时,系统(3)存在唯一的地方病平衡点E*=(S*,V*,I*).
-
定理1 当R0 < 1时,无病平衡点E0局部渐近稳定.
证 系统(3)在E0处的特征方程为
则
另一个根由
$\lambda-\mathrm{e}^{-(\lambda+\mu) \tau}\left(S_0^* f^{\prime}(0)+\beta V_0^* f^{\prime}(0)+\mu+\gamma\right)=0$ 决定,假设Re(λ3)≥0,则矛盾,故当R0 < 1时,无病平衡点E0局部渐近稳定.
定理2 当R0 < 1时,无病平衡点E0全局渐近稳定.
证 定义如下Lyapunov泛函:
则对V1(t)沿着系统(3)的轨线求导得
由条件(H2)可知f(I)≤f′(0)I,所以
因此,如果R0 < 1则V′1(t)≤0,且仅在E0处V′1(t)=0,故由Lyapunov-LaSalle不变集原理[16]知E0全局渐近稳定.
系统(3)在地方病平衡点E*处的特征方程为
其中
定理3 当R0>1,τ≥0时,地方病平衡点E*局部渐近稳定.
证 当τ≥0时,由系统(3)的第三个方程可得
所以由假设(H2)得
从而
故g(λ)不存在零根.
假设λ=iω(ω>0)是g(λ)=0的一个纯虚根,代入特征方程(6)并分离实部和虚部得
将方程组(7)两个等式两边分别平方并相加得
其中
由于
$A_3+B_3 \mathrm{e}^{-\mu \tau}>0$ ,又因此
故g(λ) 不会存在纯虚根.
假设g(λ)存在一根λ0>0,使得g(λ0)=0,即
因为
所以
因此可知
因为
所以
这与g(λ0)=0矛盾. 所以g(λ)=0不存在正根. 综上可得g(λ)=0只存在负实部根. 故定理3得证.
定理4 当R0>1时,地方病平衡点E*全局渐近稳定.
证 首先,定义函数h(x)=x-1-ln x. 显然,
$h(x) \geqslant 0(\forall x>0)$ ,且当且仅当x=1时,h(x)=0. 定义如下Lyapunov泛函:则对V2(t)沿着系统(3)的轨线求导得
由系统(3)的第2个方程知
$\beta V^* f\left(I^*\right)-\varepsilon S^*=-(\mu+\sigma) V^*$ ,结合条件(H3)可得V′2(t)≤0,且仅在E*处V′2(t)=0,故由Lyapunov-LaSalle不变集原理[16]知当R0>1时E*全局渐近稳定.
-
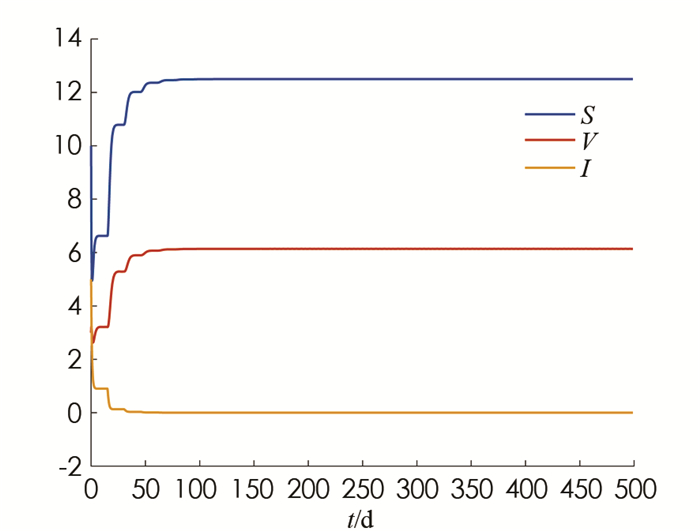
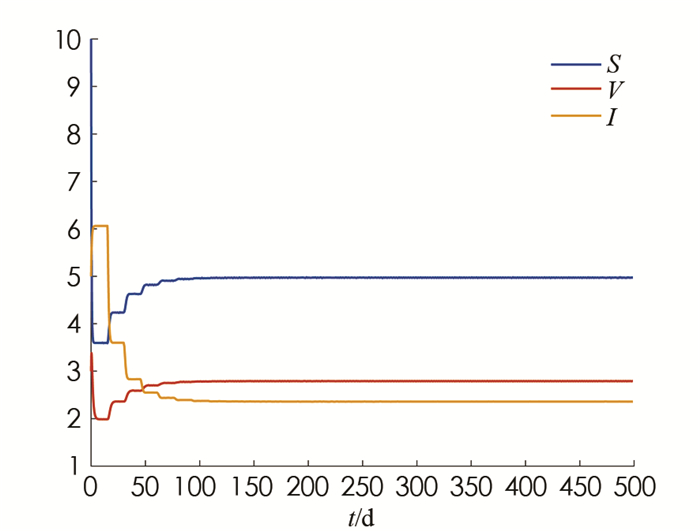
下面利用MATLAB软件进行数值模拟来验证理论分析的结果. 图 1和图 2分别模拟了无病平衡点和地方病平衡点的全局稳定性.
在这里,我们选取
$f(I)=\frac{I}{1+\alpha I}$ ,显然f(I)满足假设(H1),(H2),(H3). 根据水痘的疾病特点,在系统(3)中选择参数A=10,μ=0.24,ε=0.56,α=0.3,β=0.02,σ=0.90,γ=0.96,τ=15,则有R0≈0.287 < 1. 由图 1知,此时无病平衡点全局渐近稳定. 选择参数A=10,μ=0.07,ε=0.56,α=0.3,β=0.02,σ=0.90,γ=0.96,τ=15,则有R0≈5.498>1. 由图 2知,此时地方病平衡点全局渐近稳定.本文建立并研究了一类具有一般发生率和潜伏期时滞的水痘传播动力学模型,证明了解的非负性和有界性,给出了基本再生数R0的表达式,通过构造Lyapunov泛函并应用LaSalle不变集原理得出:当R0 < 1时无病平衡点E0全局渐近稳定,当R0>1时地方病平衡点E*全局渐近稳定.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: