-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
围食膜(Peritrophic matrix,PM)位于昆虫中肠最内侧,是由中肠上皮细胞和贲门瓣基部细胞分泌的非细胞结构的薄膜,主要由几丁质与蛋白质构成[1],是中肠抵御随食物摄入的病原及药物的第一道天然屏障,也是害虫防治的重要切入点之一[2]. 多种农药增效因子如昆虫病毒增效蛋白、几丁质酶、荧光增白剂和外源凝集素等通过与围食膜上特异位点的结合,可破坏围食膜结构,促进病原微生物对害虫的感染[3-6],从而达到杀灭害虫的目的. 增效因子作用于围食膜在害虫防治方面成为研究热点,在多种鳞翅目昆虫中已有报道[7-8]. Zimmermann等[9]研究发现,荧光增白剂Calcofluor能够显著增强围食膜的通透性;朱蓉等[10]用荧光增白剂M2R处理甜菜夜蛾、草地螟幼虫,发现围食膜消失,且围食膜中几丁质结合蛋白的含量受到影响.
几丁质合成抑制剂和几丁质合成酶抑制剂能阻止昆虫围食膜基质的形成,其中灭幼脲类杀虫剂已成为创制新农药的一个非常活跃的领域,灭幼脲对一些害虫(如黏虫、黄粉虫甲幼虫)的毒理作用和防治效果已有报道[11]. 龚国玑等[12]在灭幼脲对小地老虎、黏虫及黄粉虫甲幼虫内部器官和组织的作用研究中,提出“经灭幼脲处理后,含几丁质组分的体壁表皮层、气管壁内膜和中肠围食膜等组织,部分出现明显可辨的组织学改变和病理症状”. 灭幼脲对家蚕的影响仅停留在毒性试验[13-14]和中毒症状[15]的研究上,对围食膜通透性和结构的影响方式和程度还未见报道. 除此之外,Harper[16]在凝集素对欧洲玉米螟(ECB)幼虫围食膜影响的研究中发现,经WGA处理后,幼虫围食膜孔隙变大,能穿透杆菌,且在扫描电镜下观察到“无定型、球形的电子致密结构”.
尤斯灌流室(Ussing Chamber)技术能在离体情况下模拟胃肠道生理环境[17],早期用于研究上皮组织的离子转运,但在围食膜通透性的应用研究上还未见报道. Spence等[18]在研究通透性时提出双室设备,Peng等[19]在研究杆状病毒对围食膜的作用时,对该装置进行了改进. 本研究以鳞翅目模式生物家蚕(Bombyx mori L.)为研究对象,通过添食荧光增白剂FB28、凝集素和灭幼脲,观察家蚕围食膜在不同处理下的形态和结构变化,应用尤斯灌流室技术在体外测定不同处理后围食膜通透性的变化,结合蛋白质谱分析围食膜蛋白的变化,探究这些农药增效因子对围食膜结构、功能和成分的影响,为围食膜作为害虫防治靶标提供依据,同时也为增效因子的应用和新型农药的开发提供参考.
HTML
-
供试蚕种“871”由重庆市蚕业科学技术研究院提供. 荧光增白剂FB28,凝集素(WGA),sigma公司;灭幼脲(Diflubenzuron),河南安林生物化工有限责任公司;蓝色葡聚糖(180 D,5 kD,40 kD,110 kD,2 000 kD),瑞典TDBcons公司.
尤斯灌流室(C4300),北京金工鸿泰科技有限公司,样本夹型号P2303A,开孔2.67 mm×3.95 mm,面积0.1 cm2,带固定别针.
-
1%荧光增白剂FB28,0.05%凝集素采用点涂法均匀涂抹在桑叶上,25%灭幼脲用无菌水稀释1 000倍浸渍桑叶,均自然晾干后饲喂5龄的家蚕2 d.
-
在处理后不同时间剖取家蚕PM,拍照记录PM形态学特征,Thermo Scientific Quattro环扫电镜下直接观察表面结构.
-
将取出的PM纵向剖开,用蒸馏水轻轻冲洗干净后裁取PM中部约0.5 cm2的小块固定于样本夹上,加入同体积葡聚糖溶液和蒸馏水于样本夹两侧腔室内,一段时间后取少量测吸光值,每个样品取3个不同时间点,对照葡聚糖标准曲线,计算表观渗透系数.
-
取各时期蛋白质样品20 μg分别加入5倍上样缓冲液,配制5%浓缩胶和12%分离胶进行SDS-PAGE电泳,初始电压80 V. 当溴酚蓝条带泳动至浓缩胶与分离胶的界限处时,将电压调至120 V;当溴酚蓝条带泳动至凝胶下缘时结束电泳. 用BeyoBlue考马斯亮蓝快速染色,拍照观察,切下差异条带进行质谱.
-
供试品经过还原和烷基化处理后,加入Trypsin(质量比1∶50),在37 ℃下酶解20 h. 酶解产物脱盐后冻干,复溶于0.1%甲酸溶液中,-20 ℃保存待用.
-
A液为0.1%甲酸的水溶液,B液为0.1%甲酸的乙腈水溶液(乙腈为84%). 色谱柱以95%的A液平衡后,样品由自动进样器上样至Trap柱,1 h梯度.
-
多肽和多肽碎片的质量电荷比按每次全扫描后采集20个碎片图谱.
-
质谱测试原始文件用Mascot 2.2软件检索相应的数据库,最后得到蛋白质鉴定结果.
1.1. 实验材料及仪器
1.2. 实验方法
1.2.1. 药物处理方法
1.2.2. 形态及表面结构观察
1.2.3. 通透性测定
1.2.4. SDS-PAGE电泳
1.2.5. 蛋白质谱分析
1.2.5.1. 供试品酶解
1.2.5.2. 质谱分析
1.2.5.3. 质谱数据采集
1.2.5.4. 数据分析
-
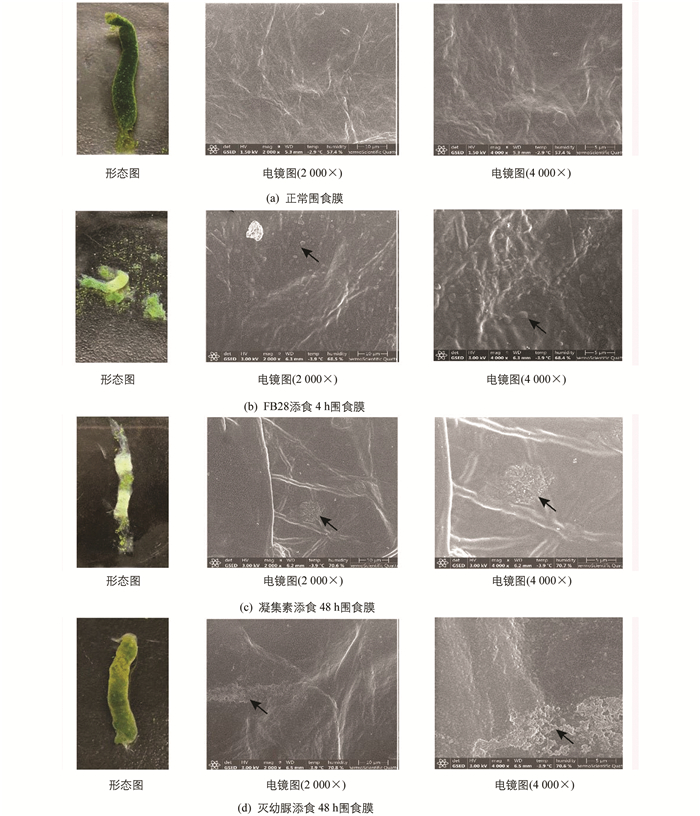
家蚕正常的PM是一层厚薄均匀的长管状薄膜,由中肠前端延伸至后肠,将肠腔和中肠上皮细胞层分开,富有弹性,易于清洗至无色透明. 环扫电镜观察表明,PM内表面(肠腔侧)结构光滑致密,有一些细小皱褶(图 1a).
-
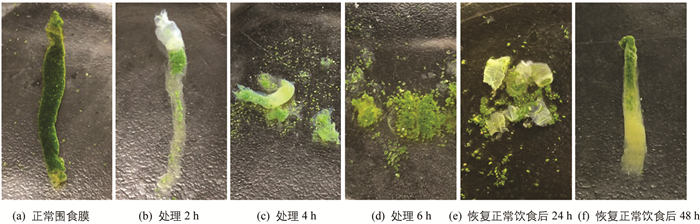
FB28添食后1 h,PM结构完整,表面均匀光滑,有韧性,与正常PM无异;2 h时PM结构仍相对完整,但前端在散射光下可见蓝紫色荧光;添食4 h后,食物外渗,PM碎片化,韧性差,碎片呈现蓝紫色荧光;6 h后PM基本消失、解离,与食物混在一起,家蚕拒食. 改喂正常新鲜桑叶,24 h后PM重新形成,但韧性较差,用无菌PBS冲洗即成碎片;48 h后PM重新恢复完整(图 2). 环扫电镜观察表明,FB28添食4 h时PM内表面不光滑,结构不再致密有序,表面附着很多PM碎片,2 000倍数下能观察到表面有1.4 μm左右的圆形凸起(图 1b).
-
凝集素添食后,24 h时PM外观与正常组无异,48 h能观察到部分PM内部食物减少,厚度不均一,中部增厚. 环扫电镜观察发现PM表面形成异常的无定型的、球形的电子致密结构,聚集成数个集团,4 000倍数下能观测到每个球形凸起大小约300 nm(图 1c).
-
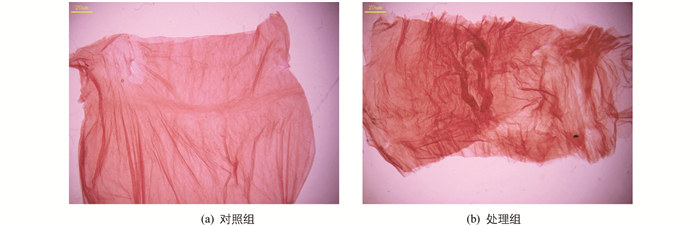
灭幼脲添食后2~3 h蚕体即表现出中毒症状,家蚕发生咀嚼障碍、拒食. 24 h,48 h均观察到围食膜肠腔侧出现气泡,解剖过程中发现围食膜与正常对照组相比差异明显,对其进行刚果红染色观察,发现围食膜多层结构异常,层与层之间变疏松、皱褶增多(图 3). PM内食物堆积、不易漂洗、消化液变浑浊. 环扫电镜观察显示,PM出现横向的结构紊乱带,表面有附着物,凹凸不平(图 1d).
-
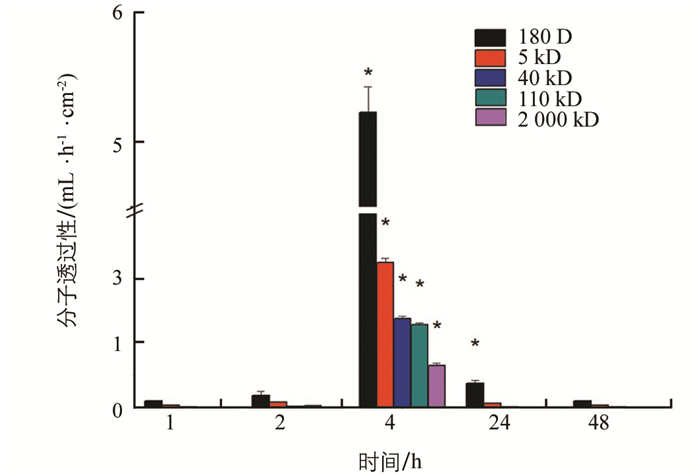
测量不同处理后围食膜对5种分子量(180 D,5 kD,40 kD,110 kD,2 000 kD)葡聚糖的透过性,结果表明:正常对照组的围食膜能通过40 kD分子,荧光增白剂FB28处理后,能透过2 000 kD分子,凝集素处理后围食膜最大能透过110 kD分子,而灭幼脲处理后能透过最大分子依然为40 kD(表 1).
-
荧光增白剂FB28处理后,2 h左右PM通透性开始增大,4 h时对180 D分子的透过性增大到5.231 mL/(h·cm2),对2 000 kD分子的透过性为0.65 mL/(h·cm2). 6 h时已不能取到相对完整的PM. 改喂正常桑叶后PM通透性又逐渐降低,48 h后恢复正常(图 4).
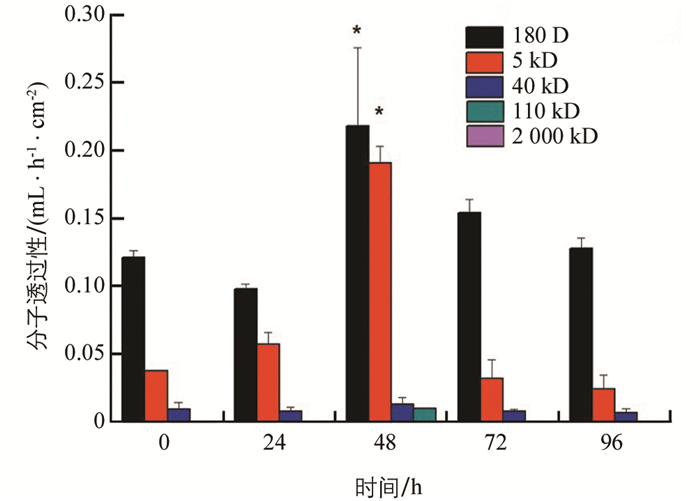
凝集素处理后,PM通透性先略降低后升高,48 h时通透性显著增大,对180 D分子透过性增大到0.218 mL/(h·cm2);能透过的最大分子为110 kD,透过性为0.009 8 mL/(h·cm2). 72 h后又逐渐降低恢复至正常,始终不能透过2 000 kD分子(图 5).
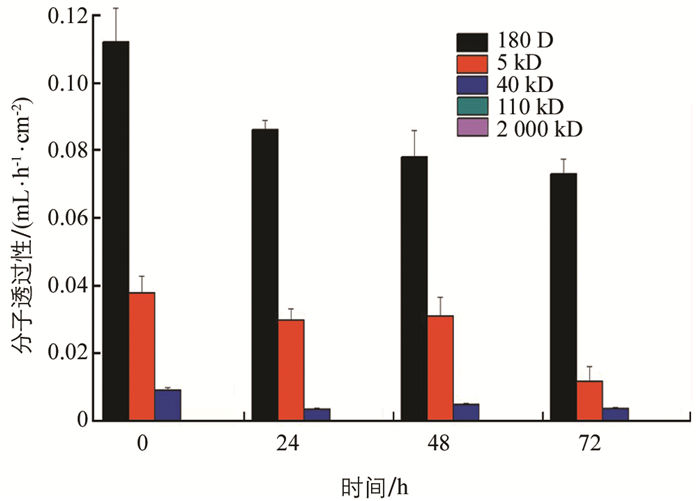
灭幼脲处理后,家蚕PM通透性降低,72 h时对180 D分子透过性由0.11 mL/(h·cm2)降为0.074 mL/(h·cm2),对40 kD分子的透过性由0.009 2 mL/(h·cm2)降至0.003 7 mL/(h·cm2)(图 6).
-
对荧光增白剂FB28添食2 h,4 h和恢复正常饮食后的家蚕围食膜蛋白做电泳检测,正常5龄3 d家蚕围食膜作为对照(CK). 结果显示,荧光增白剂FB28处理2 h和4 h后,高分子蛋白明显减少,特别是210 kD和37 kD蛋白减少,而在17 kD左右出现了最亮的条带,恢复正常饮食后该条带减弱,高分子蛋白条带重新出现,24 h后蛋白基本恢复正常(图 7).
-
对17 kD蛋白条带做质谱检测,CK,2 h,4 h鉴定总蛋白数分别为171,180,158个,其中约2/3为未命名蛋白. FB28处理2 h,4 h跟对照组相比,减少了家蚕贮藏蛋白(Silkworm storage protein)、钙黏蛋白样膜蛋白(Cadherin-like membrane protein)、血淋巴保幼激素结合蛋白(Hemolymph juvenile hormone binding protein)、组蛋白H4(Histone H4)等23种蛋白. 新增了与免疫(Apolipophorin-III,Beta-1,3-glucanase)、昆虫生殖能力和抗逆能力(Methuselah-like protein 5)和蛋白质结合(60s ribosomal export protein NMD3)相关的12种蛋白(表 2).
2.1. 添食荧光增白剂FB28、凝集素和灭幼脲对家蚕围食膜形态结构的影响
2.1.1. 正常围食膜(PM)的形态结构
2.1.2. 荧光增白剂FB28(以下简称FB28)对围食膜形态结构的影响
2.1.3. 凝集素对围食膜形态结构的影响
2.1.4. 灭幼脲对围食膜形态结构的影响
2.2. 围食膜通透性的变化
2.2.1. 不同处理后围食膜能透过的最大分子量
2.2.2. 各处理在不同时间对不同大小葡聚糖分子的透过性
2.3. 荧光增白剂FB28对围食膜蛋白的影响
2.3.1. SDS-PAGE检测结果
2.3.2. 质谱检测结果
-
围食膜作为昆虫防御的屏障,一方面需要保证结构的完整致密,阻挡病原及药物入侵;另一方面又要保持一定的通透性,便于物质流通,保证昆虫的正常生理活动. 在防治害虫时围食膜通透性的增强有利于病原及药物的入侵、加速感染进程、减少致死时间和增强杀虫效果. 本实验中,荧光增白剂FB28对家蚕围食膜的破坏最为强烈和迅速,2~4 h围食膜通透性显著增强,4 h时已能透过2 000 kD葡聚糖分子,通过环扫电镜观察到此时围食膜表面不光滑,并出现1.4 μm左右的圆形凸起;6 h时围食膜基本消失. 凝集素对家蚕围食膜也有一定影响,但作用不如荧光增白剂FB28强烈,48 h观察到围食膜依然相对完整,但膜厚度不均,同时电镜观察到“无定型的、球形的电子致密结构”,此结构与Harper[16]在凝集素对欧洲玉米螟(ECB)幼虫围食膜影响的研究中观察到的现象一致,推测是由于凝集素的多位点结合能力可以凝集糖蛋白,使其具有较强的电子密度;同时凝集素将导致蛋白凝集缺陷,使围食膜通透性显著增大.
Mitsui等[11]认为灭幼脲抑制了几丁质合成的生化过程,由于几丁质前体物尿苷二磷酸乙酰氨基葡萄糖在皮细胞内向膜外的转运受阻,使处在膜上的几丁质合成酶无法进行几丁质合成的最后聚合步骤,这是对几丁质合成受阻较为深入的假说. 本实验中灭幼脲处理后,围食膜通透性并未显著升高,反而有降低的趋势,围食膜多层结构异常,层与层之间变疏松、皱褶增多;结合电镜观察围食膜表面结构粗糙,凹凸不平,推测是由于几丁质合成被抑制导致蛋白结合紊乱,层状结构异常,物质通过缓慢,从而使通透性降低. 灭幼脲除能影响几丁质合成以外,还可能存在其他机制,其对围食膜的作用机制和效果有待进一步的研究.
对荧光增白剂FB28处理后的围食膜做SDS-PAGE检测和质谱分析,发现进食2 h后,高分子蛋白明显减少,2 h和4 h时在17 kD左右都出现了最亮的条带,此结果说明荧光增白剂FB28竞争结合围食膜几丁质,可解离部分围食膜蛋白,其对昆虫围食膜的作用具有普遍性,但作用的效果可能不同. 质谱检测发现,与对照组相比,新增了与免疫(Apolipophorin-III,Beta-1,3-glucanase)、昆虫生殖能力和抗逆能力(Methuselah-like protein 5)和蛋白质结合(60s ribosomal export protein NMD3)相关的蛋白,推测荧光增白剂FB28添食可能导致昆虫产生免疫反应,使免疫相关蛋白高量表达.
通过对家蚕围食膜结构和通透性的研究,更直观地反映农药及增效因子的作用效果,可以为害虫防治提供新的思路及参考.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: