-
银纳米颗粒(AgNPs)具有独特的局域表面等离子体共振(Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance,LSPR)性质[1-2].但是它们在溶液中稳定性较差,同时表面修饰困难.而SiO2具有良好的化学稳定性和光学通透性,并且SiO2比AgNPs更易于进行表面功能化修饰[3-4].因此,本研究利用AgNPs强烈的LSPR特性和SiO2光透性好、易于修饰的特点,制备了Ag@SiO2NPs作为光散射(Light Scattering,LS)探针,并结合磁性颗粒(Magnetite Particles,MPs)在外磁场作用下易于分离的特点,设计了一种分析检测腺苷的新方法.即将腺苷的核酸适配体裁剪为两段DNA单链[5],一段修饰在Ag@SiO2NPs上,另一段修饰在MPs上.当体系中不存在腺苷时,Ag@SiO2NPs与MPs之间不能通过DNA链发生相互结合,在进行磁分离后,Ag@SiO2NPs依然分散在溶液中,此时,上清液表现出较强的LS信号;而当有腺苷存在时,Ag@SiO2NPs与MPs上的DNA链通过腺苷发生相互作用,两者结合,此时再进行磁分离,Ag@SiO2NPs就会与MPs一同从溶液中分离,上清液的LS信号减弱.通过对溶液中Ag@SiO2NPs的LS信号的监测,实现了腺苷的检测.
HTML
-
F-4500荧光分光光度计(日本日立公司);UV-3010紫外-可见分光光度计(日本日立公司);S-4800型扫描电子显微镜(SEM,日本日立公司);SZCL-控温磁力搅拌器(巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司).
DNA1:5'-NH2-TTT TTT TTT TAC CTG GGG GAG TAT-3',DNA2:5'-NH2-TTT TTT TTT TTG CGG AGG AAG GT-3',DNA3:5'-NH2-TTT TTT TTT TCT TAC GGT GGG GCA ATT-3'(上海生物工程技术有限公司);腺苷(Adenosine)、鸟苷(Guanosine)、胸苷(Thymidine)(上海蓝季科技发展有限公司);正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)、三乙基氨基硅烷(APTES)、牛血清白蛋白(BSA)(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);pH=7.4的Tris-HCl缓冲溶液(50 mmol/L);实验用水均为二次蒸馏水,所用无机试剂均为分析纯.
-
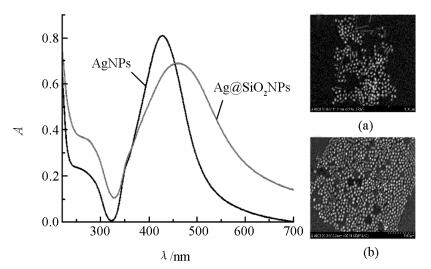
Ag@SiO2NPs的制备[3, 6]:称取9 mg AgNO3溶于50 mL水中,在剧烈搅拌下,加入1 mL 1%的柠檬酸三钠溶液并剧烈搅拌1 h.将制备好的AgNPs于棕色广口瓶中避光储存.测得AgNPs的吸收峰约在428 nm处(图 1),统计其平均粒径约为(60±3) nm(图 1(a)).取一定量的AgNPs加入到100 mL无水乙醇中,搅拌加入2 mL氨水.继续搅拌并向溶液中加入5 mL 10 mmol/L的TEOS,待反应24 h结束后,测得其吸收峰位于462 nm处(图 1). Ag@SiO2NPs平均粒径约为(83±3) nm,硅壳平均厚度约为(11±3) nm(图 1(b)).取一定量Ag@SiO2NPs在搅拌下逐滴加入200 μL APTES,反应30 min结束后洗去多余的APTES,最后将产物干燥. Ag@SiO2NPs的修饰:将上述干燥产物重新超声分散于5 mL水中,再加入500 μL 25%的戊二醛,充分反应1 h后,产物用Tris-HCl洗涤3次,之后加入500 μL DNA2,37 ℃孵育过夜,结束后产物用Tris-HCl洗去未连接的DNA2,之后用BSA在37 ℃孵育30 min,封闭未反应的醛基活性位点,最后用Tris-HCl洗去多余的BSA,定容至5 mL,于4 ℃温度下保存备用.
-
MPs的制备[7-8]:称取2.7 g FeCl3·6H2O和1.8 g FeSO4·7H2O溶于100 mL水中,在80 ℃水浴中搅拌15 min后,加入2.8 g NaOH,待生成Fe3O4后继续搅拌30 min,反应完全后洗去未反应的原料,产物用无水乙醇定容至100 mL.取4 mL MPs于25 mL无水乙醇中,搅拌下先加入1 mL TEOS再加入500 μL氨水,继续反应2 h后洗去多余的原料.重新分散后,在搅拌下加入250 μL APTES,反应30 min后用无水乙醇洗去多余的APTES,最后将MPs干燥并收集固体待用.取10 mg上述固体MPs分散于4 mL水中,然后加入1.6 mL水与400 μL 25%的戊二醛混合液,30 min反应结束后,用水洗去多余的戊二醛,再向MPs溶液中加入400 μL的DNA1,定容至4 mL,密封后以37 ℃孵育过夜;将反应的MPs用Tris-HCl清洗3次,之后用BSA在37 ℃孵育30 min,封闭未反应的醛基活性位点,最后用Tris-HCl洗涤3次,定容至4 mL,4 ℃储存.使用相同的方法,在MPs上修饰DNA3.
-
在2 mL离心管中依次加入Tris-HCl缓冲液,Ag@SiO2NPs,BSA,MPs,NaCl溶液以及不同量的腺苷,最后定容至500μL.溶液旋涡混匀反应40 min后磁性分离,取上清液在荧光分光光度计上以λem=λex同步扫描激发和发射单色器测定其散射光谱图,激发和发射狭缝宽度均为5.0 nm.
1.1. 仪器和试剂
1.2. 实验方法
1.2.1. Ag@SiO2NPs的制备与修饰
1.2.2. MPs的制备与修饰
1.2.3. 实验方法与步骤
-
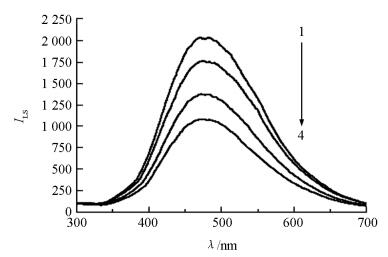
如图 2所示,Ag@SiO2NPs表现出较强的LS信号(图 2中线1),当向体系中加入一定浓度的腺苷时,腺苷与分别修饰在Ag@SiO2NPs和MPs上的DNA链相结合,形成核酸适配体与腺苷的复合物.通过磁场作用,Ag@SiO2NPs与MPs一同从溶液中分离,上清液中的LS强度减弱(图 2中线2-4).
-
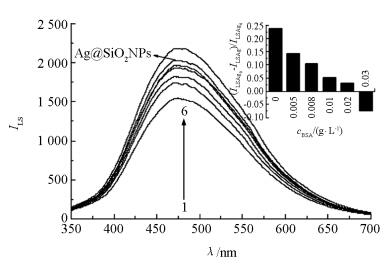
在检测过程中发现,Ag@SiO2NPs和MPs之间存在一定的非特异性吸附.因此,通过加入适量的BSA避免非特异性吸附,稳定体系的LS信号.如图 3所示,在无腺苷存在,也不加入BSA的条件下,单独Ag@SiO2NPs的LS强度明显高于磁分离后上清液中Ag@SiO2NPs的强度.但随着BSA的加入,磁分离后上清液中Ag@SiO2NPs的LS强度逐渐与单独Ag@SiO2NPs的接近.而当BSA质量浓度达到0.03 g/L时,强度超过单独Ag@SiO2NPs,说明此时BSA过量.同时,用Ag@SiO2NPs的散射强度(ILSAg0)减去加入不同量BSA后体系散射强度(ILSAg)的差值与Ag@SiO2NPs的散射(ILSAg0)相比的比值关系,即:(ILSAg0-ILSAg)/ILSAg0,也衡量了BSA对体系稳定性的影响(图 3中的嵌入图).实验最终选择加入BSA的质量浓度为0.02 g/L.
-
对NaCl浓度考察时发现,当溶液中有腺苷存在时,随着NaCl浓度的增大,体系的LS强度随之降低,说明Ag@SiO2NPs随MPs分离的量逐渐增多,并在NaCl的终浓度达到0.3 mol/L时,LS强度降低达到最大值.因此,实验选择NaCl浓度为0.3 mol/L.
-
在考察时间对反应体系的影响时发现,当反应时间达到40 min时,体系的散射强度趋于稳定.因此,实验选择40 min作为体系的反应时间.
-
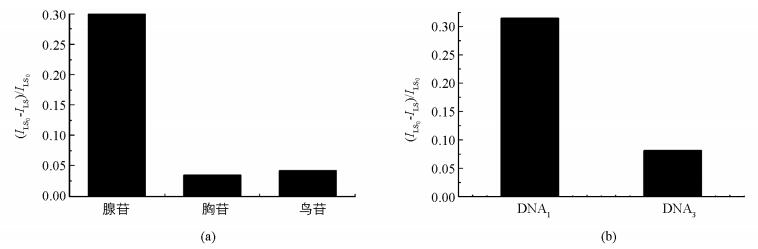
在优化条件下,考察了体系选择性.从图 4可以发现,用不同核苷(图 4(a))进行实验,体系并不会产生有意义的LS信号降低.同样,如果选用非腺苷的核酸适配体的DNA3(图 4(b))时,即便体系中有腺苷存在,LS信号响应值依然很低.实验证实此分析方法对检测腺苷具有较好的选择性.
2.1. Ag@SiO2NPs光散射光谱图
2.2. 实验条件优化
2.2.1. BSA用量的优化
2.2.2. NaCl浓度的优化
2.2.3. 反应时间的优化
2.3. 选择性实验
-
在优化条件下,Ag@SiO2NPs在475 nm左右的散射强度的降低值(ΔILS)与腺苷的浓度(c)在5.0×10-4~8.0×10-6mol/L之间有较好的线性关系:ΔILS=666.50+505.18logc,线性相关系数r=0.981 8.
-
本研究制备出以AgNPs为核、SiO2为壳的复合纳米颗粒.这种纳米颗粒不仅克服了AgNPs易聚集,不易修饰的缺点,还保持了AgNPs所固有的强散射信号.运用制备的Ag@SiO2NPs作为散射信号探针,结合MPs易于分离的优势,设计了基于磁性分离检测腺苷的新方法.对比AgNPs,Ag@SiO2NPs作为散射探针具有更好的稳定性和易于表面功能化的优点,有望在分析检测、细胞成像等领域得到更广泛的应用.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: