-
本文所研究的图均为有限无向简单图.设G=(V,E)表示点集为V且边集为E的简单图.设A (G)是图G的邻接矩阵,其邻接矩阵的特征多项式记作φ(G,λ).图G的邻接谱是由其特征方程的所有根所构成的多重集.由于矩阵A (G)是实对称矩阵,则其特征根都为实数,我们把最大的特征根λ1(G)称为图G的谱半径.一般地,将Δ和d(v)分别记作图G的最大度和点v的度.此外,记Pn和K1,n-1分别表示n个顶点的路图和星图.
图谱是图论的重要研究方向之一,在量子化学和理论物理上有着重要的应用背景.图谱理论的研究主要是利用线性代数、矩阵理论等成熟的代数理论和技巧,并结合图论和组合数学的理论来研究图谱及其图的结构性质.图矩阵的特征值不仅能反映图的结构性质,而且能提供与图能量相关的信息,图的邻接矩阵的特征值就是其中之一.对其而言,谱半径是重要的不变量,故被众多学者研究.文献[1]证明了在n阶树中星图K1,n-1具有最大的谱半径.文献[2]找到了k个悬挂点的谱半径最大的一类树图Tn,k.文献[3]给出了某些树的谱和任何树的最大特征值的界限.在解决图的分类和排序等诸多问题上,需要对谱半径的上下界进行很好的估计.而通常谱半径的界与最大度这一不变量联系紧密,众所周知的结果是
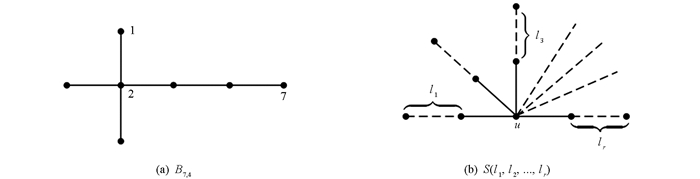
$\sqrt \Delta $ <λ1(G)<Δ(见文献[4]).当图G是树时,文献[5]证明了λ1(G)<2$\sqrt {\Delta - 1} $ .文献[6]给出了树图中拉普拉斯最大根和第二大根的下界.文献[7]给出了一些树图的谱半径的界为$\frac{{3\sqrt 2 }}{2}$ .至今,有许多关于树图谱半径的结论,可参考文献[8-11].图G∪H表示图G和H的不交并,图G-u是图G删除u点以及关联的边所得到的图.树图Bn,m是由路图Pn-m通过连接星图K1,m的任意一个悬挂点所构成的图(图 1).图S(l1,…,lr)是一个星型树有且仅有一个最大度点u,且满足
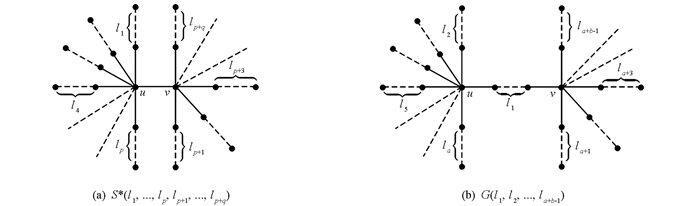
其中d(u)=r(图 1).图S*(l1,…,lp,lp+1,…,lp+q)是一个双星树,满足
其中d(u)=p+1,d(v)=q+1(图 2).广义星型树G(l1,l2,…,la+b-1)是由一个a(a≥3)度点和一个b(b≥3)度点,其余点都是2度点或1度点所构成的树,且满足
其中d(u)=a,d(v)=b(图 2).
长期以来,许多学者一直针对树的最大度这一不变量来研究谱半径的界,但是结合树的其它顶点的度对谱半径进行的研究较少.本文从改变最大度和第二大度出发,通过特征多项式的变化来研究谱半径的界.针对星型树S(l1,…,lr)和双星树S*(l1,…,lp,lp+1,…,lp+q)先给出了谱半径的上界,然后由已知的结论推出广义星型树图G(l1,l2,…,la+b-1)谱半径的界,最后通过剖分图来验证结果.
HTML
-
这一部分首先给出一些相关图特征多项式的基本结论和谱半径之间的大小排序性质.
引理1 [5] 设T是有最大度Δ的树图,则
$\lambda_{1}(T) < 2 \sqrt{\Delta-1}$ .(a)
$\varphi(G \cup H, \lambda)=\varphi(G, \lambda) \varphi(H, \lambda)$ ;(b)
$\varphi(G, \lambda)=\lambda \varphi(G-u, \lambda)-\sum\limits_{v \sim u} \varphi(G-u-v, \lambda)$ ,其中u是G的割点;(c)
$\varphi(G, \lambda)=\varphi(G-e, \lambda)-\varphi(G-x-y, \lambda)$ ,其中e=xy是G的割边.这里图G-u-v是图G删除u点和v点以及和它们关联的边得到的图.引理3 [7] 设Bn,4是一个†-型树图.则
$\lim\limits _{n \rightarrow \infty} \lambda_{1}\left(B_{n, 4}\right)=\frac{3 \sqrt{2}}{2}$ .文献[1]定义了图G的一个内部路,指的是:v0,v1,…,vk是一个路但点v0,vk与其余点的度不同,即d(vi)=2(i=1,2,…,k-1),而d(v0)>2且d(vk)>2,特别地,点v0与vk的度可以相同.
引理4 [12] 设G是不同构于轮图Wn的连通图,图Guv是通过剖分图G的内部路uv所得到的图,则λ1(Guv)<λ1(G).
对于有最大度Δ的树图Bn,m(即m=Δ时),有:
引理5 [13] 设T是有最大度Δ的任意树图,并且满足T

引理6 [14] 设Pn是n个顶点的路图,则
令λ=2cosθ.设
$t^{\frac{1}{2}}=\mathrm{e}^{i \theta}$ ,我们得到$\lambda=t^{\frac{1}{2}}+t^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ ,那么图Pn的特征多项式可以写成引理7 [15] 设G是连通图,H是G的真子图,则λ1(H)<λ1(G).
-
定理1 对星型树S(l1,…,lr),有
证 设li<m(i=1,2,…,r).对图S(m,…,m)删除割点u,由引理2(a)和(b)可得
令
$\lambda=t^{\frac{1}{2}}+t^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ ,根据引理6可得令t1是ϕ(t)的最大根.由于当t>r-1时,ϕ(t)>0,故t1<r-1.设
$f(t)=t^{\frac{1}{2}}+t^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ .当t≥1时,有故f(t)在[1,+∞)上严格递增.于是
由引理7可知
定理2 设S*=S*(l1,…,lp,lp+1,…,lp+q),则有
证 令lj<l(j=1,2,…,p+q). Si表示等l长的星型树,其中i表示u点的度.对图S*(l,l,…,l)删除割边e=uv,由引理2(c)可得
设
$\lambda=t^{\frac{1}{2}}+t^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ .由定理1可得:据引理6可得
其中(p+q)l+2=n.令t1*是ψ(t)的最大根.由于l是无穷大量,则ψ(t)的正负由t2l+2的系数决定.于是方程(t-(p-1))(t-(q-1))-t=0的最大解即为t1*的上界.解得
设
$f(t)=t^{\frac{1}{2}}+t^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ .当t≥1时,有$f^{\prime}(t)=t^{-\frac{3}{2}} \frac{(t-1)}{2} \geqslant 0$ ,故f(t)在[1,+∞)上严格递增.由$\lambda_{1}\left(S^{*}\right)=\left(t_{1}^{*}\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}+\left(t_{1}^{*}\right)^{-\frac{1}{2}}$ ,则推论1 设G=G(l1,l2,…,la+b-1),则
证 令lj<l(j=2,3,…,p+q-1).当l1=0时,点u,v的度分别为a=p+1,b=q+1.由定理2推出图G(0,l,…,l)的谱半径为
由引理7和引理4得到
根据引理5可以得到
由引理3和极限不等式,当n>n0时,有
则
由于l1位于图G(l1,l2,…,la+b-1)的内部路上,在l1上剖分时,剖分图的谱半径变化不超过1[16].故下面研究内部路不变时,改变图的最大度和剖分图的外部路对图的谱半径的影响.不妨设l1=0,则:
例1 针对图G(0,1,…,1)(l1=0,li=1,i=2,3,…,a+b-1),表 1列举了数对(a,b)中,当a,b取不同值时由MATLAB软件计算的谱半径近似值λ1和由推论1得到的谱半径上界的近似值λ1*.结果如表 1所示.
注1 当a=5,b=6时,令图G1=G(0,1,…,1)(l1=0,li=1,i=2,3,…,10).借助MATLAB软件能够得出λ1(G1)≈2.833 9.由推论1可以计算得到
$\lambda_{1}\left(G_{1}\right) < 6^{\frac{1}{2}}+6^{-\frac{1}{2}} \approx 2.8577$ .容易发现,当固定a,b时,l的变化不影响λ1*行的数值.下面讨论剖分外部路l时,图的谱半径变化.例2 当固定a=5,b=6,对图G(0,l,…,l)(l1=0,li=l,i=2,3,…,10)增大l值时,由MATLAB软件给出谱半径的近似值λ1如表 2所示.
注2 对于外部路剖分时,观察表 2中λ1行的数值变化不超过1.另外,剖分外部路时得到的λ1不超过给定的上界,由例1和例2的结果可以验证推论1是成立的.根据引理1可知
$\lambda_{1}\left(G_{1}\right) < 2 \sqrt{\Delta-1} \approx 4.4721$ .由此可见,本文找到了广义星型树图G(l1,l2,…,la+b-1)较好的界.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: