-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
当归性温味甘,归肝、心、脾经,具有补血调经、活血止痛的功效;川芎性温味辛,归肝、胆、心包经,具有活血行气、祛风止痛的功效. “当归-川芎”常形成药对增强其行气活血、补血养血的作用,如四物汤、佛手散、血府逐瘀汤、补阳还五汤、温经汤和生化汤等经典名方[1-3],但“当归-川芎”药对的物质基础及作用机制尚未阐明. 网络药理学是融合了系统生物学、生物信息学的新兴交叉学科,近年来,被广泛应用于中药的研究中,它通过构建“药物-靶点-通路”多层次网络,系统综合地观察中药对整个疾病网络的调控作用,有利于阐明中药多成分、多靶点、多途径协同作用的机制[4-5].
本研究通过TCMSP,SEA数据库和文献检索,收集“当归-川芎”药对活性成分及其靶点,构建“成分-靶点”网络,分析得到关键靶点,寻找其与美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准药物靶点的共同靶点,利用TTD和TCMSP数据库分析与共同靶点相关的疾病,建立“共同靶点-疾病”网络. 对关键靶点进行基因功能和KEGG通路分析,将活性成分和关键靶点进行分子对接验证.
HTML
-
通过检索TCMSP(http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/index.php),SEA(http://sea.bkslab.org/)数据库和文献,收集“当归-川芎”药对中当归、川芎所含成分,然后利用药代动力学参数,即口服生物利用度OB≥30%,类药性DL≥0.18及小肠上皮细胞渗透率Caco-2≥-0.40,筛选出当归、川芎的活性成分.
-
通过检索TCMSP,SEA数据库,获得当归、川芎活性成分的靶点,利用蛋白质数据库UniProt(http://www.uniprot.org/)的搜索功能,将靶点转换为UniProt ID导入STRING数据库,进行成分-靶点间关联性分析,运用Cytoscape 3.5.0软件构建出“当归-川芎”药对“成分-靶点”网络. 使用中间介数、接近中间度、度值3个指标,对网络进行分析,选择3个指标均大于平均值的靶点作为网络中的关键靶点.
-
利用Drug Bank (https://www.drugbank.ca/)和TTD(https://db.idrblab.org/ttd/)数据库,收集FDA批准药物靶点,筛选得到关键靶点和药物靶点的共同靶点. 利用TCMSP和TTD数据库获得共同靶点相关疾病,按照医学主题词表MeSH(http://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/)将疾病分类,运用Cytoscape 3.5.0软件构建出“共同靶点-疾病”网络.
-
将关键靶点导入DAVID数据库(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/),进行基因功能和KEGG通路富集分析. 从Pubchem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)中获取“当归-川芎”药对活性成分的分子结构,将其与关键靶点导入Systems Dock Web Site(http://systemsdock.unit.ois.jp/iddp/home/index)数据库进行分子对接. 对接分数为实验解离/抑制常数值(pKd/pKi)的负对数,大于4.25,表明分子与靶点具有一定的结合活性;大于5.0,表明分子与靶点结合活性较好;大于7.0,表明分子与靶点具有强烈的稳定性及活性.
1.1. “当归川芎”药对活性成分的筛选
1.2. “当归川芎”药对“成分靶点”网络的构建和关键靶点的筛选
1.3. 共同靶点的筛选以及相关疾病分析
1.4. 关键靶点的富集分析和分子对接
-
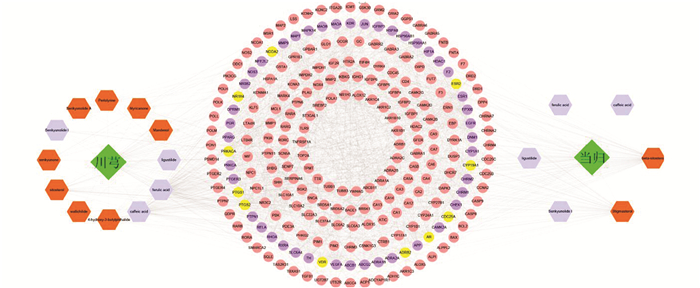
通过检索TCMSP,SEA数据库,获得当归成分125个,川芎成分189个,阈值设定为OB≥30%,DL≥0.18以及Caco-2≥-0.40,共筛选出候选活性成分8个,其中当归2个,川芎6个. 通过查阅文献获得10个活性成分,其中当归4个,川芎6个. 去除重复成分,最终得到14个活性成分,其中川芎和当归共有活性成分4个,分别是咖啡酸、阿魏酸、洋川芎内酯I、藁本内酯(表 1).
-
利用TCMSP,SEA数据库,发现川芎12个活性成分对应127个靶点,当归6个活性成分对应337个靶点,删除重复的靶点,“当归-川芎”药对14个活性成分对应257个靶点. “当归-川芎”药对的“成分-靶点”网络包含257个节点和2 388条边(图 1). 分析网络节点的中间介数、接近中间度及度值的平均值,分别为0.003 5,0.441 1,16.925 3,筛选3个指标均大于等于平均值的靶点,得到54个关键靶点,其中11个是当归和川芎共有靶点,分别是PTGS1,VDR,PTGS2,CDC25A,CYP19A1,NR1H4,PRKACA,AR,ESR2,ADRB2,NCOA2,这些靶点可能是川芎和当归协同作用的物质基础.
-
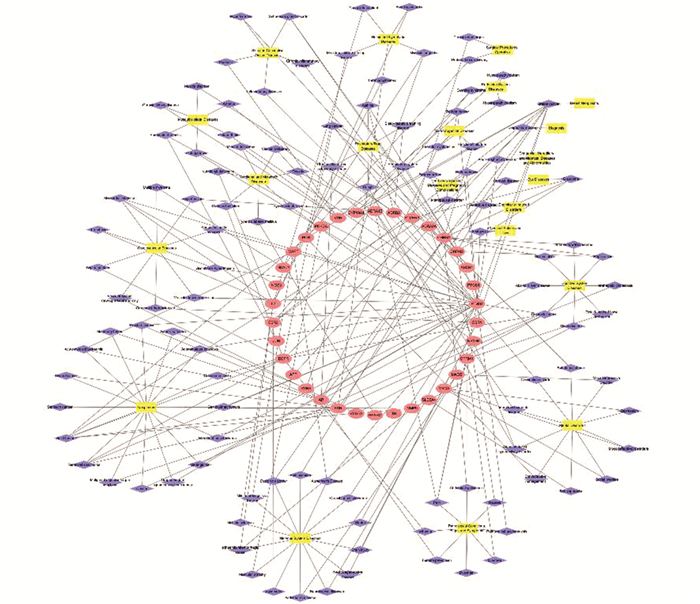
通过TTD和Drug Bank数据库,获得1 215个FDA批准药物靶点,54个关键靶点和FDA批准药物靶点有34个共同靶点. 通过TTD和TCMSP数据库分析,构建的“共同靶点-疾病”网络由168个点和264条边组成,共同靶点与21组共113种疾病相关,包括肿瘤(14.2%)、神经系统疾病(12.4%)、心血管疾病(8.8%)、心理疾病(8.8%)、病理状况(7.1%)和女性生殖系统疾病(5.9%)等(图 2),这可能是“当归-川芎”药对潜在的治疗靶点和对应的疾病.
-
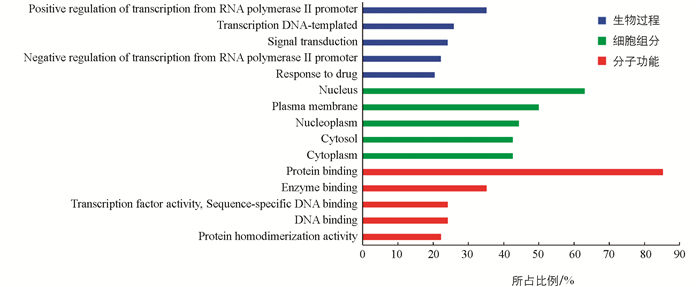
34个共同靶点提示的是“当归-川芎”药对潜在作用的疾病,而54个关键靶点能更全面地反映“当归-川芎”药对的成分靶点,因此将54个关键靶点导入DAVID数据库,从生物学过程、分子功能和细胞组分3个不同的方面对基因功能进行分析. 结果显示,54个关键靶点共涉及155个生物过程、29个细胞组分和66个分子功能,其中生物过程中排名前5的有Positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase Ⅱ promoter(19个靶点/35.2%),Transcription DNA-templated(14个靶点/25.9%),Signal transduction(13个靶点/24.1%),Negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase Ⅱ promoter(12个靶点/22.2%),Response to drug(11个靶点/20.4%). 细胞组分中排名前5的有Nucleus(34个靶点/63%),Plasma membrane(27个靶点/50.0%),Nucleoplasm(24个靶点/44.4%),Cytosol(23个靶点/42.6%),Cytoplasm(23个靶点/42.6%). 分子功能中排名前5的有Protein binding(46个靶点/85.2%),Enzyme binding(19个靶点/35.2%),Transcription factor activity,Sequence-specific DNA binding(13个靶点/24.1%),DNA binding(13个靶点/24.1%),Protein homodimerization activity(12个靶点/22.2%)(图 3). 这表明“当归-川芎”药对可能参与了人体内的多种生物过程.
KEGG通路富集分析结果显示,54个关键靶点共参与58条信号通路过程,其中包括Pathways in cancer,Estrogen signaling pathway,Proteoglycans in cancer,Calcium signaling pathway,HIF-1 signaling pathway等,涉及癌症、黏附、细胞周期、炎症、细胞凋亡、血管生成及激素调节等,表 2展示了涉及靶点数目排名前20的通路信息.
-
将“当归-川芎”药对活性成分豆甾醇、β-谷甾醇、洋川芎内酯A、藁本内酯、阿魏酸和4-羟基-3-丁基苯酞与度值排名前10的关键靶点进行分子对接. 结果表明,6个活性成分与7个靶点对接成功,其中豆甾醇、β-谷甾醇、洋川芎内酯A、藁本内酯与NCOA2,ESR2,EP300,ESR1等靶点有较好的结合活性以及稳定性(表 3).
2.1. “当归川芎”药对的活性成分
2.2. “当归-川芎”药对的“成分-靶点”网络
2.3. “共同靶点疾病”网络的构建与分析
2.4. 基因功能及KEGG通路富集分析
2.5. “当归川芎”药对活性成分与关键靶点有结合活性
-
当归、川芎都是血分之主药,当归味甘,具有养血活血之功效,川芎味辛,是血中气药,具有活血祛瘀、行血散血的功效,两者相使配伍同用,可增强活血化瘀、养血活血之功效,因此“当归-川芎”常作为活血化瘀的药对使用,但它们配伍增效的物质基础并未阐明,我们通过数据库和文献检索获得川芎和当归14个有效成分,其中4个共有成分,分别是咖啡酸、阿魏酸、洋川芎内酯I、藁本内酯. 其中咖啡酸和阿魏酸是酚酸类成分,咖啡酸在机体内儿茶酚氧位甲基转移酶的作用下可转化成阿魏酸,而阿魏酸具有抗氧化、抗血栓、降血脂、降低心肌缺氧、抗菌、抗肿瘤和脑保护等多种药理作用[6-7]. 洋川芎内酯I和藁本内酯是苯酞类成分,洋川芎内酯I具有保护脑、抗凝血作用,藁本内酯具有抗动脉粥样硬化、抗炎镇痛、抗老年痴呆、抗脑缺血、抗肿瘤、抗脂质过氧化、改善微循环等作用[8-9]. 这些共有成分可能是“当归-川芎”药对配伍增效的物质基础,可以进一步通过成分敲出、敲入等技术来验证.
“当归-川芎”常常配对使用,尤其多见于一些治疗妇科疾病的名方,比如四物汤、佛手散、血府逐瘀汤、温经汤等. 通过数据库检索发现,构建和分析“当归-川芎”药对的“成分-靶点”网络,获得54个关键靶点,其中11个是川芎和当归共有靶点,分别是PTGS1,VDR,PTGS2,CDC25A,CYP19A1,NR1H4,PRKACA,AR,ESR2,ADRB2,NCOA2. 有研究发现PTGS2是FDA批准的治疗子宫内膜异位症的靶点之一[10],而且“当归-川芎”药对中的阿魏酸和川芎嗪能抑制PTGS2的表达[11-14]. CYP19A1参与雌激素合成,ESR2是雌激素受体,分子对接结果中,豆甾醇、β-谷甾醇、洋川芎内酯A、藁本内酯与ESR2有较好的结合活性,也有研究发现阿魏酸和川芎嗪能抑制雌激素水平[4, 10],但是“当归-川芎”药对及其活性成分对CYP19A1和ESR2的作用还未见报道,值得研究. 其中34个关键靶点也是FDA批准药物靶点,PTGS2,ESR2可作为治疗女性生殖系统疾病及妊娠并发症的靶点,进一步KEGG通路富集分析发现,关键靶点调控多条与雌激素、孕激素相关的通路,包括Estrogen signaling pathway,Oxytocin signaling pathway,Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation,GnRH signaling pathway,Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption,这可能是“当归-川芎”配对用于治疗妇科疾病的机制,值得进一步深入研究.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: