-
开放科学(资源服务)标志码(OSID):

-
“滇桂艾纳香”作为广西壮族常用药材,具有活络经血、祛风除湿、止血、利尿等功效,用于治疗经期不准、产后大出血、不孕症、阴疮、风湿骨痛等症状[1-3]. 《广西中药材标准》(第2册,1996年版)、《湖南省中药材标准》(2009年版)收载假东风草Blumea riparia (Bl.) DC. 作为“滇桂艾纳香”药材基原植物,别名白花九里明、华艾纳香等. 课题组实地考察中发现,东风草B. megacephala (Randeria) Chang et Tseng别名大头艾纳香、管芽,在广西壮医临床、民间使用也常作为“滇桂艾纳香”药材使用,部分文献中也存在将这两个种混淆的情况[4-6].
假东风草和东风草在植物学形态上较为相似,“滇桂艾纳香”药材以全草入药,但湖南省、广西省标准仅收载了假东风草作为“滇桂艾纳香”的药材来源,且仅收载了假东风草的性状以及根和茎的组织切片,尚未收载叶组织结构和粉末鉴别. 目前鲜有文献对东风草的显微组织结构鉴别的报道,尚无对假东风草和东风草花粉粒形态研究的报道. 林雀跃等[7]通过对“滇桂艾纳香”及东风草的品种考证和资源调查发现:1836年假东风草被正式命名,而直到1974年东风草才被命名,且一开始是作为假东风草的一个变种来命名的,后来由于各种原因,最终将两者分列为同属两种不同的植物,也就是说东风草实际是由假东风草中分化出来的一个种,但有些学者还是保留这两个种其实为一个种的意见.
因此,本文拟从原植物形态、药材性状鉴别、显微鉴别、花粉粒电镜微形态鉴别等方面,对假东风草和东风草的植株、根、茎、叶、花粉粒进行系统的鉴别研究,基于充分的实验数据比较,为壮药材假东风草和东风草的归属、鉴别提供科学依据.
HTML
-
假东风草和东风草均由课题组采于广西省百色市、南宁市,经西南民族大学刘圆教授、李莹副教授鉴定为假东风草Blumea riparia (Bl.) DC.和东风草B. megacephala (Randeria) Chang et Tseng,标本现存于西南民族大学民族药材标本馆,采集信息见表 1.
试剂主要有水合氯醛试液、正丁醇、无水乙醇、二甲苯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司(货号:10023418);番红固绿(植物)染液,Servicebio公司(货号:G1031);FAA固定液(自配);电镜固定液,赛维尔生物;锇酸、PBS、乙酸异戊酯、冰醋酸、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇、无水乙醇,均为分析纯.
-
OLYMPUS BX41光学显微镜,日本OLYMPUS公司;JEC-1600 Auto Fire Coater镀膜器,日本JEOL公司;JJ-12J脱水机,武汉俊杰电子有限公司;JB-P5包埋机,武汉俊杰电子有限公司;RM2016病理切片机,上海徕卡仪器有限公司;JB-L5冻台,武汉俊杰电子有限公司;Nikon DS-U3成像系统,日本尼康;K850临界点干燥仪,Quorum;MSP-2Sp、离子溅射仪,IXRF;SU8100扫描电子显微镜,HITACHI.
1.1. 材料与试剂
1.2. 实验仪器
-
参照文献[8]对原植物的根、茎、叶、花等特征进行鉴别研究.
-
将采集到的假东风草、东风草选取根、茎、叶用清水清洗干净,浸泡入自制的FAA固定液中固定24 h,按常规石蜡切片法切片,番红-固绿法染色,中性树胶封片制作成永久石蜡切片[9]. 显微镜下观察,显微成像系统成像.
-
假东风草、东风草粉碎过4号筛,用解剖针挑取样品粉末少许,置载玻片的中央,分别滴加适宜的水合氯醛和稀甘油,用解剖针搅匀,盖上盖玻片观察.
-
新鲜假东风草、东风草花药投入电镜固定液室温固定2 h,再转移至4 ℃保存. 固定好的样品经0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液PB((pH值为7.4)漂洗3次,每次15 min. 1%的锇酸0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液PB(pH值为7.4)室温固定1~2 h. 0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液PB(pH值为7.4)漂洗3次,每次15 min. 样本依次入30%,50%,70%,80%,90%,95%,100%,100%酒精每次15 min,乙酸异戊酯15 min进行脱水处理,将脱水后的样本放入临界点干燥仪内进行干燥. 将干燥样本紧贴于导电碳膜双面胶上放入离子溅射仪样品台上进行喷金30 s左右,扫描电子显微镜下观察.
-
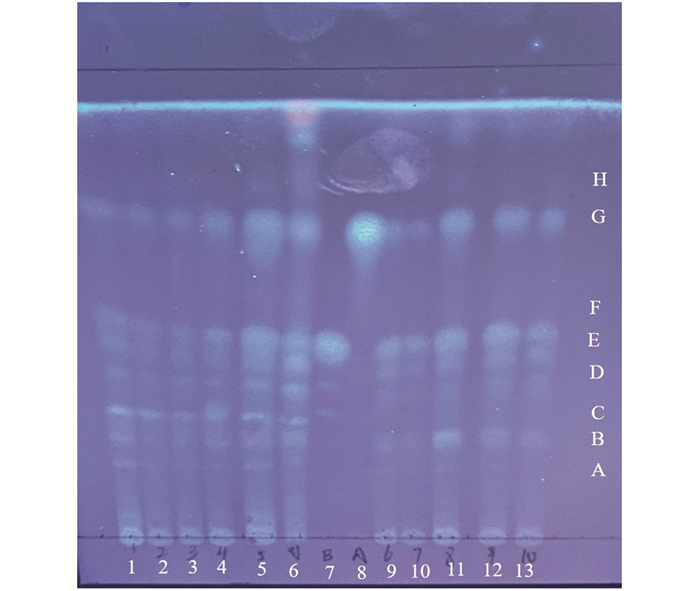
针对“滇桂艾纳香”药材现行地方标准粗浅、专属性不强的问题,参照《中国药典》(2020年版)薄层鉴别项要求和文献[7]建立假东风草和东风草的薄层色谱鉴别方法.
取药材粉末1 g,加70%甲醇40 mL,超声处理30 min,滤过,取30 mL滤液旋干,残渣加甲醇5 mL溶解定容,作为供试品溶液. 吸取上述溶液2 μL点于同一硅胶GF254板上,展开剂为乙酸乙酯、甲酸、冰醋酸和水,比例为13∶1∶1∶2,展开,取出,晾干,喷以10% 硫酸乙醇溶液,105 ℃烘约5 min,置紫外光365 nm下检视.
2.1. 原植物鉴别
2.2. 性状鉴别
2.3. 显微鉴别
2.3.1. 组织显微鉴别
2.3.2. 粉末显微鉴别
2.4. 花粉粒电镜鉴别[10-12]
2.5. 薄层鉴别
-
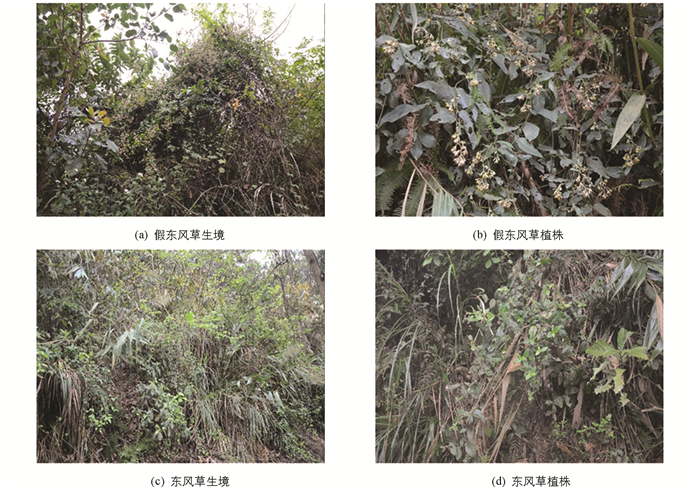
课题组通过实地考察、采集,系统比较了假东风草(小花种)与东风草(大花种)原植物特征,原植物及其详细特征见图 1至图 4,假东风草与东风草原植物比较结果见表 2.
-
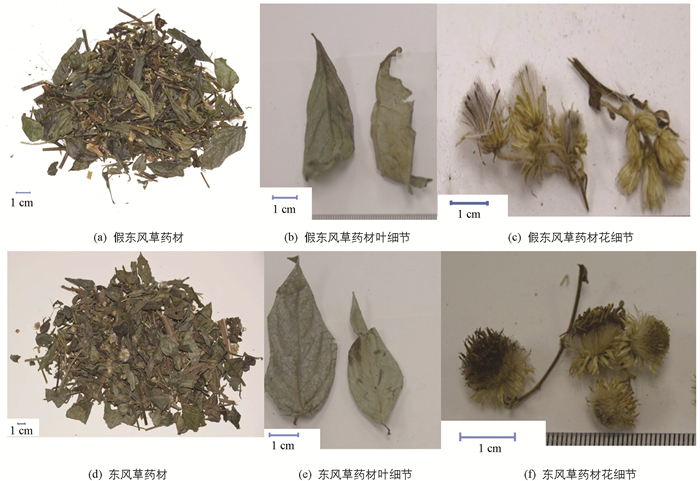
观察、比较多个批次假东风草(小花种)与东风草(大花种)药材特征,药材见图 5,假东风草与东风草药材特征比较结果见表 3.
-
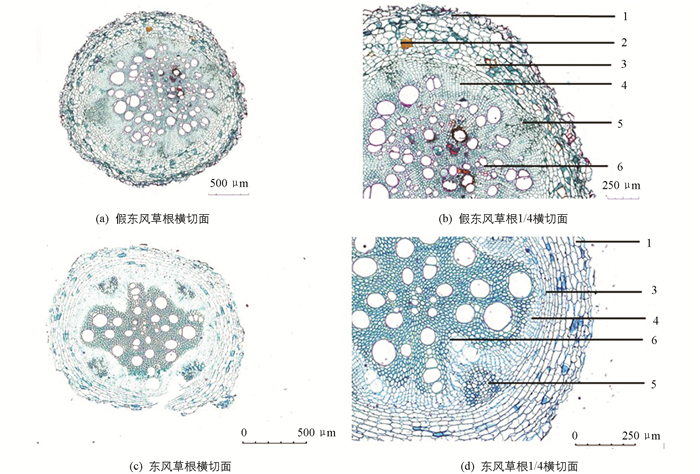
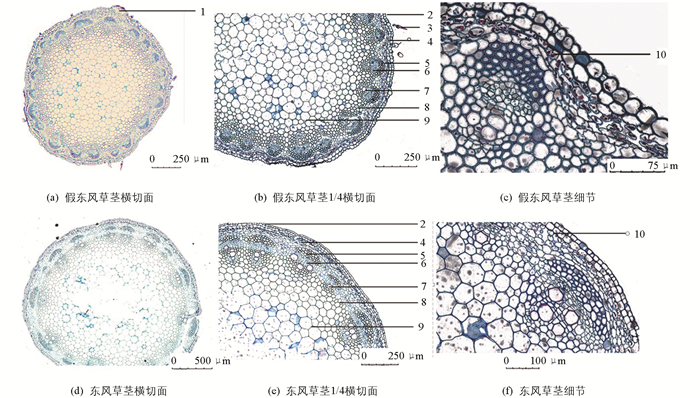
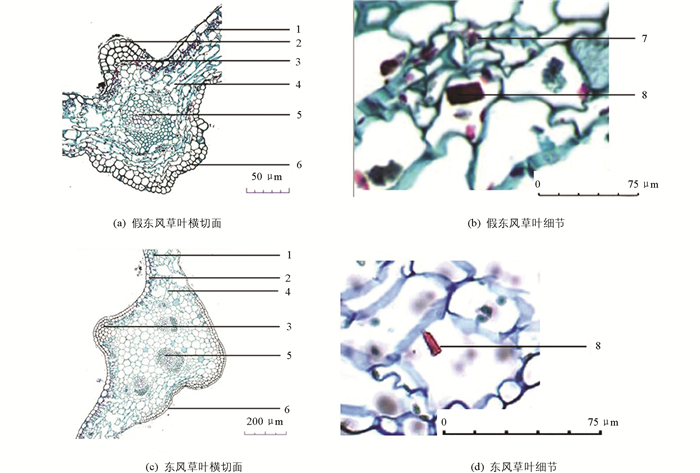
课题组通过观察多个假东风草(小花种)与东风草(大花种)根、茎、叶石蜡切片与粉末特征装片,系统比较了假东风草(小花种)与东风草(大花种)根、茎、叶和粉末显微特征,见图 6至图 9,假东风草与东风草显微鉴别特征比较结果见表 4.
-
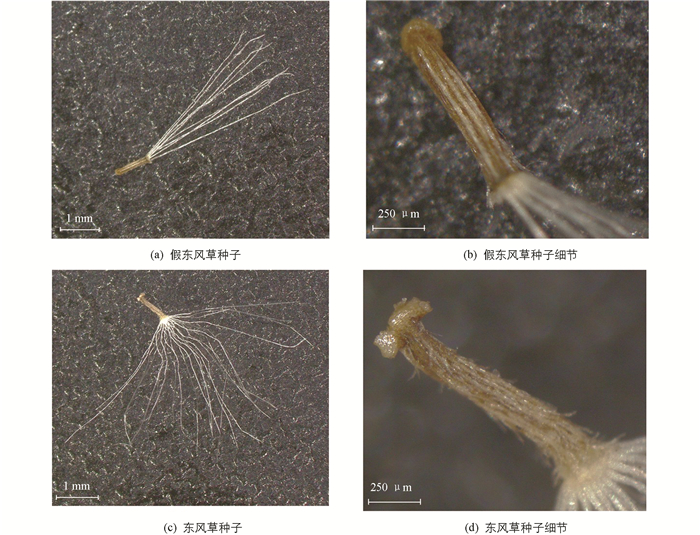
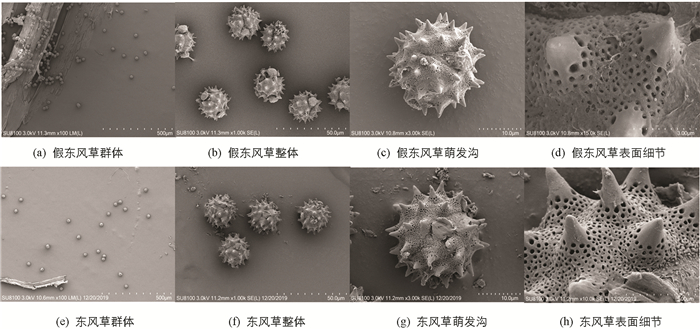
观察、测量了大约10粒外形饱满、发育较好的花粉粒,系统比较了假东风草(小花种)与东风草(大花种)花粉粒形态特征,其花粉粒形态及表面纹饰见图 10,假东风草与东风草花粉粒形态特征比较结果见表 5.
-
结果显示假东风草具特征斑点C,H,东风草不具备特征斑点C,H,见图 11. 表明该方法专属性好,可以区分假东风草和东风草.
3.1. 原植物
3.2. 性状鉴别
3.3. 显微鉴别
3.4. 花粉粒电镜鉴别
3.5. 薄层色谱鉴别
-
实验研究发现:假东风草和东风草应为菊科艾纳香属下两个不同的种. 假东风草和东风草原植物和性状特征可根据花序的大小、疏密或叶柄有无加以区分;显微组织结构特征可根据叶主脉上突明显与否、主脉维管束差异进行区分;粉末特征无明显区别;花粉粒表面特征:假东风草和东风草的花粉粒均为球形或近球形,三孔沟萌发孔;假东风草花粉粒上表面的刺状突起比东风草更尖,孔穴比东风草分布稀疏且没有不规则孔眼;假东风草花粉粒比东风草小,瘤状凸起比东风草大. 结果表明,假东风草和东风草的原植物、性状、内部显微组织结构、粉末特征、花粉粒表面特征等区别明显.
本实验参考《中国药典》(2020年版)对于中药材下所收载的项目和相关显微鉴别规定、方法等,系统地对假东风草进行了鉴别研究,同时对其易混淆且药效相似的东风草也进行了系统研究. 原植物和性状鉴别对假东风草省标“性状”项下的内容进行了补充研究;组织结构、粉末鉴别对假东风草省标“鉴别”项下的内容进行了补充研究,提供了详细的第一手彩色图像和数据. 花粉的生物特征稳定,可以作为品种间鉴别的依据,可以通过观察假东风和东风草的花粉粒结构特征,以达到快速、准确区分这两个品种.
虽然假东风草和东风草在药效上有一定的相似性,但建议后续进一步开展药效一致性评价等相关研究,探讨制药企业是否能够将东风草纳入“滇桂艾纳香”作为新的基原植物,扩大药源,以缓解假东风草的药用资源不足的问题.












 DownLoad:
DownLoad: