-
偏微分方程被用来描述很多物理现象和自然现象[1],在工业过程控制中有很多模型都是基于偏微分方程约束的控制问题和优化问题.但基于偏微分方程的最优控制问题,往往需要大量的时间来求解[2-3],无法满足现有优化与控制的需求,因此如何快速求解偏微分方程模型或者对偏微分方程模型进行降阶显得十分必要.
目前常见的偏微分方程的求解方法为有限差分法和有限体积法,都是对偏微分方程进行时间与空间的离散[4-5],将偏微分方程化简为一系列代数方程来求解.但是随着系统复杂度的日益提升,离散所得的代数方程的维数往往很高,计算时间很长.文献[6-7]基于有限元的方法来求解偏微分方程最优控制问题,虽然提高了计算精度,依然存在着计算时间长的不足.文献[8-10]提出了基于伽辽金方法来求解偏微分方程的思想,大大降低了该问题的计算量,但是并没有给出一种较好的基函数选取方法,因此求解的准确性相对较差.文献[11-12]提出了基于奇异值分解的方法来降低代数方程的阶次,从而达到简化计算的目的.
本文在结合了伽辽金方法的基础上引入正交基的概念,将原系统空间的能量投影到低维空间中,先采用有限差分法离散偏微分方程,然后根据这些离散的递归高阶代数方程生成快照.在此基础之上,本文提出了偏微分方程的模型降阶方法,能够提取高维状态空间模型的特性来获得一个低维状态空间模型.该方法能够快速准确地求解偏微分方程.本文以一个偏微分方程的最优控制问题为例,进行了仿真实验.实验表明该方法可以快速准确地求解偏微分方程,满足优化问题求解的需求.
HTML
-
偏微分方程一般用来描述常见的物理现象,模型采用常见的抛物型偏微分方程,同时含有对流项与扩散项,如式(1)
式中y(x,t)表示温度场,L表示长度,D表示扩散系数.
-
一般选择有限差分法作为偏微分方程的离散化方法对式(1)进行离散,可以得到式(2)
同理对边界条件离散化之后,带入式(2)可以得到式(3)
对于边界上的点有所不同,可得式(4)
其中
$\alpha = \frac{{v\tau }}{{2\Delta x}}$ ,$\beta = D\frac{{\Delta t}}{{\Delta {x^2}}}$ ,$\gamma = \frac{{2v\Delta x}}{D}$ ,由此易知可以将得到离散之后的递推代数方程式整理成状态空间的形式易知
其中k1=1-2β-(α+β)Φ,从上式分析可知,矩阵A与维数和空间离散的步长有关,如果是大规模的问题,A的维数会随之大大增加,此时对该偏微分方程的计算会耗费很多时间.
1.1. PDE模型的描述
1.2. PDE模型的离散
-
对上面所示的状态空间方程进行处理,首先可知
从集合y的k个列向量中选取L个列向量构成子集{y}L,通常情况下L≪M,将这L个列向量构成的集合称为瞬像.在解决实际问题的时候,该瞬像集合通常由对以前的实验或者模拟结果组成,例如在解数值天气预报方程时,可以利用以前的天气结果来构成瞬像集合.
在得到该方程的瞬像之后,利用奇异值分解的方法来研究该偏微分方程的差分格式.首先将瞬像的集合表示成矩阵的形式
对于矩阵z,进行奇异值分解[13]
上式中U∈RM×M,V∈RL×L都是正交矩阵,S是一个对角矩阵,S=diag(σ1,σ2,σL+1),其对角线的元素就是矩阵Z的正奇异值.
若令U=(φ1,φ2,…φM),V=(ψ1,ψ2,…ψL).定义矩阵的范数为‖A‖α,β=sup
$\frac{{{{\left\| {Ax} \right\|}_\alpha }}}{{{{\left\| x \right\|}_\beta }}}$ ,令ZM=$\sum\limits_{i = 1}^M {{\sigma _i}{\varphi _i}{\psi _i}} $ ,如果M < r=rank(Z),有如下表达式成立这就表明了ZM是Z的最优逼近.令Z的L+1个列向量为aML=(z1l,z2l,…zMl),利用矩阵范数和向量范数的相容性有
式中PM(aMl)=
$\sum\limits_{i = 1}^M $ (φi,aMl)φi(aMl,φi)是向量φi和向量aMl的标准内积,在对ZM构造的过程中发现Φ=(φ1,φ2,…φM)是一组最优基.在定义了矩阵范数的情况下,求Φ={φ1,φ2,…φm}即最小化目标函数
Φ={φ1,φ2,…φm}可以理解为标准化正交基的集合
因此可得
将式(15)带入到式(5)中可得
有φTφ=I,由此可得
式中Ar=φTAφ,Br=φTB,cr=cφ.降阶模型的解可以由式(18)表示
通过使用伽辽金投影方法,可知该模型由M+1阶降到了r阶.采用降阶模型可以大大简化在差分求解中的运算量.在实际的使用过程中如果瞬像的能量达到了真实模型的99.5%以上,就认为该降阶模型可以很好地去逼近原模型.
-
下面对降阶模型的解的误差进行简要分析,设ZK为有限差分的真实解,Z*K为降阶模型的解,根据式(16)可得
对于上式的前半部分,瞬像集合是由如下空间构成
于是存在如下的常数ri,使得式(21)成立
式(19)的后半部分有
由式(19)和式(22)可知
对上式整理可得
如上式所示,记Z中的L+1个列向量为
εL+1i是除第L个分量为1,其余为0的单位列向量,同时令
$\sum\limits_{i = 0}^L $ |rik|=Bk,‖ΦΦTA‖2,2=C,从上一小节的推导中已经证明了ZM是Z的最优逼近,因此有然后根据矩阵范数和向量范数的相容性,有如下表达式成立
由此可得
将上式展开可得
由式(24)和式(29)可知
综上所述,可以得到
由此可以证明,采用模型降阶方法得到的近似解和真实解之间的距离是有界的.在适当选取其中参数的情况下,可以保证近似解能够较好地逼近真实解.
2.1. PDE模型降阶
2.2. 解的误差估计
-
考虑式(31)所示的一个对流扩散的优化问题
首先采用有限差分法对该优化问题进行离散化处理,由此可以得到式(32)所示的一个最优控制问题.
通过线性二次调节器的反馈控制设计可知
S是通过求解黎卡提方程得到的
在求解该问题的过程中,分别采用不同阶次的简化模型和真实模型进行对比.
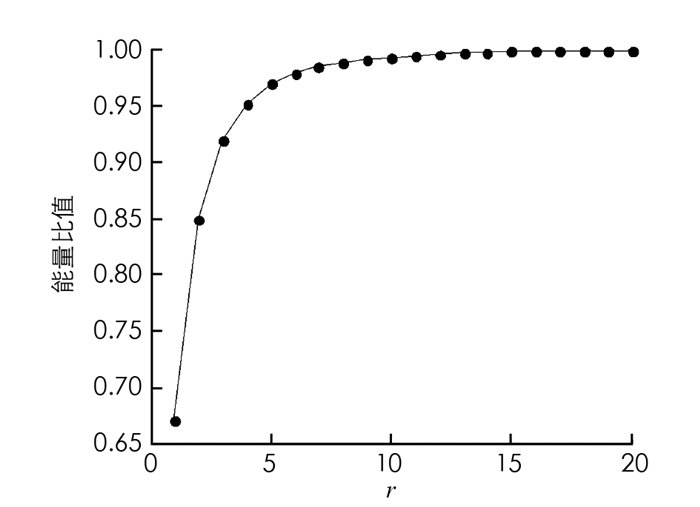
根据经验值得到表 1中实验参数,并按照表 1中参数进行实验. 图 1给出了采用本文方法中近似模型不同阶次r与总能量的关系.
由此可以得到当近似模型的阶次达到10以上时,总能量已经解决100%了.由一般的工程经验可知,若瞬像的总能量达到了原系统总能量的99.5%以上,那么就认为有较好的近似效果.
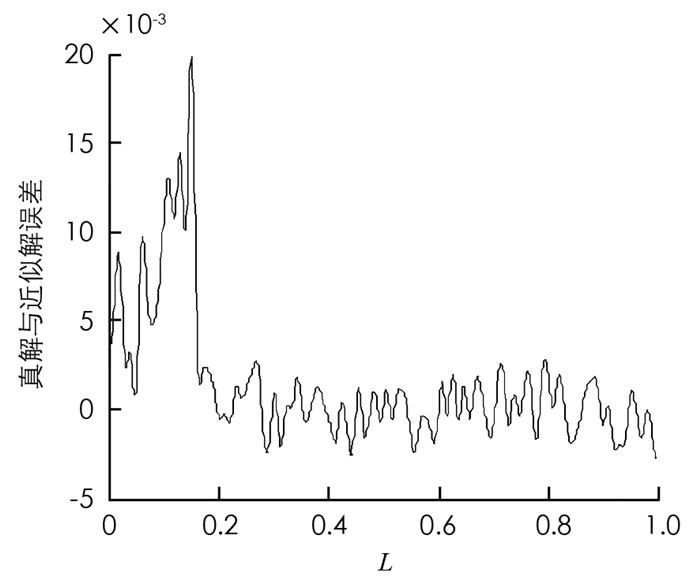
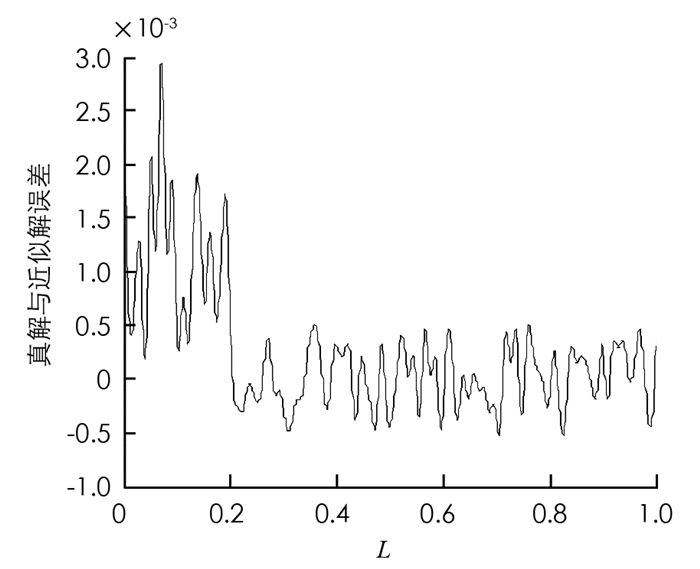
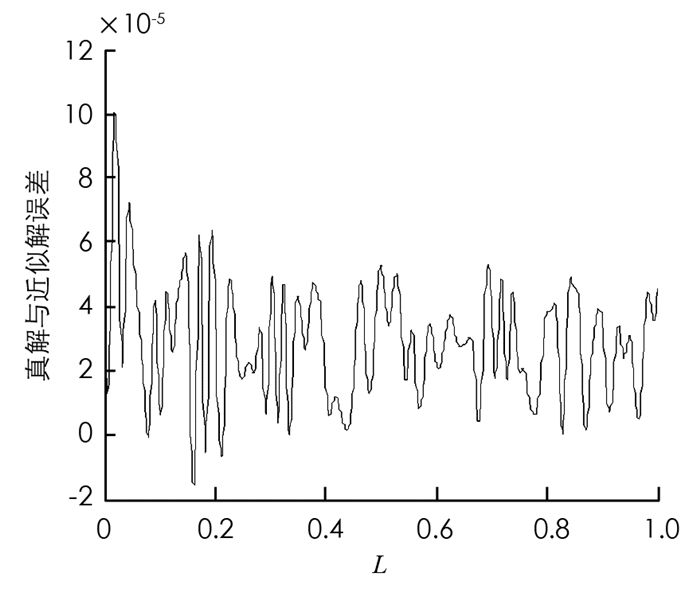
图 2、图 3和图 4分别是近似模型阶次依次选取10,15,20时,真解与近似解的误差曲线.从分析可以看出,当r=10时真解与近似解的误差最大,r=20时真解与近似解的误差最小.但总体而言,近似模型阶次若大于10,则可以较好地逼近原模型.
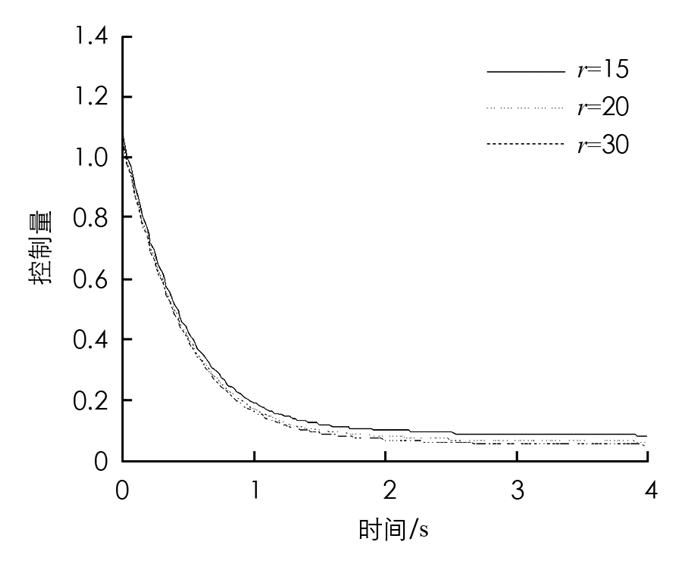
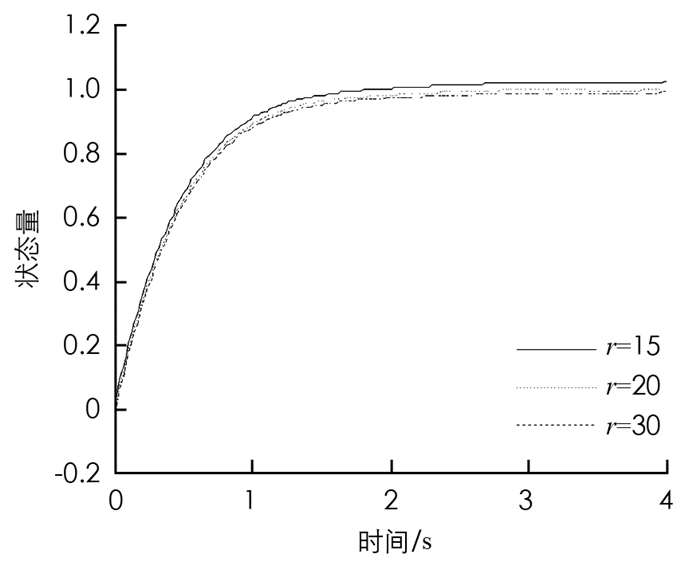
图 5是近似模型阶次依次选取10,15,20时,优化求解的控制量的大小变化曲线,从图 5中分析可知,控制量大小几乎是重合的. 图 6是近似模型阶次依次选取10,15,20时,优化求解的控制量的大小变化曲线和控制量一样,状态量在不同阶次模型中几乎重合.
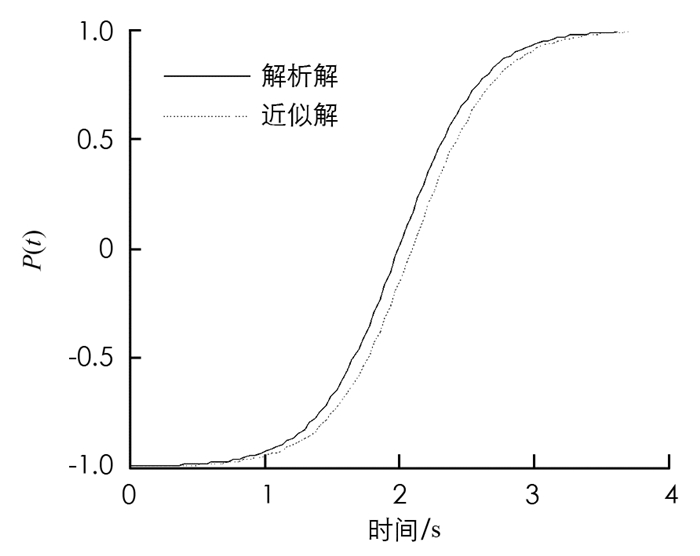
如图 7所示,分别使用近似模型和真实模型的解析解对比,从图 7中分析可知,使用近似模型求解的结果和真实模型解析解的结果几乎一致,由此说明了该方法的有效性.
-
本文在分析了几种偏微分方程求解方法的基础上,基于伽辽金投影法,通过合理地选取正交基函数来近似高阶代数方程,从而达到简化计算的目的.在理论上证明了该方法的近似解可以收敛于真实解,并且以一个最优控制问题为例进行了仿真实验,证明了该方法的有效性.本文接下来的研究方向是考虑将优化的一些思想运用到降阶模型中,建立一个更加准确的降阶模型.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: