-
在自然界和人工系统中,交互信息的个体之间的状态同步是一种普遍存在的现象.自文献[1-2]提出混沌同步这一概念以来,有关同步的研究结果已经广泛应用于自然科学[3-4]和工程领域[5-7].神经元状态的聚类行为[8-9]已被检测为一种大脑信号的同步状态.在生命科学的一些领域(如哺乳动物视觉皮层),神经元状态的完全同步已经被实验所证实[10-11].完全同步作为同步状态的一种特殊形式,已被证实是人脑中信息编码和传递的一种机制[12].
在描述神经元动力学行为的模型中,有一类是离散时间类型的[13-16],如Rulkov模型、Aihara模型和Chialvo模型等.
受到文献[16]的启示,本文考虑了由两个二维Aihara神经元通过电耦合交互的耦合系统达到完全同步的以下问题:研究系统参数区间对系统最大Lyapunov指数的影响;在电突触耦合下,从数值和理论上,研究两个同质Aihara神经元状态完全同步的存在性;实现耦合系统状态同步的参数区域的可视化.
HTML
-
考虑如下的二维Aihara神经元模型[15]:
其中:x(t)表示神经元在离散时间t=0,1,2,…时刻的输出状态;y(t)表示神经元在t-1时刻的时滞内部状态;k1,k2表示神经元不应性阻尼系数;α>0和c>0为模型的调节参数.函数f为以ε为参数的坡度函数:
文献[15]以系统参数k2为分岔参数,观察到了Aihara神经元的峰放电现象.
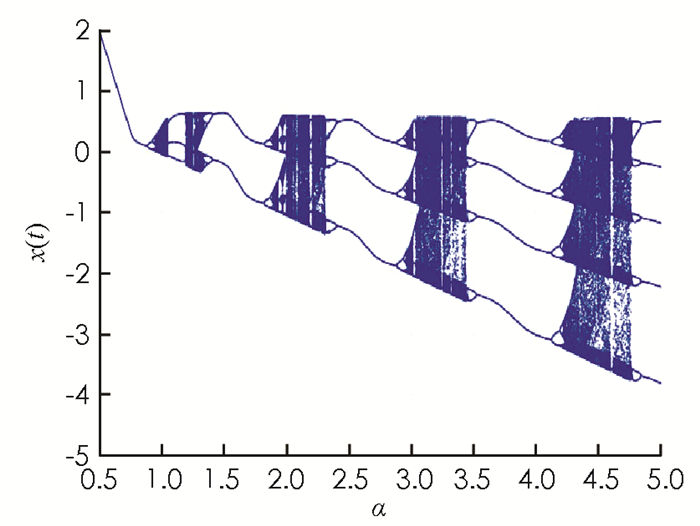
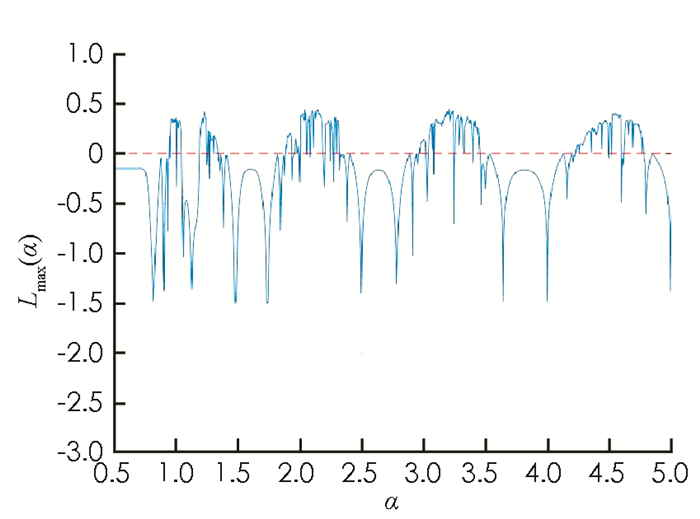
本文以α为分岔参数来对模型进行研究.为便于数值模拟,取定模型(1)中的部分参数为:k1=0.8,k2=0.05,ε=0.05,c=0.8.利用数值模拟,首先给出模型(1)随参数α在[0.5,5]上的状态分岔图(图 1),图形表明参数α某些特定值会导致神经元状态的混沌现象.利用主稳定函数作为系统稳定性的分析工具,图 2则展示了模型(1)的最大Lyapunov指数Lmax(α)关于参数α在[0.5,5]上的分布曲线,当Lmax(α)≥0时,模型(1)处于不稳定的混沌状态;当Lmax(α) < 0时,模型(1)处于稳定状态.
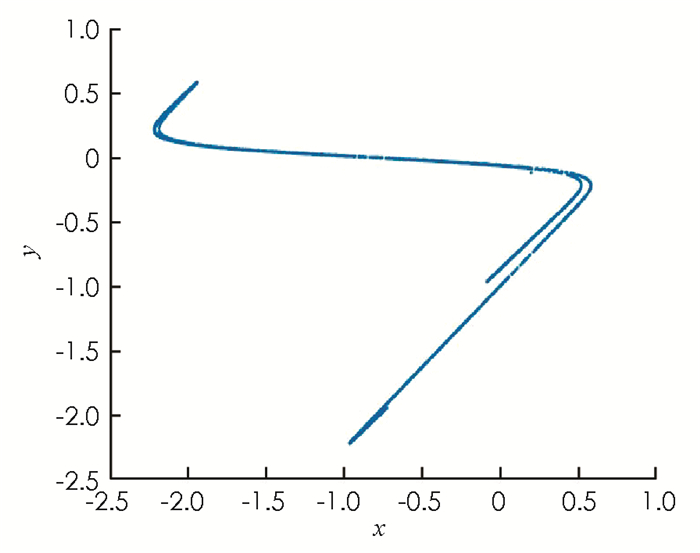
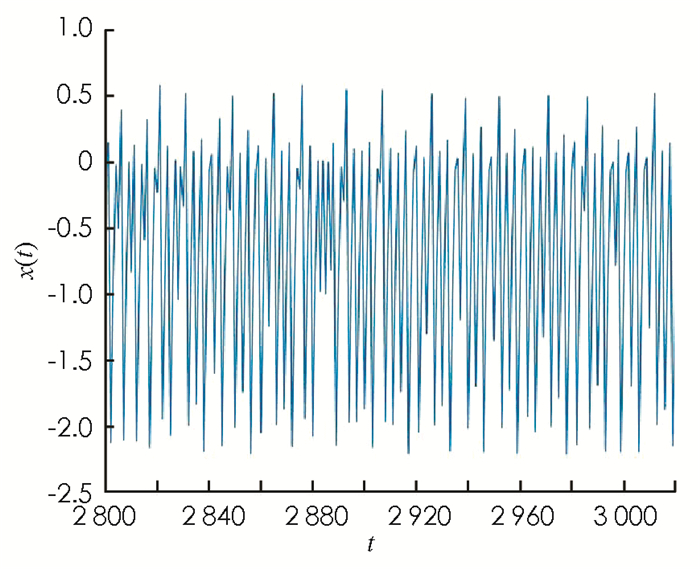
当参数α=3.2以及初始条件x(0)=1.2,y(0)=-0.12时,图 3展示了模型(1)在(x,y)平面上的相图. 图 4描绘了模型(1)在t∈[2800, 3020]上神经元状态的波形图.如图 3和图 4所示,当α=3.2时,模型(1)所描述的神经元处于混沌尖峰放电状态.
-
文献[16]建立了电突触耦合下两个Rulkov神经元的耦合模型.我们将此模型应用于两个同质性态的Aihara神经元耦合模型,建立如下的耦合系统:
其中参数σ为神经元的耦合强度.当σ>0时,神经元的电突触耦合是刺激性的;当σ < 0时,耦合是抑制性的.
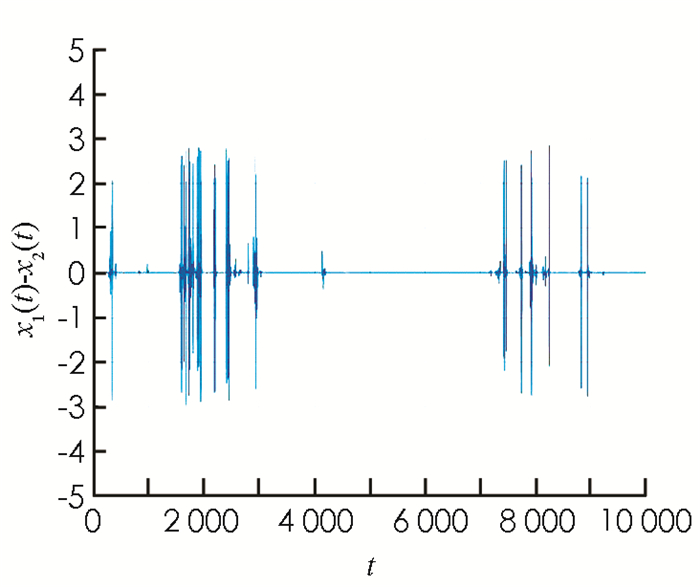
图 5考虑了在参数σ=0.2和α=3.2时,两个初始条件分别为(-1.97,-3.14)和(-1.7,-3.5)的处于混沌尖峰放电状态的Aihara神经元在t∈[7880, 8050]的状态波形图. 图 6展示了两个神经元的状态差x1(t)-x2(t),t=0,1,…,10 000.数值结果表明,这两个神经元的状态出现了“间歇性同步现象”.
1.1. 单个的二维Aihara神经元模型及其动力学性态
1.2. 两个2维Aihara神经元的电突触耦合
-
在本节中利用主稳定函数(Master Stability Function)为分析工具讨论耦合神经元模型(3)的参数与模型中两个神经元状态完全同步的关系.
主稳定函数分析法是讨论一个动力学系统稳定性的基本方法,主稳定函数反映了动力系统的最大Lyapunov指数与系统参数之间的函数关系.此外,判定由混沌系统分解出的子系统之间能否实现同步的主要判据之一就是系统的Lyapunov指数皆为负值.
为模型(3)引入外部和内部耦合矩阵如下,
则模型(3)等价地转化为如下矩阵形式
其中:
$\boldsymbol{X}(t)=\left(\boldsymbol{X}_{1}^{\mathrm{T}}(t), \boldsymbol{X}_{2}^{\mathrm{T}}(t)\right)^{\mathrm{T}}$ ,$\left.\boldsymbol{X}_{2}^{\mathrm{T}}(t)\right)^{\mathrm{T}}, \boldsymbol{X}_{i}(t)=\left(x_{i}(t), y_{i}(t)\right)^{\mathrm{T}}$ ,i=1,2.$ \otimes $ 代表矩阵的Kronecker积.向量函数F (X (t))定义为设s (t)=(sx(t),sy(t))T是系统(5)中两个神经元的同步解,由于耦合矩阵G具有行和为零的性质,所以s (t)满足如下方程:
这里,
$\mathit{\boldsymbol{g}}(\mathit{\boldsymbol{s}}(t)) = {\left({{k_1}{s_x}(t) + {k_2}{s_y}(t) - \alpha f\left({{s_x}(t)} \right) + c, {s_x}(t)} \right)^{\rm{T}}}$ .定理1 对于耦合系统(5),如果下列2维系统
的零解是渐近稳定的,那么系统(5)的两个神经元能达到局部状态完全同步.记
其中Lmax(·)为方程(8)相应的主稳定函数.那么,耦合系统(5)中的两个神经元关于参数σ,α能达到状态完全同步的必要条件是参数对(σ,α)∈SD.
证 记
$\boldsymbol{E}_{i}(t)=\boldsymbol{X}_{i}(t)-\boldsymbol{s}(t)$ ,i=1,2,$\boldsymbol{E}(t)=\left(\boldsymbol{E}_{1}^{\mathrm{T}}(t), \boldsymbol{E}_{2}^{\mathrm{T}}(t)\right)^{\mathrm{T}}$ ,那么系统(5)的相应变分系统为其中:
$\boldsymbol{S}(t)=\left(\boldsymbol{s}^{\mathrm{T}}(t), \boldsymbol{s}^{\mathrm{T}}(t)\right)^{\mathrm{T}}, \boldsymbol{D} \boldsymbol{F}(\boldsymbol{S}(t))$ ,DF (S (t))表示向量函数F在S (t)处的Jacobian矩阵,即其中I2表示2阶单位矩阵.另一方面,耦合矩阵G是对称矩阵且特征值λ1=0和λ2=-2,故存在正交矩阵P使得PTGP = Λ =diag(λ1,λ2).作变换
$\mathit{\boldsymbol{Z}}(t) = \left({{\mathit{\boldsymbol{P}}^{\rm{T}}} \otimes {\mathit{\boldsymbol{I}}_2}} \right)\mathit{\boldsymbol{E}}(t)$ ,则(9)式可转化为记
$\mathit{\boldsymbol{Z}}(t) = \left({\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{Z}}_1}(t)}\\ {{\mathit{\boldsymbol{Z}}_2}(t)} \end{array}} \right)$ ,Zi(t)∈R2,则(11)式分解为当i=2时,由于λ2=-2,由(12)式得,
显然,(13)式与(8)式等价.因此,当系统(8)的零解渐近稳定时,系统(5)的解S(t)渐近稳定,即两个同质的Aihara神经元系统达到完全同步.
记系统(8)相应的最大Lyapunov指数(即主稳定函数)为Lmax(σ,α),根据系统最大Lyapunov指数的定义,若系统(5)达到完全同步状态s(t),那么对应于系统(8)中参数σ,α的取值,Lmax(σ,α) < 0.因此,系统(5)中两个神经元达到状态完全同步的必要条件是参数对(σ,α)使得Lmax(σ,α) < 0,即
证毕.
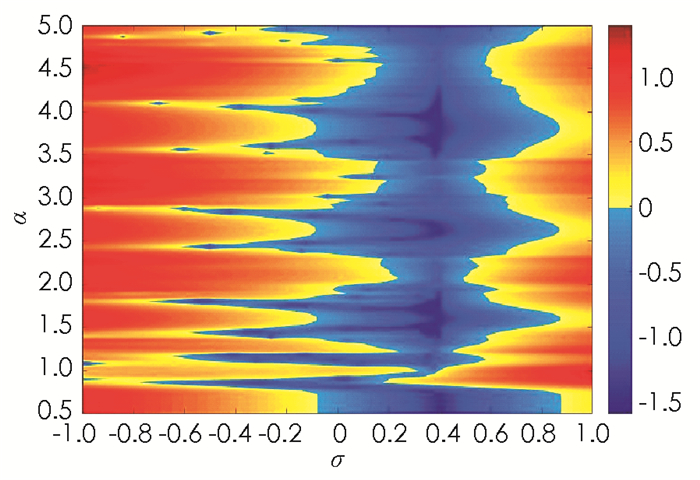
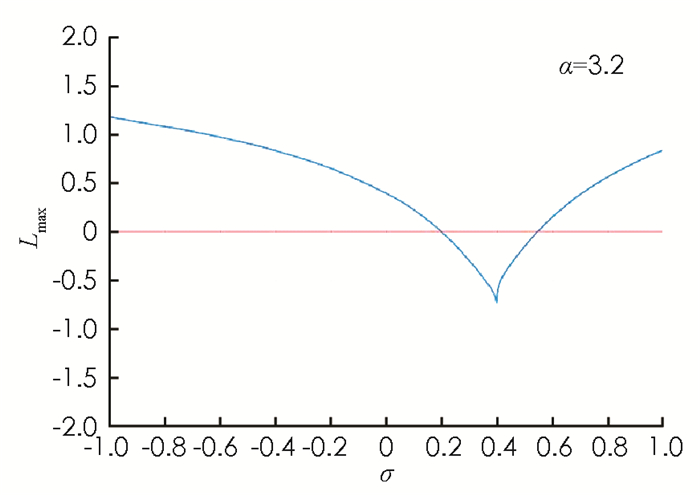
为可视化系统(8)对应的主稳定函数Lmax(σ,α)的分布情况,做如下设计:把矩形域[-1, 1]×[0.5,5]分割为100×100的网格并把网格交点处的坐标值作为参数对(σ,α)的取值.对每一对(σ,α)的取值,采取2 500次迭代数值计算系统(8)的最大Lyapunov指数值. 图 7中利用颜色的渐变展示了主稳定函数Lmax(σ,α)关于参数σ,α的函数值分布情况:当参数对(σ,α)的取值位于蓝色区域时,所对应的主稳定函数值小于零,系统(5)中的神经元能实现状态完全同步;当参数对(σ,α)的取值位于蓝色区域之外时,所对应的主稳定函数值大于等于0,系统(5)中的神经元不能达到状态完全同步. 图 8给出了系统(8)中参数α=3.2时函数Lmax随耦合强度σ∈[-1, 1]的变化曲线.从图 7,8中不难发现,对于离散型耦合神经元系统而言,过大或过小的耦合强度都不能使耦合系统达到状态的完全同步,这与连续型耦合神经元系统有本质上的区别.
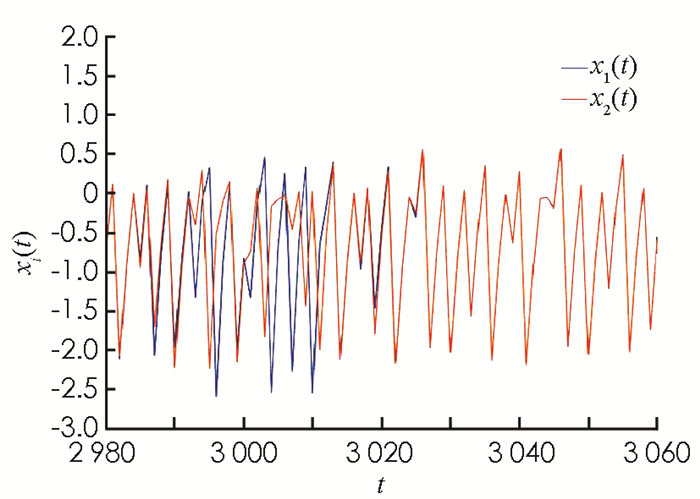
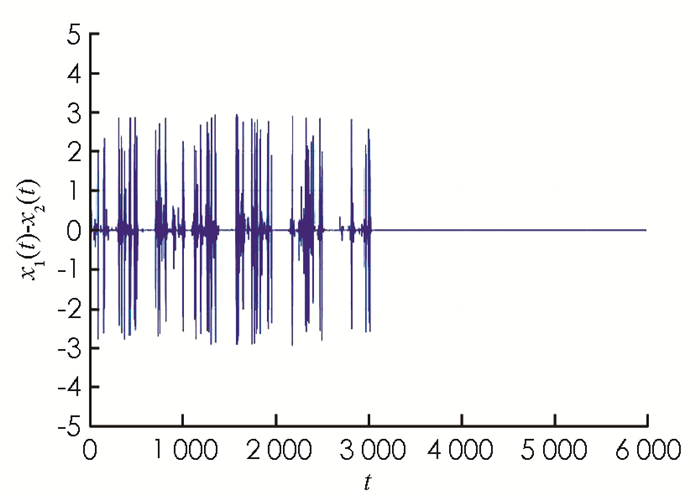
为了进一步检验理论结果的有效性,考虑系统(5)的参数α=3.2和耦合强度σ=0.18,0.22两种情形.系统(5)在前3 000次迭代里,取耦合强度σ=0.18,由定理1及图 9,10知,系统(5)中的两个神经元状态不能达到完全同步;后3 000次迭代取σ=0.22,系统(5)中的两个神经元状态能达到完全同步. 图 9展示了系统(5)中的两个神经元在t∈[2980, 3060]时的状态波形图,图 10展示了两个神经元状态差x1(t)-x2(t)的变化情况,数值仿真结果与理论结果相符.
-
本文研究了两个同质的Aihara神经元在电突触耦合系统的完全同步问题.利用主稳定函数这一工具,选取单个神经元的调节参数和系统耦合强度为变量讨论系统的最大Lyapunov指数值的变化情况.在理论上给出了耦合系统关于上述两个参数实现状态完全同步的一个必要条件和完全同步化的双参数平面区域.借助于数值计算,实现了该同步区域的可视化.值得注意的是,只要耦合强度在一定有限范围内,刺激和抑制也能实现系统神经元的状态完全同步.文中所设计的数值仿真实例验证了上述理论结果的正确性.最后,在文中仅考虑了两个同质的Aihara神经元的电突触耦合,而异质的神经元耦合、其它耦合方式(如化学突触)以及推广两个神经元到多个神经元构成的网络等,都是值得继续深入探讨的问题.







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: