-
硫化锌(ZnS)是典型的直接带隙半导体,具有良好的光学性能和电学性能,在光电器件、LED材料等诸多领域应用广泛,目前已有一些文献对三维ZnS材料的性质,特别是光学性质进行了研究[1-3].文献[4]的研究发现:SiC,ZnS等除具有三维结构外,还具有与石墨烯类似的二维六角结构,人们将这类材料称为类石墨烯.文献[5-7]用密度泛函方法研究了SiC等二维类石墨烯的稳定性,证明了这些化合物可以存在.这类材料因其独特的性质和广泛的应用前景,已引起人们极大的兴趣,并对它们的性能进行了一些研究.文献[8]利用哈里森键联轨道法,研究了ANB8-N化合物的弹性和介电性质,文献[9]还研究了π键对类石墨烯的有效电荷、内聚能和力常数的贡献,但这些研究未对具体物质作计算分析,特别是对具有重要应用价值的光电材料ZnS类石墨烯的热力学性质研究很少,而且研究中认为原子是静止的,其结果不能反映其性质随温度的变化规律.文献[10-11]研究表明:ZnS类石墨烯这类二维结构,存在大小、剪切等多种形变,这些形变和原子的非简谐振动对ZnS类石墨烯的性质有重要的影响.探索它的热膨胀系数、弹性模量和有效电荷等的变化规律和特点,无论在应用还是理论上都是一个待解决的重要问题.为此,本文将在考虑到形变和原子作非简谐振动情况下,应用固体物理理论和方法,对这一问题进行研究.
HTML
-
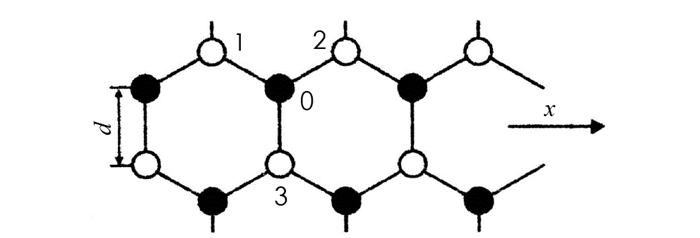
ZnS类石墨烯是由Zn原子和S原子构成的二维六角格子平面系统,设这两种原子各自总原子数为N,最近邻原子间距离为d(称键长),取任一原子为坐标系原点,平面为OXY平面,φ(d)轴垂直向上,坐标系选取见图 1.
按文献[9],考虑到短程作用后,ZnS类石墨烯的原子相互作用能为
其中,V1为金属化能,
$V_{2}=\eta \hbar^{2} / m d^{2}$ 是σ键的共价能,η=3.26;$V_{2}^{*}=\eta_{p p \pi} \hbar^{2} / m d^{2}$ 是π键的共价能,ηppπ=0.63(文献[12]);V3和V3*分别是σ键和π键的极化能,αp和αp*分别是σ键和π键的极性参量,而αc和αc*分别是σ键和π键的共价参量,其值为:式中的常数C为短程作用参量,文献[10]给出C=0.20 eV.
为了克服文献[9]不能研究热力学性质随温度变化规律的不足,本文认为,在(1)式所示原子相互作用能的作用下,原子不是静止的,而是在平面内在平衡位置附近作非简谐振动.将φ(d)在平衡位置d0附近展开,偏离δ=d-d0很小时,有
其中,ε0,ε1,ε2分别是简谐系数、第一和第二非简谐系数.由(1)式求得:
-
当温度不太高时,键长的平均位移ζ与温度的关系为[11]
由(7)式求得在温度不太低和不太高时的热膨胀系数
$\alpha_{l}=\frac{1}{d_{0}} \frac{d \xi}{d T}$ 为弹性模量B随温度的变化为
其中,Ω为ZnS类石墨烯的原胞面积,它与最近邻原子间距离d0的关系为
$\Omega=(\sqrt{3} / 2) d_{0}^{2}$ .
-
有效电荷,是指化合物中的实际电荷.当正、负离子组成化合物时,有效电荷与它们单独存在时的电荷不同.对ZnS类石墨烯,正、负离子有效电荷(以e为单位)分别为[9]
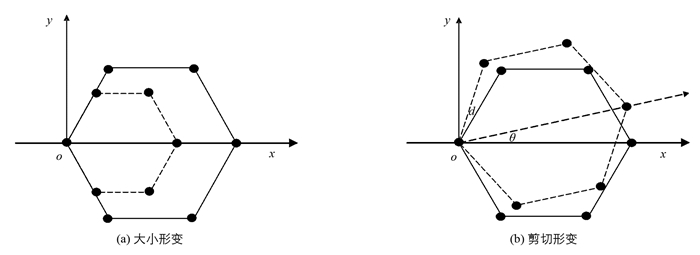
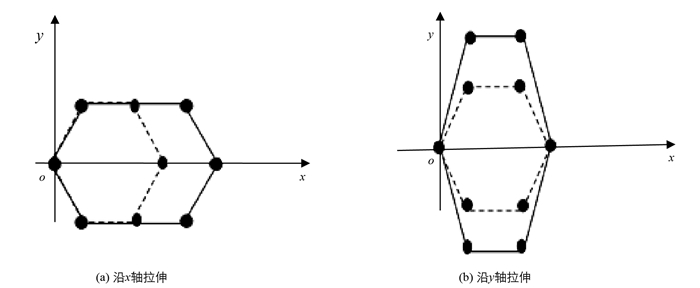
类石墨烯是二维材料,易发生形变,造成极性参量发生改变,进而引起有效电荷发生改变.它所发生的形变,包括两离子间距离变化的大小形变(图 2(a)、系统绕垂直平面的轴发生旋转的剪切形变(图 2(b)),还有单轴形变(图 3)等.
形变使其极性参量发生改变.大小形变使极性参量由αp改变为αp′,αp*改变为αp′*.它们对d的相对变化量
$\delta_{p}=d_{0}\left(\partial \alpha_{p} / \partial d\right)_{d_{0}}, \delta_{p}^{*}=d_{0}\left(\partial \alpha_{p}^{*} / \partial d_{0}\right)_{d_{0}}$ 称为键长形变极性变化率,剪切形变引起的对θ的变化τp=$\left(\partial^{2} \alpha_{p} / \partial \theta^{2}\right)_{\theta=0}, \tau_{p}^{*}=\left(\partial^{2} \alpha_{p}^{*} / \partial \theta^{2}\right)_{\theta=0}$ 称为剪切形变极性变化率.由αp和V2的表示式可求得:这里的λ为表征剪切形变引起共价能V2变化程度的参量,按文献[13],取λ=0.66.
类石墨烯的极性改变,导致键长等的变化,进而导致ZnS有效电荷发生改变.
大小形变造成有效电荷Z+,Z-的改变随键长的变化率
$\zeta_{\pm}=\left(\partial Z_{\pm} / \partial d\right)_{d_{0}}$ 经计算为:剪切形变引起正负离子有效电荷改变量随转角θ的变化率
$\eta_{\pm}=\left(\partial^{2} Z_{\pm} / \partial \theta^{2}\right)_{\theta=0}$ 经计算为:单轴形变因改变离子电荷分布而产生有效电荷,其中,沿x轴的单轴形变产生的有效电荷为:
式中ζ为黎曼相对位移参量,由ζ=(1-λ)/(1+λ)求得.
沿y轴轴向形变产生新的有效原子电荷为:
由(13)-(16)式,可得几种形变造成的ZnS类石墨烯的正、负有效电荷(以e为单位)的改变量ΔZ+,ΔZ-为:
由(10)和(17)式,就得到ZnS类石墨烯形变后的有效电荷Z±′=Z±+ΔZ±.
-
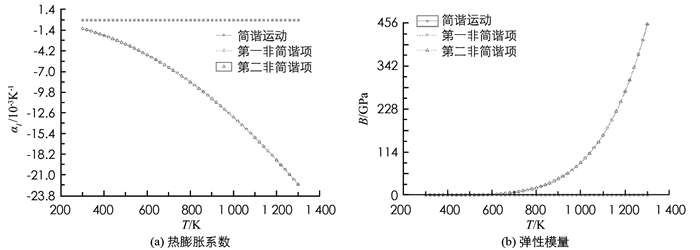
文献[8]给出ZnS类石墨烯有关数据为:d0=2.19×10-10m,V1=2.80 eV,V2=7.75 eV,V2*=1.52 eV,V3*=2.94 eV,由(2)式求得αp=0.710,αp*=5.221,αc=0.704,αc*=0.141.代入(4)、(5)、(6)式,求得:ε0=3.97×102J/m2,ε1=-2.53×1012J/m3,ε2=3.20×1022J/m4.还可求得Ω=4.154×10-20m3.将ε0,ε1,ε2以及玻尔兹曼常数kB代入(8)式和(9)式,得到ZnS类石墨烯热膨胀系数和弹性模量随温度的变化见表 1.表中的(0),(1),(2)分别是简谐近似、计算到第一非谐项、同时计算到第一、二非谐项的结果.变化曲线见图 4.
由表 1和图 4看出:①在所讨论的温度范围内,ZnS类石墨烯的热膨胀系数αl为负值,且随温度升高而数值增大,其数值在1.178×10-3-22.323×10-3K-1之间;②ZnS类石墨烯的弹性模量随温度升高而增大,其数值在0.241 405~453.253 5 GPa之间,其中,温度低于700 K时变化很小,而温度高于700 K后则迅速增大;③简谐近似下的热膨胀系数为零,弹性模量为常量.考虑非简谐项后,αl和B均随温度升高而变化.温度愈高,非简谐效应愈显著;④第一非谐项和第二非谐项引起的αl和B的差异极小.
将文献[14]以及前面计算的αp等数据代入(11)、(12)式,求得:ZnS类石墨烯的大小形变和剪切形变引起的极性变化率δp,δp*,τp分别为:δp=0.704,δp*=0.039,τp=0.465.这表明:①大小形变引起键长形变极性变化率比剪切形变引起的极性变化率大,大小形变对其影响可达到70.4%,剪切形变对其影响仅为46.5%;②形变使ZnS类石墨烯的极性参量变大,而共价参量变小.
将上述数据代入(13)和(14)式,得到ZnS类石墨烯的3种形变对ZnS的几个有效电荷的影响参量(ζ+,ζ-,η+,η-),结果是:对大小形变,ζ+=2.820,ζ-=-2.820;对剪切形变,η+=1.395,η-=-1.395.其余形变的ζ+,ζ-,η+,η-均为零.这表明:①单轴形变不会引起ZnS类石墨烯正负离子有效电荷的变化,而大小形变引起的变化比剪切形变引起的变化要大;②大小形变与剪切形变引起的正负离子有效电荷的变化相同.
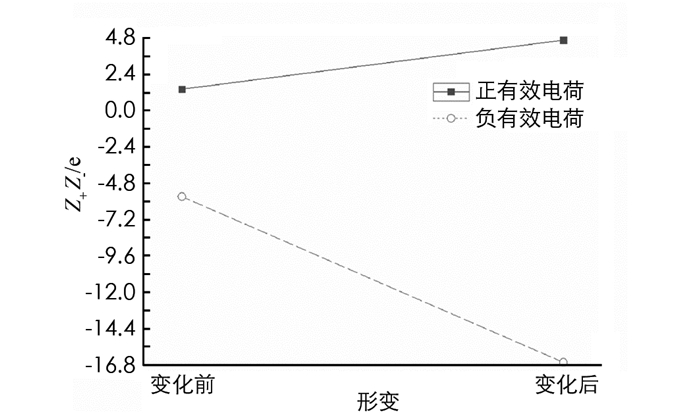
将上述数据代入(15)-(16)式,求得:ZnS类石墨烯的有效电荷形变前为:Z+=1.417,Z-=-5.676,而形变后为Z′+=4.658,Z′-=-16.621.其中大小形变、剪切形变、单轴形变对形变后有效电荷的贡献见表 2,而形变前后总有效电荷的变化见图 5.
由表 2和图 5看出:①形变使ZnS类石墨烯的正有效电荷由Z+=1.417增大到Z′+=4.658,负有效电荷由Z-=-5.676变为Z′-=-16.621,形变对负电荷的影响大于正电荷;②3种形变中,大小形变和单轴形变对正、负有效电荷的影响最大,剪切形变的影响最小.
-
1) 在所讨论的温度范围内,ZnS类石墨烯的热膨胀系数为负值,且随着温度的升高而数值增大,其数值在1.178×10-3-22.323×10-3K-1之间.简谐近似下的热膨胀系数为零;考虑非简谐项后,热膨胀系数随温度升高而变化.温度愈高,简谐与非简谐的值的差愈大.非简谐项中,第二非简谐项的影响极小;
2) 弹性模量随温度升高而增大,数值在0.241 405~453.253 5 GPa之间.温度低于700 K时变化很小,而温度高于700 K后则迅速增大;简谐近似下为常数;考虑非简谐项后则随温度升高而增大.温度愈高,非简谐效应愈显著;温度较低时第二非谐项的影响才明显;
3) 单轴形变不会引起ZnS类石墨烯有效电荷的变化,而大小形变引起的变化大于剪切形变.形变对负电荷的影响大于正电荷;大小、剪切、单轴形变这3种形变中,大小形变对正有效电荷和单轴形变对负有效电荷影响最大,剪切形变的影响最小.
4) 大小形变对极性的影响可达到70.4%,剪切形变的影响仅为46.5%.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: