-
独活为重齿毛当归Angelica pubescens Maxim. f. biserrata Shan et Yuan的干燥根[1].始载于《神农本草经》,被列为上品,其主要成分包括香豆素类、挥发油类、甾醇和糖类等[2-4],具有抗肿瘤、抗炎、镇痛镇静、降压、抗皮肤老化和增强骨折修复等作用[5-11],其祛风除湿、通痹止痛的效用明显,自古被作为治疗风湿痹痛的要药.历代本草对独活的植物来源诸说不一,《中药大辞典》共收载了13种[12],《中药志》记载的独活种类也有8种[13];据饶高雄等[14]调查统计,在我国及日、韩等地,伞形科有70多种植物被作为独活、羌活使用,这造成了市场上独活药材来源复杂、质量不一、真伪难辨.本文测定蛇床子素和二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数并结合HPLC指纹图谱,比较独活及其混伪品之间蛇床子素和二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数的差异性,为独活的质量评价体系的完善以及混伪品鉴别提供依据.
HTML
-
所用样品均经重庆市药物种植研究所刘正宇研究员鉴定,结果详见表 1.
-
取不同采收期的独活样品置干燥箱中40 ℃恒温干燥后,除尽泥沙和杂质,粉碎过100目筛备用.
-
取供试品粉末约0.5 g,精密称定,按《药典》2015年版一部“独活”质量分数测定方法(高效液相色谱法)测定[1].
-
1) 总灰分测定
称取样品粉末3 g,精密称定,置恒质量的坩埚中,加盖后,置箱式电阻炉中,缓慢升温(由120 ℃→520 ℃),待完全碳化后,升温至650 ℃,连续加热7h,取出,放冷后,测定质量,计算.
2) 酸不溶灰分测定法
“总灰分测定”实验后,在含有总灰分的坩锅中小心加入稀盐酸约10 mL,用表面皿覆盖坩锅,置水浴上加热10 min,表面皿用热水5 mL冲洗,洗液并入坩埚中,用无灰滤纸滤过,坩埚内的残渣用水洗于滤纸上,并洗涤至洗液不显氯化物反应为止.将滤渣连同滤纸移置同一坩埚中,干燥,炽灼至恒质量.根据残渣质量,计算供试品中酸不溶性灰分的质量分数(%).
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
1.2.1. 样品加工
1.2.2. 指标成分
1.2.3. 灰分测定
-
从表 2可知,重齿毛当归中蛇床子素质量分数为0.716 4%,二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数为0.118 7%,均高于《药典》标准.长尾叶当归、大叶当归、芹菜当归、短毛独活、牛尾独活、城口独活药材都检测出了蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯;金山当归、狭翅独活中只检测出二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯,未检出蛇床子素;中药羌活未检测出蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯两个成分,卵叶羌活中检测出了蛇床子素,未检测出二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯.金山当归中二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数为0.777 4%,高于正品重齿毛当归中二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯的质量分数,更高于《药典》质量标准,但单一的某个指标成分不能作为衡量质量的标准.
-
从表 3中可以看出,不同产地的正品独活样品中蛇床子素质量分数差异较大,除了甘肃产蛇床子素质量分数(<0.50%)没有达到《药典》标准要求外,其他的均达到要求,其中巫山产地质量分数最高,为0.941 5%,其次是湖北、巫溪,分别为0.784 6%和0.716 4%;不同产地独活样品中二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数以甘肃样品中质量分数最高,为0.338 1%,其他产地的质量分数差别不大,但均达到《药典》标准要求.这可能与产区的生态环境(土壤、气候、海拔等)有关[15].
-
样品按《药典》2015年版一部“独活”质量分数测定方法(高效液相色谱法)进行供试品溶液的制备. LC-20AT色谱仪,SHIMADZU VP-ODS色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm).流速1 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,进样量10 μL,检测波长254 nm,乙腈与0.2%醋酸水溶液梯度洗脱.梯度洗脱程序见表 4.
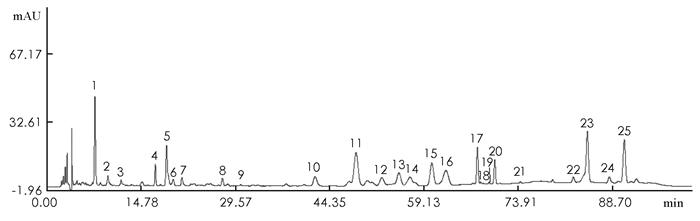
记录独活样品的色谱图,从不同产地独活样品的HPLC图谱中确定了25个共有峰(图 1),其中23号峰、25号峰保留时间及紫外光谱与蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹当归酸酯相吻合,23号、25号特征峰分别为蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹当归酸酯.以峰面积较大、峰分离较好的二氢欧山芹当归酸酯为参照峰,计算其他各峰的相对保留时间,结果表明,25个共有峰的相对保留时间的RSD均在0.8%以下,各样品的共有峰谱图比较一致. 25个共有指纹峰结果可靠,可以用于建立独活HPLC指纹图谱,建立的独活指纹图谱见图 2.对照图谱中各共有峰的保留时间分别为7.461,9.488,11.566,16.901,18.628,19.648,21.049,27.395,30.193,41.853,48.152,52.195,54.872,56.637,60.089,62.319,67.445,67.982,69.287,70.185,74.216,82.545,84.742,88.175,90.537 min.
-
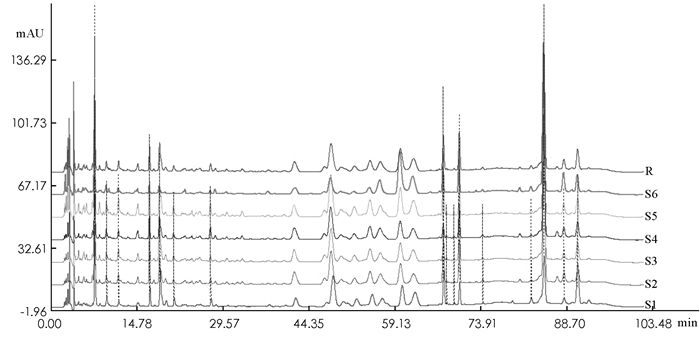
将独活药材样品与对照指纹图谱相比较,利用相似度评价软件对不同产地的独活药材的HPLC图谱进行分析,甘肃华亭、四川彭山、湖北巴东、重庆巫溪、重庆巫山、陕西陇县指纹图谱的相似度分别为0.901,0.991,0.989,0.998,0.985,0.950.结果表明不同产地独活药材图谱与对照指纹图谱间具有高度相似性,所建立健全的指纹图谱稳定、可靠,能够对独活药材进行评价和质量控制.
2.1. 独活及混伪品种质资源的指标成分质量分数比较
2.2. 不同产地独活指标成分质量分数比较
2.3. 独活HPLC指纹图谱的比较
2.3.1. 独活共有峰的确定及指纹图谱的建立
2.3.2. 相似度评价
-
以指标成分质量分数结合中药指纹图谱对中药材进行质量评价或控制,既有别于化学药单一成分定量的质量控制模式,又可以完善表述中药的整体特征,符合中医药整体性的思想.本实验采集不同产地独活进行系统的质量分析,建立多指标与指纹图谱相结合的质量评价体系.在独活的主产区采集样品,用HPLC建立指纹图谱,所建立的对照指纹图谱有6个共有峰,不同产地独活的指纹图谱与对照指纹图谱的相似度均在0.9以上,可以作为不同产地独活药材评价和质量控制的科学依据.
蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯属于香豆素类化合物,是正品独活中的主要成分,现代药理研究表明具有较强的抗炎、抗肿瘤等[2]多种活性.本实验中正品独活除甘肃样品的蛇床子素质量分数略低于《药典》要求外,其余样品的蛇床子素质量分数、二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数均高于《药典》标准;而混伪品中的蛇床子素质量分数远低于正品独活中的质量分数,这是独活正品区别于混伪品的一个重要特征.因此,可以根据蛇床子素、二氢欧山芹醇当归酸酯质量分数作为独活内在质量判定依据,而以蛇床子素质量分数作为独活正品和混伪品鉴别的重要化学指标.
本实验表明,产地对独活药材的质量影响较大,不同产地的独活指标成分质量分数存在较大差异,综合其中两个成分的质量分数结果可以看出重庆巫山的独活质量较优,这与石红艳等[16]研究结果相似.由高到低依次为巫山产地,湖北产地,巫溪产地,四川产地,陕西产地,甘肃产地,从这顺序中可以看出具有地域性,故有必要建立不同地域的独活的质量标准,以确保合理、安全用药.甘肃产独活蛇床子素没有到达《药典》标准要求,这可能由于生态环境(土壤、海拔、气候等)、种植技术等因素的不同而导致该区域所产的独活在蛇床子素成分质量分数上还存在差异,从而影响到了药材质量,关于这一问题有待于进一步研究.






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: