-
随着科学技术的变革,教育研究范式逐渐从经验主义向科学主义转变,教育者也应遵从数据探索教育规律,从而作出科学的教育决策。与此同时,当前的学生正处于数字化时代,其生活环境和生活方式受到数据的深刻影响,那些关于兴趣的、活动的、情绪的、考试的、家庭的、特长的、试错的数据,均可转化为有用的信息。例如,教师可基于数据对学生的学业表现进行个性化评估[1],并反思自身教学、促进专业发展、增强教学效果等。可以说,数据在当下的教育中扮演了越来越重要的角色。而数据价值的真正彰显离不开教师的参与,教师的数据素养是保障数据服务教育实践的关键。近年来,教师数据素养已逐渐受到研究者的广泛关注。当前,国内也有不少学者围绕教师数据素养展开研究,如刘雅馨等人的《大数据时代教师数据素养模型构建》、林秀清等人的《中小学教师数据素养的发展路径与培养策略》等。然而,这些研究大多聚焦于教师数据素养的概念内涵、评价指标以及发展路径等单一方面,较少针对教师数据素养进行全面分析和系统把握,尤其缺乏对国外新近相关研究与实践的梳理和总结。鉴于此,本研究从文献分析的视角出发,通过对国外教师数据素养相关文献的梳理,重点分析关于教师数据素养的概念内涵、理论架构、核心内容、专业培训以及评估等方面的研究和实践,并在此基础上提炼出适合当下我国教师数据素养发展的有益经验,以期为我国未来的教师数据素养研究与发展提供有效参考。
全文HTML
-
教师身处于一个复杂的系统当中,不同的利益相关者对教师的身份角色认知和行为标准期待可能有所不同,这直接导致他们难以在对教师数据素养的理解上达成共识。厘清数据素养基本的概念内涵,是探究教师数据素养的前提和基础。Schield认为,可从信息素养和统计素养这两个相似概念入手,对数据素养的内涵进行界定和理解[2]。美国图书馆协会(ALA)认为,信息素养是识别信息需求并有效定位、评估和使用所需信息的一系列能力[2]。这些能力具体包括:确定需要哪些方面的信息、知道如何收集所需信息、能够鉴别信息的来源并对其质量进行评估、掌握信息的存储方法和技能、善于使用信息解决问题或达成某种目标、熟悉并遵循信息收集和使用的道德规范与法律要求。与信息素养不同,统计素养则更加注重在提供证据的过程中对统计学知识的使用,即如何定义、选择和呈现统计数据并对数据进行批判性的描述和解释[3]。Joel Best指出,所有统计都是基于社会建构而成的,人们出于特定的目的选择计算或度量数据,采取适当方法汇总或比较数据,以及采取一定的策略交流和传播数据,这其中都渗入了一定的社会性[4]。相较于信息素养与统计素养,数据素养的技术性要求较弱,其主要关注数据的访问、获取、转化、操作、分析、解释以及评估等,可被理解为一种通过数据来支持个体行为决策的能力[5]。
为进一步厘清数据素养的内涵,减少相似概念之间的模糊性,Mandinach和Gummer曾专门召集数十位数据领域的专家以及其他利益相关者,如教师专业发展机构人员、赞助商、行政人员、政策制定者等,就教师数据素养的概念界定进行了研讨协商[6]。同时,他们对数据驱动型决策与评估以及教师专业发展的相关文献进行了系统分析,总结出与教师数据素养相关的范畴或领域,主要包括:数据使用的先决条件(如学校愿景、学校文化、与其他发展举措的联系、对变革过程的理解)、数据使用的探究过程(如调查目的、使用方式)、数据属性(如数据类型、数据质量)、数据分析(如数据呈现、统计方法)和数据理解(如将数据与学生表现相联结、将数据与教学实践相联结、将数据与项目规划相联结)等。最终,他们在数据的“收集、分析、解释、转化为决策或行动”等能力层面取得了共识,认为教师数据素养是指教师对多元化教育数据(如学生作业、项目、课程、考试、出勤、测验、反馈、课堂行为、活动参与、性别、特殊教育需求等数据)进行收集、分析和解释,并将其转化为可利用的、有价值的信息,从而帮助教师科学地作出教学决策的能力。此外,一些具有国际影响力的数据研究与服务组织也曾对教师数据素养作出解释。美国“数据质量运动”(Data Quality Campaign)认为,教师数据素养是指教师通过合法渠道,从多种来源(如政府部门、学校、家庭)获取相关数据,并对其加以分析、解释和使用,以此来提升学生的学术表现和学业成就的一种专业技能[7]。教师数据素养由一套具体的技能库组成,使教师能够将数据转化为信息,并最终转化为指导行动的知识[8]。这些技能主要包括:识别、收集、组织、汇总和排列数据,提出问题,分析数据,解释数据,以及制订计划、实施行为和监测行动等。由此可见,在进一步厘清数据素养内涵的过程中,数据的“收集、分析、解释、转化为决策或行动”等技能再次得到确认,而“数据使用”则是教师数据素养的关键技能。
-
从数据素养的概念内涵可以看出,数据素养是一个十分复杂的概念。基于不同的学科背景及研究目的,研究者所关注的内容重点可能有所不同,因此需要一个较为系统的理论框架来指导并帮助人们有效认识教师数据素养。如前文所述,教师需要具备一系列的知识和技能才能理解和使用学生数据,从而建立教学与数据之间的内在联系,对学生给予个性化指导[9]。同时,教师要能够提出指向教学实践的具体问题,找到正确的数据来源,解释数据的含义,从而使数据具有意义,并将其用于指导个人教学规划[9]。此外,如果教师缺乏与教学内容或教学方法相关的教育知识,那么其在解释数据并将数据应用于教学的过程中也会存在一定的问题[10]。因此,为了有效使用数据,教师需要掌握广泛的知识和技能,利用自己的专业智慧来理解数据,并将其融入教学实践活动[11]。在具体指向上,很多研究者认为,教师数据素养应包括以下知识和技能:进行差异化教学,满足不同学生学习需求的知识和技能[12];获得和使用多种来源学生数据的知识和技能[13];根据形成性、总结性等评估数据以及学生的课堂其他数据制定决策的知识和技能[14];根据所收集的数据对教学实践进行反思和变革的知识和技能[15];对数据使用结果进行监测的技能[8]。由此可见,教师数据素养所需的知识和技能十分复杂,需要建立明确的、系统的理论架构,才能够更好地认识教师数据素养并指导实践。
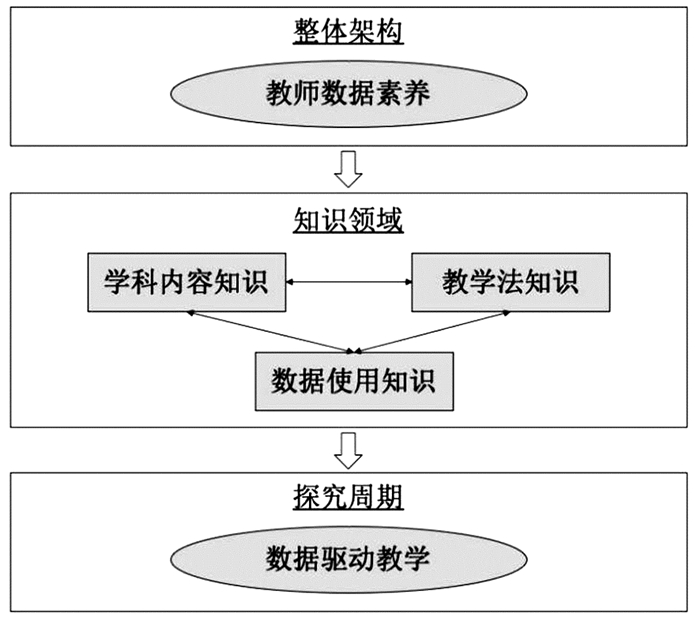
Gummer和Mandinach通过对大量文献的梳理和分析,系统建构了教师数据素养的一般性理论框架,对教师必备的知识和技能进行了全面归纳与总结,如图 1所示[16]。该框架可分为三个层面,从上到下依次为整体架构(construct)、知识领域(domain)和探究周期(inquiry cycle)。其中,第二个层面清晰地指出了教师数据素养所包含的三个知识领域:学科内容知识、教学法知识和数据使用知识,前文所提及的多种知识与技能均可覆盖。从系统性的视角来看,这三个知识领域相互支持、相互联结,教师的数据使用需要以具体的学科内容和有效的教学方法为指导,数据使用反过来又可促进和优化学科内容的传递以及教学方法的实施,三者皆是构成教师数据素养的必要组成部分,缺一不可。教师数据素养的教育、培养、训练及评估等研究与实践均可参考该理论框架。
为使所建立的理论框架更具指导性,研究者对第三个层面(即数据驱动教学的探究周期)进行了进一步的解释说明:将其细分为六个主要部分,以展示教师数据素养的内在结构和联结。这六个部分依次为:问题识别、问题架构、数据使用、将数据转化为信息、将信息转化为决策以及结果评估。其中,“问题识别”涉及查找问题、发现问题、了解问题;“问题架构”涉及数据使用目的以及对问题与数据之间关系的确定与澄清;“数据使用”涉及理解数据的属性、质量和应用方法;“将数据转化为信息”涉及分析数据、提出假设、考虑结果及影响;“将信息转化为决策”涉及了解决策背景,并决定下一步行动(如诊断、监控和进行教学调试等);“结果评估”涉及反馈循环、检查结果和检验假设等。以上六部分内容是数据驱动教学的具体化呈现,同时也是对教师数据素养的进一步解释。除此之外,为使所建构的理论框架更加契合实践及更具操作性,研究者还对“数据使用”的具体要求和能力水平进行了细分。例如,在理解数据属性层面,教师要能够辨别数据的类型或来源,如定性数据或定量数据;在理解数据质量层面,要把握数据的准确性与完整性,善于发现问题数据,形成数据反思;在理解数据应用方法层面,教师要学会数据管理、查找、定位、访问和恢复等具体技能。由此可见,该理论框架兼具一般性和具体性双重属性,可拓展为多个层级,涵盖多种指标,使得整体结构更加完备且更具操作性,可有效指导教师数据素养的研究与实践。
-
从教师数据素养的理论架构可以看出,教师数据素养是一个系统性概念,与数据使用和课堂教学的各个环节均息息相关。为了更好地培养教师的数据素养、有效地促进教师的教学实践,需要进一步梳理和澄清数据素养的核心内容。在国外相关研究中,很多研究者对教师数据素养核心内容进行了界定。Maybee和Zilinski基于对过往研究的总结,提炼出教师数据素养的七个核心内容:(1)数据意识,即理解数据的概念内涵以及数据在社群或社会中的角色与作用;(2)数据访问,即识别、定位、使用数据集和数据库;(3)数据运作,即评估、分析、组织和解释现行数据,同时根据数据作出决策;(4)管理数据,即拟定关于数据安全、数据存储以及数据共享等的方案与协议;(5)数据交流,即整理数据并使用可视化手段呈现数据;(6)数据伦理,即确认数据的来源渠道并评估数据使用可能存在的风险;(7)数据保存,即长期存储数据和数据再应用的策略与方法[17]。Light等人则重点关注数据、信息和知识三者之间的区别与联系,强调数据以原始状态存在,即数据本身不具有任何意义,仅是一些抽象的文本或符号;信息具有较强的背景脉络性,是被赋予了具体含义的数据;知识即有用的信息整合,具有最终的行动力,可以用于指导实践。基于此,Light等人提出教师数据素养所蕴含的六个核心能力:收集数据、组织数据、分析数据、总结数据、将数据整合为有效信息以及将数据信息转化为知识并辅助决策[18]。相较而言,Mandinach等人的研究更加贴近教学实践,其从教育者培养视角提出了教师数据素养七个方面的核心内容:(1)探究过程,即首先明确问题,然后理解情境,最终形成假设;(2)思维习惯,即具有数据使用倾向,形成评判性的数据思维与信念;(3)数据使用,即具备数据使用的通用技能,了解数据使用的伦理规范;(4)数据属性,即正确区分定性数据和定量数据,并了解数据的质量和类型,从而使用恰当的数据来解决相应的问题;(5)程序技能,即了解并掌握数据使用的系列过程,如查找与检索、收集与存储、处理与分析、评估与反思等;(6)信息转化,包括以适当的方式整合、总结、呈现数据,并基于数据分析得出可靠的推论或结论;(7)实践转化,即根据数据结果采取相应的实践行动,如调整教学行为[19]。从上述观点来看,不同研究者对教师数据素养核心内容的理解和看法既有区别也有联系。例如,虽然在核心内容的维度划分上,不同研究者的划分略有差异,但是从具体内容来看,多数研究者都聚焦数据的探究过程,重点关注如何使用数据。
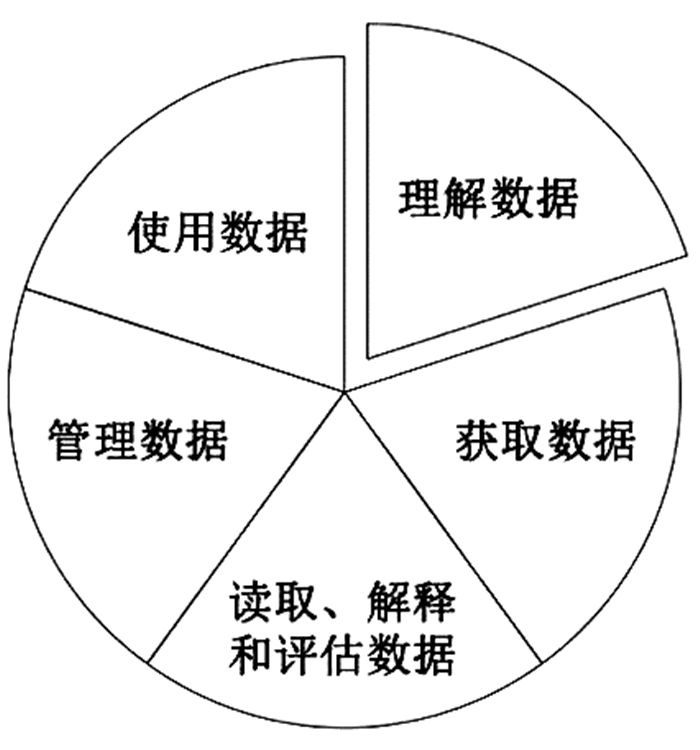
在众多核心内容框架中,Prado等人的研究相对更为清晰,结果颇具指导性。他们在综合了大量研究之后,提出了一个比较具有代表性和一般适用性的教师数据素养核心内容框架[20],如图 2所示。其将教师数据素养的核心内容凝练为五个方面。(1)理解数据:教师需要理解数据的含义,知道数据的类型,了解数据在社会中的价值。通过理解数据,教师可以判别数据质量,知道哪些数据可用、哪些不可用,同时也能知道数据是如何产生的、应该如何使用。(2)获取数据:教师需要了解数据的各种来源,能够根据教学或研究目的,选择适合于当前所需、与教学或研究最为相关的数据源。同时,教师还需要掌握一定的获取原始数据的方法,能够根据需要获取真实可靠的数据。(3)读取、解释和评估数据:教师需要了解数据的不同表现形式(如文字、数字、图表或符号),并能够解释它们。此外,更重要的是,教师要能够依据一定标准批判性地评估数据。(4)管理数据:教师需要对数据进行收集与整理。这一素养要求教师具有良好的数据管理和存储意识,掌握一定的数据管理工具与技术方法。(5)使用数据:教师需要掌握数据的处理、呈现与表达方法,例如使用分析工具(如Excel、R、SPSS和Stata等)进行数据分析,并根据数据性质、研究目的和受众对象,以恰当的形式表达数据分析的结果。另外,数据使用还涉及道德伦理等问题,即教师在数据使用的过程中应合乎道德伦理,确保数据来源、处理过程和结果呈现等符合规范,真实可信。
上述五个方面在众多研究文献中均有提及,既是教师数据素养的一般性能力内容,即对教师数据素养提出的基础性和基本性要求,又是教师数据素养的核心能力内容,是系统提升教师数据素养的关键着力点。该框架对于教师数据素养的研究及培养等具有较强的指导性。在设计数据素养课程时,可依据这五个方面进行课程内容的优化、筛选和编制;在评价教师数据素养时,可依据这五个方面进行量表研发与设计。
-
除在理论层面进行探究外,不少国际组织也在实践层面为促进教师数据素养的有效发展采取行动、展开探索,并积累了一定成功经验,如美国科学课教师数据素养培训项目、TERC联盟“数据使用”项目、荷兰“数据团队”项目以及俄勒冈数据项目等。以俄勒冈数据项目为例。在俄勒冈大学为教师开设的职前课程中,“数据驱动”这一概念贯穿始终,学校期望通过教会教师正确使用数据和证据来指导个人教学和学生学习,从而形成一种基于数据和证据的文化氛围。自2007年起,俄勒冈州承担起为教师提供数据培训的任务。目前,该项目已经成为教师数据素养专业培训的典范。该项目的目标是通过为教师提供收集、分析和使用纵向数据的资源,培养其关于数据使用等方面的知识和技能,从而改善教师的课堂实践、增强学生的学习效果。该项目主要通过以下四种方式促进目标的达成:(1)对领域需求进行评估;(2)根据需求开发培训模型;(3)创建教学培训团队;(4)提供嵌入式数据培训。俄勒冈州与阿肯色大学的研究人员协同合作,对该项目既定目标实现的有效性进行评估。在实施之初,参与项目的学校和未参与项目的学校的学生之间存在着成绩差距。参与项目的教师经过两年的专业培训,取得了以下成果:在州级考试中,参与培训的教师所在学校学生的成绩明显高于未参与学校的学生;两组学校学生在阅读和数学上的表现整体差距明显缩小。2011年,俄勒冈州发布了一份项目报告,详细阐述了其在教师数据素养培养方面所取得的成就,其中之一便是与没有接受过数据培训的教师相比,参与项目培训的教师更有助于学生学习成绩的提高[21]。除了学生的学业成就得到显著改善以外,该项目还在俄勒冈州学校中创建了一种新的数据使用文化。在项目实施之初,大多数参与培训的教师担心这些数据会给自己和学生带来负面影响,对数据的不信任使得教师只能使用其他方法来增强学生的学习效果。此外,教师对自己在课堂上解释数据并利用数据作出决策的能力缺乏信心。然而,在评估阶段结束时,一些教师变得信任数据,并愿意在课堂上访问、解释和使用数据。俄勒冈数据项目比传统的教师专业发展项目走得更远,它解决了教师对数据使用的信心问题,并为教师在课堂上使用数据提供了有效策略。正是这种能力建设与文化变革的结合,促使了教师数据素养的有效发展、学生学习成绩的显著提升。
除此之外,国外许多高等院校也开发了与数据素养相关的培训课程或项目。以雪城大学开发的一套数据素养培训课程为例。该课程由以下三个模块和主题组成:(1)基础科学数据,包括数据生命周期、数据类型和数据描述等;(2)数据管理方法,包括数据收集、数据用户和组织规划等;(3)其他相关问题,包括数据技术、数据呈现和数据共享等[22]。另外,马萨诸塞大学和伍斯特理工学院联合开发了一套数据素养培训课程,用于培养科学、健康科学以及工程专业的本科生和研究生的数据素养,同时对教师数据素养的落地实施亦颇具启发意义。该课程主要包括七个模块:(1)研究数据管理概述,包括研究数据界定、数据生命周期、数据管理需求以及数据管理对项目实施的影响;(2)数据性质,包括数据的各种类型、格式以及相应的收集方法和策略;(3)元数据,包括元数据的界定,数据标准的识别与确立;(4)数据存储、备份和安全,包括数据存储与备份的重要性以及数据安全性保障;(5)法律和伦理,包括数据使用在知识产权、隐私和引用等方面的道德和法律问题;(6)数据共享与重新使用,包括开放科学和开放数据的含义、数据重新使用的条件、数据的格式转换以及数据访问的级别建立;(7)数据的归档和保存,包括数据存储库的使用策略与目的[23]。
上述国际组织和高等院校的实践案例各有侧重,有的从系统性角度考量数据素养培养的完整周期,有的基于数据素养的核心内容,从课程开发的角度进行模块化训练,这些实践案例的有效实施对于国内教师数据素养的培养和研究均具有一定的启发意义。
-
在教师数据素养的评估方面,国外也进行了一定的研究和实践探索。通常,在评估教师数据素养时,国外研究者主要关注教师是否能够基于数据作出科学的教学决策(DBDM),即前文提及的“教师通过设定目标,收集、分析和解释数据并采取指导性行动的能力”[24-26]。在最为广泛的共识性研究中,设定目标、收集数据、分析数据、解释数据和采取指导行动等五个模块被视为实施DBDM的框架依据。荷兰特温特大学基于上述五个模块,提出了一套教师数据素养评估的分析架构。该架构通过以下八个步骤:(1)定义问题、(2)提出假设、(3)收集数据、(4)检查数据质量、(5)分析数据、(6)解释和结论、(7)实施改进措施、(8)评估,考察教师使用数据进行教学决策的能力[27]。上述八个步骤是对教师数据素养五个模块内容的具体呈现。例如,教师在DBDM的第一和第二个步骤中,需要利用“设定目标”的能力。在DBDM的第一个步骤中,教师通过反思使用数据的动机和原因来明确使用数据的目的,如深入了解三年级学生的保留率或期末考试结果。在DBDM的第二个步骤中,教师针对问题的潜在原因确定假设(定量研究)或提出问题(定性研究),以更具体地捕捉使用数据的目的。又如,在DBDM的第一、第三、第八步骤中,教师需要利用“收集数据”的能力,包括收集和生成多种类型的定量和定性数据。在第一个步骤中,教师收集数据以确定问题范围、明确目标;在第三个步骤中,教师通过收集数据寻找问题的根本原因,确定假设是否正确;在第八个步骤中,教师通过收集数据,评估问题是否得到解决,目标是否得以实现。再如,在DBDM的第一、第六、第八步骤中,教师需要利用“解释数据”的能力,通过阅读和解释数据表格和图表,并从各种数据分析中解释信息,从而将数据转换为信息,得出结论。在第一个步骤中,教师解释有关问题的数据,如通过解释学生成绩数据的平均值来制定基于数据的特定目标;在第六个步骤中,教师解释有关假设或问题的数据,例如通过检查数据之间相关性的强度,得出结论或对假设进行解释;在第八个步骤中,教师解释所采取的指导性行为的数据,如通过比较采取某种行为之前和之后的学生成绩,来评估该行为是否达到预期效果。
关于教师数据素养的具体评估策略,当前较为常用的方式是数据素养测试、教师访谈、会议评估和教师日志等。“数据素养测试”(data literacy test)的开发主要基于以下两点:(1)与数据驱动教学决策的八个步骤相关的现有知识测试[28];(2)与数据素养相关的最新研究成果[29]。例如,Wilma B. Kippers等人基于DBDM框架开发的教师数据素养测试包含十二个开放式问题,要求教师在三十分钟内完成测试。当然,数据素养测试也包括结构化和半结构化的问题,通过对教师的回答进行计分来判定其数据素养的发展水平。“教师访谈”主要通过定性分析考察教师在数据驱动教学决策过程中的能力收获以及困难,访谈过程中可提出如“在数据使用过程中,你学到了哪些关于分析数据的知识”等问题。“会议评估”也是通过提问和对话的方式来考察教师在数据驱动教学过程中的表现情况,通常由数据精通者(如数据培训师)担任主要评价考核者,提问和对话的内容将被记录下来作为评估的原始资料。随后,可通过一定的编码技术进行资料分析,从而判定教师在数据驱动教学过程中的成长和收获。“教师日志”是教师在数据驱动教学决策过程中所形成的记录材料,用来反映教师在数据收集、数据分析、数据解释以及指导教学行动等方面的进步与困惑。总体而言,国外已经具备了较为成熟的评估策略和工具,它们可用于评价教师数据素养的发展和表现情况。
-
在信息化时代,教师应着力提升数据素养,这对于促进教师专业发展、改善教学实践具有十分重要的意义。基于对国外相关文献的研究和分析,发现其中一些有益的经验和做法可为我国教师数据素养的培养和研究提供借鉴与启示。未来,我们宜从以下四个方面进行考量:
第一,做好教师数据素养培养顶层设计。从长远来看,教师数据素养既关系到新时代教师队伍建设的质量,同时也制约着教育现代化目标的达成,要提升教师的数据素养,做好顶层设计是其中至关重要的一步。有效的顶层设计至少应包括三个方面。其一,制订总体发展规划,并通过相应的政策或标准来保证教师数据素养计划的实施。国家层面的规划能够为教师数据素养的长远发展建立明晰的目标愿景和提供方向性的引导。同时,国家层面的政策能够在很大程度上减少教师数据素养发展过程中的阻力干扰,有助于使教师数据素养发展作为一项重要教育议程而得到真正落地实施。采用行政命令方式推广具有明显的问责性质,能促使行为主体及参与者持续地投入到行动当中。其二,确保充足的经费及基础资源支持,满足教师的基本数据需求。教育资源的优化配置需要依靠政府层面的统筹规划和推进实施。例如,划拨教师数据素养培训专项经费,建立国家/地方/学校等各级各类教育数据服务系统,实施基础薄弱地区教师数据提升计划,完善与数据相关的基础设施建设等。政府层面的顶层设计,有助于从全局性和系统性视角处理好各教育要素与资源配置之间的关系。其三,将教师数据素养发展纳入教师准入资格和教师专业标准,将其视为教师职业资格的必要组成部分,以资质和标准的形式赋予教师数据素养“官方合法”身份。
第二,鼓励多方力量协同参与发展。教师身处于复杂的社会网络之中,培养教师的数据素养并非教育机构或教师群体独有的责任,它更需要多方力量共同助力参与[30]。作为教育事业的参与者和教师发展的直接利益相关者,政府部门、学校、学生、家长、教师教育培训机构、教育信息技术部门等,都应该承担其相应的职责。就其作用而言,在国家层面,教育行政部门宜支持建设各级各类数据库(如学生学业成绩数据库、学生自我评价数据库、教师学习数据库和教学管理数据库等),从而为教师获取数据提供便利。在学校层面,学校领导可以营造数据使用的文化氛围,将数据驱动教学、数据驱动发展、数据驱动决策作为一种主流校园文化,使教师和学生都能自觉地培养数据方面的意识和思维。在社会层面,各类教师进修培训机构以及教育信息技术部门可专门开设教师数据素养培训课程或研习工作坊,搭建数据交流、展示和分享平台,以教师实践共同体的方式促进教师数据素养的提升。在当前社会背景下,社会各方应以一种开放的姿态,重视并允许社会力量的协同参与,一方面吸纳社会要素的先进理念、技术和优势资源,另一方面,接受社会群体的监督,将教师发展、教师数据素养提升作为社会事业的重要组成部分,促使社会机构由“旁观者”“局外人”向“参与者”“责任人”的身份角色转变。
第三,提供终身性专业支持和服务。良好教师数据素养的形成绝非一朝一夕之事,而是一项长期工程,需要为教师提供持续的、系统的专业训练和培训服务。这种训练或培训不是临时的或短期的,而应该贯穿教师职业生涯始终。首先,在师范教育阶段,应鼓励高校开设教师数据素养课程,通过正规的课程教学,将数据素养作为师范生的专业考核内容,使师范生在正式承担教师角色之前就具备一定的数据知识和使用技能。其次,对在职教师开展数据培训。一方面,可通过国培、省级培训、校级培训的方式为在职教师提供系统性的数据素养培训和学习机会,全面提升在职教师的整体数据素养水平;另一方面,可以进行专题培训,根据不同教师的学习兴趣、工作特性和数据使用熟练程度,提供具有针对性和灵活性的专题练习,满足教师的个性化发展需求。同时,也可以项目为依托,采用任务驱动的方式,鼓励教师在实践中加深对数据的理解和认识,形成一种数据使用的文化习惯。最后,可采用数据教练(data coach)的发展模式,建立一批具有丰富经验的数据分析专家库,专门对在职教师进行数据指导,包括提供适宜的学习内容、进行及时的答疑解难、制订具有针对性的反馈和改进方案、对教师的数据学习效果进行评估等。总而言之,在未来的教育实践中,教师数据素养培训应当成为一项长期性事业,融入教师职前、职中和职后一体化发展当中,作为教师终身学习的重要内容。
第四,加强教师数据素养理论研究。教师数据素养的发展和提升,不仅需要在实践层面通过一定的政策和培训活动加以推动,也需要通过加强教师数据素养的学术研究对其进行理论指导。第一,要加强对教师数据素养影响因素的研究。对教师数据素养的研究不应只停留在教师数据素养的内涵、价值、内容和结构方面,还应关注到影响教师数据素养发展的各种因素。教师数据素养受到多种因素影响,除了教师所应具备的数据技能之外,教师对数据的信念、教师对数据的感知、教师的数据效能感、数据的属性和类型、学校领导力、数据的隐私性和安全性、教师评价标准、教育问责等,都有可能影响教师的数据素养。第二,要加强对教师数据素养评估的研究。当前,国外在教师数据素养评估方面已积累了诸多可以参考和借鉴的经验,包括评估架构的建立、评估实施的具体操作步骤以及评估的具体策略和工具等。这些经验对我们如何进行教师数据素养评估、了解教师数据素养的发展现状,具有很好的启发意义。未来,我国应继续加强教师数据素养评估研究,除了开发教师数据素养的测评指标体系外,更应重点关注评价工具的开发和评估适用性的研究。



 下载:
下载: