-
休闲农业作为现代农业的一种形态,近年来呈现出爆发式增长局面.这主要源于2个原因:①源于城镇化进程中城市居民对悠闲宁静生活的渴望,②适逢国家政策的大力支持.统计数据显示,2016年全国休闲农业接待游客21亿人次,营业收入达到5 700亿元,带动672万户农民受益.然而,随着我国城乡居民可支配收入的持续增长,人们对休闲农业产品与服务的品质及品位有了更高的要求.当今世界已经进入到品牌经济时代[1],休闲农业的竞争逐渐由经营内容的拓展上升到品牌竞争.
品牌(Brand)是一种识别标志、一种精神象征、一种价值理念,是品质优异的核心体现.对一个企业来说,品牌是其最重要的无形资产.关于品牌的理论研究已经持续了大半个世纪,1960年美国营销学会(AMA)将品牌定义为:品牌是将企业的产品或服务与竞争者区分开来的一种名称、符号、标记或设计,或者他们的综合体[2].而品牌的理论研究中,品牌价值的概念也被学术界重视.美国品牌专家Longwell[3]提出,品牌评价要素应涵盖品牌知名度、品牌认知度、品牌忠诚度、品牌联想以及品牌其他资产.该观点从消费者的角度,以消费者对品牌反映的差异体现品牌的价值.具体到休闲农业,品牌建设有其独特之处,王晓丽等[4]认为品牌是休闲农业差异化竞争的手段,是休闲农业推广与丰厚利润的来源,品牌能帮助休闲农业经营找准定位.方世敏等[5]提出,休闲农业品牌建设的目的是打造休闲农业特色,形成独特的核心竞争力,争取目标顾客认同,并在顾客心里留下对品牌的感性认知,让休闲农业与品牌融为一体,促使休闲农业的价值在品牌的包裹下顺利让渡给顾客.
品牌建设研究在商业领域已经趋于完善,然而在休闲农业方面,关于其发展中遇到的障碍及其解决对策的研究较多,但涉及休闲农业品牌发展及提升战略的研究较少,运用定量分析方法对一个地区休闲农业园区品牌发展进行评价,并提出品牌提升策略的研究更少.基于此,本研究在对重庆市休闲农业园区发展进行总体测度的基础上,对消费者进行问卷调查,获取相关数据并在此基础上建立模糊评级指标体系,通过对其隶属矩阵的整合运算,得出重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值消费者调查分数,并通过不同层级各个指标间的分数差异发现重庆市休闲农业园区品牌建设中存在的不足,且以此为基础提出提升该地区休闲农业品牌价值,旅游知名度与消费忠诚度的策略.
全文HTML
-
重庆地形多样,交通优势明显,是内陆唯一的直辖市、世界特大库区中心城市,其农村和农业经济发展在国民经济中有着十分重要的作用.重庆在成为直辖市之后,全市的政治、经济、文化都得到空前的发展.随着重庆市人民生活水平的逐渐提高,城市居民对物质文化生活也有了更高的要求.但另一方面,城市工作的巨大压力和生活环境的紧张喧嚣,使得人们愈发想亲近自然,因此休闲农业的发展迎合了都市居民想要回归自然、返璞归真的消费心理,巨大的乡村旅游需求使得休闲农业蓬勃发展. “十三五”时期,重庆市仍将休闲农业列为重点发展项目,以促进全市特别是贫困地区的农旅融合,实现乡村旅游的转型发展.然而,重庆的多种休闲农业园区同质化严重,园区管理者对品牌发展不重视,所以加快实施农业品牌化战略、大力推进现代休闲农业品牌化建设是发展重庆市休闲农业园区、提高顾客忠诚度的重要途径.
-
重庆市直辖以来,经济实力有了很大的发展,2016年全市实现地区生产总值1.75万亿人民币,比上年增加10.7%左右.从全国范围来看,都保持持续较快发展的态势.随着经济不断发展与产业结构的逐步优化,都市居民的消费结构也向多元化发展,旅游消费需求逐渐增加,都市居民双休、假日会选择在近郊休闲娱乐,通过体验农家生活来达到休闲放松的目的. 2016年重庆市乡村旅游接待游客1.52亿人次,与2015年相比增加0.3亿人次;营业收入349亿元,与2015年相比增加139亿元,同比增长66.20%,占全年旅游总收入的十分之一.由此可见,重庆市休闲农业园区具有很大的吸引力,都市居民对休闲农业的消费需求逐年扩大,这种需求促进了休闲农业园区的发展,而休闲农业园区为了更好地满足消费者的需求也应注重品牌发展和服务质量的提升.
-
2016年,重庆市共创建了10个全国休闲农业与乡村旅游示范区县,23个示范点,23个最美休闲乡村和中国美丽田园;打造休闲农业和乡村旅游景区景点3 000余个,休闲果园及农庄7 500多个,带动就业50余万人.部分区县虽然乡村旅游起步较晚,但仍取得了不凡的成果:2016年,铜梁区接待游客758.61万人次,比上年增长25.0%;旅游收入达到33.10亿元,比上年增长56.1%.黔江区2016年接待游客829.47万人次,比上年增长24.1%;旅游总收入33.73亿元,比上年增长27.6%. 2016年丰都县乡村旅游接待游客604万人次,综合收入达29.8亿元,带动了2万多人脱贫增收;2016年南岸区接待游客总计562万人次,实现收入4.7亿元.重庆市各区县遍地开花,游客接待能力大大提升,休闲农业带动当地大量就业和经济增长,发展成为当地的支柱产业.
-
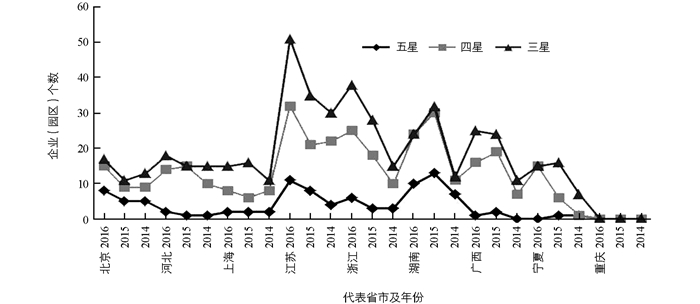
近年来,重庆市休闲农业的发展取得了较多成就,但由于起步晚、基础差,休闲农业园区建设及品牌状况落后于国内大部分省市.在中国旅游协会休闲农业与乡村旅游分会公布的2016年、2015年与2014年全国休闲农业与乡村旅游星级示范企业(园区)中,重庆市的休闲观光农业企业(园区)无一上榜,虽然星级企业的评选只是一个指标,但对于一个地区休闲农业园区或企业来说,这是对园区发展水平和品牌建设的重要评判.从全国范围来看,东部地区中江苏(51家)、浙江(28家)是现代农业与旅游业发展较好的地区,其星级农业园区的数量和质量都处于全国领先水平;湖南(24家)在中部地区遥遥领先;西部地区中广西(25家)、宁夏(15家)在西部处于优势地位;同时我们也可以看出重庆(0家)地区休闲农业的整体实力与品牌建设还有待提升(图 1).
1.1. 重庆市休闲农业需求分析
1.2. 重庆市休闲农业园区发展状况
1.3. 重庆市休闲农业园区品牌建设状况
-
休闲农业园区的品牌价值不仅可以体现农业园区的发展现状及前景,同时关系到消费者对企业的感性认知和对产品的理性认知,也是消费者进行消费选择的重要依据.乡村旅游资源开发、休闲农业园区建设以及进行旅游产品品牌建设都是一种手段,其根本目的是树立该地区本身的品牌形象,为休闲农业园区所在地的产业发展和经济发展提供强有力的保障.在对休闲农业园区品牌价值进行测度的过程中,用怎样的分析工具必须要考虑.本文选取模糊评价法与层次分析法相结合,具有传统AHP(层次分析)的优点,并且还可以判断模糊性[6],对品牌价值进行量化Fuzzy-AHP是一个较为理想的模型.本文根据品牌价值分析框架,结合乡村旅游方面专家、学者的意见,利用Fuzzy-AHP原理构建目标层—准则层—指标层的3级指标评价体系及其相关权重;通过发放调查问卷的方式,对到重庆市休闲农业园区进行休闲旅游的消费者进行关于旅游目的地与相关产品的调查,将得到的数据进行整理,根据调查数据建立隶属矩阵;通过一级指标矩阵、二级隶属矩阵及整合运算,得出重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值消费者调查分数,评估休闲农业园区的品牌价值,并发现园区在品牌建设中存在的问题,提出改进措施.
-
由于休闲农业有其独特的产业特征,致使其品牌资产的评估指标和方法很难统一.休闲农业是第一产业和第三产业的融合,因此其品牌价值评价指标的构建不能从单一产业的视角出发.哈丹·卡宾等[7]在其研究中以新疆农业为例,构建了区域农业品牌价值最大化指标体系,以产品价值最大化和产业链价值最大化为一级指标,二级指标分别是资源禀赋差异、产品创新水平、创意设计水平、市场营销水平及产业链一体化、产业规模性、产业链标准化、产业链创新型.李建军[8]在基于农业产业链的农产品品牌建设模式研究中构建了包括品牌知名度、品牌联想、质量与品牌认知、价格合适度及品牌忠诚的农产品品牌建设严肃理论指标体系. Pike[9]提出应该从品牌内涵、品牌个性特征、品牌组合及品牌与消费者的共鸣这4个方面构建旅游地品牌评价模型.
本文结合农业和旅游业品牌价值评价指标,针对休闲农业的行业特征,借鉴文献[8, 10-11]提出的品牌资产5个要素,建立重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值评估体系,其中目标层是重庆休闲农业园区品牌价值,准则层的要素是品牌感性认知度、品牌竞争力和品牌联想.
在品牌感性认知度指标下有品牌知名度、品牌忠诚度以及顾客满意度这3个指标维度,主要考察消费者对休闲农业园区品牌的感知度、在园区消费的满意度和重复消费的可能性.在品牌竞争力维度下有品牌营销策略、竞争优势这2个二级指标维度,主要考量的是重庆休闲农业园区各种体验项目、活动营销方式以及与传统农家乐相比是否具有竞争优势.品牌联想指标的下级指标有重庆休闲农业园区品牌联想度及园区品牌个性特色,其主要消费者是否对重庆休闲农业园区的品牌个性、差异性和吸引力表示认可的分析.根据分析框架,依据层次分析法原理构建如表 1的评价模型.
-
本文的调研对象是在重庆休闲农业园区内体验过的消费者,问卷采用现场调查的形式,即在重庆市抽取10个休闲农业园区,分别是:九龙坡区西彭现代农业园区;北碚区金果园和巴南区二圣现代农业园区;涪陵区南沱现代农业园区、南川区十二金钗大观园以及万盛经开区黑山现代农业园区;万州区永胜村大观园、奉节县兴隆休闲农业园区;武隆县白马现代农业园区和彭水县摩围山现代农业园区.在这些园区中对正在体验的消费者进行问卷调查.本研究共发放调查问卷400份,回收372份,其中有效问卷349份,问卷有效率为87.25%.
从表 2数据统计显示,消费者的性别比接近1: 1;在年龄上,来重庆市休闲农业观光农业园区消费者的年龄主要集中在是30岁左右,这部分消费者有稳定收入,大部分是以家庭为单位进行消费;从受教育程度来看,82.81%的被调查者为大专及以上学历,说明到重庆休闲农业园区消费的被调查者学历较高;从工作单位性质来看,在休闲农业园区消费的多是政府及事业单位的顾客,这部分顾客上下班时间规律,有固定的节假日,因此可以利用周末和节假日去游玩;在个人收入方面,被调查者大多属于中等偏上的收入水平;只有20.35%的被调查者月收入在5 000元以下,其余被调查者月收入水平均超过5 000元,说明到重庆市休闲农业园区的消费者经济实力较强;就去休闲农业园区消费的目的来看,排在前3位的理由分别是亲近自然、放松身心以及与亲友增进感情,说明多数游客去休闲农业园区进行消费主要是为了亲近自然.
-
本文用层次分析法进行重庆市休闲农业园区的品牌价值模糊评价,该方法通过两两比较的方式确定每一个层级中各个指标的重要程度.本研究利用Yaahp10.3AHP分析软件进行分析,首先根据表 1的重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值指标体系构建层次分析评价模型,然后在软件中构建判断矩阵,运用软件对各级评价指标的权重进行计算,最后进行一致性检验.通过软件可得到各级指标的权重.
要素层各指标的权重
指标层各指标的权重
其中W1代表在消费者感性认知指标下的品牌知名度、品牌忠诚度和顾客满意度这3个指标的权重;W2代表在品牌竞争力指标下的园区营销策略、竞争优势这2个指标的权重;W3代表的是在品牌联想指标下重庆市休闲农业园区品牌联想度与重庆市休闲农业园区品牌特色这2个指标的权重.在问卷调研中,消费者根据各个指标对园区进行打分,得分为5级设定,最高分是100分,其次分别是80分、60分、40分和20分.统计数据分析见表 3.
评价值E=(100,80,60,40,20)
将消费者品牌感性认知下的2级指标权重与问卷所得数据矩阵相乘得到隶属矩阵
将品牌竞争力下的2级指标权重与问卷所得数据矩阵相乘得到隶属矩阵
将品牌联想下的2级指标权重与问卷所得数据矩阵相乘得到隶属矩阵
将1级指标的权重与2级指标隶属矩阵相乘,得到
最后,将评价值与1级指标隶属矩阵计算得到N,即重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值评价值.
最终通过模糊评级法计算得到重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值的分值为60.42分,属于第3等级,说明从总体来看重庆市休闲农业园区品牌建设不到位,在品牌提升方面还有很大提升空间.从1级指标隶属矩阵中计算要素层消费者品牌感性认知度、品牌竞争力及品牌联想这3个指标的得分,依次为64.05,64.69及55.45;从得分看这3个1级指标也属于第3等级,而重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值在品牌联想这一方面得分最低,未能达到及格水平.
2.1. 休闲农业品牌价值评价体系构建
2.2. 评价指标的选取
2.3. 数据收集与处理(表 2)
2.4. 重庆市休闲农业园区品牌价值模糊评价
-
消费者品牌感性认知程度是由品牌知名度、品牌忠诚度和客户满意度这3个部分内容构成.由消费者品牌感性认知度的得分可以看出,重庆市休闲农业园区品牌建设方面仍存在很大问题,首先是由于休闲农业园区品牌知名度不高,休闲农业园区同质化现象严重,消费者表示去哪里都一样,因此他们在进行消费选择时随机性较强,在没有固定目标的前提下一般会选择就近园区进行消费.而在消费的过程中,园区如果没有优质的农家产品、良好的服务以及独特的体验项目,就很难使消费者感到满意,也就更加难以形成顾客忠诚度.
-
休闲农业园区品牌竞争力是园区竞争力的外在表现,但重庆市多个休闲农业园区却不具备品牌竞争力,主要表现在品牌竞争优势不明显、营销策略单一.重庆市休闲农业园区的经营主体多为个体或民营业主,其受教育程度不高,对品牌建设的重视不够,导致整个地区的休闲农业园区没有特色,园区定位、项目和产品同质化相当严重,难以形成规模,且档次偏低;竞争力不强的另一个表现形式是营销手段单一,在互联网高度发达的今天,重庆市休闲农业园区仍然用传统的手段进行宣传,难以达到吸引消费者的目的.
-
重庆市休闲农业品牌价值不高的另一个表现是园区品牌联想度不够.由于休闲农业都被大多数人当成是农家乐,在这样的环境下休闲农业的营业主体也没有把休闲农业当成是一种旅游产品进行开发和设计,品牌定位缺乏独特的卖点,休闲农业园区与农家乐的区别不明显,园区内提供的服务与产品缺乏独特的内涵,旅游体验项目缺乏对农耕文化、乡村民俗等人文资源的开发;不同休闲农业园区之间宣传标语相互抄袭,体验项目盲目跟风,游乐形式单一,很难形成一个园区独特的文化与品牌特色,就很难使消费者对品牌产生好的联想.
3.1. 休闲农业园区消费者品牌感性认知程度低
3.2. 休闲农业园区品牌竞争力不强
3.3. 休闲农业园区品牌联想度不够
-
对于任何类型的企业来说,顾客满意都是企业赖以生存的法宝,而顾客忠诚则意味着消费者对企业的高度认可.因此,休闲观光园区在提升消费者满意度、忠诚度方面有许多工作要做.首先,充分发挥园区从业人员的主人翁意识,调动当地居民发展休闲农业的主动性[12];对从业人员展开专业技术培训,帮助村民树立品牌意识,提高其工作积极性,基于顾客满意的原则,全方位提高服务质量.其次,对消费市场及顾客需求进行调研,开发一些消费者喜欢的、具有自身特色的体验项目,给消费者带来新意,提升顾客满意度.最后,注重园区生态建设,在保持休闲农业园区景色优美、田园气息的同时,也要注重生态环境的可持续发展以及消费者与园区的和谐发展.
-
培育品牌竞争优势是塑造品牌价值的关键.园区经营主体应该转变经营观念,将休闲农业园区当作一个企业来经营,找准园区的品牌定位,培养核心竞争力.休闲农业园区品牌建设必须以游客体验为核心,发挥体验营销策略[13].首先,以地方民俗文化为卖点,结合园区特色定期举办一些游园会、消费品展销等活动,吸引消费者来观光体验.其次,利用产品组合的营销策略,将旅游产品与其他商品进行有机的结合,增加有一些可以让消费者自己动手的体验项目,在产品制作完成后还可以将其带走留作纪念,以增加消费者和园区之间的情感联系.最后,加速“互联网+休闲农业”布局,发挥互联网对休闲农业发展的推动作用[14],利用各种的网络社交渠道进行营销,通过微博、微信公众号、门户网站等平台,对休闲农业园区进行宣传,不定期推出一些针对不同消费群体的优惠活动,吸引各个群体到园区进行休闲体验.
-
休闲农业区别于农家乐的最大特点就是它的人文性、文化性和社会性,其赖以生存的基础是“大农业”的人文景观和自然资源[15].因此,休闲农业园区在进行品牌建设的过程中必须结合当地的特色,挖掘当地的历史文化[16-17],着重突出农耕文化、乡土文化,不断开发民间技艺、节庆活动、农耕展示、民间歌舞等旅游活动,以增加当地休闲农业的文化内涵[18].重庆市民俗文化丰富多彩,且具有悠久的历史,较为出名的有重庆市綦江农民版画,石柱盐运民俗,涪陵榨菜传统制作工艺等.各地的休闲农业园区可以根据当地民俗,打造不一样的体验项目来吸引游客.比如,重庆市涪陵榨菜极其出名,所以当地的休闲农业园区可以以涪陵榨菜传统制作为卖点,在园区内举办一些榨菜制作教学活动,吸引游客到园区体验,在游客进行消费的过程中对榨菜制作的传统工艺进行推广与宣传,同时提升涪陵休闲农业园区的品牌联想度.在用文化吸引游客的基础上,创建具有当地特色的休闲农业民俗品牌,提高社会知名度,增强休闲农业园区品牌价值.



 下载:
下载: