-
思茅松毛虫(Dendrolimu kikuchii),又名褐色松毛虫,鳞翅目(Lepidopera)枯叶蛾科(Lasiocampidae)松毛虫属(Dendrolimus),最早在云南思茅被发现而命名[1].中国主要分布在云南、贵州、四川、广东、广西、湖北、湖南、江苏、浙江、安徽、江西、福建、台湾、海南等省[2].思茅松毛虫主要以思茅松(Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis)、云南松(P.yunnanensis)、华山松(P. aimandi)等松科植物为食,在云南思茅地区主要为害思茅松,而在昆明周边主要为害滇油杉[3].思茅松毛虫是为害最为严重的6种松毛虫之一,严重时会使大批量松科植物枯萎死亡,状如火烧,严重影响相关地区的生态环境及旅游业,给当地人们的生产生活带来极大不便[4-6].由于地理位置不同,思茅松毛虫在中国南方分布具有特异性[7-8].因此,国外对思茅松毛虫研究较少,国内取得的研究成果颇丰[9-12].观察思茅松毛虫各生命阶段的形态特征及生活习性为思茅松毛虫的防治提供理论基础.
全文HTML
-
网袋、高枝剪、新鲜的云南油杉枝条(30~40 cm)、毛笔、镊子、喷壶、4 ℃冰箱、养虫笼.
-
地点在西南林业大学树木园,选取新鲜的枝条,用高枝剪在背离枝条顶端30~40 cm处将枝条剪断带回实验室.刚采回来的枝条用喷壶在油杉叶表面喷适量的水,放入塑料袋中密封好,然后将塑料袋放入4 ℃保鲜冰箱中保存,可以保鲜20 d左右.刚采集回来的油杉枝条放置在4 ℃冰箱里,可以延长保鲜时间,减少采集次数,降低饲养成本.思茅松毛虫是由云南安宁地区捉来的幼虫或卵孵化出来的.
将适量新鲜的油杉枝条放入网内,用镊子或者毛笔将孵化出来或者从野外采回来的思茅松毛虫幼虫转移到网内的油杉枝条上.每30条幼虫放1个枝条,所用枝条的量取决于所养幼虫的数量.每1~2 d更换1次油杉枝条,并且清理网内的粪便和枯萎枝叶.
对于卵的观察,随机取100颗野外采集的卵,用电子螺旋测微器测量其长直径和短直径,并观察其表面形态.各龄期幼虫,观察各龄期幼虫的形态特征并记录,用测微器测量各龄期幼虫的体长和头壳宽.虫茧和蛹,观察茧的表面形态特征,取100只茧用剪刀将外皮剪开得到里面的蛹,进行形态观察并用测微器测量其最大直径和长度.雌雄成虫分别取100只,用螺旋测微器分别测量雌雄成虫翅展、体长和头部触角的长度和宽度,并且进行形态学观察.
1.1. 材料
1.2. 方法
-
通过对思茅松毛虫的饲养和观察,对思茅松毛虫生命各阶段形态特征以及生活习性的描述如下:
-
思茅松毛虫虫卵为扁球形,长直径为1.9~2.0 mm,短直径为1.4~1.5 mm.卵表面颜色由棕色和白色圆环交替组成.中间最大环上有一个棕色小点,点周围颜色为白色.卵一般成堆出现在松针或其他树叶上,一只雌蛾能产下50~300颗卵.卵在9~14 d以后就会变成1龄幼虫.在人工状态下由于空间小等诸多因素限制了蛾的交配,导致大部分卵都未经过受精,孵化率极低.人工状态下卵的初始形态与自然状态下无差别,未受精的卵隔10 d后就变得干瘪.
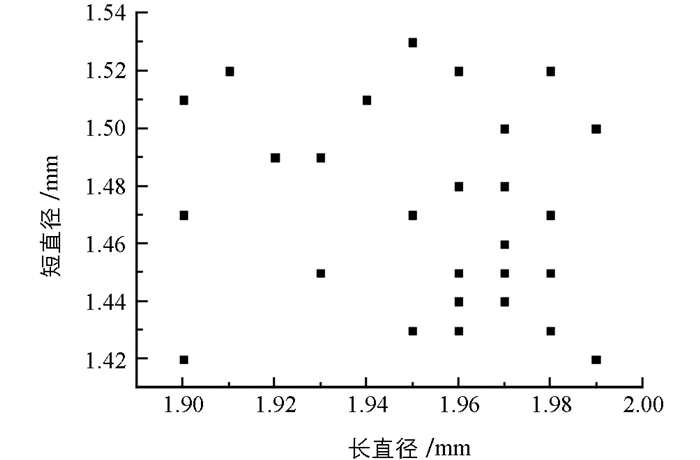
对卵的长直径与短直径的相关关系做散点图(图 1).
将思茅松毛虫卵的长直径与短直径做线性回归分析,得到R2=0.037 9,因此认定卵的长直径与短直径无线性关系.
-
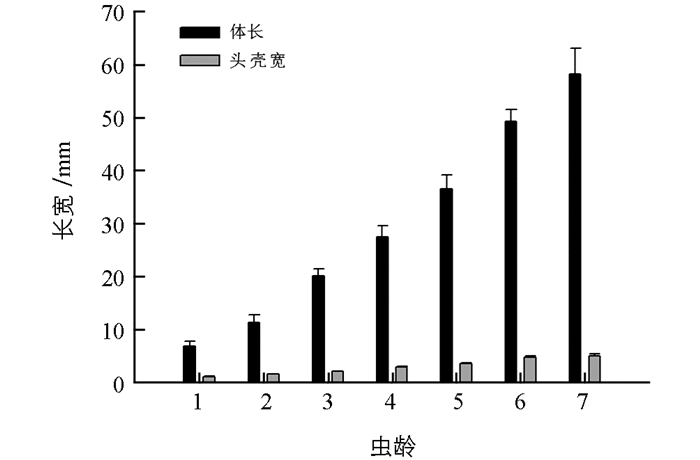
思茅松毛虫幼虫共有7个龄期,每2个龄期之间所用的时间为10~15 d.头后有4束较长的毛束,毛束基部凸起且为黑色,毛束顶部为乳白色.头与腹足之间,并且在虫体的背面有一簇较长的毛簇,颜色为橙黄色. 1~4龄的思茅松毛虫幼虫背面有若干条较长的黑色毒毛且以背中线为对称轴呈轴对称.具有3对腹足和4对尾足.尾部具有一对毛束且以背中线为对称轴呈轴对称,基部颜色为黑色.背部具有一条明显的中线,由一串倒置的等腰三角形组成.卵刚孵化出来的1龄幼虫虫体具有白色绒毛,背中线为白色,过3~4 h之后背中线变成黄色.头壳颜色为橘黄色,头后具有4束较长毛束,头后毛束基部为黑色,顶端为白色.腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色.背中线两侧颜色为黑色,虫体两侧颜色为橘黄色间白色.虫体长度为5~10 mm.幼虫头壳颜色为棕色,头后毛束基部为黑色,顶端为白色.腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色.背中线颜色较1龄深为深黄色.背中线两侧颜色为黑色间黄色,虫体两侧颜色为橘黄色间白色.虫体长度为10~15 mm. 3龄幼虫头壳颜色为棕色,头后毛束基部为黑色,顶端为白色.腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色.背中线颜色较1龄深为深黄色.背中线两侧颜色为乳白色,虫体两侧颜色为橘黄色间白色.虫体长度为15~20 mm. 4龄幼虫头壳颜色为棕色,腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色.背中线颜色为橙黄色,虫体两侧颜色为棕色间乳白色.背中线两侧颜色为灰色间黄色.虫体长度为20~35 mm. 4龄开始幼虫进食量明显增大. 5龄的思茅松毛虫幼虫背部毛束发生明显变化,出现8对较长的毛束,每对毛束都以背中线为对称轴呈轴对称,且颜色为白色.虫体两侧出现8对较长毛束且为白色,每束毛束位于相邻两足基部之间.尾部有一对较长的毛束,以背中线为对称轴呈轴对称,尾部基部凸起且为黑色,毛束顶部为乳白色.头壳颜色为棕黄间黑色,腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色.背中线颜色为橙黄色,背中线两侧颜色为橙黄间黑色,虫体两侧颜色为乳白间黑色.虫体长度为35~50 mm. 6龄以后的思茅松毛虫头部卷曲不好动,经过外界干扰容易从口中吐出绿色的毒液.背中线两侧和虫体两侧的毛束颜色变为黄色,后面有1~5对毛束仍为白色.所有毛束较5龄的长.头壳颜色为棕黄间黑色,腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色,背中线颜色为黑色间橙色.背中线两侧颜色为橙黄间黑色,虫体两侧颜色为橙黄间黑色.虫体长度为50~60 mm. 7龄幼虫毛束颜色加深变为橙红色,背中线两侧毛束与虫体两侧毛束颜色前几对为橙红色,后面为白色,白色毛束有1~5对不等.头壳颜色为棕黄间黑色,腹足与尾足颜色为黑色间淡黄色,背中线颜色为黑色.背中线两侧颜色为橘黄色,虫体两侧颜色为黑色间淡黄色.虫体长度为60~70 mm.
-
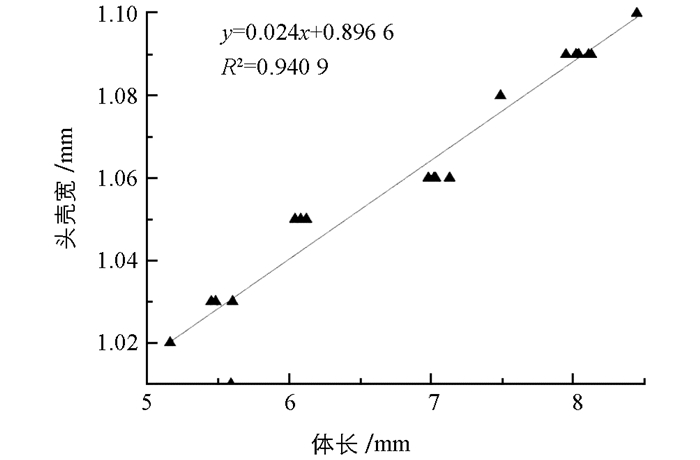
用Sigmaplot绘图软件对思茅松毛虫各龄期幼虫的体长和头壳宽作图(图 2),用Origin数据分析软件分析思茅松毛虫体长与头壳宽有无相关性(图 3).
由图 3可以得出,思茅松毛虫幼虫头壳宽与体长存在线性关系,其线性关系为Y=0.024X+0.896 6(Y表示头壳宽,X表示体长),R2=0.940 9.
-
人工与自然2种状态下思茅松毛虫幼虫的形态相同.自然状态下思茅松毛虫幼虫各龄期体长要比人工状态下的体长要长,人工状态下7龄思茅松毛虫体长为60~70 mm,而自然条件下思茅松毛虫7龄幼虫体长最长可达130 mm(图 4、图 5).
用SPSS软件对7龄幼虫在p=0.01水平下做单因素方差分析,结果如表 1所示.
从表 1可以看出,人工条件下7龄思茅松毛虫与自然条件下的体长存在差异,并且差异极具有统计学意义,自然条件下要比人工条件下平均长27.5 mm.原因是:①人工状态下思茅松毛虫幼虫活动空间要明显小于自然条件下的活动空间,人工条件下每条虫子的平均活动空间为100 cm2,而自然条件下思茅松毛虫的活动空间足够充足;②自然条件下的环境要比人工条件差,而在自然条件下能够生存下来的思茅松毛虫都是能够适应恶劣环境的.
-
虫茧形状为梭形,颜色为黄色或褐色,周围布满成列的、褐色或深紫色毒刺,一般附着在较细的枝条或树叶上.蛹包裹在茧里面,形状为长椭圆形,颜色为褐色,长度为30~40 mm,最大直径为10 mm,蛹腹部一般8节且密布黄色短毛.自然条件与人工条件下茧和蛹的形态无明显差异,自然条件下蛹长要比人工条件下的长,蛹最长可达45 mm.
-
成虫全体为红棕色,头部、体表以及翅周围都布满棕色绒毛,体长在30~50 mm之间.头部触角双栉状,颜色为深褐色,长度为12 mm,最大宽度为3 mm.具一对前翅和一对后翅,颜色为褐色且后翅较前翅颜色深,翅展50~100 mm.腹部分8节,雄蛾尾部较雌蛾窄.
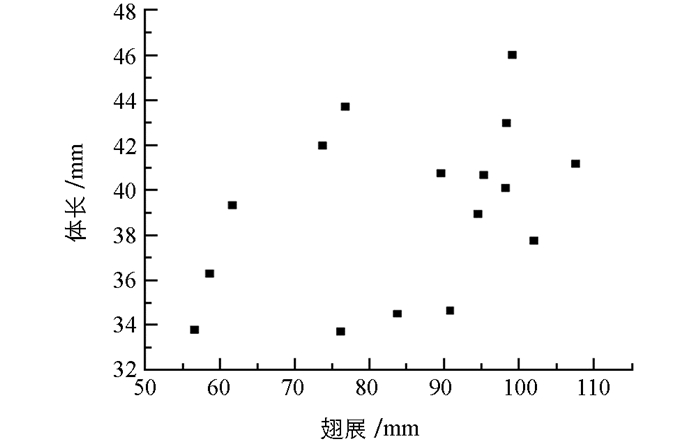
如图 6所示,将思茅松毛虫成虫体长与翅展作线性回归分析,得到R2=0.179 5,因此认为体长与翅展无线性关系.自然条件下成虫与人工条件下的形态无明显差异,自然条件下成虫体长和翅展要比人工条件下的长,自然条件下雌蛾体长最大可达55 mm,翅展最长可达115 mm;雄蛾体长最大可达45 mm,翅展最长可达45 mm.
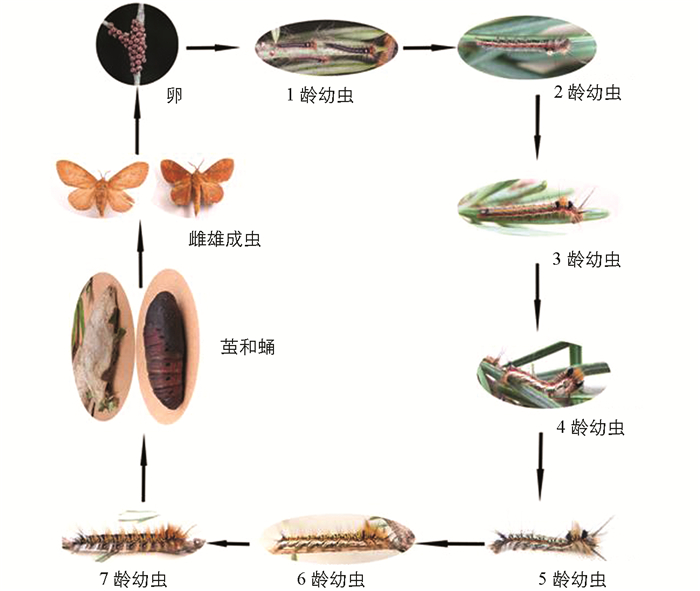
在昆明地区思茅松毛虫卵出现时间为6月中旬-7月中旬,从卵到1龄幼虫所需时间为15~20 d.各相邻龄期幼虫时间间隔为10 d左右,从4龄幼虫开始取食量逐渐增大且形态特征变化明显,7龄幼虫行动缓慢不好动且头部易卷曲. 7龄幼虫到化茧时间为10 d左右,初化茧时虫体收缩吐出白色或黄色丝状物缠绕虫体周围,且身体周围丝状物越来越多变成茧,茧一般结在小枝或树下灌木上.蛹期约1个月后变为成虫,成虫不进食,有趋光性,雌虫产卵量为50~300粒.从11月份开始,思茅松毛虫就停止生长,以3龄幼虫越冬,越冬时死亡率较高(图 7).
2.1. 虫卵形态特征
2.2. 幼虫形态特征
2.2.1. 思茅松毛虫各龄期幼虫形态
2.2.2. 思茅松毛虫幼虫体长与头壳宽的线性分析
2.2.3. 人工状态与自然条件下7龄幼虫的差异分析
2.3. 虫茧和蛹形态特征
2.4. 思茅松毛虫成虫形态特征
-
思茅松毛虫卵呈扁球形,一般成堆存在于枝条或树叶上,长直径为1.9~2.0 mm,短直径为1.4~1.5 mm.人工状态下未受精的思茅松毛虫卵初始与自然条件下的卵在形态上无明显差异,10 d后就变为干瘪的状态,不能孵化为幼虫.长椭圆形蛹被梭形茧包裹着,蛹长为30~40 mm,最长直径为10 mm;茧为黄色或乳白色,周围布满黑色毒刺,起到保护作用.自然条件下茧和蛹与人工条件下的形态无明显差异,自然条件下蛹长要比人工条件下的长,蛹最长可达45 mm.人工条件下7龄思茅松毛虫与自然条件下的体长存在差异,并且差异极具有统计学意义,自然条件下要比人工条件下平均长27.5 mm.
对思茅松毛虫生命各阶段形态进行观察可知,1~4龄幼虫形态相近,5龄形态开始出现明显变化.思茅松毛虫幼虫共7个龄期,1~4龄幼虫的取食量较少,5~7龄幼虫的取食量较多,因此主要为害松科植物的生命阶段是5~7龄幼虫时期.卵的长直径和短直径无线性相关关系.用Origin数据分析软件对思茅松毛虫体长与头壳宽的线性分析结果表明,思茅松毛虫幼虫头壳宽与体长存在线性关系,线性关系为Y=0.024X+0.896 6(Y表示头壳宽,X表示体长),R2=0.940 9.成虫的翅展与体长之间无线性相关关系.该研究为思茅松毛虫灾害的预测和防治提供了参考资料.



 下载:
下载: